队列:只允许在一端进行插入数据操作,在另一端进行删除数据操作的特殊线性表,队列具有先进先出FIFO(First In First Out) 入队列:进行插入操作的一端称为队尾 出队列:进行删除操作的一端称为队头
那么我们应该用顺序变来实现队列还是用链表来实现呢
队列的实现无非就是顺序表链表的尾插和头删
如果是用顺序表的话:
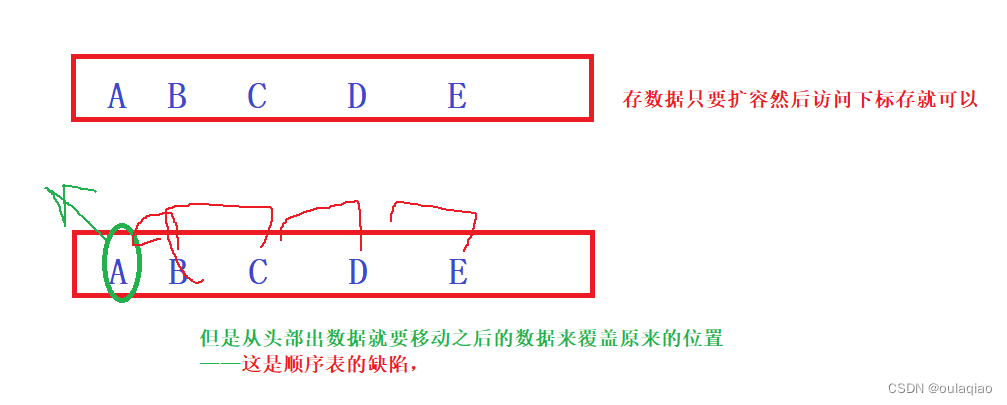
所以我们选择用链表来实现队列
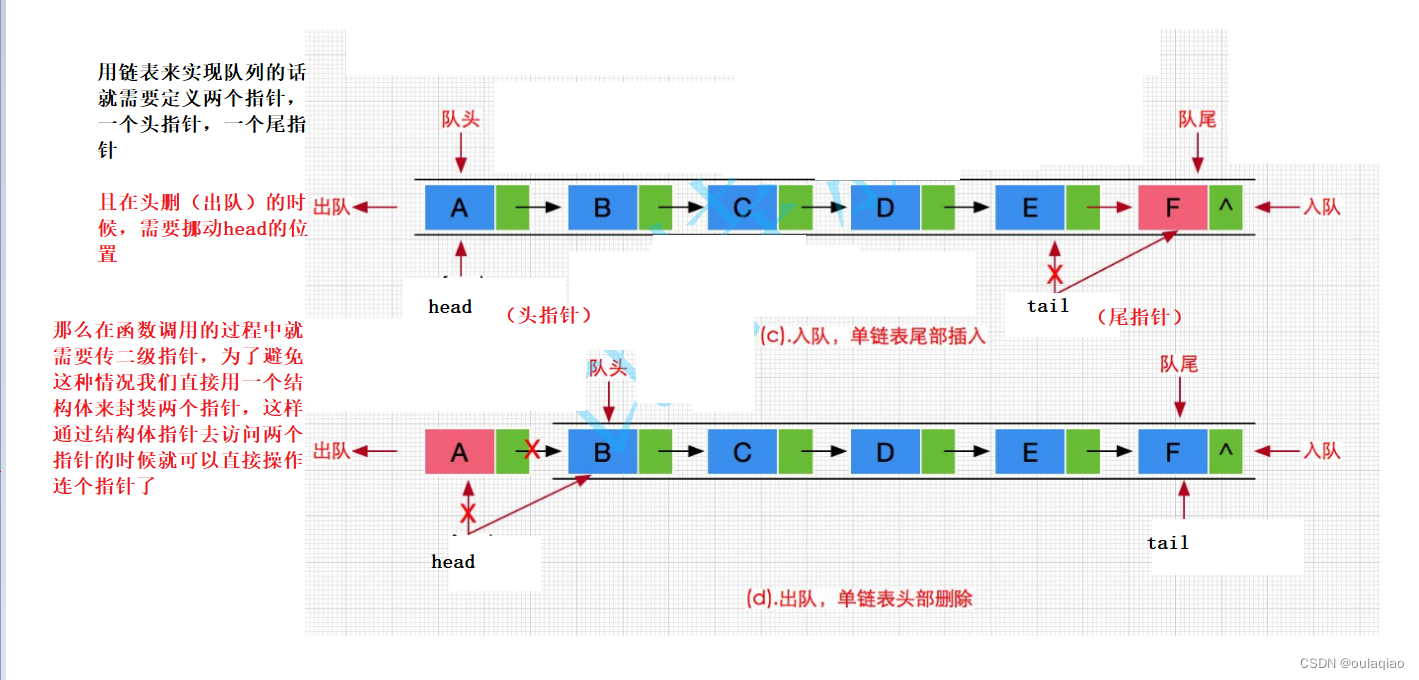
代码思路:先定义一个结构体用于开辟链表节点,在定义一个结构体来封装指向链表的两个指针,
//Queue.h
typedef int QDataType;
typedef struct QNode
{
struct QNode* next;
QDataType data;
}QNode;
typedef struct Queue
{
QNode* head;
QNode* tail;
int size;
}Queue;
void QueueInit(Queue* pq);//初始化
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x);//插入数据
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq);//判空
void QueueBack(Queue* pq);//头删
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq);//返回头值
QDataType QueueBront(Queue* pq);//返回尾值
int QueueSize(Queue* pq);//返回长
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq);//释放
然后通过链表的尾插头删来实现队列的先进先出
#include"Queue.h"
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)//初始化
{
assert(pq);
pq->head = NULL;
pq->tail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x)//插入数据
{
assert(pq);
QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("mallos fail");
exit(-1);
}
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
if (pq->tail == NULL)
{
pq->tail = pq->head = newnode;
