Java语言特性系列
- Java5的新特性
- Java6的新特性
- Java7的新特性
- Java8的新特性
- Java9的新特性
- Java10的新特性
- Java11的新特性
- Java12的新特性
- Java13的新特性
- Java14的新特性
- Java15的新特性
- Java16的新特性
- Java17的新特性
- Java18的新特性
- Java19的新特性
- Java20的新特性
- Java21的新特性
- Java22的新特性
序
本文主要讲述一下Java21的新特性
版本号
java -version
openjdk version "21" 2023-09-19
OpenJDK Runtime Environment (build 21+35-2513)
OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM (build 21+35-2513, mixed mode, sharing)
从version信息可以看出是build 21+35
特性列表
JEP 430: String Templates (Preview)
在java21之前,字符串拼接或者字符串与表达式组合主要是用StringBuilder、String::format、java.text.MessageFormat,不过可读性都不是太好,java21引入了StringTemplate(java.lang.StringTemplate)来解决这个问题。
@PreviewFeature(feature=PreviewFeature.Feature.STRING_TEMPLATES)
public interface StringTemplate {
List<String> fragments();
List<Object> values();
default String interpolate() {
return StringTemplate.interpolate(fragments(), values());
}
default <R, E extends Throwable> R
process(Processor<? extends R, ? extends E> processor) throws E {
Objects.requireNonNull(processor, "processor should not be null");
return processor.process(this);
}
static String interpolate(List<String> fragments, List<?> values) {
Objects.requireNonNull(fragments, "fragments must not be null");
Objects.requireNonNull(values, "values must not be null");
int fragmentsSize = fragments.size();
int valuesSize = values.size();
if (fragmentsSize != valuesSize + 1) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("fragments must have one more element than values");
}
JavaTemplateAccess JTA = SharedSecrets.getJavaTemplateAccess();
return JTA.interpolate(fragments, values);
}
Processor<String, RuntimeException> STR = StringTemplate::interpolate;
Processor<StringTemplate, RuntimeException> RAW = st -> st;
@PreviewFeature(feature=PreviewFeature.Feature.STRING_TEMPLATES)
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Processor<R, E extends Throwable> {
R process(StringTemplate stringTemplate) throws E;
static <T> Processor<T, RuntimeException> of(Function<? super StringTemplate, ? extends T> process) {
return process::apply;
}
@PreviewFeature(feature=PreviewFeature.Feature.STRING_TEMPLATES)
public sealed interface Linkage permits FormatProcessor {
MethodHandle linkage(List<String> fragments, MethodType type);
}
}
}
StringTemplate是个接口,它定义了fragments、values、interpolate、process方法,同时提供了interpolate、process方法的默认实现;同时内置了两个processor,分别是STR和RAW,他们的区别在于RAW可以获取到StringTemplate类型,STR则是StringTemplate执行了interpolate方法之后的结果,获得到的是最终结果String;其基本语法就是用
\{}来包含变量或者表达式
RAW示例
@Test
public void testRaw() {
int x = 10;
int y = 20;
StringTemplate st = RAW."\{x} + \{y} = \{x + y}";
List<String> fragments = st.fragments();
List<Object> values = st.values();
log.info("fragments:{}, values:{}, st:{}", fragments, values, st.interpolate());
}
输出fragments:[, + , = , ], values:[10, 20, 30], st:10 + 20 = 30
STR示例
@Test
public void testStr() {
String name = "Joan";
String info = STR."My name is \{name}";
System.out.println(info);
}
输出My name is Joan
也支持方法调用和表达式
@Test
public void testStrExpression() {
String filePath = "tmp.dat";
File file = new File(filePath);
String msg = STR. "The file \{ filePath } \{ file.exists() ? "does" : "does not" } exist" ;
System.out.println(msg);
}
最后输出The file tmp.dat does not exist
对于还有格式化需求的,提供了java.util.FMT
@Test
public void testFmt() {
record Rectangle(String name, double width, double height) {
double area() {
return width * height;
}
}
Rectangle[] zone = new Rectangle[] {
new Rectangle("Alfa", 17.8, 31.4),
new Rectangle("Bravo", 9.6, 12.4),
new Rectangle("Charlie", 7.1, 11.23),
};
String table = FMT."""
