一个带有EPICS支持的虚拟电机控制器。
1)Status类:其实例化对象代表一个电机轴的状态。
#!/usr/bin/env python
'''
Status类代表一个电机处于的状态:
1、DIRECTION状态位:设置运动方向
2、DONE_MOVING状态字:置位表示结束运动
3、MOVING状态字:置位表示正在运动
4、HIGH_LIMIT状态字:置位表示触发高限位
5、LOW_LIMIT状态字:置位表示触发低限位
6、HOMING:置位表示正在寻HOME位
7、HOMING_LIMIT:置位表示触发HOME开关
8、HOMED:置位表示寻HOME结尾
9、ERROR:置位表示出错
'''
class Status:
'''
代表轴状态的类:初始化这个对象
'''
def __init__(self):
# 初始化方向,方向1表示正方向
self.direction = 1
# 初始化运动状态为静止
self.doneMoving = 1
self.moving = 0
# 初始化高低限位信号为无效
self.highLimitActive = 0
self.lowLimitActive = 0
# 初始化归位:未在归位中,归位无效
self.homing = 0
self.homed = 0
self.homeSwitchActive = 0
# 初始化错误:没有
self.error = False
self.errorMessage = None
# 状态位定义:每种状态所在的位
#方向:第0BIT、结束运行:第1BIT、移动中:第2BIT
# 高限位:第3BIT、低限位:第4BIT、归位中:第5BI
# 归位开关:第6BIT,已经归位:第7BIT,错误:第8BIT
self.DIRECTION = 1 << 0
self.DONE_MOVING = 1 << 1
self.MOVING = 1 << 2
self.HIGH_LIMIT = 1 << 3
self.LOW_LIMIT = 1 << 4
self.HOMING = 1 >> 5
self.HOME_LIMIT = 1 << 6
self.HOMED = 1 << 7
self.ERROR = 1 << 8
# 初始状态为0,通过以上状态定义计算状态
self.status = 0
self.calcStatus()
# 设置错误状态码和错误消息
def setError(self, flag, message):
self.error = flag # 设置错误标记
self.errorMessage = message
# 错误标记非0,状态中置位ERROR对应的BIT位状态
# 错误标记为0, 状态中复位ERROR对应的BIT位状态
if self.error:
self.status |= self.ERROR
else:
self.status &= ~self.ERROR
# 设置为运动,结束移动的标志置0,运动的标志置1,状态中对结束移动标的志置0,对运动标志置1
def setMoving(self):
self.doneMoving = 0
self.moving = 1
self.status |= self.MOVING
self.status &= ~self.DONE_MOVING
# 设置为结束,结束移动的标志置1,运动的标志置0,状态中对结束移动标的志置1,对运动标志置0
def setDoneMoving(self):
self.doneMoving = 1
self.moving = 0
self.status |= self.DONE_MOVING
self.status &= ~self.MOVING
# 设置正方向,方向标志为1
def setDirPositive(self):
self.direction = 1
self.status |= self.DIRECTION
# 设置负方向,方向标志为0
def setDirNegative(self):
self.direction = 0
self.status &= ~self.DIRECTION
# 设置高限位为1
def setHighLimit(self):
self.highLimitActive = 1
self.status |= self.HIGH_LIMIT
# 重置高限位
def resetHighLimit(self):
self.highLimitActive = 0
self.status &= ~self.HIGH_LIMIT
# 设置低限位
def setLowLimit(self):
self.lowLimitActive = 1
self.status |= self.LOW_LIMIT
# 重置低限位
def resetLowLimit(self):
self.lowLimitActive = 0
self.status &= ~self.LOW_LIMIT
# 返回当前状态
def getStatus(self):
return self.status
# 根据方向标志、结束运行的标志、移动的标志,高限位的标志,低限位的标志,归位的标志、归位开关标志、归位结束的标志,以及
# 错误标志,构造状态
# 根据Status对象的diretion, doneMoving, moving, highLimitActive, lowLimitActive, homing, homed, homeSwitchActive
# error成员的状态计算成员status
def calcStatus(self):
status = 0
if self.direction:
status |= self.DIRECTION
if self.doneMoving:
status |= self.DONE_MOVING
if self.moving:
status |= self.MOVING
if self.highLimitActive:
status |= self.HIGH_LIMIT
if self.lowLimitActive:
status |= self.LOW_LIMIT
if self.homing:
status |= self.HOMING
if self.homeSwitchActive:
status |= self.HOME_LIMIT
if self.homed:
status |= self.HOMED
if self.error:
status |= self.ERROR
self.status = status
return2) Axis类,其实例化代表电机的一个运动轴:
#!/usr/bin/env python
import status
import datetime
import math
import time
class Axis:
"""
代表电机一个运动轴的类
"""
def __init__(self, index):
self.index = index
# 基速度和匀速速度
self.baseVelocity = 0
self.velocity = 400