pq->size++;
}
else
{
pq->tail->next = newnode;//尾插
pq->tail = newnode;//移动
pq->size++;
}
}
void QPrint(Queue* pq)//打印
{
QNode* cur = pq->head;
while (cur)
{
printf("%d", cur->data);
cur = cur->next;
}
}
void QueueBack(Queue* pq)//头删
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
QNode* per = pq->head->next;
free(pq->head);
pq->head = per;
if (pq->head->next == NULL)
{
pq->tail = NULL;
}
pq->size--;
}
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)//返回头值
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->head);
return pq->head->data;
}
QDataType QueueBront(Queue* pq)//返回尾值
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->head);
return pq->tail->data;
}
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)//判空
{
assert(pq);
return pq->head == NULL;
}
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)//返回长
{
assert(pq);
return pq->size;
}
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq)//释放
{
assert(pq);
QNode* cur = pq->head;
while(cur)
{
QNode* per = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = per;
}
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
最后补充:
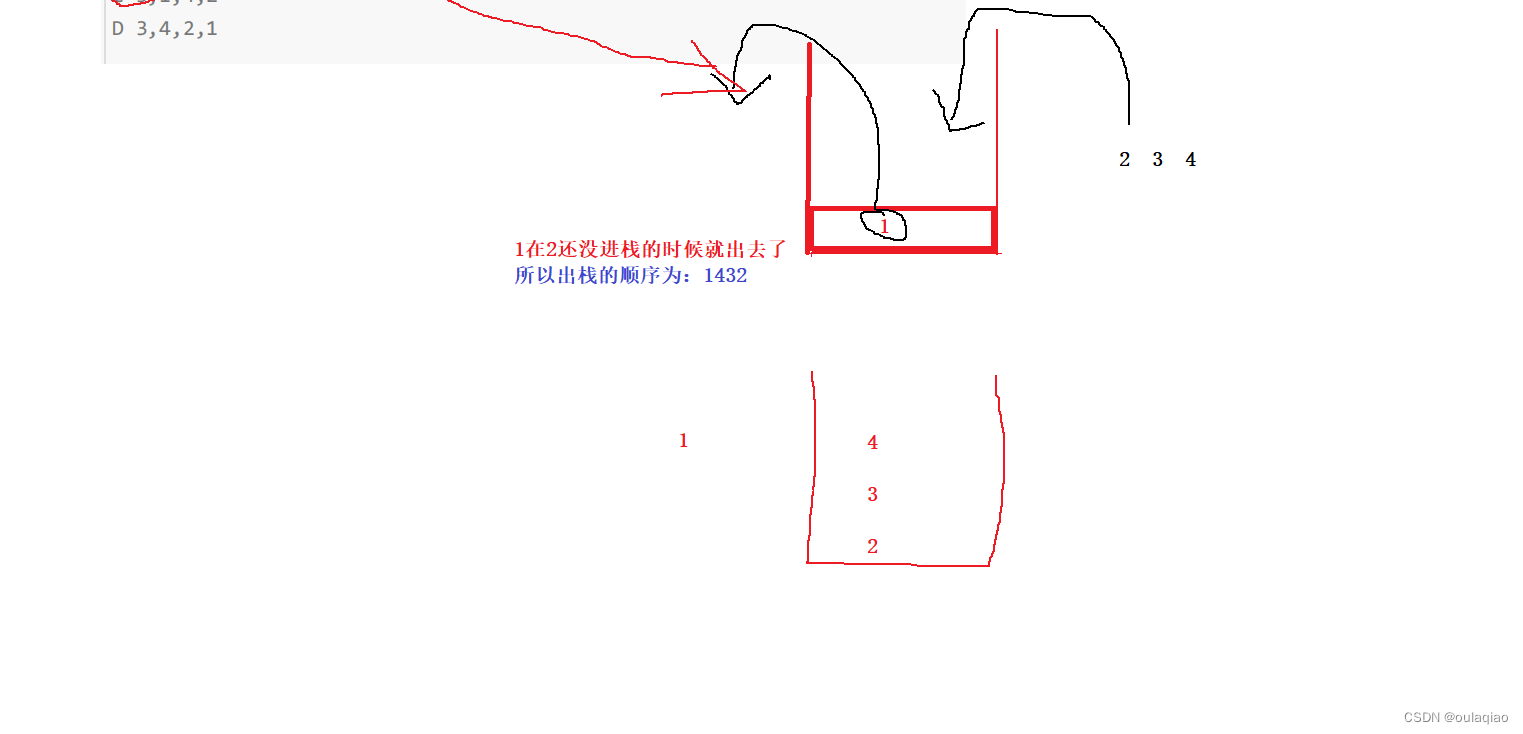
队列因为是尾查头删的特性一定是先进先出的
但是栈虽然是后进先出,但也会在边进边出,所以先进去的数也有可能在后面的数还没进的时候就已经出去了