Description Width Height Area
%-12s\{zone[0].name} %7.2f\{zone[0].width} %7.2f\{zone[0].height} %7.2f\{zone[0].area()}
%-12s\{zone[1].name} %7.2f\{zone[1].width} %7.2f\{zone[1].height} %7.2f\{zone[1].area()}
%-12s\{zone[2].name} %7.2f\{zone[2].width} %7.2f\{zone[2].height} %7.2f\{zone[2].area()}
\{" ".repeat(28)} Total %7.2f\{zone[0].area() + zone[1].area() + zone[2].area()}
""";
System.out.println(table);
}
也可以自定义processor
@Test
public void testCustomProcessor() {
var MYJSON = StringTemplate.Processor.of(
(StringTemplate st) -> com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON.parseObject(st.interpolate())
);
String name = "Joan Smith";
String phone = "555-123-4567";
String address = "1 Maple Drive, Anytown";
JSONObject doc = MYJSON."""
{
"name": "\{name}",
"phone": "\{phone}",
"address": "\{address}"
}
""";
System.out.println(doc);
}
JEP 431: Sequenced Collections
java21引入了java.util.SequencedCollection、java.util.SequencedMap来统一各类集合的顺序方法方法
public interface SequencedCollection<E> extends Collection<E> {
SequencedCollection<E> reversed();
default void addFirst(E e) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
default void addLast(E e) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
default E getFirst() {
return this.iterator().next();
}
default E getLast() {
return this.reversed().iterator().next();
}
default E removeFirst() {
var it = this.iterator();
E e = it.next();
it.remove();
return e;
}
default E removeLast() {
var it = this.reversed().iterator();
E e = it.next();
it.remove();
return e;
}
}
SequencedCollection继承了Collection接口,同时定义了reversed,提供了addFirst、addLast、getFirst、getLast、removeFirst、removeLast的default实现;List、SequencedSet接口都继承了SequencedCollection接口
public interface SequencedMap<K, V> extends Map<K, V> {
SequencedMap<K, V> reversed();
default Map.Entry<K,V> firstEntry() {
var it = entrySet().iterator();
return it.hasNext() ? new NullableKeyValueHolder<>(it.next()) : null;
}
default Map.Entry<K,V> lastEntry() {
var it = reversed().entrySet().iterator();
return it.hasNext() ? new NullableKeyValueHolder<>(it.next()) : null;
}
default Map.Entry<K,V> pollFirstEntry() {
var it = entrySet().iterator();
if (it.hasNext()) {
var entry = new NullableKeyValueHolder<>(it.next());
it.remove();
return entry;
} else {
return null;
}
}
default Map.Entry<K,V> pollLastEntry() {
var it = reversed().entrySet().iterator();
if (it.hasNext()) {
var entry = new NullableKeyValueHolder<>(it.next());
it.remove();
return entry;
} else {
return null;
}
}
default V putFirst(K k, V v) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
default V putLast(K k, V v) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
default SequencedSet<K> sequencedKeySet() {
class SeqKeySet extends AbstractMap.ViewCollection<K> implements SequencedSet<K> {
Collection<K> view() {
return SequencedMap.this.keySet();
}