# 加速度和减速度
self.acceleration = 400
self.deceleration = 400
# 上下限位
self.highLimit = 40000
self.lowLimit = -40000
# 单位
self.units = "counts"
# 分辨率
self.resolution = 1.0
# 启动开始时刻,移动取消时刻
self.moveStartTime = None
self.abortTime = None
# 轴的上次位置,当前位置,当前偏移量,目标位置,方向,移动速度
self.lastPosition = 0
self.currentPosition = 0
self.currentDisplacement = 0
self.targetPosition = 0
self.direction = 1
self.moveVelocity = self.velocity
# 加速持续时间,加速阶段的距离,减速持续时间,减速阶段的距离
self.accelDistance = 0.0
self.accelDuration = 0.0
self.decelDistance = 0.0
self.decelDuration = 0.0
# 移动距离,匀速持续时间,减速启动时间,移动持续时间
self.moveDistance = 0
self.constVelDuration = 0.0
self.decelStartTime = 0.0
self.moveDuration = 0.0
# 默认执行限位检查
self.enforceLimits = True
# 实例化一个默认的Status对象,代表电机轴的状态
self.status = status.Status()
def move(self, targetPosition):
# 已经移动,则忽略,检查启动时刻是否已经存在
if self.moveStartTime != None:
return "Busy"
self.targetPosition = targetPosition
self.lastPosition = self.currentPosition
# 比较当前位置和目标位置,来设置方向
# 此处的direction用于计算位置
if self.targetPosition < self.lastPosition:
self.direction = -1
self.status.setDirNegative()
else:
self.direction = 1
self.status.setDirPositive()
print("move:direction:" , self.direction)
# 检查上下限位情况
if (self.enforceLimits == True) and (self.direction == 1) and (self.status.highLimitActive == 1):
self.status.setError(True, "Can't move in positive direction when high limit is active")
print("hh")
elif (self.enforceLimits == True) and (self.direction == -1) and (self.status.lowLimitActive == 1):
self.status.setError(True, "Can't move in negative direction when low limit is active")
print("ll")
else:
# 设置启动时刻,表示电机轴开始移动了
self.moveStartTime = datetime.datetime.now()
# 计算移动距离
self.moveDistance = abs(self.targetPosition - self.lastPosition)
print("moveDistance , ", self.moveDistance)
# 加速时间
self.accelDuration = (self.velocity - self.baseVelocity) / self.acceleration
# 加速过程中,移动的距离:vb*t+1/2*a*t^2,a=(v-vb)/t==>vb*t+0.5*(v-vb)*t
self.accelDistance = self.baseVelocity * self.accelDuration + self.accelDuration * 0.5 * (self.velocity - self.baseVelocity)
# 减速时间,减速过程的距离
self.decelDuration = (self.velocity - self.baseVelocity) / self.deceleration
#! debug: print("decelDuration = ", self.decelDuration)
self.decelDistance = self.baseVelocity * self.decelDuration + self.decelDuration * 0.5 * (self.velocity - self.baseVelocity)
if self.moveDistance < (self.accelDistance + self.decelDistance):
# 这点距离不能使得轴达到运行速度,加速到一个峰值速度后,就进行减速
peakVelocity = math.sqrt(2 * self.acceleration * self.deceleration * self.moveDistance / (self.acceleration + self.deceleration))
print("---------+-------------")
print("peakVelocity = ", peakVelocity)
self.moveVelocity = peakVelocity
# 重新计算:加速所用时间,加速的距离,减速所用时间,减速的距离
self.accelDuration = (peakVelocity - self.baseVelocity) / self.acceleration
self.accelDistance = self.baseVelocity * self.accelDuration + self.accelDuration * 0.5 * (peakVelocity - self.baseVelocity)
self.decelDuration = (peakVelocity - self.baseVelocity) / self.deceleration
self.decelDistance = self.baseVelocity * self.decelDuration + self.decelDuration * 0.5 * (peakVelocity - self.baseVelocity)
