开始吧,做时间的主人!
把时间分给睡眠,分给书籍,分给运动,
分给花鸟树木和山川湖海,
分给你对这个世界的热爱,
而不是将自己浪费在无聊的人和事上。
思维导图
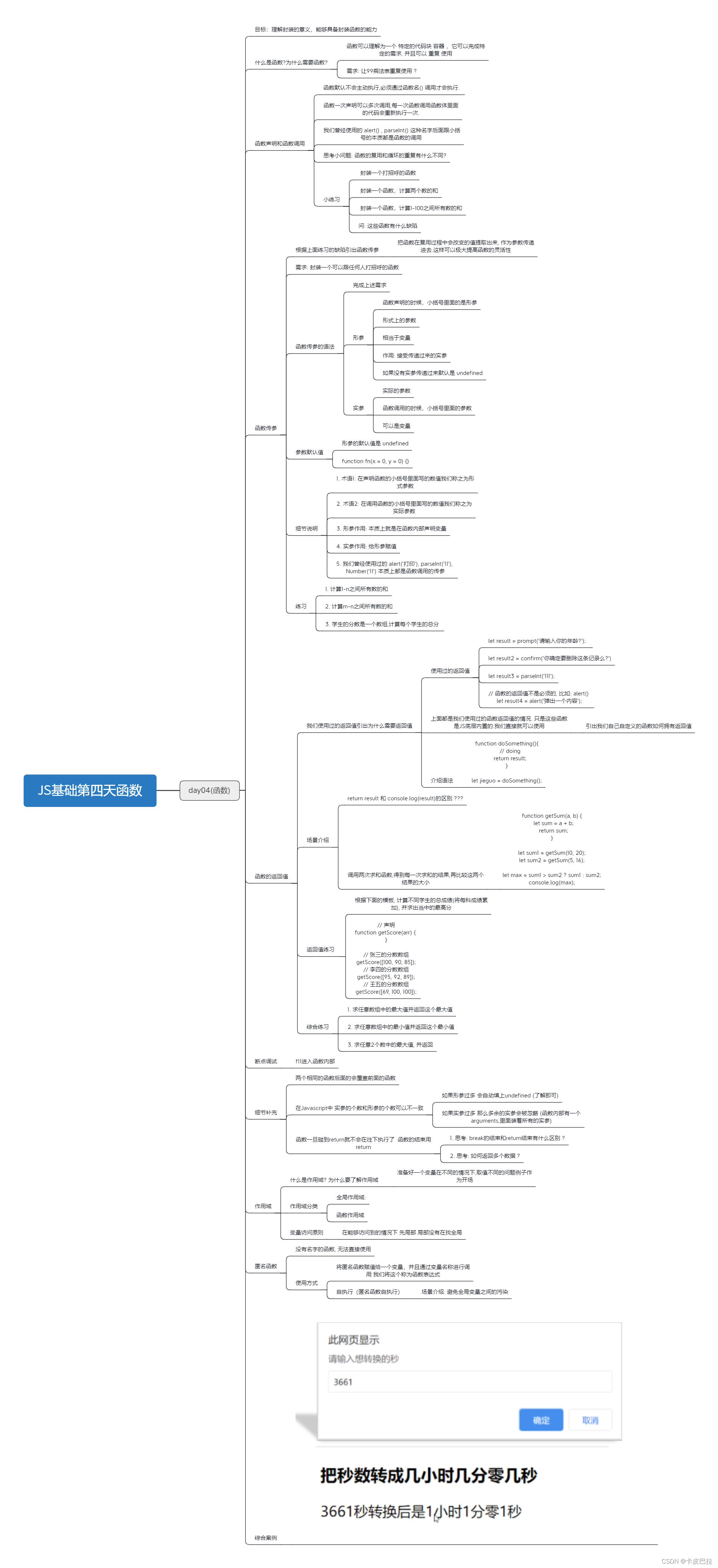
函数
为什么需要函数


