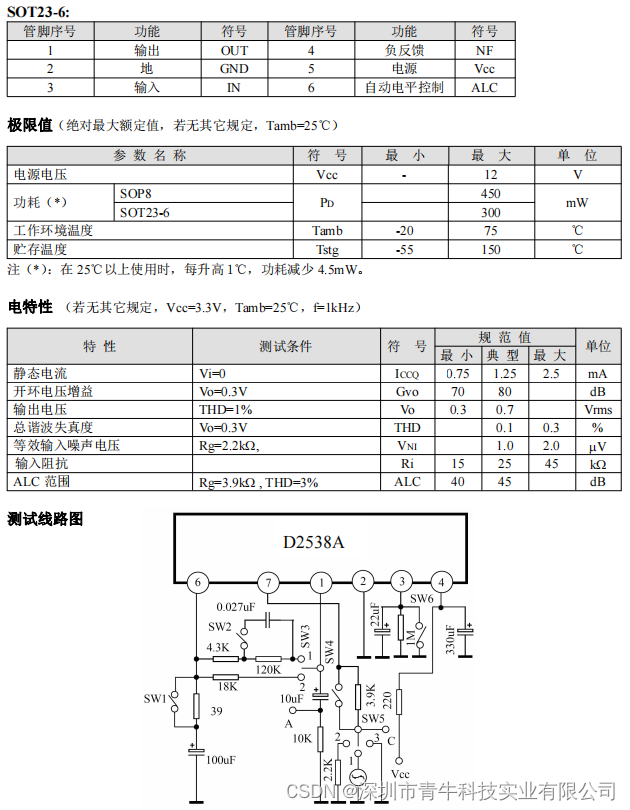
现实世界中有无数种颜色,每一个物体都有它们自己的颜色。我们需要使用(有限的)数值来模拟真实世界中(无限)的颜色,所以并不是所有现实世界中的颜色都可以用数值来表示的。然而我们仍能通过数值来表现出非常多的颜色,甚至你可能都不会注意到与现实的颜色有任何的差异。颜色可以数字化的由红色(Red)、绿色(Green)和蓝色(Blue)三个分量组成,它们通常被缩写为RGB。仅仅用这三个值就可以组合出任意一种颜色。例如,要获取一个珊瑚红(Coral)色的话,我们可以定义这样的一个颜色向量:
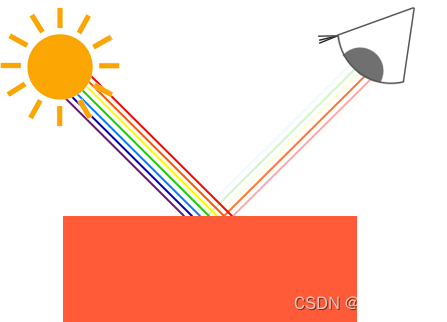
glm::vec3 coral(1.0f, 0.5f, 0.31f);我们在现实生活中看到某一物体的颜色并不是这个物体真正拥有的颜色,而是它所反射的(Reflected)颜色。换句话说,那些不能被物体所吸收(Absorb)的颜色(被拒绝的颜色)就是我们能够感知到的物体的颜色。例如,太阳光能被看见的白光其实是由许多不同的颜色组合而成的(如下图所示)。如果我们将白光照在一个蓝色的玩具上,这个蓝色的玩具会吸收白光中除了蓝色以外的所有子颜色,不被吸收的蓝色光被反射到我们的眼中,让这个玩具看起来是蓝色的。下图显示的是一个珊瑚红的玩具,它以不同强度反射了多个颜色。
当我们在OpenGL中创建一个光源时,我们希望给光源一个颜色。在上一段中我们有一个白色的太阳,所以我们也将光源设置为白色。当我们把光源的颜色与物体的颜色值相乘,所得到的就是这个物体所反射的颜色(也就是我们所感知到的颜色)
glm::vec3 lightColor(1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f);
glm::vec3 toyColor(1.0f, 0.5f, 0.31f);
glm::vec3 result = lightColor * toyColor; // = (1.0f, 0.5f, 0.31f);我们可以看到玩具的颜色吸收了白色光源中很大一部分的颜色,但它根据自身的颜色值对红、绿、蓝三个分量都做出了一定的反射。这也表现了现实中颜色的工作原理 。
glm::vec3 lightColor(0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f);
glm::vec3 toyColor(1.0f, 0.5f, 0.31f);
glm::vec3 result = lightColor * toyColor; // = (0.0f, 0.5f, 0.0f);只有绿色分量能被反射和感知到,红色和蓝色都不能被我们所感知到。这样做的结果是,一个珊瑚红的玩具突然变成了深绿色物体。现在我们来看另一个例子,使用深橄榄绿色(Dark olive-green)的光源:
glm::vec3 lightColor(0.33f, 0.42f, 0.18f);
glm::vec3 toyColor(1.0f, 0.5f, 0.31f);
glm::vec3 result = lightColor * toyColor; // = (0.33f, 0.21f, 0.06f);可以看到,我们可以使用不同的光源颜色来让物体显现出意想不到的颜色
创建一个光照场景
首先我们需要一个物体来作为被投光(Cast the light)的对象,我们将使用前面教程中的那个著名的立方体箱子。我们还需要一个物体来代表光源在3D场景中的位置。简单起见,我们依然使用一个立方体来代表光源。
我们首先需要一个顶点着色器来绘制箱子。与之前的顶点着色器相比,容器的顶点位置是保持不变的(虽然这一次我们不需要纹理坐标了),因此顶点着色器中没有新的代码。我们将会使用之前教程顶点着色器的精简版:
#version 330 core
layout (location = 0) in vec3 aPos;