self.constVelDuration = 0.0
else:
self.moveVelocity = self.velocity
# 匀速移动距离,匀速移动时间
self.constVelDuration = (self.moveDistance - self.accelDistance - self.decelDistance) / self.moveVelocity
# 开始减速的时刻
self.decelStartTime = self.accelDuration + self.constVelDuration
# 整个移动时间
self.moveDuration = self.decelStartTime + self.decelDuration
# 打印轴移动的信息:
# 轴编码,起始位置,终止位置,移动距离,移动持续时间,加速距离,匀速时间
# 减速时刻,减速持续时间,减速距离
print("+-----------motor %d :" % (self.index + 1))
print("Start Position: ", self.lastPosition, self.units)
print("End Position: ", self.targetPosition, self.units)
print()
print("Move Duration : ", self.moveDuration, "seconds")
print("Move Distance : ", self.moveDistance, self.units)
print()
print("Accel Duration: ", self.accelDuration, "seconds")
print("Accel Distance: ", self.accelDistance, self.units)
print()
print("Constant Vel Duration: ", self.constVelDuration, "seconds")
print("Decel Start Time : ", self.decelStartTime, "seconds")
print()
print("Decel Duration : ", self.decelDuration, "seconds")
print("Decel Distance : ", self.decelDistance, self.units)
print()
return "OK"
def moveRelative(self, displacement):
if self.moveStartTime != None:
return "Busy"
self.lastPosition = self.currentPosition
targetPosition = self.lastPosition + displacement
print("current %s to target %s" % (self.lastPosition, targetPosition))
retval = self.move(targetPosition)
return retval
def jog(self, velocity):
print("Velocity: ", velocity)
displacement = velocity * 3600.0
retval = self.moveRelative(displacement)
return retval
def stop(self):
if self.moveStartTime == None: #未开始移动
self.abortTime = None
else:
if self.abortTime != None: # 已经发送了取消命令
pass
else:
# 记录当前取消时刻
self.abortTime = datetime.datetime.now()
# 到取消时刻已经运行了多少时间
abortTimeDelta = self.abortTime - self.moveStartTime
abortTimeSeconds = abortTimeDelta.total_seconds()
# 重新计算移动的距离
if abortTimeSeconds < self.accelDuration: # 在加速阶段就取消了
self.accelDuration = abortTimeSeconds
self.accelDistance = self.baseVelocity * abortTimeSeconds + 0.5 * self.acceleration * abortTimeSeconds * abortTimeSeconds
peakVelocity = self.acceleration * abortTimeSconds
self.constVelDuration = 0.0
self.decelDuration = (peakVelocity - baseVelocity)/ self.deceleraction
self.decelDistance = self.baseVelocity * self.decelDuration + 0.5 * self.deceleration * self.decelDuration * self.decelDuration
# 实际移动距离=加速的距离+减速的距离
self.moveDistance = self.accelDistance + self.decelDistance
# 实际移动时间=加速所用时间+减速所用时间
self.moveDuration = self.accelDuration + self.decelDuration
# 移动峰值速度
self.moveVelocity = peakVelocity
elif abortTimeSeconds < self.decelStartTime: # 在匀速阶段取消
self.decelStartTime = abortTimeSeconds
# 匀速运动所用时间
self.constVelDuration = abortTimeSeconds - self.accelDuration
# 移动距离
self.moveDistance = self.accelDistance + self.moveVelocity * self.constVelDuration + self.decelDistance
# 移动的时间
self.moveDuration = self.accelDuration + self.constVelDuration + self.decelDuration
elif abortTimeSeconds <= self.moveDuration: # 在减速阶段取消
pass
else:
print("Error: Stop received after a move shoud have been complete.")
