1. 数据集
- 数据集地址:Credit Card Fraud Detection
- 数据集整体浏览:
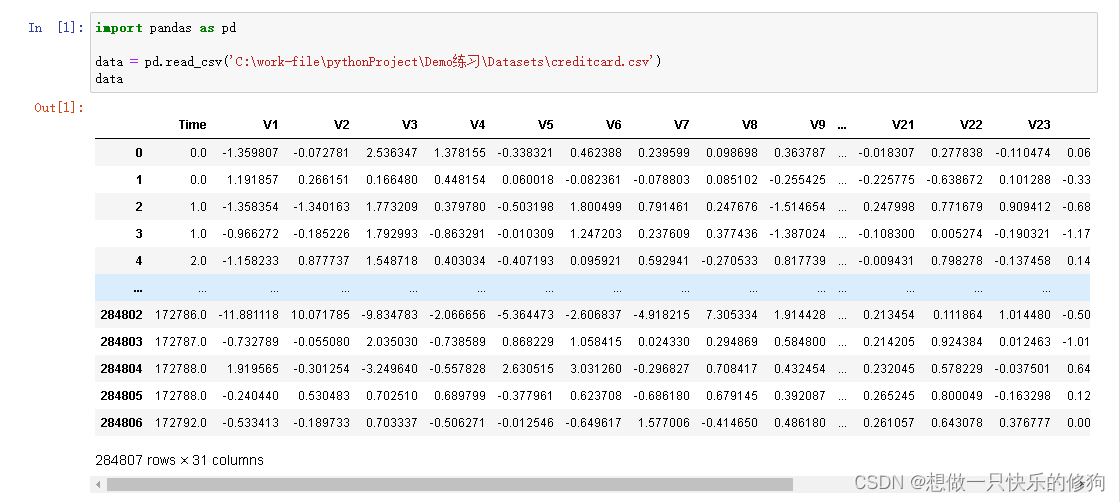
- 284807个样本,30个特征,1个分类标签Class
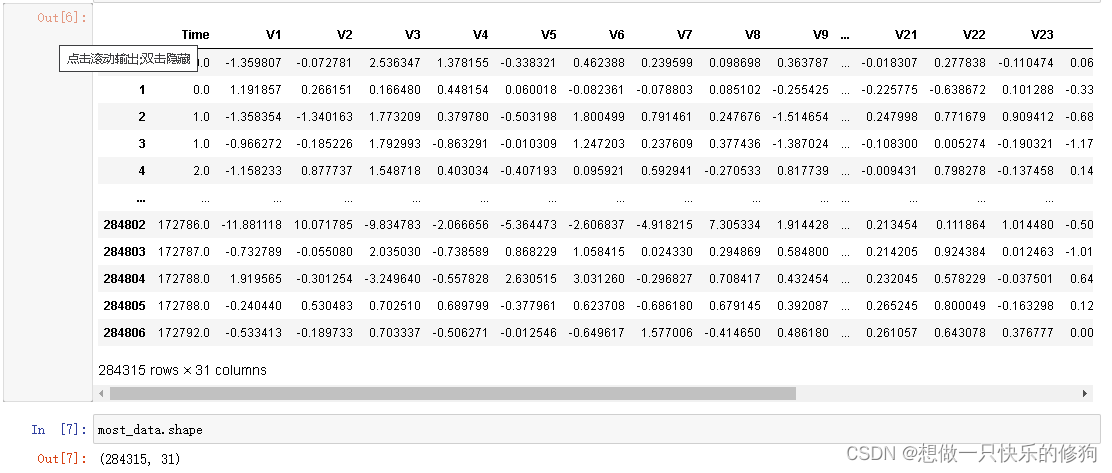
- Class为0的是多数类,一共有284315个样本。
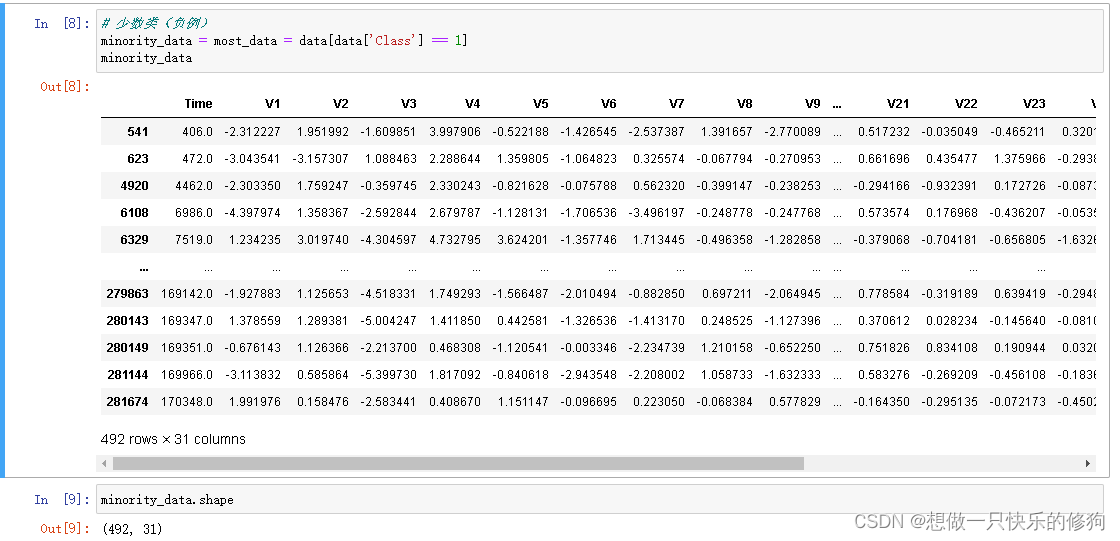
- Class为1的是少数类,一共有492个样本,可见数据集是不平衡的。
2. 对Adaboost的代码进行修改,构造代价调整函数,并对数据集进行分类
- 代码结构:

- adacost.py
import numpy as np
from sklearn.ensemble import AdaBoostClassifier
from scipy.special import xlogy
class AdaCostClassfier(AdaBoostClassifier):
def _boost_real(self, iboost, X, y, sample_weight, random_state):
'''
权重更新的公式在这里
'''
estimator = self._make_estimator(random_state=random_state)
estimator.fit(X, y, sample_weight=sample_weight)
y_predict_proba = estimator.predict_proba(X)
if iboost == 0:
self.classes_ = getattr(estimator, 'classes_', None) # 获取estimator的classes_属性值
self.n_classes_ = len(self.classes_)
y_predict = self.classes_.take(np.argmax(y_predict_proba, axis=1), axis=0)
# 分类不正确的实例
incorrect = y_predict != y
# 误差分数
estimator_error = np.mean(np.average(incorrect, weights=sample_weight, axis=0))
# 如果分类器完美,那么就停止
if estimator_error <= 0:
return sample_weight, 1.0, 0.0
n_classes = self.n_classes_
classes = self.classes_
y_codes = np.array([-1.0 / (n_classes - 1), 1.0])
y_coding = y_codes.take(classes == y[:, np.newaxis])
proba = y_predict_proba # 别名
np.clip(proba, np.finfo(proba.dtype).eps, None, out=proba)
