文章目录
- 1.红黑树的介绍
- 1.0红黑树的来源
- 1.1红黑树的概念
- 1.2红黑树的性质
- 2.红黑树构建示例
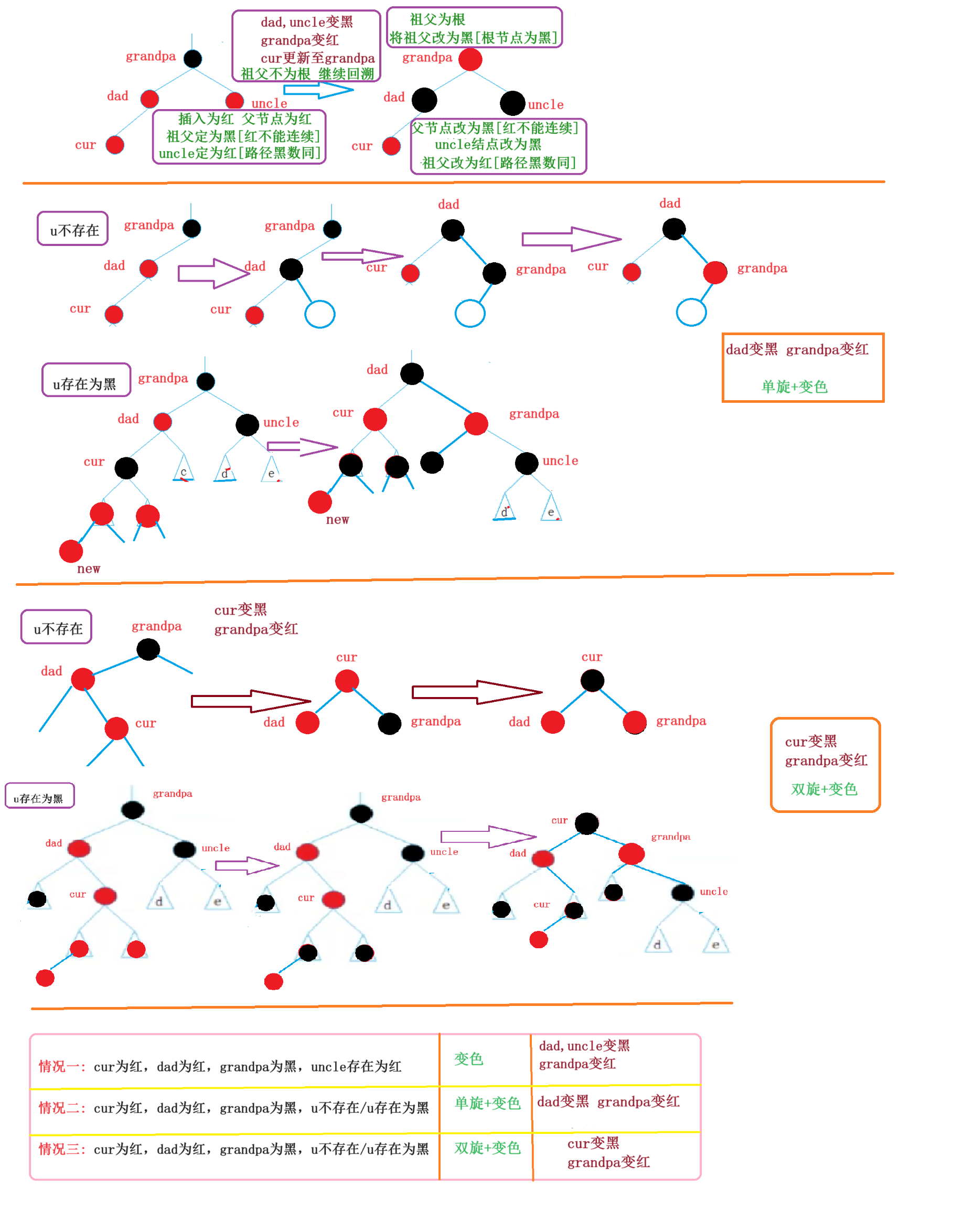
- 2.1只变色
- 1.祖父为根/不为根
- 2.连续回溯
- 2.2变色+旋转
- 3.红黑树构建情况分类
- 3.0默认插入结点颜色
- 3.1情况一:变色
- 1.未知树为空
- 2.未知树不空
- 3.2情况二:单旋+变色
- 1.uncle不存在
- 2.uncle存在为黑
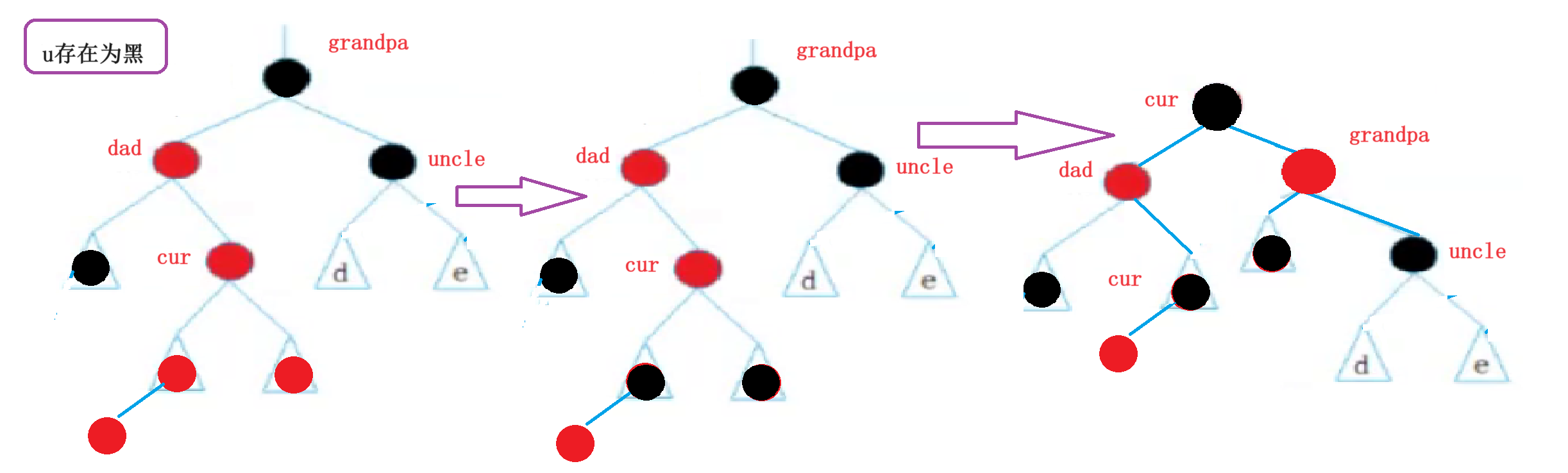
- 3.3情况三:双旋+变色
- 1.uncle不存在
- 2.uncle存在为黑
- 3.4总结
- 4.看图写代码[有手就行]
- 4.1RedBlackTree.h
- 4.2Test.cpp
1.红黑树的介绍
想了解红黑树,首先需要对AVL树有一定的认识.点击上篇博客浅浅学习一下吧~AVL树
1.0红黑树的来源
AVL树绝对平衡[左右高度不超过1]===>红黑树近似平衡–最长路径不超过最短路径的2倍
查找:AVL- logN 红黑树 logN~2logN
插入/删除:红黑树旋转次数较少
- 红黑树是因为AVL树在某种情况下不太优的情况下出现的.
