上篇文章对栈和队列的一个经典题目——Leetcode.225-用队列实现栈进行讲解。本篇文章将对另一个题目Leetcode.232-用栈实现队列进行讲解
1. Leetcode.232——用栈实现队列:
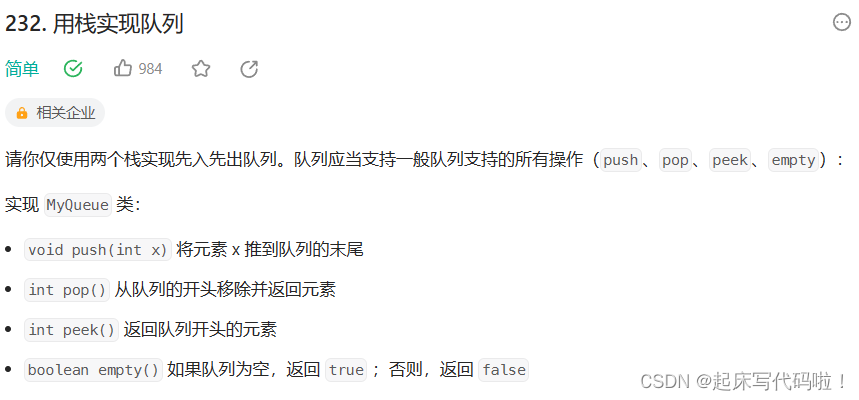
题目如下:
1.1 大体思路分析:
题目要求需要实现下列函数所表示的功能,即:(创建队列),
(用栈实现队列尾插),
(返回队列的开头元素),
(移除、返回队列开头元素),
(探空),myQueueFree(释放问题解决过程中开辟的空间)。
对于上述给出需要实现的功能中,较为重要的是:(返回队列的开头元素),
(移除、返回队列开头元素),在本部分,将介绍这两种功能的实现思路。
对于栈,可以看作只能在尾部进行插入删除的线性表,对于队列,是尾部进行插入,头部进行删除的线性表。下面给出一个包含若干元素的栈,即:
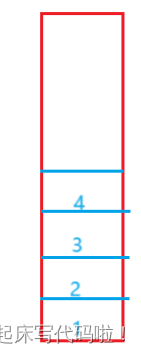
题目要求用两个栈来实现队列,则,将上述栈中的元素插入到另一个栈后,及: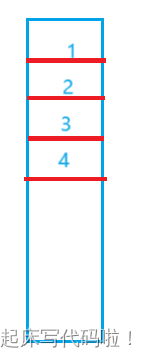
此时,栈的尾部存储的元素为,按照栈的规则,尾部插入元素,尾部删除元素,则可以达到上述给出的函数(移除、返回队列开头元素)所对应的移除开头元素的功能。对于返回队列开头元素,只需要在移除元素之前,单独创建一个变量用于存储元素
,移除元素,最后返回用于存储元素
的变量即可。
在利用队列实现栈的题目中,需要一个结构体指针指向一个保持为空的队列,令一个结构体指针指向的队列 用于插入元素。通过上面给出思路可知,本题需要的两个栈,一个用来接受插入的元素,将这个栈定义为,另一个栈需要接受
的栈顶元素,并在之后通过出栈顶元素来实现队列关于头元素的各项功能。
1.2 功能实现:
1.2.1 栈的创建及初始化:
初始化的过程与上篇文章的中初始化原理相同,不过多赘述,只给出代码:
typedef struct {
ST pushst;
ST Popst;
} MyQueue;
MyQueue* myQueueCreate() {
MyQueue* obj = (MyQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyQueue));
STInit(&obj->pushst);
STInit(&obj->Popst);
return obj;
}1.2.2 通过栈顶插入元素 myQueuePush:
虽然栈与队列在删除元素时由一定不同,但是在插入元素时,队列是在队尾插入,栈是在栈顶,即同样是队尾插入,所以,直接调用函数,向队尾位置插入元素即可,代码如下:
void myQueuePush(MyQueue* obj, int x) {
STPush(&obj->pushst,x);
}1.2.3 返回队列的开头元素myQueuePeek:
上面给出了实现本功能的大体思路。但是需要区分下面两种情况,即:栈中为空、
栈中已经存在元素。对于前一种情况,需要将
中的所有元素都插入到
,最后取栈顶元素返回即可。对于后一种情况,直接取栈顶元素返回即可。
对应代码如下:
int myQueuePeek(MyQueue* obj) {
if( STEmpty(&obj->Popst))
{
while(!STEmpty(&obj->pushst))
{
STPush(&obj->Popst,STTop(&obj->pushst));
STPop(&obj->pushst);
}
}
return STTop(&obj->Popst);
}1.2.3 从队头删除并返回队头元素 :
:
上个功能中,已经实现了返回栈顶元素,所以在实现本功能时,只需要创建一个变量用于存储
的返回值,再移除栈顶元素,最后返回
即可。对应代码如下:
int myQueuePop(MyQueue* obj) {
int front = myQueuePeek(obj);
STPop(&obj->Popst);
return front;
}1.2.4 探空 :
:
原理较为简单,只给出代码,不做多余解释:
bool myQueueEmpty(MyQueue* obj) {
return STEmpty(&obj->Popst) && STEmpty(&obj->pushst);
}1.2.5 释放解决问题所开辟的空间myQueueFree:
同样,只给出代码,不做多余解释:
void myQueueFree(MyQueue* obj) {
STDestory(&obj->pushst);
STDestory(&obj->Popst);
free(obj);
}2. 结果及代码总览:
2.1 运行结果:

2.2 代码总览:
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType* a;
