文章目录
- 1. @Async异步任务概述
- 2. 深入@Async的底层
- 2.1 @Async注解
- 2.2 @EnableAsync注解
- 2.3 默认线程池
1. @Async异步任务概述
在Spring3.X的版本之后,内置了@Async解决了多个任务同步进行导致接口响应迟缓的情况。
使用@Async注解可以异步执行一个任务,这个任务的返回值必定为null,所以在使用@Async推荐返回值为NULL。
那么该如何使用@Async开启一个异步任务呢?
很简单,需要知道两个重要的注解:
@EnableAysnc:启动类上开启异步模式@Async:需要异步处理的方法
@EnableAsync
@SpringBootApplication
public class MyApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(MyApplication.class, args);
log.info("Project running .....");
}
}
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Async
public void test() {
log.info("test");
}
}
需要注意的是,@Async的异步任务是基于AOP实现的,如果是自调用的情况下,@Async是不会生效的喔。
2. 深入@Async的底层
@Async注解可以将一个任务异步调用,那么就说明其底层帮我们创建了一个线程池,使用线程池的线程调用这个异步方法,那我们就开始扒一扒这个注解的底层是什么东东吧。
2.1 @Async注解
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface Async {
/**
* A qualifier value for the specified asynchronous operation(s).
* <p>May be used to determine the target executor to be used when executing
* the asynchronous operation(s), matching the qualifier value (or the bean
* name) of a specific {@link java.util.concurrent.Executor Executor} or
* {@link org.springframework.core.task.TaskExecutor TaskExecutor}
* bean definition.
* <p>When specified on a class-level {@code @Async} annotation, indicates that the
* given executor should be used for all methods within the class. Method-level use
* of {@code Async#value} always overrides any value set at the class level.
* @since 3.1.2
*/
String value() default "";
}
指定异步操作的限定符值。 可用于确定执行异步操作时要使用的目标执行器,与特定executor或TaskExecutor bean定义的限定符值(或bean名称)匹配。 当在类级别@Async注释上指定时,指示给定的执行器应用于类中的所有方法。方法级别对Async#值的使用始终覆盖在类级别设置的任何值。
自: 3.1.2
从注解的注释来看,可以看出这个@Async里只有一个value属性,这个属性其实就是Bean的名称,如果不为null,则从Spring容器中获取这个Bean。
并且@Async的返回值只能是 void 或 Future。
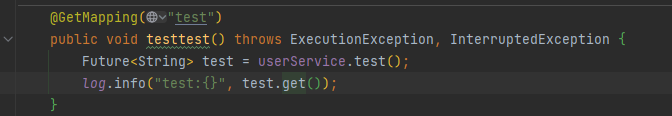
当我们需要返回值的时候,可以使用 对象对返回结果包一层,否则就会返回NULL