<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
span {
display: inline-block;
width: 100px;
padding: 5px 10px;
border: 1px solid pink;
margin: 2px;
border-radius: 5px;
box-shadow: 2px 2px 2px rgba(255, 192, 203, .4);
background-color: rgba(255, 192, 203, .1);
text-align: center;
color: hotpink;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<script>
// // 1. 外层循环控制行数
// for (let i = 1; i <= 9; i++) {
// // 2. 里层循环控制列数
// for (let j = 1; j <= i; j++) {
// document.write(`<span>${j} X ${i} = ${i * j}</span>`)
// }
// // 换行
// document.write('<br>')
// }
// // 1. 外层循环控制行数
// for (let i = 1; i <= 9; i++) {
// // 2. 里层循环控制列数
// for (let j = 1; j <= i; j++) {
// document.write(`<span>${j} X ${i} = ${i * j}</span>`)
// }
// // 换行
// document.write('<br>')
// }
// // 1. 外层循环控制行数
// for (let i = 1; i <= 9; i++) {
// // 2. 里层循环控制列数
// for (let j = 1; j <= i; j++) {
// document.write(`<span>${j} X ${i} = ${i * j}</span>`)
// }
// // 换行
// document.write('<br>')
// }
// 声明
function sheet99() {
for (let i = 1; i <= 9; i++) {
// 2. 里层循环控制列数
for (let j = 1; j <= i; j++) {
document.write(`<span>${j} X ${i} = ${i * j}</span>`)
}
// 换行
document.write('<br>')
}
}
// 调用
sheet99()
sheet99()
sheet99()
sheet99()
</script>
</body>
</html>代码复用,生成多个99乘法表



