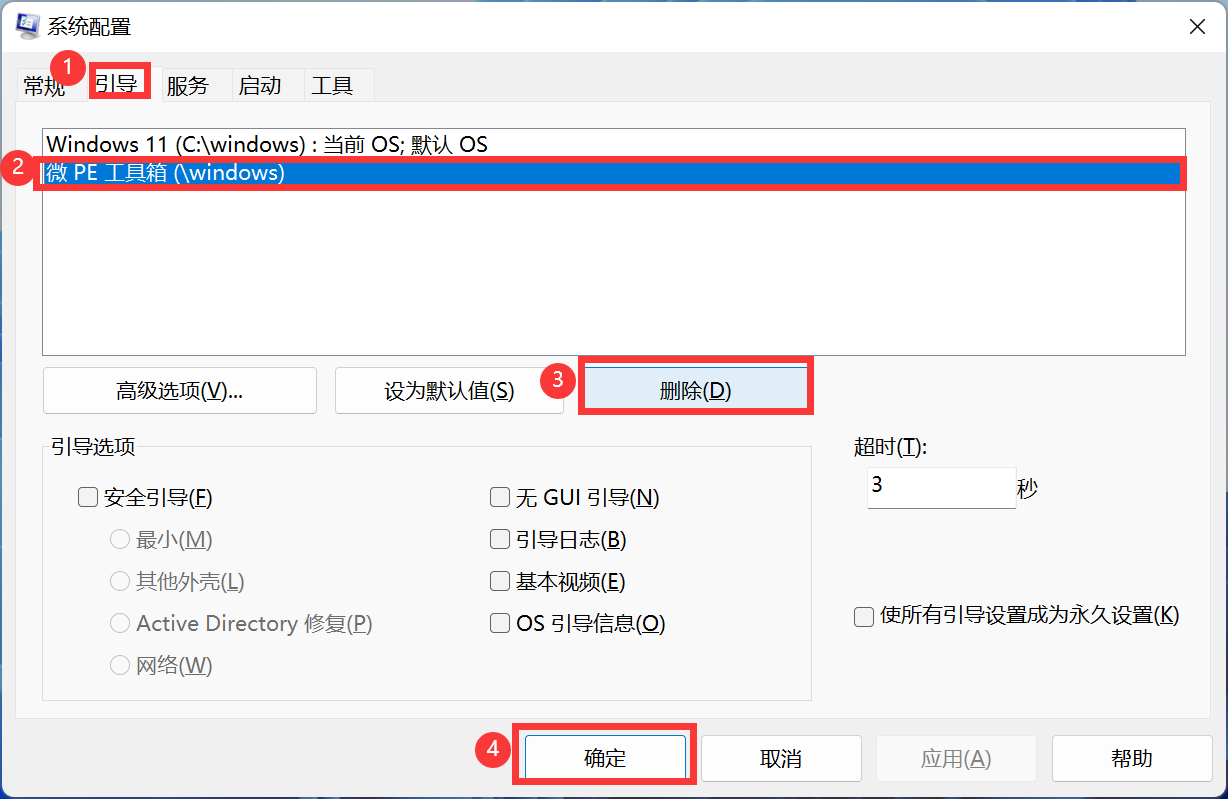
意图:在不破坏封装性的前提下,捕获一个对象的内部状态,并在该对象之外保存这个状态,这样就可以在以后将该对象恢复到原先保存的状态。
上下文:某些对象的状态在转换过程中,可能由于某种需要,要求程序能够回溯到对象之前处于某个点时的状态。如果使用一些公共接口来让其他对象得到对象的状态,便会暴露对象的细节实现。如何实现对象状态的保存与恢复,但同时又不会因此而破坏对象本身的封装性?

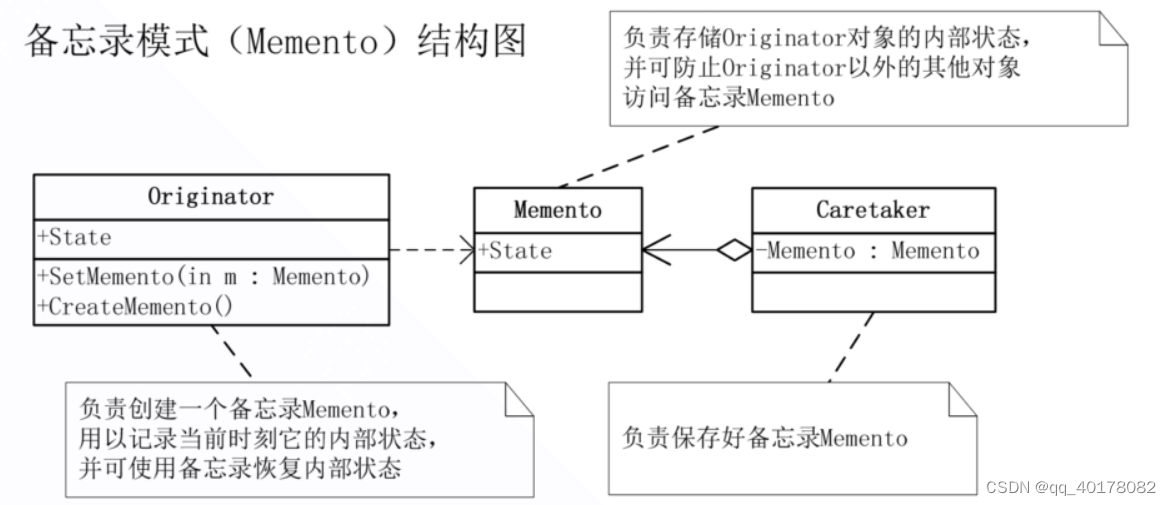
Memento:存储Originator(原发器)的内部状态,原发器根据需要决定Memento存储自己的哪些内部状态;防止Originator以外的其他对象访问Memento。Memento实际有两个接口,Caretaker只能看到其窄接口(只能将Memento传递给其他对象);而Originator可以看到一个宽接口(允许访问返回到之前状态所需的数据)。理想情况是,只允许生成该Memento的那个Originator访问该Memento的内部状态。
Originator:创建一个Memento,用以记录当前时刻的内部状态;使用Memento恢复内部状态。
Caretaker:负责保存Memento;不能对Memento的内容进行操作或检查。
代码
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
class Memento;
class Originator{
public:
string state;
string getState() const;
void setState(const string &value);
Memento *CreateMemento();
void SetMemento(Memento *memento);
void show();
};
class Memento
{
public:
string state;
Memento(string s):state(s){
}
string getState() const;
};
string Memento::getState() const
{
return state;
}
Memento *Originator::CreateMemento(){
return new Memento(state);
}
void Originator::SetMemento(Memento *memento)
{
this->state = memento->state;
}
void Originator::show()
{
cout << "state:" << this->state << endl;
}
class Caretaker
{
public:
Memento *memento;
Memento *getMemento() const;
void setMemento(Memento *value);
};
Memento *Caretaker::getMemento() const
{
return memento;
}
void Caretaker::setMemento(Memento *value)
{
memento = value;
}
string Originator::getState() const
{
return state;
}
void Originator::setState(const string &value)
{
state = value;
}
int main(void)
{
Originator *o = new Originator();
o->state = "on";
o->show();
Caretaker *c = new Caretaker();
c->memento = o->CreateMemento();
o->state = "off";
o->show();
o->SetMemento(c->memento);
o->show();
}
结果
state:on
state:off
state:on