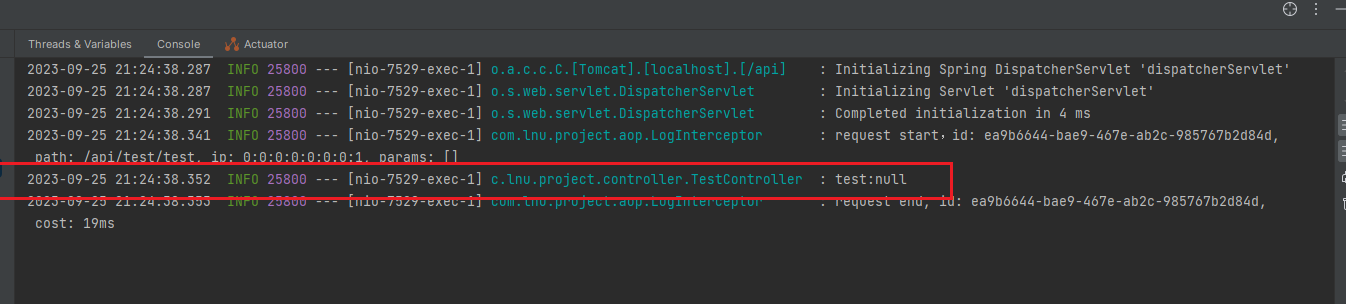
但是当我们使用AsyncResult包一层,就会获取返回结果的对象。

2.2 @EnableAsync注解
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Import(AsyncConfigurationSelector.class)
public @interface EnableAsync {
/**
* Indicate the 'async' annotation type to be detected at either class
* or method level.
* <p>By default, both Spring's @{@link Async} annotation and the EJB 3.1
* {@code @javax.ejb.Asynchronous} annotation will be detected.
* <p>This attribute exists so that developers can provide their own
* custom annotation type to indicate that a method (or all methods of
* a given class) should be invoked asynchronously.
*/
Class<? extends Annotation> annotation() default Annotation.class;
/**
* Indicate whether subclass-based (CGLIB) proxies are to be created as opposed
* to standard Java interface-based proxies.
* <p><strong>Applicable only if the {@link #mode} is set to {@link AdviceMode#PROXY}</strong>.
* <p>The default is {@code false}.
* <p>Note that setting this attribute to {@code true} will affect <em>all</em>
* Spring-managed beans requiring proxying, not just those marked with {@code @Async}.
* For example, other beans marked with Spring's {@code @Transactional} annotation
* will be upgraded to subclass proxying at the same time. This approach has no
* negative impact in practice unless one is explicitly expecting one type of proxy
* vs. another — for example, in tests.
*/
boolean proxyTargetClass() default false;
/**
* Indicate how async advice should be applied.
* <p><b>The default is {@link AdviceMode#PROXY}.</b>
* Please note that proxy mode allows for interception of calls through the proxy
* only. Local calls within the same class cannot get intercepted that way; an
* {@link Async} annotation on such a method within a local call will be ignored
* since Spring's interceptor does not even kick in for such a runtime scenario.
* For a more advanced mode of interception, consider switching this to
* {@link AdviceMode#ASPECTJ}.
*/
AdviceMode mode() default AdviceMode.PROXY;
/**
* Indicate the order in which the {@link AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor}
* should be applied.
* <p>The default is {@link Ordered#LOWEST_PRECEDENCE} in order to run
* after all other post-processors, so that it can add an advisor to
* existing proxies rather than double-proxy.
*/
int order() default Ordered.LOWEST_PRECEDENCE;
}
在@EnableAsync注解中,最重要的一行代码就是@Import(AsyncConfigurationSelector.class),其他的不作解释,感兴趣的可以自行阅读源码的注释理解学习。
在@Import(AsyncConfigurationSelector.class)这行代码中,引入了相关的配置类,让我们看可以看AsyncConfigurationSelector这个类有什么东西
public class AsyncConfigurationSelector extends AdviceModeImportSelector<EnableAsync> {
private static final String ASYNC_EXECUTION_ASPECT_CONFIGURATION_CLASS_NAME =
"org.springframework.scheduling.aspectj.AspectJAsyncConfiguration";
/**
* Returns {@link ProxyAsyncConfiguration} or {@code AspectJAsyncConfiguration}
* for {@code PROXY} and {@code ASPECTJ} values of {@link EnableAsync#mode()},
* respectively.
*/
@Override
@Nullable
public String[] selectImports(AdviceMode adviceMode) {
switch (adviceMode) {
case PROXY:
return new String[] {ProxyAsyncConfiguration.class.getName()};
case ASPECTJ:
return new String[] {ASYNC_EXECUTION_ASPECT_CONFIGURATION_CLASS_NAME};
default:
return null;
}
}
}
里面只有一个方法selectImports,这个方法就是一个选择器,根据不同的代理模式,加载不同的配置类。
首先我们看看ProxyAsyncConfiguration这个配置类。
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
public class ProxyAsyncConfiguration extends AbstractAsyncConfiguration {
@Bean(name = TaskManagementConfigUtils.ASYNC_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
public AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor asyncAdvisor() {
Assert.notNull(this.enableAsync, "@EnableAsync annotation metadata was not injected");
//初始化AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor类型的bean
AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor bpp = new AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor();
//设置执行器和异常处理器
bpp.configure(this.executor, this.exceptionHandler);
Class<? extends Annotation> customAsyncAnnotation = this.enableAsync.getClass("annotation");
//设置annotation
if (customAsyncAnnotation != AnnotationUtils.getDefaultValue(EnableAsync.class, "annotation")) {
bpp.setAsyncAnnotationType(customAsyncAnnotation);
}
//设置注解属性
bpp.setProxyTargetClass(this.enableAsync.getBoolean("proxyTargetClass"));
bpp.setOrder(this.enableAsync.<Integer>getNumber("order"));
return bpp;
}
}
ProxyAsyncConfiguration配置类继承了AbstractAsyncConfiguration类,这个类用于配置异步任务的线程池与执行器。它提供了一些默认实现,可以使配置变得更加简单和快捷,并且易于扩展和定制。
在这ProxyAsyncConfiguration配置类中,初始化了一个AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor,AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor是Spring框架中的一个后置处理器,用于处理带有@Async注解的方法。它的主要作用是将这些方法转换为异步执行的任务,并使用适当的线程池进行调度和管理。
asyncAdvisor方法定义了一个Bean后置处理器,负责解析带@Async注解的方法,并将其包装成一个异步任务
那么异步任务在哪包装的呢?
我们把目光投到org.springframework.aop.interceptor.AsyncExecutionAspectSupport类中,里面有一个invoke方法,这个方法负责拦截给定方法的调用,将方法的实际调用提供给正确的任务执行器,并返回个调用者
@Override
@Nullable
public Object invoke(final MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {
Class<?> targetClass = (invocation.getThis() != null ? AopUtils.getTargetClass(invocation.getThis()) : null);
Method specificMethod = ClassUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(invocation.getMethod(), targetClass);
final Method userDeclaredMethod = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(specificMethod);
// 获取线程池
AsyncTaskExecutor executor = determineAsyncExecutor(userDeclaredMethod);
if (executor == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"No executor specified and no default executor set on AsyncExecutionInterceptor either");
}
// 将方法调用封装成一个任务
Callable<Object> task = () -> {
try {
Object result = invocation.proceed();
if (result instanceof Future) {
return ((Future<?>) result).get();
}
}
catch (ExecutionException ex) {
handleError(ex.getCause(), userDeclaredMethod, invocation.getArguments());
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleError(ex, userDeclaredMethod, invocation.getArguments());
}
return null;
};
// 提交任务
return doSubmit(task, executor, invocation.getMethod().getReturnType());
}
determineAsyncExecutor方法分为三个部分
- 获取
@Async注解的value值,这个值其实就是Bean的名称,如果不为空则从Spring容器获取对应的Bean - 如果value为null,则找到默认线程池
- 最后,不论是默认的线程池还是 Spring 容器中我们自定义的线程池,都会以方法为维度,在 map 中维护方法和线程池的映射关系。