uniform mat4 model;
uniform mat4 view;
uniform mat4 projection;
void main()
{
gl_Position = projection * view * model * vec4(aPos, 1.0);
}因为我们还要创建一个表示灯(光源)的立方体,所以我们还要为这个灯创建一个专门的VAO。当然我们也可以让这个灯和其它物体使用同一个VAO,简单地对它的model(模型)矩阵做一些变换就好了,然而接下来的教程中我们会频繁地对顶点数据和属性指针做出修改,我们并不想让这些修改影响到灯(我们只关心灯的顶点位置),因此我们有必要为灯创建一个新的VAO。
unsigned int lightVAO;
glGenVertexArrays(1, &lightVAO);
glBindVertexArray(lightVAO);
// 只需要绑定VBO不用再次设置VBO的数据,因为箱子的VBO数据中已经包含了正确的立方体顶点数据
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, VBO);
// 设置灯立方体的顶点属性(对我们的灯来说仅仅只有位置数据)
glVertexAttribPointer(0, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 3 * sizeof(float), (void*)0);
glEnableVertexAttribArray(0);这段代码对你来说应该非常直观
#version 330 core
out vec4 FragColor;
uniform vec3 objectColor;
uniform vec3 lightColor;
void main()
{
FragColor = vec4(lightColor * objectColor, 1.0);
}这个片段着色器从uniform变量中接受物体的颜色和光源的颜色
// 在此之前不要忘记首先 use 对应的着色器程序(来设定uniform)
lightingShader.use();
lightingShader.setVec3("objectColor", 1.0f, 0.5f, 0.31f);
lightingShader.setVec3("lightColor", 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f);为了实现这个目标,我们需要为灯的绘制创建另外的一套着色器,从而能保证它能够在其它光照着色器发生改变的时候不受影响。顶点着色器与我们当前的顶点着色器是一样的,所以你可以直接把现在的顶点着色器用在灯上。灯的片段着色器给灯定义了一个不变的常量白色,保证了灯的颜色一直是亮的:
#version 330 core
out vec4 FragColor;
void main()
{
FragColor = vec4(1.0); // 将向量的四个分量全部设置为1.0
}使用这个灯立方体的主要目的是为了让我们知道光源在场景中的具体位置。我们通常在场景中定义一个光源的位置,但这只是一个位置,它并没有视觉意义。为了显示真正的灯,我们将表示光源的立方体绘制在与光源相同的位置。我们将使用我们为它新建的片段着色器来绘制它,让它一直处于白色的状态,不受场景中的光照影响。
我们声明一个全局vec3变量来表示光源在场景的世界空间坐标中的位置:
然后我们把灯位移到这里,然后将它缩小一点,让它不那么明显:
model = glm::mat4();
model = glm::translate(model, lightPos);
model = glm::scale(model, glm::vec3(0.2f));
绘制灯立方体的代码应该与下面的类似:
lampShader.use();
// 设置模型、视图和投影矩阵uniform
...