self.status.setError(True, "Error: Stop received after a move should been complete.")
return "OK"
# 读取当前位置
def readPosition(self):
if self.moveStartTime == None: # 电机轴未移动
pass
else:
# 设置移动标志
moveFlag = True
currentTime = datetime.datetime.now()
# 计算移动时间:当前时间 - 启动时间
movingTimeDelta = currentTime - self.moveStartTime
movingTimeSeconds = movingTimeDelta.total_seconds()
print("readPosition timedelta: ", movingTimeSeconds)
self.currentDisplacement = 0
if movingTimeSeconds < self.accelDuration: # 加速阶段中,偏移量
self.currentDisplacement = self.baseVelocity * movingTimeSeconds + 0.5 * self.acceleration * movingTimeSeconds * movingTimeSeconds
elif movingTimeSeconds < self.decelStartTime: # 匀速阶段中,偏移量
self.currentDisplacement = self.baseVelocity * self.accelDuration + 0.5 * self.acceleration * self.accelDuration * self.accelDuration + (movingTimeSeconds - self.accelDuration) * self.moveVelocity
elif movingTimeSeconds < self.moveDuration: # 减速阶段中,偏移量
self.currentDisplacement = self.baseVelocity * self.accelDuration + 0.5 * self.acceleration * self.accelDuration * self.accelDuration + self.constVelDuration * self.moveVelocity + self.baseVelocity * (movingTimeSeconds - self.decelStartTime) + 0.5 * self.deceleration * (movingTimeSeconds - self.decelStartTime) * (movingTimeSeconds - self.decelStartTime)
else: # 已经超出了运行时间, 设置移动标志
moveFlag = False
#print("In readPosition--> currentDisplacement", self.currentDisplacement)
print("in readPosition: direction : ", self.direction)
if moveFlag == True:# 还在移动,计算当前位置
self.currentPosition = self.lastPosition + self.direction * self.currentDisplacement
else:
if self.abortTime == None: # 运动自然结束
self.currentPosition = self.targetPosition
else:# 运动被取消
self.currentPostion = self.lastPosition + self.direction * self.moveDistance
self.abortTime = None
self.latPosition = self.currentPosition
self.moveStartTime = None
return self.currentPosition
def setPosition(self, newPostion):
if self.moveStartTime == None: # 电机轴未移动
self.currentPosition = newPosition
self.lastPosition = self.currentPosition
else:
pass
return "OK"
def readStatus(self):
if self.moveStartTime == None:
self.status.setDoneMoving()
else:
currentTime = datetime.datetime.now()
movingTimeDelta = currentTime - self.moveStartTime
movingTimeSeconds = movingTimeDelta.total_seconds()
if movingTimeSeconds < self.moveDuration:
self.status.setMoving()
else:
self.status.setDoneMoving()
if self.enforceLimits == True:
if self.currentPosition > self.highLimit:
self.status.setHighLimit()
if (self.status.doneMoving == 0) and (self.direction == 1):
self.stop()
else:
self.status.resetHighLimit()
if self.currentPosition < self.lowLimit:
self.status.setLowLimit()
if (self.status.doneMoving == 0) and (self.direction == -1):
self.stop()
else:
self.status.resetLowLimit()
else:
self.status.resetLowLimit()
self.status.resetHighLimit()
return self.status.getStatus()
def setVelocity(self, velocity):
self.velocity = abs(velocity)
return "OK"
def getVelocity(self):
return self.velocity
def setBaseVelocity(self, velocity):
self.baseVelocity = abs(velocity)
return "OK"
def getBaseVelocity(self):
return self.baseVelocity
def setAcceleration(self, acceleration):
self.acceleration = acceleration