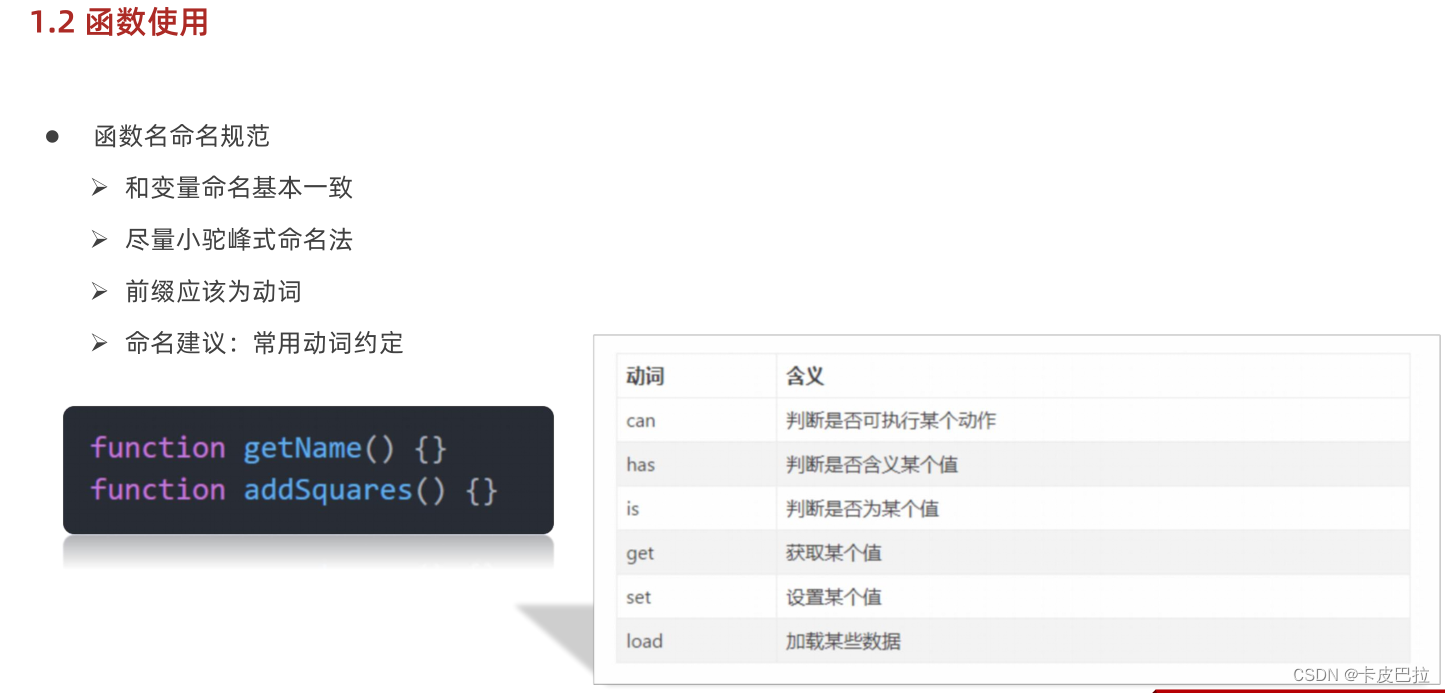
函数使用




<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
// let num = 10
// console.log(num)
// 1. 函数的声明
function sayHi() {
console.log('hi~~~')
}
// 2. 函数调用 函数不调用,自己不执行
sayHi()
sayHi()
sayHi()
</script>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
// 1. 求2个数的和
// function getSum() {
// let num1 = +prompt('请输入第一个数')
// let num2 = +prompt('请输入第二个数')
// console.log(num1 + num2)
// }
// getSum()
// 2. 求 1~100 累加和
function getSum() {
let sum = 0
for (let i = 1; i <= 100; i++) {
sum += i
}
console.log(sum)
}
getSum()
</script>
</body>
</html>函数传参



<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
// 2. 求 1~100 累加和
// function getSum(end) { // end = 50
// // console.log(end)
// let sum = 0
// for (let i = 1; i <= end; i++) {
// sum += i
// }
// console.log(sum)
// }
// getSum(50) // 1~50
// getSum(100) // 1~100
function getSum(start, end) { // end = 50
// 形参 形式上的参数
// console.log(end)
let sum = 0
for (let i = start; i <= end; i++) {
sum += i
}
console.log(sum)
}
getSum(1, 50) // 调用的小括号里面 实参 - 实际的参数
getSum(100, 200) // 实参 - 实际的参数
</script>
</body>
</html>




<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
// 1. 封装函数
// 给一个参数的默认值
function getArrSum(arr = []) {
// console.log(arr)
let sum = 0
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
sum += arr[i]
}
console.log(sum)
}
getArrSum([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
getArrSum([11, 22, 33])
getArrSum() // 0
</script>
</body>
</html>函数返回值