- AVL树的查找、插入和删除T(n)==O(logn);但是每插入/删除操作后就需要对其进行旋转处理–成本高
- 为了找到一种更好的数据结构,1972年Rudolf Bayer发明了平衡二叉B树(symmetric binary B-trees)。1978年Leo J. Guibas 和 Robert Sedgewick 修改称“红黑树”。
1.1红黑树的概念
红黑树是一种自平衡的二叉查找树,不同的是在每个结点上增加一个存储位表示结点的颜色,可以是Red或Black。 通过对任何一条从根到叶子的路径上各个结点着色方式的限制,红黑树确保没有一条路径长度是其他路径的两倍,因而接近平衡。
因为以下这种情况:
二叉搜索树,插入数据随机时接近平衡二叉树,操作效率(查询,插入,删除)效率较高,时间复杂度是O(logN)。但是当插入数据有序(递增或者递减),那么所有节点都会在一侧,此时,二叉搜索树成了一个链表,操作效率降低了,时间复杂度为O(N).
出现了AVL树,但是AVL树每插入/删除都要旋转处理,成本高,于是出现了红黑树.需要注意的是:
红黑树具备了二叉搜索树的某些特性,它是一种接近平衡的二叉树(它没有AVL树平衡因子的概念,仅靠5条性质来维持一种接近平衡的结构)。
1.2红黑树的性质
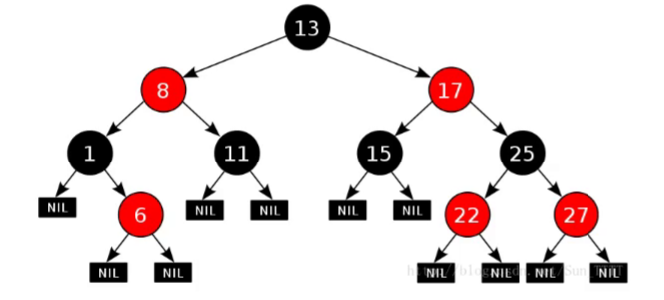
- 每个结点非黑即红
- 根节点为黑色
- 一个红色父结点的两个子结点均为黑色.[没有连续红节点][红色结点的父节点为黑色子结点为黑色][两个黑色结点的父结点不一定是红节点]
- 每个结点,从该结点到其所有后代叶结点的简单路径上,黑色结点个数相同[每条简单路径上都有相同个数黑节点]
- 空结点均为黑[计算结点个数不算空结点]
拓展性质
- 极限最短路径:全黑 极限最长路径:一黑一红
- 一棵红黑树接近满二叉树/单独取黑色结点也是接近满二叉树
- 假设黑色结点个数为N 整棵树结点数量[N, 2N]
- 最短路径logN 最长路径2logN
- 路径数目 == 根节点到空结点
思考:以上5条性质如何使得其最长路径中节点个数不会超过最短路径节点个数的两倍?