public SequencedSet<K> reversed() {
return SequencedMap.this.reversed().sequencedKeySet();
}
public boolean equals(Object other) {
return view().equals(other);
}
public int hashCode() {
return view().hashCode();
}
}
return new SeqKeySet();
}
default SequencedCollection<V> sequencedValues() {
class SeqValues extends AbstractMap.ViewCollection<V> implements SequencedCollection<V> {
Collection<V> view() {
return SequencedMap.this.values();
}
public SequencedCollection<V> reversed() {
return SequencedMap.this.reversed().sequencedValues();
}
}
return new SeqValues();
}
default SequencedSet<Map.Entry<K, V>> sequencedEntrySet() {
class SeqEntrySet extends AbstractMap.ViewCollection<Map.Entry<K, V>>
implements SequencedSet<Map.Entry<K, V>> {
Collection<Map.Entry<K, V>> view() {
return SequencedMap.this.entrySet();
}
public SequencedSet<Map.Entry<K, V>> reversed() {
return SequencedMap.this.reversed().sequencedEntrySet();
}
public boolean equals(Object other) {
return view().equals(other);
}
public int hashCode() {
return view().hashCode();
}
}
return new SeqEntrySet();
}
}
SequencedMap接口继承了Map接口,它定义了reversed方法,同时提供了firstEntry、lastEntry、pollFirstEntry、pollLastEntry、putFirst、putLast、sequencedKeySet、sequencedValues、sequencedEntrySet方法的默认实现
此次版本的变动:
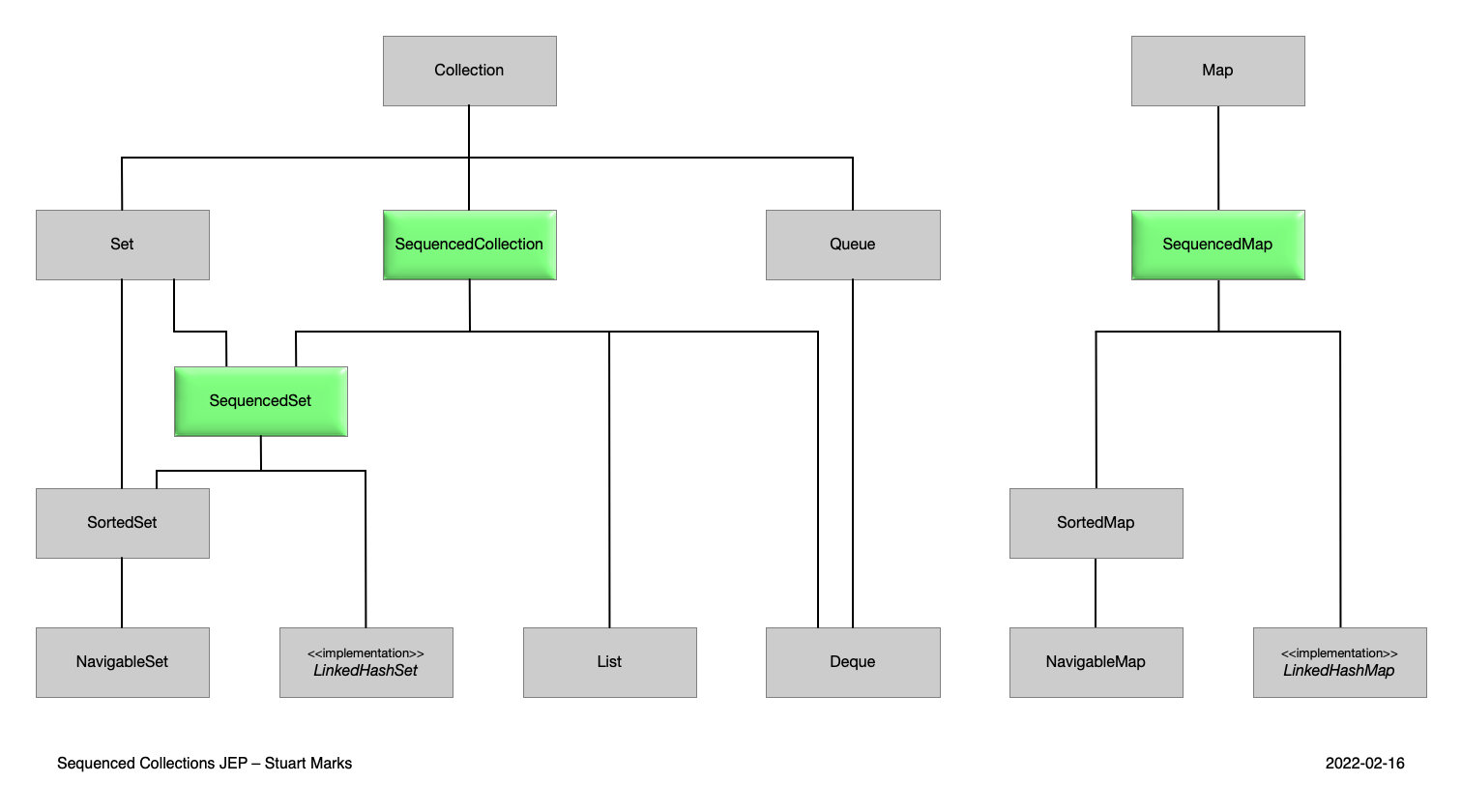
- List现在有作为其直接的超级接口,SequencedCollection
- Deque现在有作为其直接的超级接口,SequencedCollection
- LinkedHashSet另外实现SequencedSet接口
- SortedSet现在有作为其直接的超级接口,SequencedSet
- LinkedHashMap另外实现SequencedMap接口
- SortedMap现在有作为它的直接超级接口,SequencedMap
另外Collections还提供了工厂方法用于返回不可变类型
Collections.unmodifiableSequencedCollection(sequencedCollection)
Collections.unmodifiableSequencedSet(sequencedSet)
Collections.unmodifiableSequencedMap(sequencedMap)
JEP 439: Generational ZGC
ZGC分代回收无疑是一个重磅的GC特性,ZGC之前的版本不支持分代回收,此次支持分代回收的话,可以更方便地对年轻代进行收集,提高GC性能。目前是分代与非分代都支持,使用分代则通过-XX:+UseZGC-XX:+ZGenerational开启,后续版本将会把分代设置为默认的,而-XX:-ZGenerational用于开启非分代,最后将会废除非分代的支持,届时ZGenerational参数也就没有作用了。
JEP 440: Record Patterns
JDK19的JEP 405: Record Patterns (Preview)将Record的模式匹配作为第一次preview
JDK20的JEP 432: Record Patterns (Second Preview)作为第二次preview
此次在JDK21则作为正式版本发布,使用示例如下
record Point(int x, int y) {}
// As of Java 21
static void printSum(Object obj) {
if (obj instanceof Point(int x, int y)) {
System.out.println(x+y);
}
}
enum Color { RED, GREEN, BLUE }
record ColoredPoint(Point p, Color c) {}
record Rectangle(ColoredPoint upperLeft, ColoredPoint lowerRight) {}
// As of Java 21
static void printUpperLeftColoredPoint(Rectangle r) {
if (r instanceof Rectangle(ColoredPoint ul, ColoredPoint lr)) {
System.out.println(ul.c());
}
}
static void printColorOfUpperLeftPoint(Rectangle r) {
if (r instanceof Rectangle(ColoredPoint(Point p, Color c),
ColoredPoint lr)) {
System.out.println(c);
}
}
JEP 441: Pattern Matching for switch
在JDK14JEP 305: Pattern Matching for instanceof (Preview)作为preview