<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
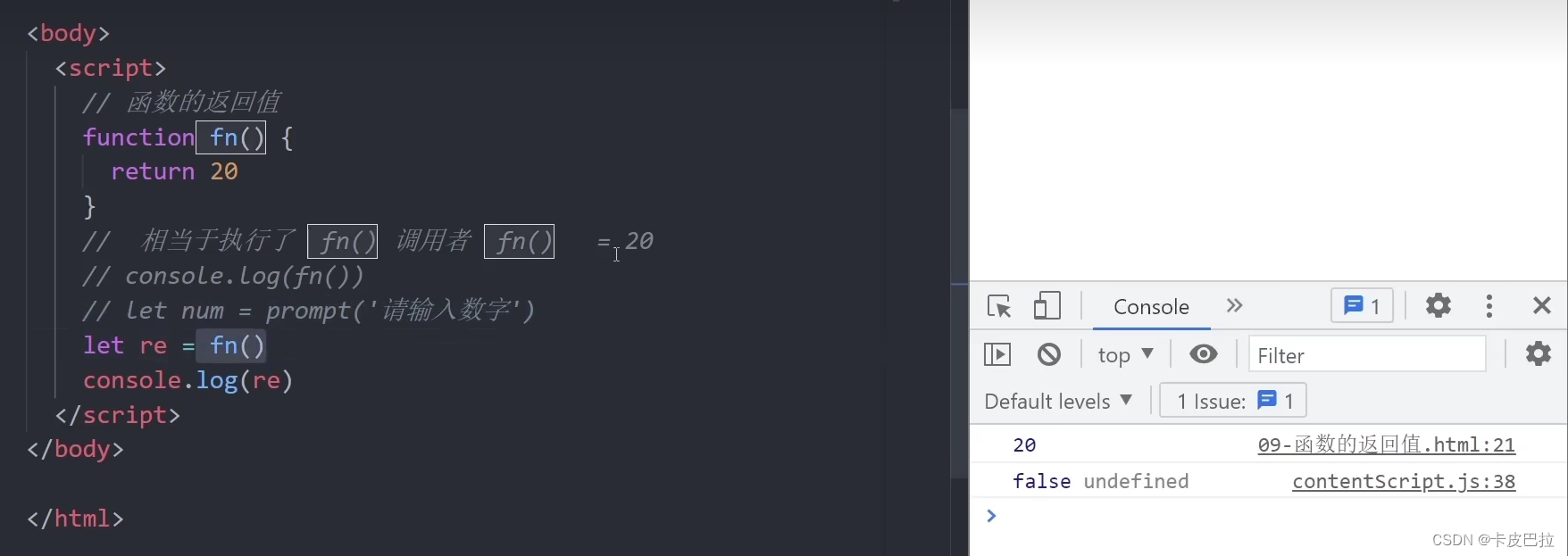
// // 函数的返回值
// function fn() {
// return 20
// }
// // fn() 调用者 相当于执行了 fn() = 20
// // return 的值返回给调用者
// // console.log(fn())
// // let num = prompt('请输入数字')
// let re = fn()
// console.log(re)
// 求和函数的写法
function getTotalPrice(x, y) {
return x + y
// return 后面的代码不会被执行
}
// console.log(getTotalPrice(1, 2))
// console.log(getTotalPrice(1, 2))
let sum = getTotalPrice(1, 2)
console.log(sum)
console.log(sum)
function fn() {
}
let re = fn()
console.log(re) // undefined
</script>
</body>
</html>


<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div></div>
<script>
// 1. 求最大值函数
// function getMax(x, y) {
// return x > y ? x : y
// }
// let max = getMax(11, 234)
// console.log(max)
// // 2. 求任意数组的最大值,并且返回
// function getArrValue(arr = []) {
// // (1)先准备一个max变量存放数组的第一个值
// let max = arr[0]
// // (2) 遍历比较
// for (let i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
// if (max < arr[i]) {
// max = arr[i]
// }
// }
// // (3) 返回值
// return max
// }
// // let max = getArrValue([1, 3, 5, 7, 9])
// // let num = prompt('请输入')
// let max = getArrValue([11, 3, 55, 7, 29])
// console.log(max)
// 3. 求任意数组的最大值和最小值,并且返回
function getArrValue(arr = []) {
// (1)先准备一个max变量存放数组的第一个值
let max = arr[0]
let min = arr[0] // 最小值
// (2) 遍历比较
for (let i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
// 最大值
if (max < arr[i]) {
max = arr[i]
}
// 最小值
if (min > arr[i]) {
min = arr[i]
}
}
// (3) 返回值 返回的是数组
return [max, min]
// return min
}
let newArr = getArrValue([11, 3, 55, 7, 29])
console.log(`数组的最大值是: ${newArr[0]}`)
console.log(`数组的最小值是: ${newArr[1]}`)
</script>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
// function getSum(x, y) {
// return x + y
// // 返回值返回给了谁? 函数的调用者 getSum(1, 2)
// // getSum(1, 2) = 3
// }
// // let result = getSum(1, 2) = 3
// // let num = parseInt('12px')
// let result = getSum(1, 2)
// console.log(result)
// 1. 函数名相同, 后面覆盖前面
// function fn() {
// console.log(1)
// }
// function fn() {
// console.log(2)
// }
// fn()
// 2. 参数不匹配
function fn(a, b) {
console.log(a + b)
}
// (1). 实参多余形参 剩余的实参不参与运算
// fn(1, 2, 3)
// (2). 实参少于形参 剩余的实参不参与运算
fn(1) // 1 + undefined = NaN
</script>
</body>
</html>作用域