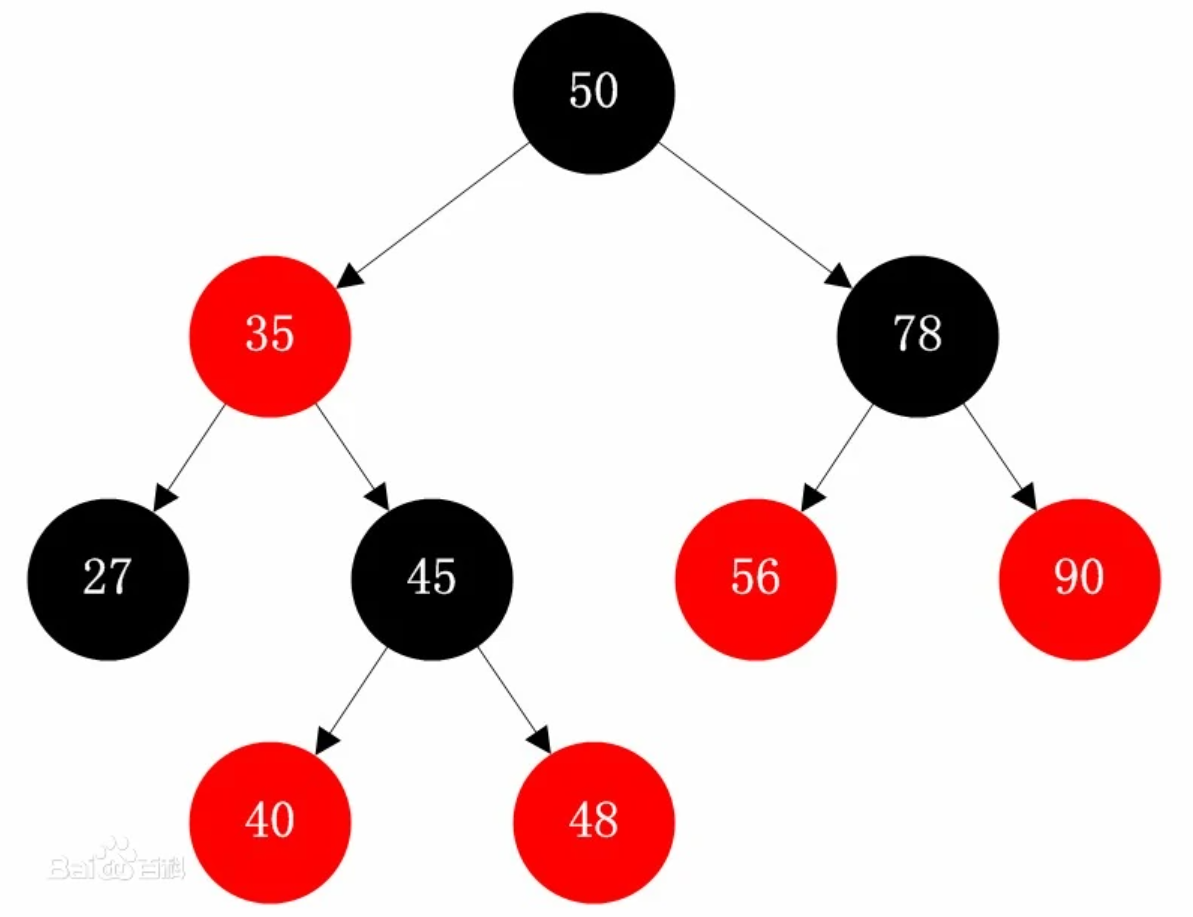
2.红黑树构建示例
插入一个红色结点可能会出现的情况
2.1只变色
1.祖父为根/不为根
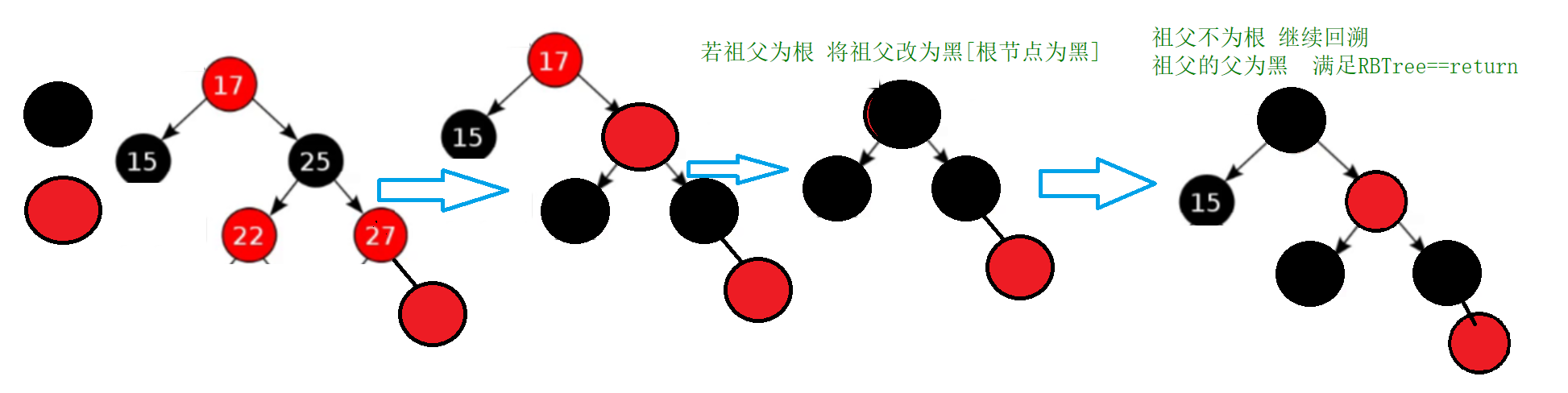
2.连续回溯
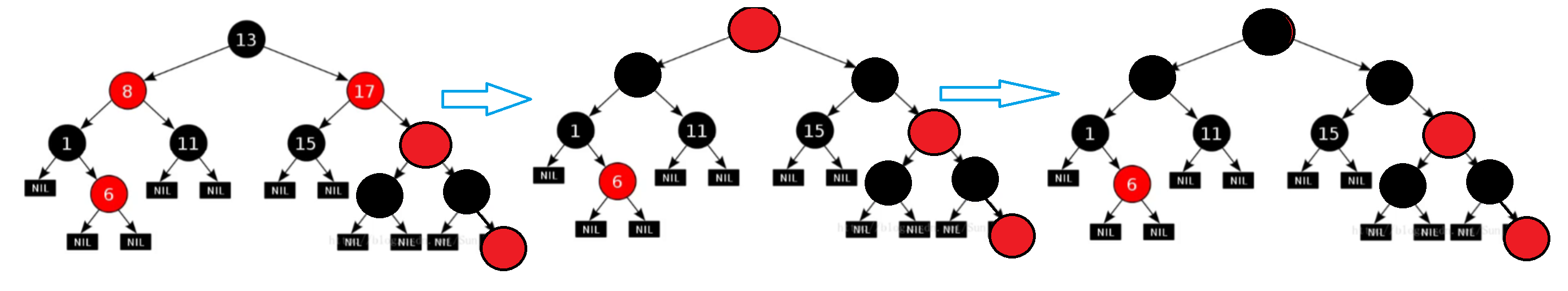
2.2变色+旋转
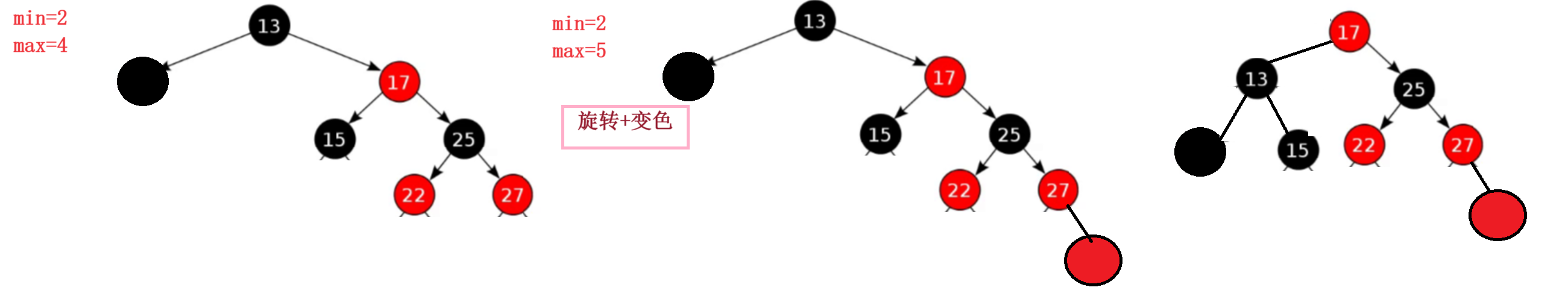
3.红黑树构建情况分类
3.0默认插入结点颜色
默认插入结点为红色
- 若为黑色 一旦插入违反性质4–error
- 插入红色 若父节点为黑不操作 若父节点为红需要操作–默认插入为红可以减少操作次数
3.1情况一:变色
1.未知树为空
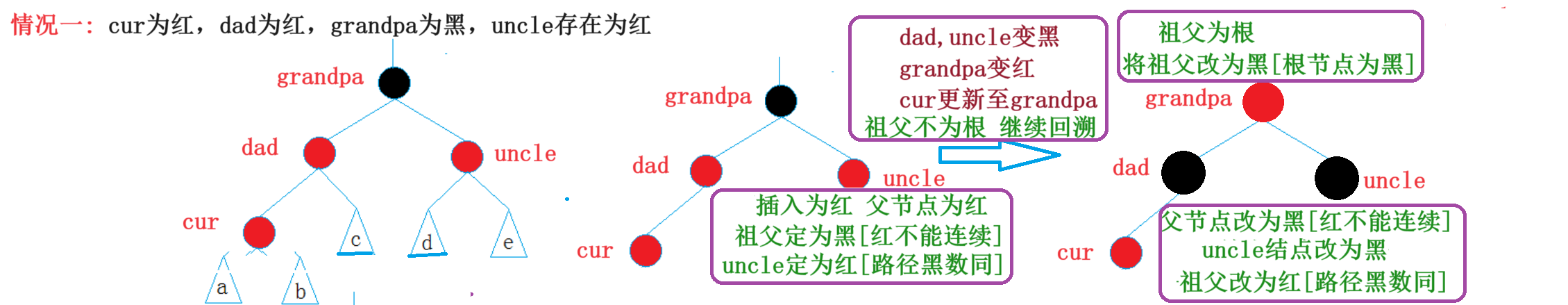
2.未知树不空
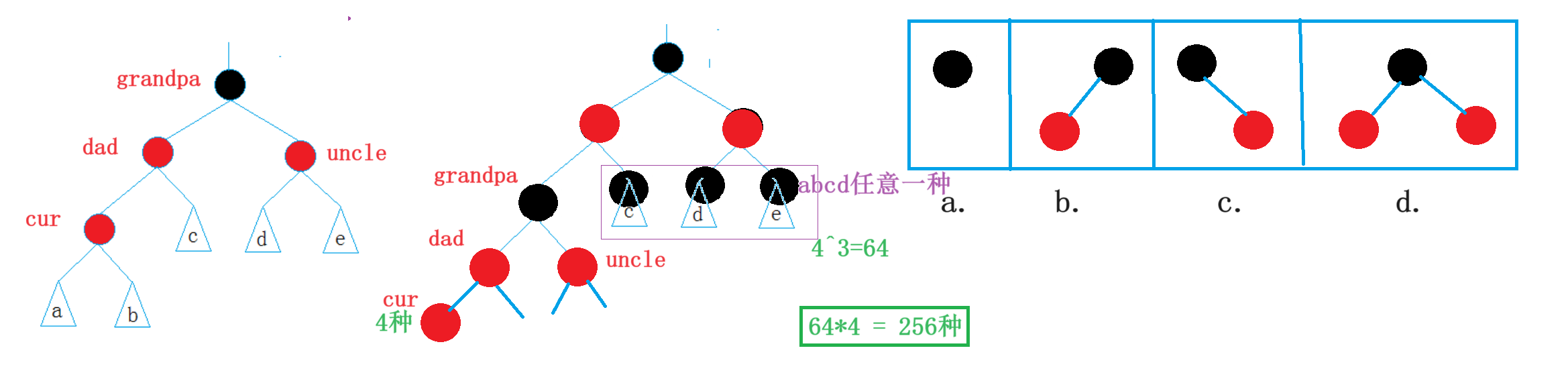
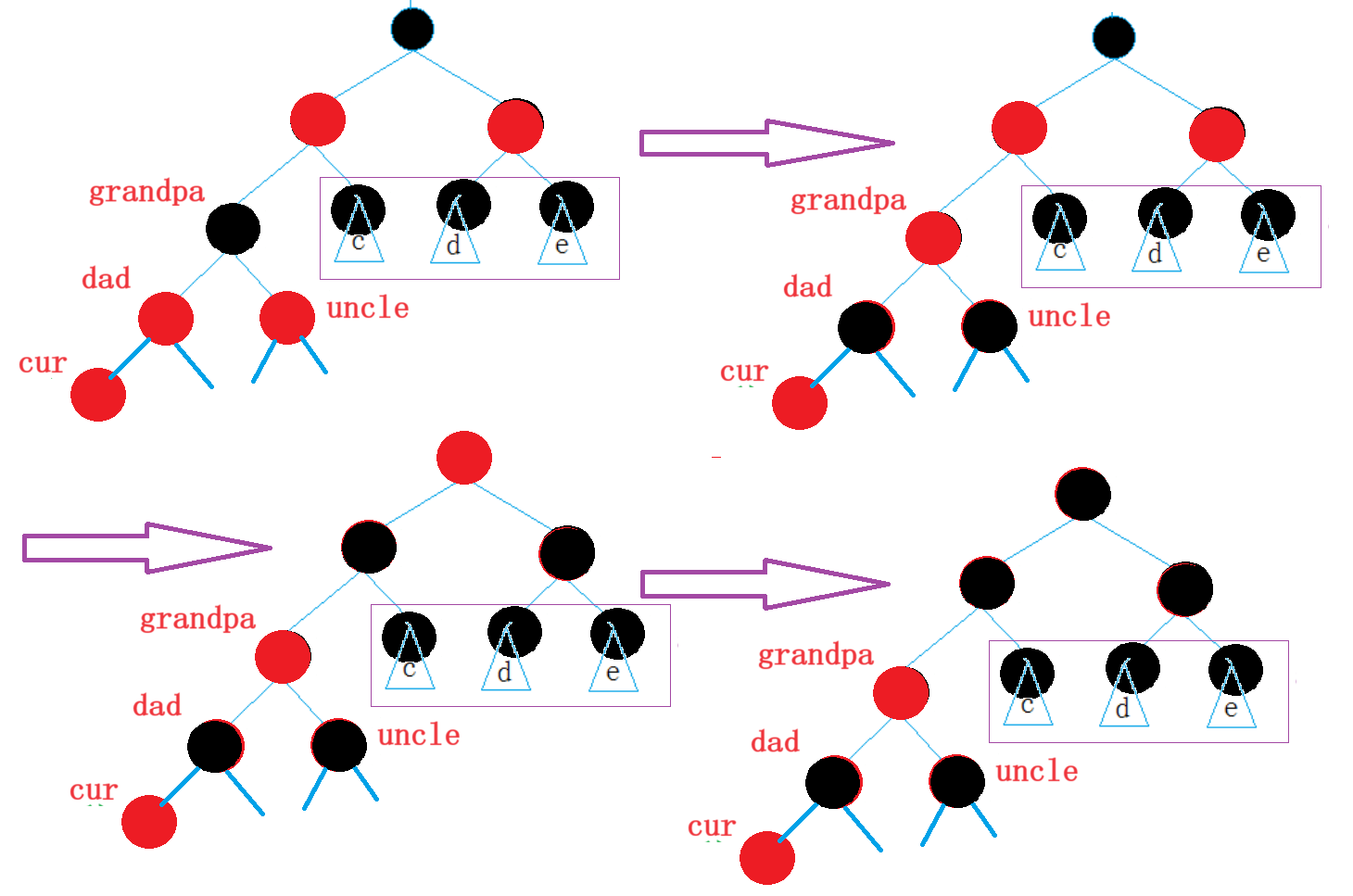
3.2情况二:单旋+变色
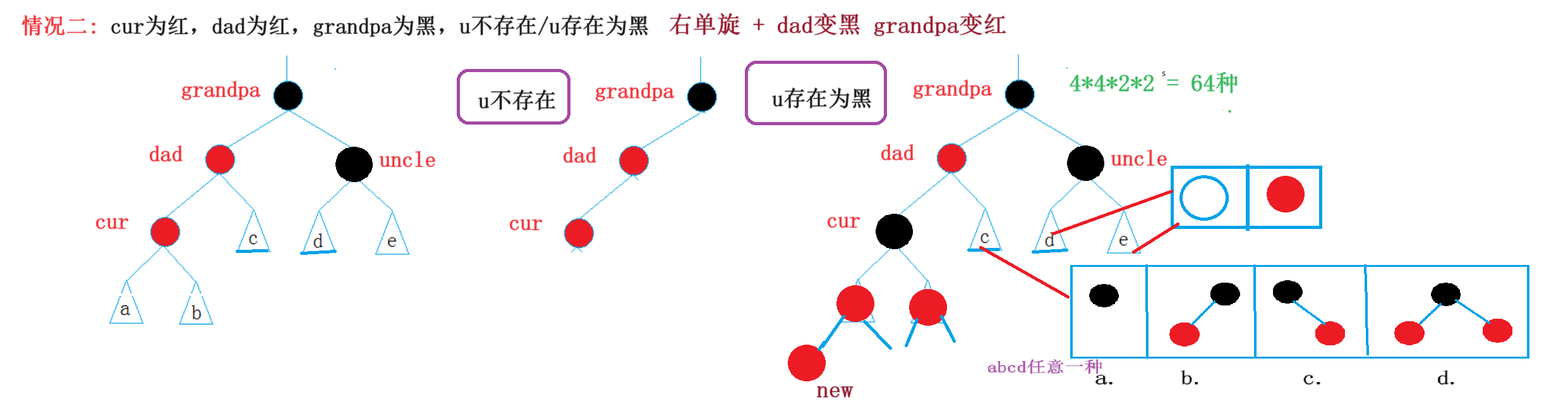
1.uncle不存在
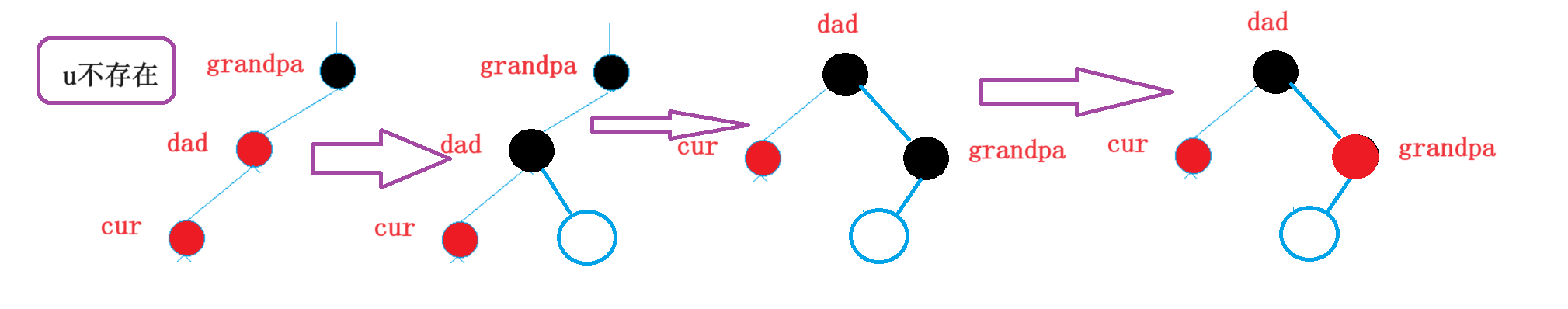
2.uncle存在为黑
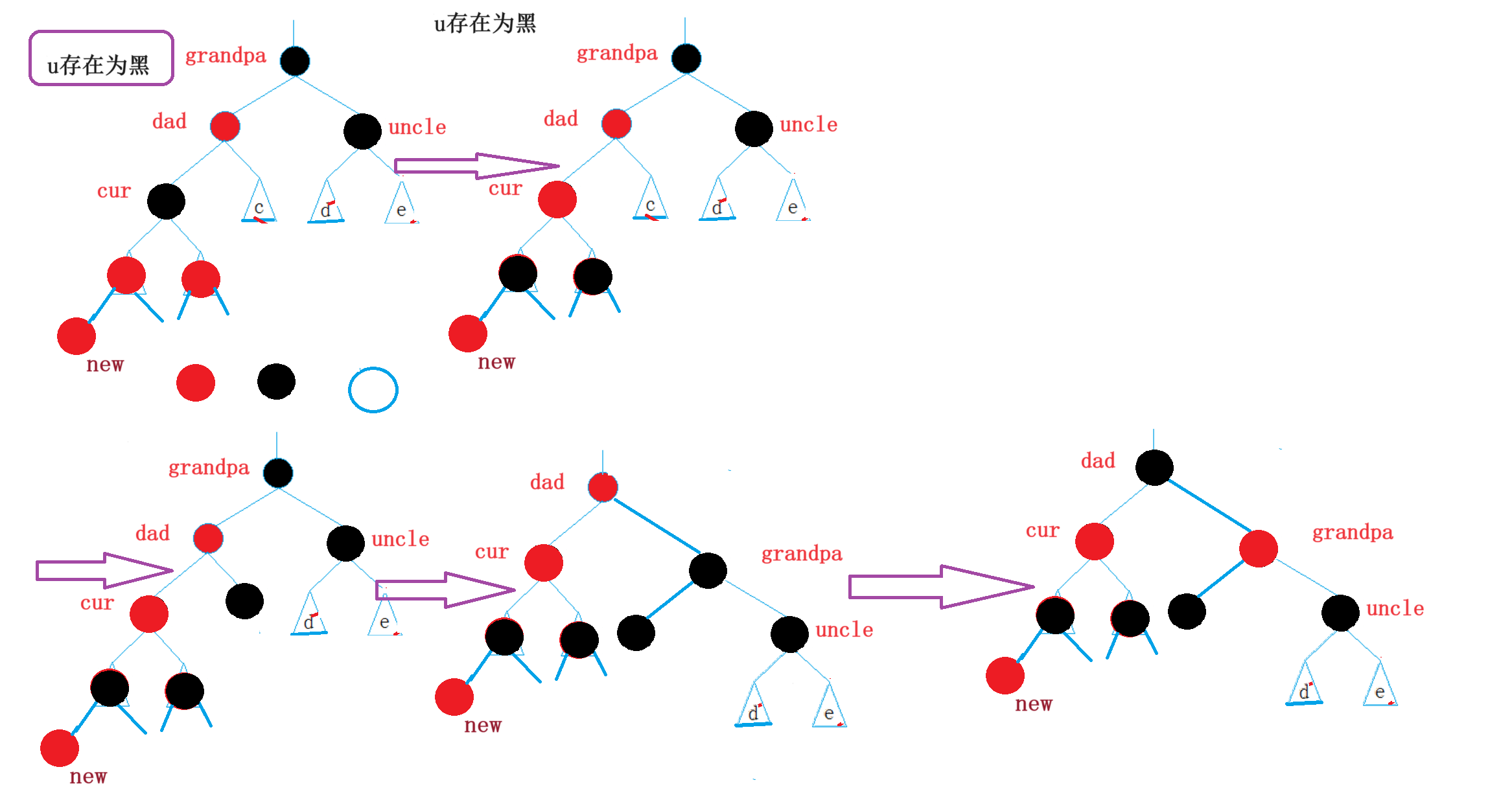
3.3情况三:双旋+变色
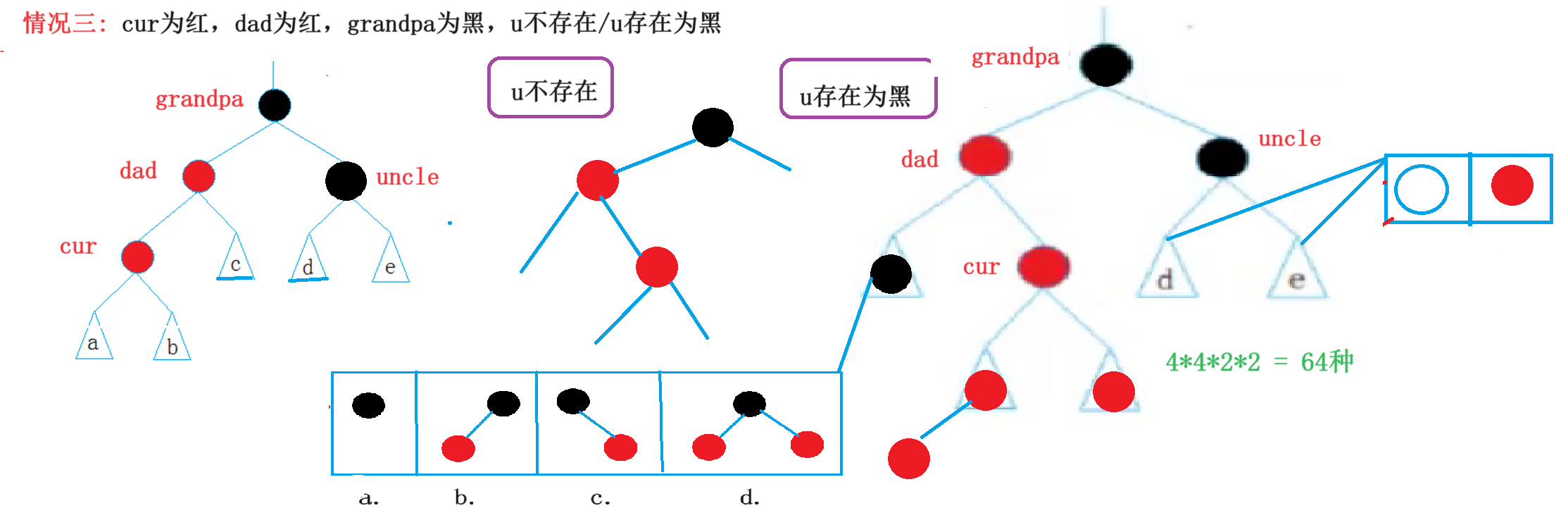
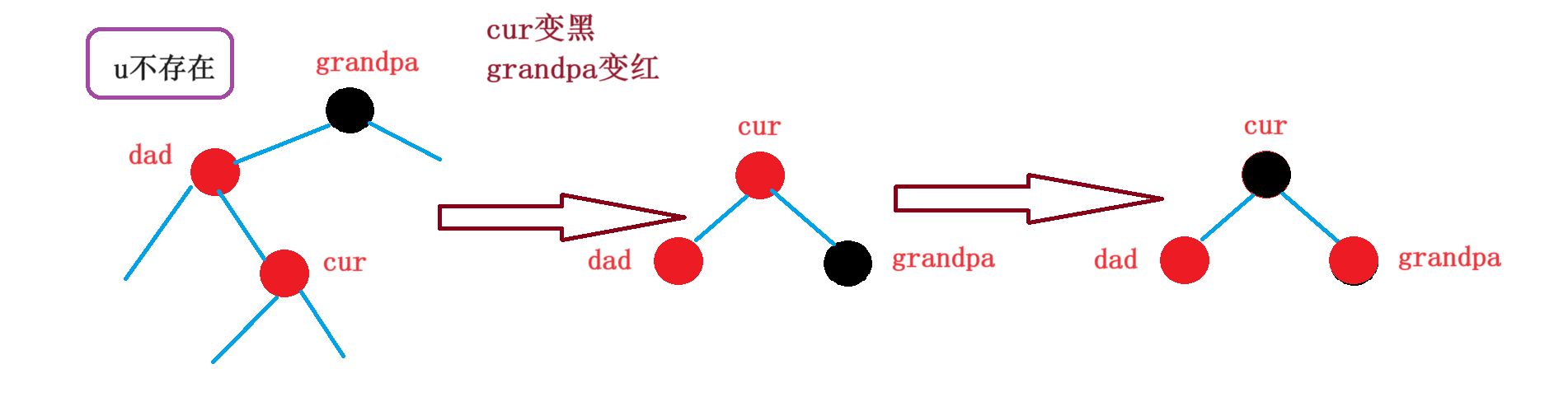
1.uncle不存在
2.uncle存在为黑
3.4总结

4.看图写代码[有手就行]
4.1RedBlackTree.h
#pragma once
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <array>
#include <time.h>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <string>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <functional>
#include <assert.h>
using namespace std;
//颜色枚举