return "OK"
def setDeceleration(self, deceleration):
self.deceleration = accceleration
return "OK"
def getAcceleration(self):
return self.acceleration
def getDeceleration(self):
return self.deceleration
def setHighLimit(self, highLimit):
self.highLimit = highLimit
return "OK"
def getHighLimit(self):
return self.highLimit
def setLowLimit(self, lowLimit):
self.lowLimit = lowLimit
return "OK"
def getLowLimit(self):
return self.lowLimit
# 以下是测试一个Axis实例的代码
if __name__ == "__main__":
print("working")
axis = Axis(1)
print("Velocity:", axis.getVelocity())
print("BaseVelocity:",axis.getBaseVelocity())
print("Acceleratoin:", axis.getAcceleration())
print("High Limit:", axis.getHighLimit())
print("Low Limit", axis.getLowLimit())
print()
print("Start Move 1", axis.move(1000))
print()
for i in range(10):
pos = axis.readPosition()
status = axis.readStatus()
print("pos: %s, status: %s" % (pos, status))
time.sleep(0.5)
print("move stop\n")
print("lastPosition: " , axis.lastPosition)
print("currentPosition: ", axis.currentPosition)
print("Start Move 2", axis.moveRelative(-1000))
for i in range(10):
pos = axis.readPosition()
status = axis.readStatus()
print("pos: %s, status: %s" % (pos, status))
time.sleep(0.5)
print("move stop\n")
print("lastPosition: " , axis.lastPosition)
print("currentPosition: ", axis.currentPosition)3) 控制器的类:一个电机控制器
#!/usr/bin/evn python3
import axis
import time
class Controller:
"""
代表电机控制器的类
"""
def __init__(self):
# 控制器中有8个轴
self.numAxes = 8
# 轴名称的列表
self.axisNameList = ['X', 'Y', 'Z','T', 'U', 'V', 'R','S']
# 轴数值编号的列表
self.axisNumberList = [str(x) for x in range(1, self.numAxes + 1)]
# 命令字典
self.commandDict = {3:{'MV': self.moveAxis,
'MR':self.moveRelative,
'JOG':self.jog,
'POS':self.setPosition,
'ACC':self.setAcceleration,
'VEL':self.setVelocity,
'BAS':self.setBaseVelocity,
'LL':self.setLowLimit,
'HL':self.setHighLimit},
2:{'POS?':self.queryPosition,
'ST?':self.queryStatus,
'ACC?':self.queryAcceleration,
'VEL?':self.queryVelocity,
'LL?':self.queryLowLimit,
'HL?':self.queryHighLimit,
'AB':self.stopAxis}
}
# 轴对象的字典
self.axisDict = {}
# 轴对象的列表
self.axisList = []
# 默认执行限位检查
self.enforceLimits = True
for i in range(self.numAxes): #实例子化八个Axis对象,
# 追加到一个列表末尾
self.axisList.append(axis.Axis(i))
# 键值对:轴名称----axis对象索引号; 轴编号----Axis对象索引号
self.axisDict[self.axisNameList[i]] = i
self.axisDict[self.axisNumberList[i]] =i
print(self.axisDict) # 打印字典
print(self.axisDict.keys()) # 打印字典的键
def refinePos(self, inputPos):
# 把来自Axis对象的raw位置转换成一个合适输出的东西
# 返回一个int,由于控制器使用单位为计数
return round(inputPos)
def handleCommand(self, command):
# 命令字符串格式: 轴名称/轴编号 命令名称 <命令参数> 或者 轴名称/轴编号 命令名称
print("In Controller <handleCommand:> ", command)
if command == '':
retVal = None
else:
args = command.split(' ')
numArgs = len(args) # 获取命令串中分隔出的参数数目
print("split params:", args, "numArgs:", numArgs)
print("commandDict.keys()", self.commandDict.keys())
print("axisDict.keys()", self.axisDict.keys())
print("2 parameters command", self.commandDict[2].keys())
print("3 parameters command", self.commandDict[3].keys())
if numArgs not in self.commandDict.keys(): # 参数数目不为2或3, 不对
retVal = "Argument error"
elif args[0] not in self.axisDict.keys():
retVal = "Axis name error" # 给的轴名称/轴编号错误