在JDK15JEP 375: Pattern Matching for instanceof (Second Preview)作为第二轮的preview
在JDK16JEP 394: Pattern Matching for instanceof转正
JDK17引入JEP 406: Pattern Matching for switch (Preview)
JDK18的JEP 420: Pattern Matching for switch (Second Preview)则作为第二轮preview
JDK19的JEP 427: Pattern Matching for switch (Third Preview)作为第三轮preview
JDK20的JEP 433: Pattern Matching for switch (Fourth Preview)作为第四轮preview
而此次JDK21将Pattern Matching for switch作为正式版本发布,示例如下
// Prior to Java 21
static String formatter(Object obj) {
String formatted = "unknown";
if (obj instanceof Integer i) {
formatted = String.format("int %d", i);
} else if (obj instanceof Long l) {
formatted = String.format("long %d", l);
} else if (obj instanceof Double d) {
formatted = String.format("double %f", d);
} else if (obj instanceof String s) {
formatted = String.format("String %s", s);
}
return formatted;
}
// As of Java 21
static String formatterPatternSwitch(Object obj) {
return switch (obj) {
case Integer i -> String.format("int %d", i);
case Long l -> String.format("long %d", l);
case Double d -> String.format("double %f", d);
case String s -> String.format("String %s", s);
default -> obj.toString();
};
}
// As of Java 21
static void testFooBarNew(String s) {
switch (s) {
case null -> System.out.println("Oops");
case "Foo", "Bar" -> System.out.println("Great");
default -> System.out.println("Ok");
}
}
// As of Java 21
static void testStringEnhanced(String response) {
switch (response) {
case null -> { }
case "y", "Y" -> {
System.out.println("You got it");
}
case "n", "N" -> {
System.out.println("Shame");
}
case String s
when s.equalsIgnoreCase("YES") -> {
System.out.println("You got it");
}
case String s
when s.equalsIgnoreCase("NO") -> {
System.out.println("Shame");
}
case String s -> {
System.out.println("Sorry?");
}
}
}
// As of Java 21
static void exhaustiveSwitchWithBetterEnumSupport(CardClassification c) {
switch (c) {
case Suit.CLUBS -> {
System.out.println("It's clubs");
}
case Suit.DIAMONDS -> {
System.out.println("It's diamonds");
}
case Suit.HEARTS -> {
System.out.println("It's hearts");
}
case Suit.SPADES -> {
System.out.println("It's spades");
}
case Tarot t -> {
System.out.println("It's a tarot");
}
}
}
// As of Java 21
sealed interface Currency permits Coin {}
enum Coin implements Currency { HEADS, TAILS }
static void goodEnumSwitch1(Currency c) {
switch (c) {
case Coin.HEADS -> { // Qualified name of enum constant as a label
System.out.println("Heads");
}
case Coin.TAILS -> {
System.out.println("Tails");
}
}
}
static void goodEnumSwitch2(Coin c) {
switch (c) {
case HEADS -> {
System.out.println("Heads");
}
case Coin.TAILS -> { // Unnecessary qualification but allowed
System.out.println("Tails");
}
}
}
// As of Java 21
static void testNew(Object obj) {
switch (obj) {
case String s when s.length() == 1 -> ...
case String s -> ...
...