enum Colour
{
RED,
BLACK
};
//结点类
template<class K, class V>
struct RBTreeNode
{
RBTreeNode<K, V>* _left;
RBTreeNode<K, V>* _right;
RBTreeNode<K, V>* _parent;
pair<K, V> _kv;
Colour _col;
RBTreeNode(const pair<K, V>& kv)
:_left(nullptr)
, _right(nullptr)
, _parent(nullptr)
, _kv(kv)
{
}
};
//RBTree类
template<class K, class V>
struct RBTree
{
typedef RBTreeNode<K, V> Node;
public:
//插入创建红黑树
bool Insert(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
///二叉搜索树插入///
//根节点为空
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(kv);
_root->_col = BLACK; //根节点颜色为黑
return true;
}
//不为空 定位至合适位置
Node* dad = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_kv.first < kv.first)
{
dad = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_kv.first > kv.first)
{
dad = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
//父连接子
cur = new Node(kv);
cur->_col = RED;
if (dad->_kv.first < kv.first)
{
dad->_right = cur;
}
else
{
dad->_left = cur;
}
//子继承父
cur->_parent = dad;
构建红黑树
//cur[红]此时定位新插入位置 若父为红
while (dad && dad->_col == RED)
{
//dad && dad->_col == RED
//二次循环来到此处
// 1.父为空 则cur为根 [最后控制cur变黑] 循环结束
// 2.父为黑 无需操作
Node* grandpa = dad->_parent;
//若父为红 祖父定存在且为黑
assert(grandpa);
assert(grandpa->_col == BLACK);
/判断uncle位置///
//父为左子树 uncle为右子树
if (dad == grandpa->_left)
{
Node* uncle = grandpa->_right;
//情况一、uncle存在为红 变色+回溯
//dad-uncle变黑 grandpa变红
if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED)
{
//变色
dad->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;
grandpa->_col = RED;
//回溯
cur = grandpa;
dad = cur->_parent;
}
//情况二-三:uncle不存在 存在且为黑
else
{
if (cur == dad->_left)
{
//情况二:右单旋+变色
RotateR(grandpa);
dad->_col = BLACK;
grandpa->_col = RED;
}
else
{
//情况三:左右双旋+变色
RotateL(dad);
RotateR(grandpa);
cur->_col = BLACK;
grandpa->_col = RED;
}
break;
}
}
//父为右子树 uncle为左子树
else
{
Node* uncle = grandpa->_left;
//情况一
if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED)
{
//变色
dad->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;
grandpa->_col = RED;
//回溯
cur = grandpa;
dad = cur->_parent;
}
else
{
if (cur == dad->_right)
{
//情况二:左单旋+变色
RotateL(grandpa);
dad->_col = BLACK;