else: #如果是3个字符串的参数,则格式如 X MV 400
if args[1] in self.commandDict[numArgs].keys(): # 命令名称出错
if numArgs == 2: # 轴 + 命令
retVal = self.commandDict[numArgs][args[1]](args[0])
elif numArgs == 3: # 轴 + 命令 + 命令参数
print("command: %s %s %s" % (args[1], args[0], args[2]))
retVal = self.commandDict[numArgs][args[1]](args[0], args[2])
else:
retVal = "Strange error"
print("retVal:", retVal)
return retVal
def queryPosition(self, axis):
# 由于控制器单位是计数,取整结果
return self.refinePos(self.axisList[self.axisDict[axis]].readPosition())
def setPosition(self, axis, pos):
return self.axisList[self.axisDict[axis]].setPosition(int(pos))
def queryStatus(self, axis):
return self.axisList[self.axisDict[axis]].readStatus()
def moveAxis(self, axis, pos):
return self.axisList[self.axisDict[axis]].move(int(pos))
def moveRelative(self, axis, pos):
return self.axisList[self.axisDict[axis]].moveRelative(int(pos))
def jog(self, axis, velocity):
return self.axisList[self.axisDict[axis]].jog(float(velocity))
def stopAxis(self, axis):
return self.axisList[self.axisDict[axis]].stop()
def setVelocity(self, axis, velocity):
return self.axisList[self.axisDict[axis]].setVelocity(float(velocity))
def queryVelocity(self, axis):
return self.axisList[self.axisDict[axis]].readVelocity()
def setBaseVelocity(self, axis, velocity):
return self.axisList[self.axisDict[axis]].setBaseVelocity(float(velocity))
def queryBaseVelocity(self, axis):
return self.axisList[self.axisDict[axis]].readBaseVelocity()
def setAcceleration(self, axis, acceleration):
return self.axisList[self.axisDict[axis]].setAcceleration(float(acceleration))
def queryAcceleration(self, axis):
return self.axisList[self.axisDict[axis]].readAcceleration()
def queryHighLimit(self, axis):
return self.axisList[self.axisDict[axis]].readHighLimit()
def setHighLimit(self, axis, highLimit):
return self.axisList[self.axisDict[axis]].setHighLimit(int(highLimit))
def queryLowLimit(self, axis):
return self.axisList[self.axisDict[axis]].readLowLimit()
def setLowLimit(self, axis, lowLimit):
return self.axisList[self.axisDict[axis]].setLowLimit(int(lowLimit))
# 此处是测试一个控制器实例的代码
if __name__ == "__main__":
controller = Controller()
print("Test X axis:")
print(controller.queryStatus("X"))
print()
print(controller.moveAxis("X",1000))
for i in range(10):
time.sleep(0.5)
pos = controller.queryPosition("X")
status = controller.queryStatus("X")
print("pos: %s, status: %s" % (pos, status))
print()
print(controller.moveAxis("X",0))
for i in range(10):
time.sleep(0.5)
pos = controller.queryPosition("X")
status = controller.queryStatus("X")
print("pos: %s, status: %s" % (pos, status))4) 服务器程序:为电机控制器提供网路服务
服务器表现类似一个8轴控制器。
默认轴值保持与半步模式的步进电机一致(每个分辨400步)。
可以用名称(X, Y, Z, T, U, V, R, S)或者数值(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8)访问轴。
控制器接受以计数单位的值。为了响应非查询命令,服务器返回一个"OK"。
启动服务器:
$ python3 server.py
这将启动这个服务器,它默认在31337端口上监听。
可以通过修改server.py中的DEFAULT_PORT更高这个端口号。
命令参考:
输入终止符: \r\n
输出终止符: \r
命令语法: <axis> <command> [argument]
命令:
- axis MV <position> # 绝对移动(计数)
- axis MR <displacement> # 相对移动(计数)
- axis JOG <velocity> # Jog (计数/s, 符号)
- axis POS <position> # 设置位置 (计数)
- axis ACC <acceleration> # 设置加速度(计数/s/s)
- axis VEL <velocity> # 设置速度 (计数/s)