estimator_weight = (
-1.0
* self.learning_rate
* ((n_classes - 1.0) / n_classes)
* xlogy(y_coding, y_predict_proba).sum(axis=1)
)
# 在此处更新,增加代价敏感系数
if not iboost == self.n_estimators - 1:
# Only boost positive weights
sample_weight *= np.exp(
estimator_weight * ((sample_weight > 0) | (estimator_weight < 0)) * self._beta(y, y_predict)
)
return sample_weight, 1.0, estimator_error
def _beta(self, y, y_hat):
'''
代价调整函数
'''
res = []
for i in zip(y, y_hat):
if i[0] == i[1]:
res.append(1) # 正确分类,系数保持不变
elif i[0] == 1 and i[1] == -1:
res.append(1.25) # 将正类(好人)判断为负类(坏人)代价更大,系数增大
elif i[0] == -1 and i[1] == 1:
res.append(1) # 将负类(坏人)判断为正类(好人)代价不变,系数保持不变
else:
print(i[0], i[1])
return np.array(res)
- AdaCost用于信用卡欺诈分类预测(与Adaboost对比).py
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import recall_score, precision_score, f1_score
from sklearn.ensemble import AdaBoostClassifier
from adacost import AdaCostClassfier
def load_creditcard_data():
'''
读取数据集,并讲正例标记为1,讲负例标记为-1
'''
df = pd.read_csv('C:\\work-file\\pythonProject\\Demo练习\\Datasets\\creditcard.csv')
df.loc[df.Class == 1, 'Class'] = -1 # 少数类
df.loc[df.Class == 0, 'Class'] = 1 # 多数类
print(df.shape) # 总样本数
print(df.Class.value_counts()) # 正例、负例的数量
return df.drop('Class', axis=1), df['Class'] # 返回X、y
def clf_compare(clfs):
'''
比较不同分类器的结果
'''
for clf in clfs:
y_pred = clf.predict(X_test)