2.3 默认线程池
从前面得知,成员变量defaultExecutor是默认的线程池,那么这个默认线程池是怎么样的呢?
这时候我们需要关注org.springframework.aop.interceptor.AsyncExecutionAspectSupport#getDefaultExecutor方法。
1、在没有配置线程池的情况下,使用ThreadPoolTaskExecutor
2、配置了线程池,但是没有用taskExecutor,会找不到,就用SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor
3、配置线程池,并且指定beanName为taskExecutor,就会直接使用这个配置的线程池
@Nullable
protected Executor getDefaultExecutor(@Nullable BeanFactory beanFactory) {
if (beanFactory != null) {
try {
// Search for TaskExecutor bean... not plain Executor since that would
// match with ScheduledExecutorService as well, which is unusable for
// our purposes here. TaskExecutor is more clearly designed for it.
return beanFactory.getBean(TaskExecutor.class);
}
catch (NoUniqueBeanDefinitionException ex) {
logger.debug("Could not find unique TaskExecutor bean. " +
"Continuing search for an Executor bean named 'taskExecutor'", ex);
try {
return beanFactory.getBean(DEFAULT_TASK_EXECUTOR_BEAN_NAME, Executor.class);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex2) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("More than one TaskExecutor bean found within the context, and none is named " +
"'taskExecutor'. Mark one of them as primary or name it 'taskExecutor' (possibly " +
"as an alias) in order to use it for async processing: " + ex.getBeanNamesFound());
}
}
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
logger.debug("Could not find default TaskExecutor bean. " +
"Continuing search for an Executor bean named 'taskExecutor'", ex);
try {
return beanFactory.getBean(DEFAULT_TASK_EXECUTOR_BEAN_NAME, Executor.class);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex2) {
logger.info("No task executor bean found for async processing: " +
"no bean of type TaskExecutor and no bean named 'taskExecutor' either");
}
// Giving up -> either using local default executor or none at all...
}
}
return null;
}
通过DEBUG可以看到默认使用的ThreadPoolTaskScheduler

参考:
- @Async注解其实也就这么回事。 - 掘金 (juejin.cn)
- Spring异步编程 | 你的@Async就真的异步吗 ☞ 异步历险奇遇记 - 掘金 (juejin.cn)
- @Async异步任务与线程池 - 掘金 (juejin.cn)
- @Async注解使用与原理分析 - 知乎 (zhihu.com)



![[尚硅谷React笔记]——第2章 React面向组件编程](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/215ab1c6d5de4cd8acefe976c585a768.png)