- axis BAS <base_velocity> # 设置基速度(计数/s)
- axis AB # 取消移动
- axis POS? # 查询位置(返回:计数)
- axis ST? # 查询状态(返回:整数)
- 状态位
- 方向: 0x1
- 结束移动: 0x2
- 移动中: 0x4
- 高限制: 0x8
- 低限位: 0x10
- 寻home: 0x20
- home限位: 0x40
- 已经找到home: 0x80
- 错误: 0x100
- axis ACC? # 查询加速度(返回:计数/s/s)
- axis VEL? # 查询速度(返回:计数/s)
- axis LL <position> # 设置低限位(计数)
- axis HL <position> # 设置高限位(计数)
- axis LL? # 查询低限位返回:计数)
- axis HL? # 查询高限位返回:计数)
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import getopt
import os
import sys
import asyncore
import asynchat
import socket
import controller
DEFAULT_PORT = 6666
class ConnectionDispatcher(asyncore.dispatcher):
def __init__(self, port):
asyncore.dispatcher.__init__(self)
self.port = port
self.device = controller.Controller()
self.create_socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
self.set_reuse_addr()
self.bind(("", port))
self.listen(5)
def handle_accept(self):
# client_info is a tuple with socket as the 1st element
client_info = self.accept()
ConnectionHandler(client_info[0], self.device)
class ConnectionHandler(asynchat.async_chat):
## regular expressions, if necessary, can go here
def __init__(self, sock, device):
asynchat.async_chat.__init__(self, sock)
self.set_terminator(b"\r")
#
self.outputTerminator = "\r\n"
self.device = device
self.buffer = ""
def collect_incoming_data(self, data):
self.buffer = self.buffer + data.decode()
def found_terminator(self):
data = self.buffer
self.buffer = ""
self.handleClientRequest(data)
def handleClientRequest(self, request):
request = request.strip()
# 打印接收到的命令
print("command from client:",request)
response = self.device.handleCommand(request)
if response != None:
self.sendClientResponse("{}".format(response))
# 打印发送给客户端的命令:
print("comand sent to client:", response)
print("send finished!")
return
def sendClientResponse(self, response=""):
data = response + self.outputTerminator
self.push(data.encode())
# 获取本程序名
def getProgramName(args=None):
# 获取命令行参数列表, args[0]即是程序名
if args == None:
args = sys.argv
if len(args) == 0 or args[0] == "-c":
return "PROGRAM_NAME"
print(args)
return os.path.basename(args[0])
# 打印这个程序的使用方法
def printUsage():
print("""\
Usage: {} [-ph]
-p, --port=NUMBER Listen on the specified port NUMBER for incoming
connections (default:{})
-h, --help Print usage message and exit""".format(getProgramName(), DEFAULT_PORT)
)
# 解析命令行参数,并且返回一个端口号
def parseCommandLineArgs(args):
# 指定长参数和短参数格式中的选项名称:-p <port> -help; --port=<port> --help
# 解析后选项被放入一个元组列表 [('-p', port), ('--port', 'port'), ...]
# 参数后面带:或者=的选项,必须有选项参数
(options, extra) = getopt.getopt(args[1:], "p:h", ["port=", "help"])
port = DEFAULT_PORT
# 用于调试
#!print(options)
#!print(extra)
# 除选项及对应的选项参数外,还有其它参数
if len(extra) > 0:
print("Error: unexpected command-line argument \"{}\"".format(extra[0]))
printUsage()
sys.exit(1)
for eachOptName, eachOptValue in options:
if eachOptName in ("-p", "--port"):
port = int(eachOptValue)
elif eachOptName in ("-h", "--help"):
printUsage()
sys.exit(0)
return port
def main(args):
port = parseCommandLineArgs(args)
server = ConnectionDispatcher(port)
print("Use Port: ", port)
try:
asyncore.loop()
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print()
print("Shutting down the server...")