print(pd.Series(y_pred).value_counts())
print(recall_score(y_test, y_pred, pos_label=-1),
precision_score(y_test, y_pred, pos_label=-1),
f1_score(y_test, y_pred, pos_label=-1), '\n') # 更关注-1的少数类
return
if __name__ == '__main__':
X, y = load_creditcard_data()
# 划分数据集
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.3, random_state=42)
print(pd.Series(y_test).value_counts()) # 测试集中正例、负例的个数统计
ada_clf = AdaBoostClassifier(n_estimators=100)
ada_clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
adacost_clf = AdaCostClassfier(n_estimators=100)
adacost_clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
clf_compare([ada_clf, adacost_clf])
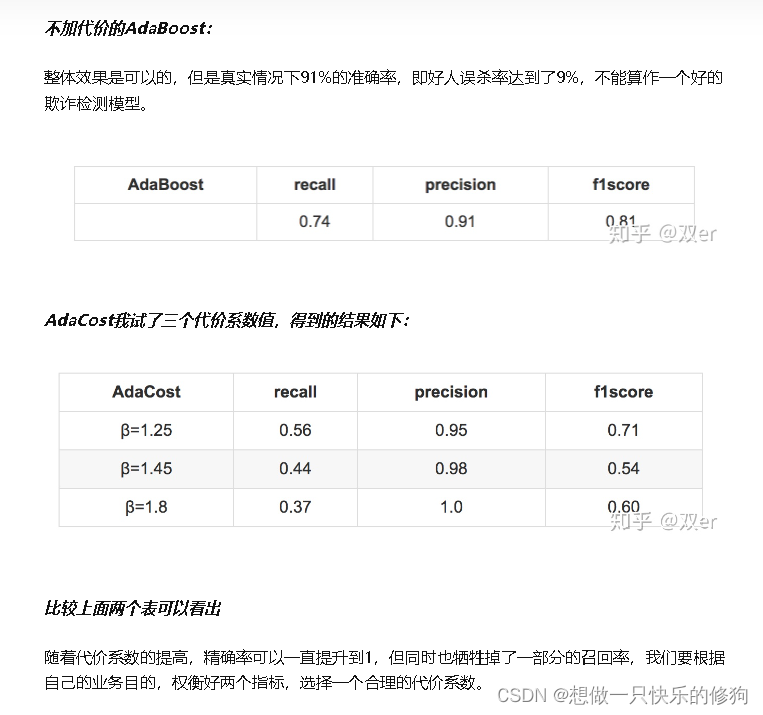
3. 结果分析
3.1 评价指标
- 查全率 R 又称之为召回率,是少数类样本被模型成功预测到的几率,体现了
机器学习模型对少数类的预测能力。查全率的取值区间为[0, 1],查全率越大,说
明模型越能有效地识别出少数类的存在。 - 查准率 P 又称之为精确率,定义为被模型预测为少数类样本之中真实的少
数类样本所占的比例,反映了模型预测出的少数类样本的可信程度。精确率的取
值区间为[0, 1],精确率越大,说明被模型预测为少数类样本的可信度越高。 - F1 值被定义为查准率和查全率的调和均值,综合考虑两个指标的作用。

3.2 结果
β=1.25的结果
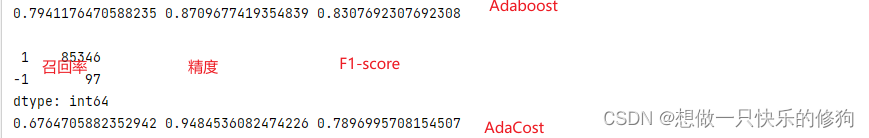
4. 参考
- 减少信用卡欺诈识别误杀:实现基于代价敏感的AdaCost算法
- machine-learning - f1_score 中的 pos_label 到底是什么意思?
- 代价敏感学习


![基础算法系列--[基本数据结构KMP]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/b939f444e5694bf7a365ea1e7367dd45.png)



![[附源码]Nodejs计算机毕业设计教师职称评定系统Express(程序+LW)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/fe478aea11c24ed98f1bbefc62c37e41.png)