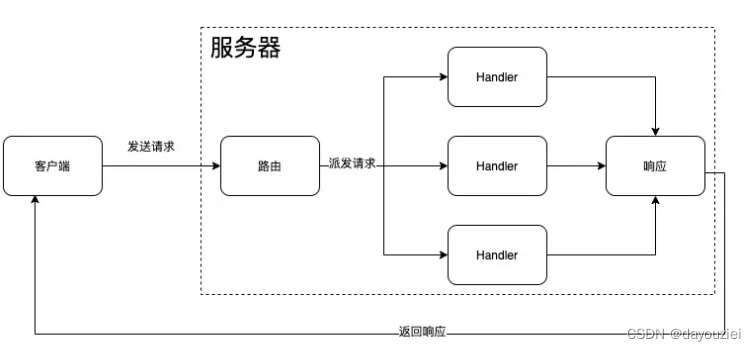
题目
并查集相信大家都不陌生,能够以极低的时间复杂度进行区间合并和区间查询,而带权并查集就是在此基础上新增了查询和维护节点到根节点距离的功能,注意此处所说的距离并不是并查集树形数据结构里节点之间的距离,而是题目里面描述和规定的距离。
比如对于这道带权并查集的经典例题洛谷P1196 银河英雄传说,它的题意如下,在这道题中距离的定义就是两个战舰之间所间隔的战舰数。
在并查集里面,为了减小时间花费,我们把一个集合里的所有结点都直接挂在根节点下面。在带权并查集中我们同样是这种做法,对于一一对父子结点,它们所代表的两艘战舰直接的距离可能是任意值。

代码
这是例题的代码,一切都写在注释里面。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 300010;
// Node结构体代表一艘战舰
struct Node{
Node* pre; // 当前节点的父节点
int preDist; // 当前节点距离pre节点的距离
int size; // 如果当前节点为根节点,那么size代表这个集合的节点数量
}nodes[N];
// find函数的作用有三:
// 1. 把node节点的父节点赋值为根节点
// 2. 更新node节点距父节点的距离
// 3. 返回node元素的父节点(根节点)
Node* find(Node* node){
if(node->pre != node){
Node* root = find(node->pre);
// 因为刚刚对父节点调用了find函数,所以此时父节点直接挂在根节点下面
// 所以当前节点的predist加上父节点的predist等于当前节点到根节点距离
node->preDist += node->pre->preDist;
node->pre = root;
}
return node->pre;
}
// 把X元素所在集合,合并到Y元素所在集合里面
void merge(Node* nodeX, Node* nodeY){
Node* rootx = find(nodeX);
Node* rooty = find(nodeY);
if(rootx != rooty){
// x根元素到父节点的距离等于y元素所在集合的节点数量
rootx->preDist = rooty->size;
// 合并之后要更新一下y所在集合的节点数量
rooty->size += rootx->size;
rootx->pre = rooty;
}
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
int t;
cin >> t;
for(int i = 1; i <= N; i++){
nodes[i].pre = nodes + i;
nodes[i].size = 1;
}
while(t--){
string s;
int x, y;
cin >> s >> x >> y;
if(s == "M"){
// 合并集合
merge(nodes + x, nodes + y);
}
else {
Node* rootx = find(nodes + x);
Node* rooty = find(nodes + y);
if(rootx != rooty){
cout << -1 << endl;
}
else {
// 因为执行过find函数,所以x,y都是直接挂在根节点下面的
cout << max(abs(nodes[x].preDist - nodes[y].preDist) - 1, 0) << endl;
}
}
}
}