目录
一、前言
二、日期类的实现
检查日期的合法性
< 运算符重载
==运算符重载
<=运算符重载
>运算符重载
>=运算符重载
!=运算符重载
进一步优化
日期+天数
日期+=天数
日期-=天数
日期-天数
前置++&&后置++
前置--&&后置--
思路:
日期-日期
三、总代码
Date.h文件
Date.cpp文件
一、前言
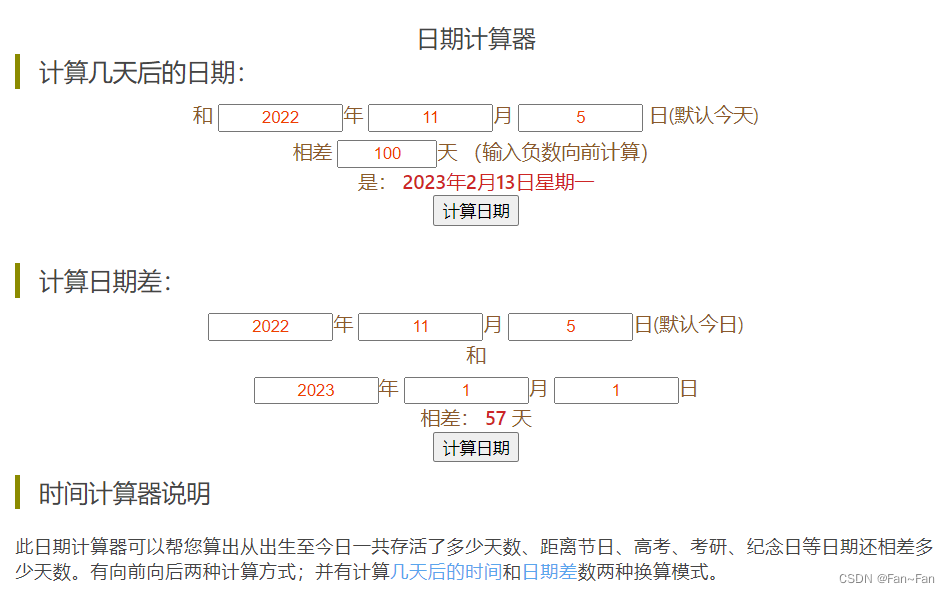
在我们的日常生活中,我们可能需要计算几天后的日期或者计算日期差等,我们计算日期可以直接用日期计算器来求得,下面我们先看一下网络上面的日期计算器截图:
现在我们就用代码自己实现一个日期计算器。
二、日期类的实现
检查日期的合法性
实现日期类的首要前提肯定就是先要检查日期的合法性。
class Date { public: bool isLeapYear(int year) //判断是否为闰年 { return (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || (year % 400 == 0); } int GetMonthDay(int year, int month) { assert(year >= 0 && month > 0 && month < 13); //加上static防止函数频繁调用开辟几十个字节大小的数组 static int monthDayArray[13] = { 0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31 }; if (month == 2 && isLeapYear(year)) return 29; //闰月29天 else return monthDayArray[month]; } Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1) { if (year >= 1 && month <= 12 && month >= 1 && day <= GetMonthDay(year, month)) { //确保日期合法 _year = year; _month = month; _day = day; } } private: int _year; int _month; int _day; };
< 运算符重载
- 思路:
运算符重载我们在上篇博文中已经讲过,这里就不再过多赘述,现在我们要写出<运算符重载,假如我们实例化出对象d1和d2,我们比较d1是否小于d2,只需要考虑如下三种情况:
- d1的年小于d2的年
- d1与d2的年相等,d1的月小于d2的月
- d1与d2的年和月都相等,d1的天小于d2的天
这三种情况任何一种情况符合,都属于d1小于d2。
- 代码如下:
// <运算符重载 bool Date::operator<(const Date& d) const //类外访问成员函数需要设定类域 { if (_year < d._year || _year == d._year && _month < d._month || _year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day < d._day) return true; else return false; }
==运算符重载
- 思路:
==运算符重载只需要判定d1和d2的年、月、日对应是否相等。
- 代码如下:
// ==运算符重载 bool Date::operator==(const Date& d) const { return _year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day == d._day; }
<=运算符重载
- 思路:
<=就是要么小于要么等于。那么我们写<=运算符重载就可以复用前面所写的<运算符重载和<=运算符重载,就无需再写大量代码了。
- 代码如下:
// <=运算符重载 bool Date::operator<=(const Date& d) const { return *this < d || *this == d; }
>运算符重载
- 思路:
>的反义就是<=,所以我们只需要复用<=运算符重载,再对其取反就可以了。
- 代码如下:
// >运算符重载 bool Date::operator>(const Date& d) const { return !(*this <= d); }
>=运算符重载
- 思路:
>=的反义就是<,所以我们只需要复用<运算符重载,再对其取反就可以了。
- 代码如下:
// >=运算符重载 bool Date::operator>=(const Date& d) const { return !(*this < d); }
!=运算符重载
- 思路:
!=的反义就是==,所以我们只需要将==取反即可。
- 代码如下:
//!=运算符重载 bool Date::operator!=(const Date& d) const { return !(*this == d); }
进一步优化
- 我们上面所写的运算符重载都是建立在声明和定义分离的,这里我们可以对其进行进一步的优化。我们以前学过内敛函数,并且对于类来说直接定义在类里面的函数默认为内敛函数,所以我们将代码量小的函数直接定义在类里面,代码量大的函数进行声明和定义分离。