grandpa->_col = RED;
}
else
{
//情况三:右左单旋+变色
RotateR(dad);
RotateL(grandpa);
cur->_col = BLACK;
grandpa->_col = RED;
}
break;
}
}
}
_root->_col = BLACK;
return true;
}
//中序遍历
void InOrder()
{
_InOrder(_root);
cout << endl;
}
//判断是否是红黑树
bool IsRBTree()
{
///空树默认为真
if (_root == nullptr)
{
return true;
}
//根节点颜色
if (_root->_col == RED)
{
cout << "根结点颜色错误!" << endl;
return false;
}
//某一条路径黑色结点数量
int certain = 0;
return PrevJudge(_root, 0, certain);
}
private:
//BNcount: black node count
bool PrevJudge(Node* root, int BNcount, int& certain)
{
//遇空 -- 当前路径结束
if (root == nullptr)
{
//指向此if时 某一条路径已结束 且 为第一条路径[第一次传参]
if (certain == 0)
{
certain = BNcount;
return true;
}
//判断性质4
if (BNcount != certain)
{
cout << "性质4违例:存在某一路径黑色节点的数量不等!" << endl;
return false;
}
else
{
return true;
}
}
//遇黑--值++
if (root->_col == BLACK)
{
++BNcount;
}
//遇红--连坐判断
if (root->_col == RED && root->_parent->_col == RED)
{
cout << "性质3违例: 存在连续红节点!" << endl;
return false;
}
return PrevJudge(root->_left, BNcount, certain)
&& PrevJudge(root->_right, BNcount, certain);
}
//中序遍历