}
}
JEP 442: Foreign Function & Memory API (Third Preview)
Foreign Function & Memory (FFM) API包含了两个incubating API
JDK14的JEP 370: Foreign-Memory Access API (Incubator)引入了Foreign-Memory Access API作为incubator
JDK15的JEP 383: Foreign-Memory Access API (Second Incubator)Foreign-Memory Access API作为第二轮incubator
JDK16的JEP 393: Foreign-Memory Access API (Third Incubator)作为第三轮,它引入了Foreign Linker API (JEP 389)
FFM API在JDK 17的JEP 412: Foreign Function & Memory API (Incubator)作为incubator引入
FFM API在JDK 18的JEP 419: Foreign Function & Memory API (Second Incubator)作为第二轮incubator
JDK19的JEP 424: Foreign Function & Memory API (Preview)则将FFM API作为preview API
JDK20的JEP 434: Foreign Function & Memory API (Second Preview)作为第二轮preview
JDK21则作为第三轮的preview,使用示例
.javac --release 21 --enable-preview ...java --enable-preview ...
// 1. Find foreign function on the C library path
Linker linker = Linker.nativeLinker();
SymbolLookup stdlib = linker.defaultLookup();
MethodHandle radixsort = linker.downcallHandle(stdlib.find("radixsort"), ...);
// 2. Allocate on-heap memory to store four strings
String[] javaStrings = { "mouse", "cat", "dog", "car" };
// 3. Use try-with-resources to manage the lifetime of off-heap memory
try (Arena offHeap = Arena.ofConfined()) {
// 4. Allocate a region of off-heap memory to store four pointers
MemorySegment pointers
= offHeap.allocateArray(ValueLayout.ADDRESS, javaStrings.length);
// 5. Copy the strings from on-heap to off-heap
for (int i = 0; i < javaStrings.length; i++) {
MemorySegment cString = offHeap.allocateUtf8String(javaStrings[i]);
pointers.setAtIndex(ValueLayout.ADDRESS, i, cString);
}
// 6. Sort the off-heap data by calling the foreign function
radixsort.invoke(pointers, javaStrings.length, MemorySegment.NULL, '\0');
// 7. Copy the (reordered) strings from off-heap to on-heap
for (int i = 0; i < javaStrings.length; i++) {
MemorySegment cString = pointers.getAtIndex(ValueLayout.ADDRESS, i);
javaStrings[i] = cString.getUtf8String(0);
}
} // 8. All off-heap memory is deallocated here
assert Arrays.equals(javaStrings,
new String[] {"car", "cat", "dog", "mouse"}); // true
JEP 443: Unnamed Patterns and Variables (Preview)
Unnamed Patterns and Variables支持用_来替代没有使用的变量声明,比如
r instanceof Point _
r instanceof ColoredPoint(Point(int x, int _), Color _)
if (r instanceof ColoredPoint(_, Color c)) { ... c ... }
switch (b) {
case Box(RedBall _), Box(BlueBall _) -> processBox(b);
case Box(GreenBall _) -> stopProcessing();
case Box(_) -> pickAnotherBox();
}
int acc = 0;
for (Order _ : orders) {
if (acc < LIMIT) {
... acc++ ...
}
}
while (q.size() >= 3) {
var x = q.remove();
var _ = q.remove();
var _ = q.remove();
... new Point(x, 0) ...
}
JEP 444: Virtual Threads
在JDK19[https://openjdk.org/jeps/425](JEP 425: Virtual Threads (Preview))作为第一次preview
在JDK20JEP 436: Virtual Threads (Second Preview)作为第二次preview,此版本java.lang.ThreadGroup被永久废弃
在JDK21版本,Virtual Threads正式发布,与之前版本相比,这次支持了threadlocal,然后也可以通过Thread.Builder来创建,而且也支持threaddump(jcmd <pid> Thread.dump_to_file -format=json <file>)
使用示例
void handle(Request request, Response response) {
var url1 = ...
var url2 = ...