sys.exit(0)
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 检测python版本
if sys.version_info < (3,0,0) and sys.version_info < (3,12,0):
sys.stderr.write("You need Python 3.0 or later (but less than 3.12) to run this script\n")
input("Press enter to quit... ")
sys.exit(1)
# Try to run the server
try:
main(sys.argv)
except Exception as e:
if isinstance(e, SystemExit):
raise e
else:
print("Error: {}".format(e))
sys.exit(1)4) 运行以上服务器代码,并且用客户端测试:
客户端测试了MV,POS?,ST?三个命令:
- MV:移动电机轴到指定位置。
- POS?:查询电机轴当前处于的位置。
- ST?:查询电机轴的状态。
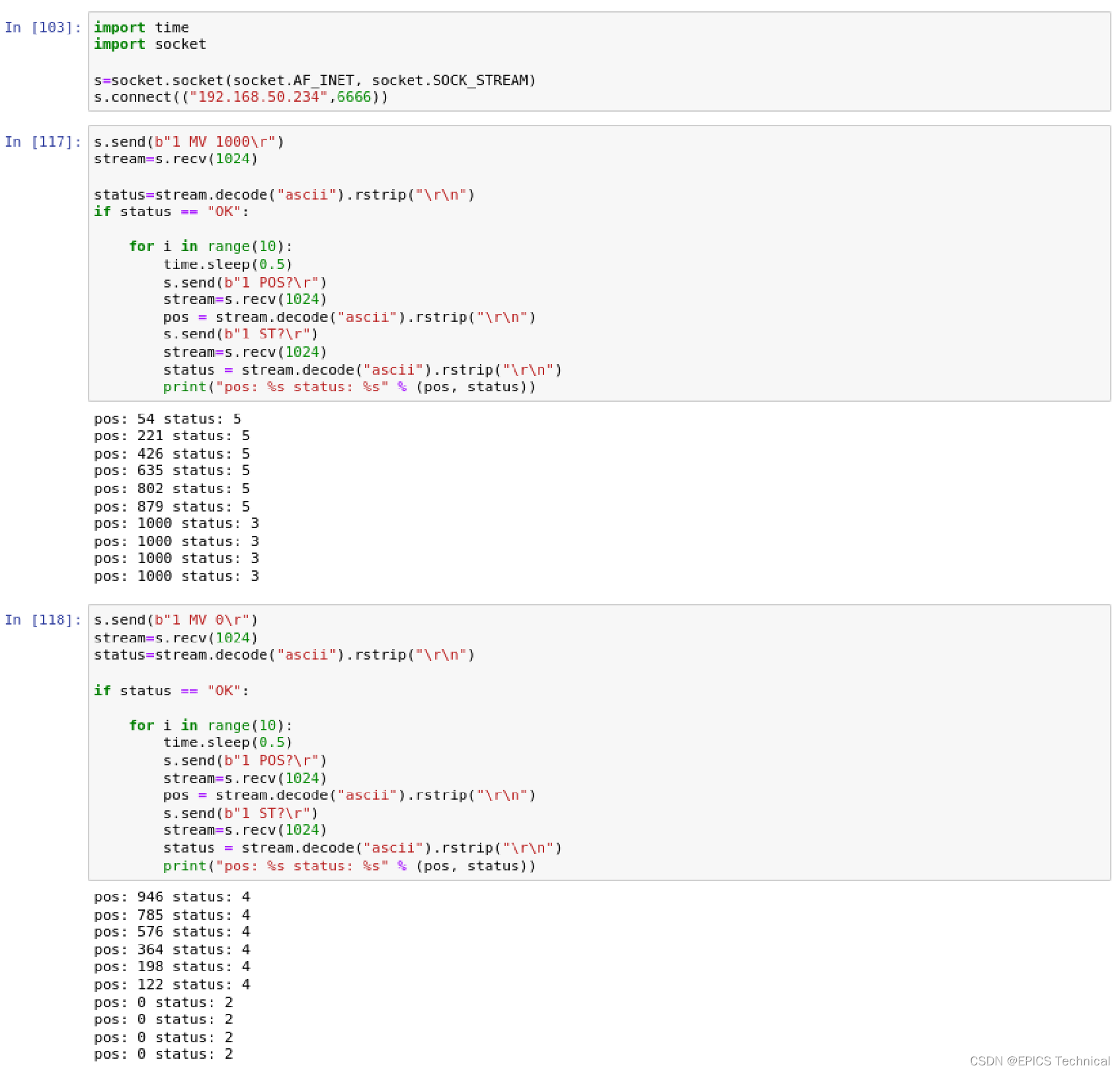
Python电机仿真程序用于练习EPICS电机控制器驱动程序的编写。