// 绘制灯立方体对象
glBindVertexArray(lightVAO);
glDrawArrays(GL_TRIANGLES, 0, 36);
请把上述的所有代码片段放在你程序中合适的位置,这样我们就能有一个干净的光照实验场地了。如果一切顺利,运行效果将会如下图所示:
#include "glad.h"
#include <GLFW/glfw3.h>
#include "stb_image.h"
#include <glm/glm.hpp>
#include <glm/gtc/matrix_transform.hpp>
#include <glm/gtc/type_ptr.hpp>
#include "shader_m.h"
#include <iostream>
#include "camera.h"
void framebuffer_size_callback(GLFWwindow* window, int width, int height);
void mouse_callback(GLFWwindow* window, double xpos, double ypos);
void scroll_callback(GLFWwindow* window, double xoffset, double yoffset);
void processInput(GLFWwindow *window);
// settings
const unsigned int SCR_WIDTH = 800;
const unsigned int SCR_HEIGHT = 600;
// camera
Camera camera(glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, 3.0f));
float lastX = SCR_WIDTH / 2.0f;
float lastY = SCR_HEIGHT / 2.0f;
bool firstMouse = true;
// timing
float deltaTime = 0.0f;
float lastFrame = 0.0f;
// lighting
glm::vec3 lightPos(1.2f, 1.0f, 2.0f);
int main()
{
// glfw: initialize and configure
// ------------------------------
glfwInit();
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_CONTEXT_VERSION_MAJOR, 3);
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_CONTEXT_VERSION_MINOR, 3);
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_OPENGL_PROFILE, GLFW_OPENGL_CORE_PROFILE);
#ifdef __APPLE__
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_OPENGL_FORWARD_COMPAT, GL_TRUE);
#endif
// glfw window creation
// --------------------
GLFWwindow* window = glfwCreateWindow(SCR_WIDTH, SCR_HEIGHT, "LearnOpenGL", NULL, NULL);
if (window == NULL)
{
std::cout << "Failed to create GLFW window" << std::endl;
glfwTerminate();
return -1;
}
glfwMakeContextCurrent(window);
glfwSetFramebufferSizeCallback(window, framebuffer_size_callback);
glfwSetCursorPosCallback(window, mouse_callback);
glfwSetScrollCallback(window, scroll_callback);
// tell GLFW to capture our mouse
glfwSetInputMode(window, GLFW_CURSOR, GLFW_CURSOR_DISABLED);
// glad: load all OpenGL function pointers
// ---------------------------------------
if (!gladLoadGLLoader((GLADloadproc)glfwGetProcAddress))
{
std::cout << "Failed to initialize GLAD" << std::endl;
return -1;
}
// configure global opengl state
// -----------------------------
glEnable(GL_DEPTH_TEST);
Shader lightingShader("/home/ss/OpenGL_learn/source/text/1_color.vs", "/home/ss/OpenGL_learn/source/text/1_color.fs");
Shader lightCubeShader("/home/ss/OpenGL_learn/source/text/1_light_cube.vs", "/home/ss/OpenGL_learn/source/text/1_light_cube.fs");
// set up vertex data (and buffer(s)) and configure vertex attributes
// ------------------------------------------------------------------
float vertices[] = {
-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f,
0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f,
0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f,
0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f,
0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f,
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f,
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f,
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f,
0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f,
0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f,
0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f,
0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f,
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f,
0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f,
0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f,
0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f,
0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f,
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f,
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f,
};
// first, configure the cube's VAO (and VBO)
unsigned int VBO, cubeVAO;
glGenVertexArrays(1, &cubeVAO);
glGenBuffers(1, &VBO);
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, VBO);
glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, sizeof(vertices), vertices, GL_STATIC_DRAW);