try (var executor = Executors.newVirtualThreadPerTaskExecutor()) {
var future1 = executor.submit(() -> fetchURL(url1));
var future2 = executor.submit(() -> fetchURL(url2));
response.send(future1.get() + future2.get());
} catch (ExecutionException | InterruptedException e) {
response.fail(e);
}
}
String fetchURL(URL url) throws IOException {
try (var in = url.openStream()) {
return new String(in.readAllBytes(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
}
}
一般用Executors.newVirtualThreadPerTaskExecutor()是想通过池化技术来减少对象创建开销,不过由于虚拟线程相比平台线程更为"廉价",因而不再需要池化,如果需要控制虚拟线程数则可以使用信号量的方式,因而提供了Thread.Builder来直接创建虚拟线程,示例如下:
Thread thread = Thread.ofVirtual().name("duke").unstarted(runnable);
Thread.startVirtualThread(Runnable)
JEP 445: Unnamed Classes and Instance Main Methods (Preview)
未命名的类和实例main方法这个特性可以简化hello world示例,方便java新手入门,示例如下
static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("static main with args");
}
static void main() {
System.out.println("static main without args");
}
void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("main with args");
}
void main() {
System.out.println("main with without args");
}
javac --release 21 --enable-preview Main.javajava --enable-preview Main
其中main方法选择的优先顺序是static的优于非static的,然后有args的优于没有args的
JEP 446: Scoped Values (Preview)
Scoped Values在JDK20的JEP 429: Scoped Values (Incubator)作为Incubator
此次在JDK21作为preview版本
ScopedValue是一种类似ThreadLocal的线程内/父子线程传递变量的更优方案。ThreadLocal提供了一种无需在方法参数上传递通用变量的方法,InheritableThreadLocal使得子线程可以拷贝继承父线程的变量。但是ThreadLocal提供了set方法,变量是可变的,另外remove方法很容易被忽略,导致在线程池场景下很容易造成内存泄露。ScopedValue则提供了一种不可变、不拷贝的方案,即不提供set方法,子线程不需要拷贝就可以访问父线程的变量。具体使用如下:
class Server {
public final static ScopedValue<User> LOGGED_IN_USER = ScopedValue.newInstance();
private void serve(Request request) {
// ...
User loggedInUser = authenticateUser(request);
ScopedValue.where(LOGGED_IN_USER, loggedInUser)
.run(() -> restAdapter.processRequest(request));
// ...
}
}
通过ScopedValue.where可以绑定ScopedValue的值,然后在run方法里可以使用,方法执行完毕自行释放,可以被垃圾收集器回收
JEP 448: Vector API (Sixth Incubator)
JDK16引入了JEP 338: Vector API (Incubator)提供了jdk.incubator.vector来用于矢量计算
JDK17进行改进并作为第二轮的incubatorJEP 414: Vector API (Second Incubator)
JDK18的JEP 417: Vector API (Third Incubator)进行改进并作为第三轮的incubator
JDK19的JEP 426:Vector API (Fourth Incubator)作为第四轮的incubator
JDK20的JEP 438: Vector API (Fifth Incubator)作为第五轮的incubator
而JDK21则作为第六轮的incubator,使用示例如下
static final VectorSpecies<Float> SPECIES = FloatVector.SPECIES_PREFERRED;
void vectorComputation(float[] a, float[] b, float[] c) {
int i = 0;
int upperBound = SPECIES.loopBound(a.length);
for (; i < upperBound; i += SPECIES.length()) {
// FloatVector va, vb, vc;
var va = FloatVector.fromArray(SPECIES, a, i);
var vb = FloatVector.fromArray(SPECIES, b, i);
var vc = va.mul(va)
.add(vb.mul(vb))
.neg();
vc.intoArray(c, i);
}
for (; i < a.length; i++) {
c[i] = (a[i] * a[i] + b[i] * b[i]) * -1.0f;
}
}
JEP 449: Deprecate the Windows 32-bit x86 Port for Removal
废弃了对Windows 32-bit x86 (x86-32)的移植,以便后续版本删除
JEP 451: Prepare to Disallow the Dynamic Loading of Agents
对将代理动态加载到正在运行的 JVM 中时发出警告,后续版本将不允许动态加载agent。
在 JDK 9 及更高版本中,可以通过
-XX:-EnableDynamicAgentLoading禁止动态加载agent。
在 JDK 21 中,允许动态加载agent,但 JVM 会在发生时发出警告。例如:
WARNING: A {Java,JVM TI} agent has been loaded dynamically (file:/u/bob/agent.jar)
WARNING: If a serviceability tool is in use, please run with -XX:+EnableDynamicAgentLoading to hide this warning
WARNING: If a serviceability tool is not in use, please run with -Djdk.instrument.traceUsage for more information
WARNING: Dynamic loading of agents will be disallowed by default in a future release
若要允许工具动态加载agent而不发出警告,用户必须在命令行上使用-XX:+EnableDynamicAgentLoading
JEP 452: Key Encapsulation Mechanism API
Key Encapsulation Mechanism(KEM)是一种现代加密技术,它使用非对称或公钥加密来保护对称密钥。传统的方法是使用公钥加密一个随机生成的对称密钥,但这需要填充,并且可能难以证明安全。相反,KEM利用公钥的属性派生一个相关的对称密钥,这不需要填充。
