强化学习
- 简介
- gym库-CliffWalking
- SARSA
- Q-learning
- 示例
- SARSA
- Q-learning
简介
机器学习:监督学习、非监督学习、强化学习
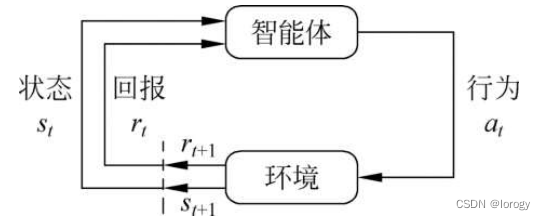
- 模仿人类和动物的试错机制进行学习
- 智能体与环境交互,根据当前的环境状态s,按照一定策略采取行动a,获得回报r
- 目标:获取最大累积期望回报
脉络介绍:

gym库-CliffWalking
安装标准化实验环境
pip install gym
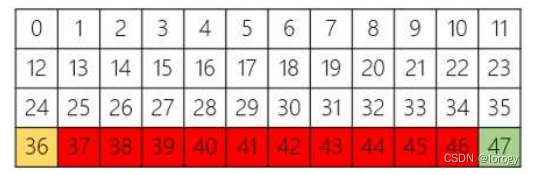
CliffWalking:悬崖寻路问题,4*12网格,红色为悬崖,36为起始,47为目标
动作:0-4,上右下左,如果移出除网络则不变
奖励:{-1,100},与悬崖为-100,否则为-1
SARSA
行动选择策略:ε-greedy,以ε的概率进行探索,以1-ε的概率进行利用
Q值更新:根据下一次实际行动更新,胆小,选择离悬崖远的路线
td_target += gamma * Q[next_state, next_action]
Q[state, action] += lr * (td_target - Q[state, action])
Q-learning
行动选择策略:ε-greedy,以ε的概率进行探索,以1-ε的概率进行利用
Q值更新:选取最优的行动更新Q值,胆大,最终选择离悬崖近的路线
td_target += gamma * max(Q[next_state, :])
Q[state, action] += lr * (td_target - Q[state, action])
示例
SARSA
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import gym
from tqdm import tqdm
def max_index(a):
# return np.argmax(a)
candidate = np.where(a == np.max(a))[0]
index = np.random.randint(0, len(candidate))
return candidate[index]
def eps_greedy(Q, state):
a = Q[state, :]
if np.random.random() < 1 - eps:
return max_index(a)
return np.random.randint(0, len(a)) # [start,end)
def calc_policy(Q):
state_number = Q.shape[0]
policy = np.zeros(shape=state_number, dtype=np.int8)
for i in range(state_number):
policy[i] = np.argmax(Q[i, :])
return policy
# 0123:{上右下左}
def print_optimal_action(pi, row, col):
print(actions)
for i in range(row):
for j in range(col):
print(actions[pi[i * col + j]], end=' ')
print()
# 比较a,b之间的差值是否小于阈值
def is_same(a, b, thresold=0.001):
e = np.abs(a - b) > thresold
return np.sum(e) == 0
if __name__ == '__main__':
eps = 0.01
lr = 0.01
gamma = 0.99
np.set_printoptions(suppress=True)
row, col = 4, 12
state_number = row * col
action_number = 4
actions = list('↑→↓←') # 上右下左:0123
Q = np.zeros((state_number, action_number), dtype=np.float64)
Q_last = [np.ones_like(Q), np.ones_like(Q), np.ones_like(Q), np.ones_like(Q), np.ones_like(Q)]
env = gym.make('CliffWalking-v0')
print('状态数量:', env.observation_space.n)
print('行为数量:', env.action_space.n)
# 10万个episode的迭代
for i in tqdm(range(1, 100000)):
env.reset()
state = 36 # 初始位置
done = False
action = eps_greedy(Q, state)
while not done:
next_state, reward, done, info = env.step(action)
# print('state, action, reward:', state, action, reward)
next_action = eps_greedy(Q, next_state)
td_target = reward
if not done:
td_target += gamma * Q[next_state, next_action]
Q[state, action] += lr * (td_target - Q[state, action])
state = next_state
action = next_action
if is_same(Q_last[0], Q):
print('Q-table迭代完成,提前退出:', i)
break
Q_last = Q_last[1:]
Q_last.append(np.copy(Q))
pi = calc_policy(Q)
print('Q Table:\n', Q)
# np.savetxt('Q_table.txt', Q, fmt='%.5f')
pd.DataFrame(Q).to_excel('Q_table.xlsx', index=True)
for s_id in range(state_number):
print(s_id, s_id // col, s_id % col, Q[s_id, :], pi[s_id], actions[pi[s_id]])
print('最优策略:', pi)
print_optimal_action(pi, row, col)
# 输出最终路径(状态及坐标)
env.reset()
state = 36
done = False
trace = [{state: (state // col, state % col)}]
while not done:
action = pi[state]
state, _, done, _ = env.step(action)
trace.append({state: (state // col, state % col)})
if len(trace) > 48:
break
print(len(trace), ':', trace)
Q-learning
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import gym
from tqdm import tqdm
def max_index(a):
candidate = np.where(a == np.max(a))[0]
index = np.random.randint(0, len(candidate))
return candidate[index]
def eps_greedy(Q, state):
a = Q[state, :]
if np.random.random() < 1-eps:
return max_index(a)
return np.random.randint(0, len(a))
def calc_policy(Q):
state_number = Q.shape[0]
policy = np.zeros(shape=state_number, dtype=np.int8)
for i in range(state_number):
policy[i] = np.argmax(Q[i, :])
return policy
# 0123:{上右下左}
def print_optimal_action(pi, row, col):
a = list('↑→↓←')
print(a)
for i in range(row):
for j in range(col):
print(a[pi[i*col+j]], end=' ')
print()
if __name__ == '__main__':
eps = 0.1 # 10%概率探索,90%概率利用
lr = 0.01
gamma = 0.99
np.set_printoptions(suppress=True)
row = 4
col = 12
state_number = row * col
action_number = 4 # 上下左右
Q = np.zeros((state_number, action_number), dtype=np.float64)
env = gym.make('CliffWalking-v0')
for i in tqdm(range(10000)): # 10000个episode的训练
env.reset()
state = 36
done = False
action = eps_greedy(Q, state)
while not done:
next_state, reward, done, info = env.step(action)
next_action = eps_greedy(Q, next_state)
td_target = reward
if not done:
td_target += gamma * max(Q[next_state, :]) # Q-learning
Q[state, action] += lr * (td_target - Q[state, action])
state = next_state
action = next_action
pi = calc_policy(Q)
print('Q Table:\n', Q)
pd.DataFrame(Q).to_excel('Q_table.xlsx', index=True)
for s_id in range(state_number):
print(s_id, s_id//col, s_id % col, Q[s_id, :], pi[s_id])
print_optimal_action(pi, row, col)
# 输出最终路径
env.reset()
state = 36
done = False
trace = [{state: (state // col, state % col)}]
while not done:
action = np.argmax(Q[state, :])
state, _, done, _ = env.step(action)
trace.append({state: (state//col, state % col)})
if len(trace) > 48:
break
print(len(trace), ':', trace)