glBindVertexArray(cubeVAO);
// position attribute
glVertexAttribPointer(0, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 3 * sizeof(float), (void*)0);
glEnableVertexAttribArray(0);
// second, configure the light's VAO (VBO stays the same; the vertices are the same for the light object which is also a 3D cube)
unsigned int lightCubeVAO;
glGenVertexArrays(1, &lightCubeVAO);
glBindVertexArray(lightCubeVAO);
// we only need to bind to the VBO (to link it with glVertexAttribPointer), no need to fill it; the VBO's data already contains all we need (it's already bound, but we do it again for educational purposes)
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, VBO);
glVertexAttribPointer(0, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 3 * sizeof(float), (void*)0);
glEnableVertexAttribArray(0);
// render loop
// -----------
while (!glfwWindowShouldClose(window))
{
// per-frame time logic
// --------------------
float currentFrame = static_cast<float>(glfwGetTime());
deltaTime = currentFrame - lastFrame;
lastFrame = currentFrame;
// input
// -----
processInput(window);
// render
// ------
glClearColor(0.1f, 0.1f, 0.1f, 1.0f);
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT);
// be sure to activate shader when setting uniforms/drawing objects
lightingShader.use();
lightingShader.setVec3("objectColor", 1.0f, 0.5f, 0.31f);
lightingShader.setVec3("lightColor", 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f);
// view/projection transformations
glm::mat4 projection = glm::perspective(glm::radians(camera.Zoom), (float)SCR_WIDTH / (float)SCR_HEIGHT, 0.1f, 100.0f);
glm::mat4 view = camera.GetViewMatrix();
lightingShader.setMat4("projection", projection);
lightingShader.setMat4("view", view);
// world transformation
glm::mat4 model = glm::mat4(1.0f);
lightingShader.setMat4("model", model);
// render the cube
glBindVertexArray(cubeVAO);
glDrawArrays(GL_TRIANGLES, 0, 36);
// also draw the lamp object
lightCubeShader.use();
lightCubeShader.setMat4("projection", projection);
lightCubeShader.setMat4("view", view);
model = glm::mat4(1.0f);
model = glm::translate(model, lightPos);
model = glm::scale(model, glm::vec3(0.2f)); // a smaller cube
lightCubeShader.setMat4("model", model);
glBindVertexArray(lightCubeVAO);
glDrawArrays(GL_TRIANGLES, 0, 36);
// glfw: swap buffers and poll IO events (keys pressed/released, mouse moved etc.)
// -------------------------------------------------------------------------------
glfwSwapBuffers(window);
glfwPollEvents();
}
// optional: de-allocate all resources once they've outlived their purpose:
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------
glDeleteVertexArrays(1, &cubeVAO);
glDeleteVertexArrays(1, &lightCubeVAO);
glDeleteBuffers(1, &VBO);
// glfw: terminate, clearing all previously allocated GLFW resources.
// ------------------------------------------------------------------
glfwTerminate();
return 0;
}
// process all input: query GLFW whether relevant keys are pressed/released this frame and react accordingly
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void processInput(GLFWwindow *window)
{
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_ESCAPE) == GLFW_PRESS)
glfwSetWindowShouldClose(window, true);
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_W) == GLFW_PRESS)
camera.ProcessKeyboard(FORWARD, deltaTime);
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_S) == GLFW_PRESS)
camera.ProcessKeyboard(BACKWARD, deltaTime);
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_A) == GLFW_PRESS)
camera.ProcessKeyboard(LEFT, deltaTime);
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_D) == GLFW_PRESS)
camera.ProcessKeyboard(RIGHT, deltaTime);
}
// glfw: whenever the window size changed (by OS or user resize) this callback function executes
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void framebuffer_size_callback(GLFWwindow* window, int width, int height)
{
// make sure the viewport matches the new window dimensions; note that width and
// height will be significantly larger than specified on retina displays.