此次新增了javax.crypto.KEM、javax.crypto.KEMSpi
package javax.crypto;
public class DecapsulateException extends GeneralSecurityException;
public final class KEM {
public static KEM getInstance(String alg)
throws NoSuchAlgorithmException;
public static KEM getInstance(String alg, Provider p)
throws NoSuchAlgorithmException;
public static KEM getInstance(String alg, String p)
throws NoSuchAlgorithmException, NoSuchProviderException;
public static final class Encapsulated {
public Encapsulated(SecretKey key, byte[] encapsulation, byte[] params);
public SecretKey key();
public byte[] encapsulation();
public byte[] params();
}
public static final class Encapsulator {
String providerName();
int secretSize(); // Size of the shared secret
int encapsulationSize(); // Size of the key encapsulation message
Encapsulated encapsulate();
Encapsulated encapsulate(int from, int to, String algorithm);
}
public Encapsulator newEncapsulator(PublicKey pk)
throws InvalidKeyException;
public Encapsulator newEncapsulator(PublicKey pk, SecureRandom sr)
throws InvalidKeyException;
public Encapsulator newEncapsulator(PublicKey pk, AlgorithmParameterSpec spec,
SecureRandom sr)
throws InvalidAlgorithmParameterException, InvalidKeyException;
public static final class Decapsulator {
String providerName();
int secretSize(); // Size of the shared secret
int encapsulationSize(); // Size of the key encapsulation message
SecretKey decapsulate(byte[] encapsulation) throws DecapsulateException;
SecretKey decapsulate(byte[] encapsulation, int from, int to,
String algorithm)
throws DecapsulateException;
}
public Decapsulator newDecapsulator(PrivateKey sk)
throws InvalidKeyException;
public Decapsulator newDecapsulator(PrivateKey sk, AlgorithmParameterSpec spec)
throws InvalidAlgorithmParameterException, InvalidKeyException;
}
它主要是提供了newEncapsulator、newDecapsulator方法,使用示例如下
// Receiver side
KeyPairGenerator g = KeyPairGenerator.getInstance("ABC");
KeyPair kp = g.generateKeyPair();
publishKey(kp.getPublic());
// Sender side
KEM kemS = KEM.getInstance("ABC-KEM");
PublicKey pkR = retrieveKey();
ABCKEMParameterSpec specS = new ABCKEMParameterSpec(...);
KEM.Encapsulator e = kemS.newEncapsulator(pkR, specS, null);
KEM.Encapsulated enc = e.encapsulate();
SecretKey secS = enc.key();
sendBytes(enc.encapsulation());
sendBytes(enc.params());
// Receiver side
byte[] em = receiveBytes();
byte[] params = receiveBytes();
KEM kemR = KEM.getInstance("ABC-KEM");
AlgorithmParameters algParams = AlgorithmParameters.getInstance("ABC-KEM");
algParams.init(params);
ABCKEMParameterSpec specR = algParams.getParameterSpec(ABCKEMParameterSpec.class);
KEM.Decapsulator d = kemR.newDecapsulator(kp.getPrivate(), specR);
SecretKey secR = d.decapsulate(em);
// secS and secR will be identical
JEP 453: Structured Concurrency (Preview)
在JDK19的JEP 428: Structured Concurrency (Incubator)作为第一次incubator
在JDK20的JEP 437: Structured Concurrency (Second Incubator)作为第二次incubator
此次在JDK21则作为preview,使用示例如下
Response handle() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
try (var scope = new StructuredTaskScope.ShutdownOnFailure()) {
Supplier<String> user = scope.fork(() -> findUser());
Supplier<Integer> order = scope.fork(() -> fetchOrder());
scope.join() // Join both subtasks
.throwIfFailed(); // ... and propagate errors
// Here, both subtasks have succeeded, so compose their results
return new Response(user.get(), order.get());
}
}
细项解读
上面列出的是大方面的特性,除此之外还有一些api的更新及废弃,主要见JDK 21 Release Notes,这里举几个例子。
添加项
- Math.clamp() and StrictMath.clamp() Methods (JDK-8301226)
- New String indexOf(int,int,int) and indexOf(String,int,int) Methods to Support a Range of Indices (JDK-8302590)
- New splitWithDelimiters() Methods Added to String and java.util.regex.Pattern (JDK-8305486)
- System.exit() and Runtime.exit() Logging (JDK-8301627)