void _InOrder(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return;
}
_InOrder(root->_left);
cout << root->_kv.first << ":" << root->_kv.second << endl;
_InOrder(root->_right);
}
//左单旋
void RotateL(Node* parent)
{
Node* subR = parent->_right;
Node* subRL = subR->_left;
parent->_right = subRL;
if (subRL)
subRL->_parent = parent;
Node* grandpa = parent->_parent;
subR->_left = parent;
parent->_parent = subR;
if (_root == parent)
{
_root = subR;
subR->_parent = nullptr;
}
else
{
if (grandpa->_left == parent)
{
grandpa->_left = subR;
}
else
{
grandpa->_right = subR;
}
subR->_parent = grandpa;
}
}
//右单旋
void RotateR(Node* parent)
{
Node* subL = parent->_left;
Node* subLR = subL->_right;
parent->_left = subLR;
if (subLR)
{
subLR->_parent = parent;
}
Node* grandpa = parent->_parent;
subL->_right = parent;
parent->_parent = subL;
if (_root == parent)
{
_root = subL;
subL->_parent = nullptr;
}
else
{
if (grandpa->_left == parent)
{
grandpa->_left = subL;
}
else
{
grandpa->_right = subL;
}
subL->_parent = grandpa;
}
}
private:
Node* _root = nullptr;
};
void TestRBTree1()
{
int a[] = { 4, 2, 6, 1, 3, 5, 15, 7, 16, 14 };
int b[] = { 16, 3, 7, 11, 9, 26, 18, 14, 15 };
int c[] = { 4, 2, 6, 1, 3, 5, 15, 7, 16, 14, 0, 5, 30, 25, 20, 4, 13, 30, 28,27 };
RBTree<int, int> tree;
for (auto e : c)
{
tree.Insert(make_pair(e, e));
}
cout << "此树中序遍历" << endl;
tree.InOrder();
if (tree.IsRBTree())
{
cout << "此树为红黑树!" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "此树不是红黑树!" << endl;
}
}
void TestRBTree2()
{
srand(time(0));
size_t N = 10;
RBTree<int, int> tree;
for (size_t i = 0; i < N; ++i)
{
int x = rand();
cout << "Insert:" << x << ":" << i << endl;
tree.Insert(make_pair(x, i));
}
if (tree.IsRBTree())
{
cout << "此树为红黑树!" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "此树不是红黑树!" << endl;
}
}
4.2Test.cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <array>
#include <time.h>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <string>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <functional>
using namespace std;
#include "RedBlackTree.h"
int main()
{
TestRBTree2();
return 0;
}