int top;
int capacity;
}ST;
//栈的初始化:
void STInit( ST* ps )
{
assert(ps);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->top = ps->capacity = 0;
}
//栈的销毁:
void STDestory(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
free(ps->a);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->top = ps->capacity = 0;
}
void STPush(ST* ps, STDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->top == ps->capacity)
{
int newcapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? ps->capacity = 4: ps->capacity * 2;
STDataType* newnode = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->a,sizeof(STDataType) * newcapacity);
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("realloc");
}
ps->a = newnode;
ps->capacity = newcapacity;
}
ps->a[ps->top] = x;
ps->top++;
}
void STPop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->top > 0);
ps->top--;
}
int size(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top;
}
bool STEmpty(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top == 0;
}
STDataType STTop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->top > 0);
return ps->a[ps->top-1];
}
//栈的初始化:
void STInit(ST* ps);
//栈的销毁
void STDestory(ST* ps);
//通过栈顶向栈中插入元素
void STPush(ST* ps, STDataType x);
//删除栈中的元素:
void STPop(ST* ps);
//记录size
int size(ST* ps);
//找空
bool STEmpty(ST* ps);
//获取栈顶元素
STDataType STTop(ST* ps);
typedef struct {
ST pushst;
ST Popst;
} MyQueue;
MyQueue* myQueueCreate() {
MyQueue* obj = (MyQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyQueue));
STInit(&obj->pushst);
STInit(&obj->Popst);
return obj;
}
void myQueuePush(MyQueue* obj, int x) {
STPush(&obj->pushst,x);
}
int myQueuePeek(MyQueue* obj) {
if( STEmpty(&obj->Popst))
{
while(!STEmpty(&obj->pushst))
{
STPush(&obj->Popst,STTop(&obj->pushst));
STPop(&obj->pushst);
}
}
return STTop(&obj->Popst);
}
int myQueuePop(MyQueue* obj) {
int front = myQueuePeek(obj);
STPop(&obj->Popst);
return front;
}
bool myQueueEmpty(MyQueue* obj) {
return STEmpty(&obj->Popst) && STEmpty(&obj->pushst);
}
void myQueueFree(MyQueue* obj) {
STDestory(&obj->pushst);
STDestory(&obj->Popst);
free(obj);
}