- The java.net.http.HttpClient Is Now AutoCloseable (JDK-8267140)
- New StringBuilder and StringBuffer repeat Methods (JDK-8302323)
- Last Resort G1 Full GC Moves Humongous Objects (JDK-8191565)
移除项
- Removed SECOM Trust System’s RootCA1 Root Certificate (JDK-8295894)
- java.io.File’s Canonical Path Cache Is Removed (JDK-8300977)
- Removal of the java.compiler System Property (JDK-8041676)
- The java.lang.Compiler Class Has Been Removed (JDK-8205129)
- Remove the JAR Index Feature (JDK-8302819)
- Removal of G1 Hot Card Cache (JDK-8225409)
- Obsolete Legacy HotSpot Parallel Class Loading Workaround Option -XX:+EnableWaitForParallelLoad Is Removed (JDK-8298469)
- The MetaspaceReclaimPolicy Flag has Been Obsoleted (JDK-8302385)
废弃项
- Deprecate GTK2 for Removal (JDK-8280031)
- Deprecate JMX Subject Delegation and the JMXConnector.getMBeanServerConnection(Subject) Method for Removal (JDK-8298966)
重要bug修复
- Error Computing the Amount of Milli- and Microseconds between java.time.Instants (JDK-8307466)
- Disallow Extra Semicolons Between “import” Statements (JDK-8027682)
已知问题
- JVM May Crash or Malfunction When Using ZGC and Non-Default ObjectAlignmentInBytes (JDK-8312749)
- Validations on ZIP64 Extra Fields (JDK-8313765)
- java.util.regex.MatchResult Might Throw StringIndexOutOfBoundsException on Regex Patterns Containing Lookaheads and Lookbehinds (JDK-8132995)
- JVM May Hang When Using Generational ZGC if a VM Handshake Stalls on Memory (JDK-8311981)
其他事项
- ObjectInputStream::readObject() Should Handle Negative Array Sizes without Throwing NegativeArraySizeExceptions (JDK-8306461)
- File::listRoots Changed to Return All Available Drives on Windows (JDK-8208077)
- Thread.sleep(millis, nanos) Is Now Able to Perform Sub-Millisecond Sleeps (JDK-8305092)
- FileChannel.transferFrom Extends File if Called to Transfer Bytes to the File (JDK-8303260)
- Clarification of the Default Charset Initialization with file.encoding (JDK-8300916)
- java.util.Formatter May Return Slightly Different Results on double and float (JDK-8300869)
- JVM TI ThreadStart and ThreadEnd Events Not Sent for Virtual Threads (JDK-8307399)
- Add final Keyword to Some Static Methods (JDK-8302696)
小结
Java21主要有如下几个特性
- JEP 430: String Templates (Preview)
- JEP 431: Sequenced Collections
- JEP 439: Generational ZGC
- JEP 440: Record Patterns
- JEP 441: Pattern Matching for switch
- JEP 442: Foreign Function & Memory API (Third Preview)
- JEP 443: Unnamed Patterns and Variables (Preview)
- JEP 444: Virtual Threads
- JEP 445: Unnamed Classes and Instance Main Methods (Preview)
- JEP 446: Scoped Values (Preview)
- JEP 448: Vector API (Sixth Incubator)
- JEP 449: Deprecate the Windows 32-bit x86 Port for Removal
- JEP 451: Prepare to Disallow the Dynamic Loading of Agents
- JEP 452: Key Encapsulation Mechanism API
- JEP 453: Structured Concurrency (Preview)
其中JEP 439: Generational ZGC及JEP 444: Virtual Threads应属于重磅级的特性,而JEP 430: String Templates (Preview)、JEP 431: Sequenced Collections、JEP 440: Record Patterns及JEP 441: Pattern Matching for switch则在语言表达力层面上有了增强
另外java21是继JDK 17之后最新的长期支持(LTS)版本,将获得至少8年的支持。
doc
- JDK 21 Features
- JDK 21 Release Notes
- Consolidated JDK 21 Release Notes
- Java SE 21 deprecated-list
- The Arrival of Java 21
- JDK 21 G1/Parallel/Serial GC changes
- Java 21, the Next LTS Release, Delivers Virtual Threads, Record Patterns and Pattern Matching
- JDK 21 and JDK 22: What We Know So Far
- Java 21 New Features: “The ZGC is generational and will further improve performance for suitable applications”
- Java 21 is Available Today, And It’s Quite the Update







![MongoDB【部署 02】mongodb使用配置文件启动、添加为系统服务及自启动(一个报错:[13436][NotMasterOrSecondary])](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/d9f243d80b764bb6b382c6393a64d803.jpeg#pic_center)