glViewport(0, 0, width, height);
}
// glfw: whenever the mouse moves, this callback is called
// -------------------------------------------------------
void mouse_callback(GLFWwindow* window, double xposIn, double yposIn)
{
float xpos = static_cast<float>(xposIn);
float ypos = static_cast<float>(yposIn);
if (firstMouse)
{
lastX = xpos;
lastY = ypos;
firstMouse = false;
}
float xoffset = xpos - lastX;
float yoffset = lastY - ypos; // reversed since y-coordinates go from bottom to top
lastX = xpos;
lastY = ypos;
camera.ProcessMouseMovement(xoffset, yoffset);
}
// glfw: whenever the mouse scroll wheel scrolls, this callback is called
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------
void scroll_callback(GLFWwindow* window, double xoffset, double yoffset)
{
camera.ProcessMouseScroll(static_cast<float>(yoffset));
}camera.h
#ifndef CAMERA_H
#define CAMERA_H
#include <glad/glad.h>
#include <glm/glm.hpp>
#include <glm/gtc/matrix_transform.hpp>
#include <vector>
// Defines several possible options for camera movement. Used as abstraction to stay away from window-system specific input methods
enum Camera_Movement {
FORWARD,
BACKWARD,
LEFT,
RIGHT
};
// Default camera values
const float YAW = -90.0f;
const float PITCH = 0.0f;
const float SPEED = 2.5f;
const float SENSITIVITY = 0.1f;
const float ZOOM = 45.0f;
// An abstract camera class that processes input and calculates the corresponding Euler Angles, Vectors and Matrices for use in OpenGL
class Camera
{
public:
// camera Attributes
glm::vec3 Position;
glm::vec3 Front;
glm::vec3 Up;
glm::vec3 Right;
glm::vec3 WorldUp;
// euler Angles
float Yaw;
float Pitch;
// camera options
float MovementSpeed;
float MouseSensitivity;
float Zoom;
// constructor with vectors
Camera(glm::vec3 position = glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f), glm::vec3 up = glm::vec3(0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f), float yaw = YAW, float pitch = PITCH) : Front(glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f)), MovementSpeed(SPEED), MouseSensitivity(SENSITIVITY), Zoom(ZOOM)
{
Position = position;
WorldUp = up;
Yaw = yaw;
Pitch = pitch;
updateCameraVectors();
}
// constructor with scalar values
Camera(float posX, float posY, float posZ, float upX, float upY, float upZ, float yaw, float pitch) : Front(glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f)), MovementSpeed(SPEED), MouseSensitivity(SENSITIVITY), Zoom(ZOOM)
{
Position = glm::vec3(posX, posY, posZ);
WorldUp = glm::vec3(upX, upY, upZ);
Yaw = yaw;
Pitch = pitch;
updateCameraVectors();
}
// returns the view matrix calculated using Euler Angles and the LookAt Matrix
glm::mat4 GetViewMatrix()
{
return glm::lookAt(Position, Position + Front, Up);
}
// processes input received from any keyboard-like input system. Accepts input parameter in the form of camera defined ENUM (to abstract it from windowing systems)
void ProcessKeyboard(Camera_Movement direction, float deltaTime)
{
float velocity = MovementSpeed * deltaTime;
if (direction == FORWARD)
Position += Front * velocity;
if (direction == BACKWARD)
Position -= Front * velocity;
if (direction == LEFT)
Position -= Right * velocity;
if (direction == RIGHT)
Position += Right * velocity;
}
// processes input received from a mouse input system. Expects the offset value in both the x and y direction.
void ProcessMouseMovement(float xoffset, float yoffset, GLboolean constrainPitch = true)
{
xoffset *= MouseSensitivity;
yoffset *= MouseSensitivity;
Yaw += xoffset;
Pitch += yoffset;
// make sure that when pitch is out of bounds, screen doesn't get flipped
if (constrainPitch)
{
if (Pitch > 89.0f)
Pitch = 89.0f;
if (Pitch < -89.0f)
Pitch = -89.0f;
}
// update Front, Right and Up Vectors using the updated Euler angles
updateCameraVectors();
}
// processes input received from a mouse scroll-wheel event. Only requires input on the vertical wheel-axis
void ProcessMouseScroll(float yoffset)
{
Zoom -= (float)yoffset;
if (Zoom < 1.0f)
Zoom = 1.0f;
if (Zoom > 45.0f)
Zoom = 45.0f;
}
private:
// calculates the front vector from the Camera's (updated) Euler Angles
void updateCameraVectors()
{
// calculate the new Front vector
glm::vec3 front;
front.x = cos(glm::radians(Yaw)) * cos(glm::radians(Pitch));
front.y = sin(glm::radians(Pitch));
front.z = sin(glm::radians(Yaw)) * cos(glm::radians(Pitch));
Front = glm::normalize(front);
// also re-calculate the Right and Up vector
Right = glm::normalize(glm::cross(Front, WorldUp)); // normalize the vectors, because their length gets closer to 0 the more you look up or down which results in slower movement.
Up = glm::normalize(glm::cross(Right, Front));
}
};
#endif