<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
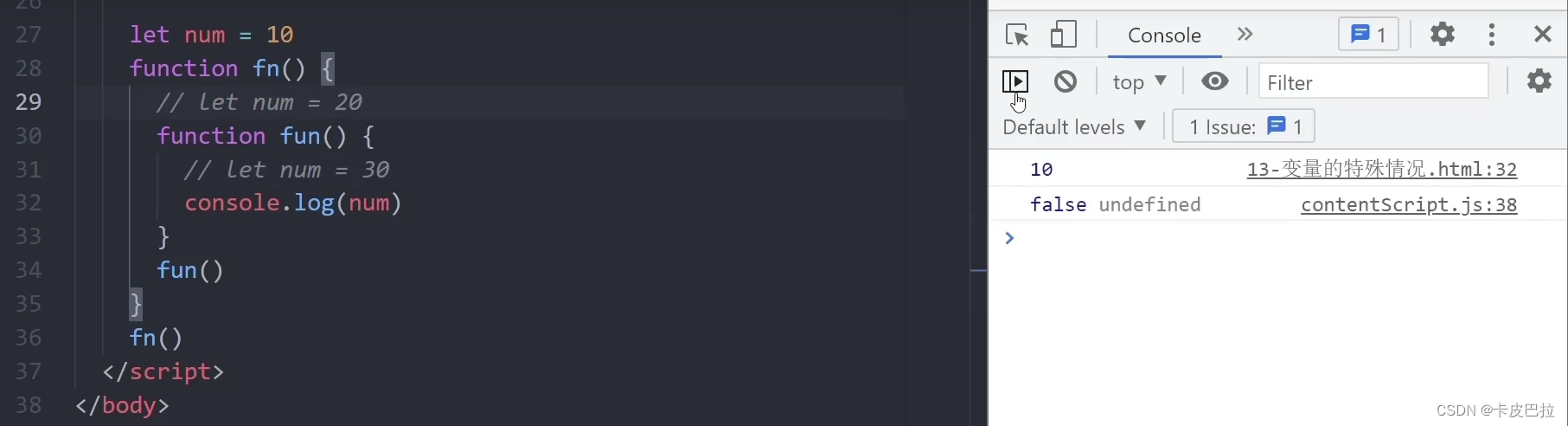
let num = 10 // 1. 全局变量
console.log(num)
function fn() {
console.log(num)
}
fn()
// 2. 局部变量
function fun() {
let str = 'pink'
}
console.log(str) // 错误
</script>
</body>
</html>

函数内部,第一次出现的局部变量被当做全局变量

无let变量声明关键词,甚至覆盖同名全局变量(强烈不推荐)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
// let num = 20
// function fn() {
// num = 10 // 全局变量来看 强烈不允许
// }
// fn()
// console.log(num)
// function fun(x, y) {
// // 形参可以看做是函数的局部变量
// console.log(x)
// }
// fun(1, 2)
// console.log(x) // 错误的
// let num = 10
function fn() {
// let num = 20
function fun() {
// let num = 30
console.log(num)
}
fun()
}
fn()
</script>
</body>
</html>





匿名函数




第三方js文件(具名立即执行函数),担心变量名冲突:

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
// age = age + 1
// 1. 用户输入
let second = +prompt('请输入秒数:')
// 2.封装函数
function getTime(t) {
// console.log(t) // 总的秒数
// 3. 转换
// 小时: h = parseInt(总秒数 / 60 / 60 % 24)
// 分钟: m = parseInt(总秒数 / 60 % 60)
// 秒数: s = parseInt(总秒数 % 60)
let h = parseInt(t / 60 / 60 % 24)
let m = parseInt(t / 60 % 60)
let s = parseInt(t % 60)
h = h < 10 ? '0' + h : h
m = m < 10 ? '0' + m : m
s = s < 10 ? '0' + s : s
// console.log(h, m, s)
return `转换完毕之后是${h}小时${m}分${s}秒`
}
let str = getTime(second)
document.write(str)
console.log(h)
</script>
</body>
</html>