- Dath.h文件:
#pragma once #include <iostream> #include <assert.h> using std::cout; using std::cin; using std::endl; class Date { public: bool isLeapYear(int year) //判断是否为闰年 { return (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || (year % 400 == 0); } int GetMonthDay(int year, int month);//获取某年某月天数 //构造函数 Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1); //打印 void Print() const { cout << _year << "-" << _month << "-" << _day << endl; } //<运算符重载 bool operator<(const Date& d) const; //==运算符重载 bool operator==(const Date& d)const; //<=运算符重载 bool operator<=(const Date& d)const { return *this < d || *this == d; } //>运算符重载 bool operator>(const Date& d)const { return !(*this <= d); } //>=运算符重载 bool operator>=(const Date& d)const { return !(*this < d); } //!=运算符重载 bool operator!=(const Date& d)const { return !(*this == d); } private: int _year; int _month; int _day; };
- Dath.cpp文件:
#include "Date.h" //<运算符重载 bool Date::operator<(const Date& d)const { if (_year < d._year || _year == d._year && _month < d._month || _year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day < d._day) return true; else return false; } //==运算符重载 bool Date::operator==(const Date& d)const { return _year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day == d._day; } //获取某年某月天数 int Date::GetMonthDay(int year, int month) { assert(year >= 0 && month > 0 && month < 13); static int monthDayArray[13] = { 0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31 }; if (month == 2 && isLeapYear(year)) { return 29; } else { return monthDayArray[month]; } } //构造函数 Date::Date(int year, int month, int day) { if (year >= 1 && month <= 12 && month >= 1 && day >= 1 && day <= GetMonthDay(year, month)) { _year = year; _month = month; _day = day; } else { cout << "日期非法" << endl; } }
日期+天数
- 思路:
日期+天数我们得到的还是一个日期,需要注意的就是进位的问题(天满了往月进,月满了往年进)。
- 加过天数后超过该月的最大天数,需要进位。
- 当月进位到13后,年进位+1,月重置为1。
- 法一:
Date Date::operator+(int day) const { Date ret(*this); //拷贝构造,拿d1去初始化ret ret._day += day; while (ret._day > GetMonthDay(ret._year, ret._month)) { ret._day -= GetMonthDay(ret._year, ret._month); ret._month++; if (ret._month == 13) { ret._year++; ret._month = 1; } } return ret; }出了作用域,对象ret就不在了,它是一个局部对象,我们这里不能用引用,用了的话,返回的就是ret的别名,但是ret又已经销毁了,这就有可能访问野指针,所以出了作用域,如果对象不在了,就不能用引用返回,要用传值返回。
- 法二:复用日期+=天数
此种方法是建立在日期+=天数的基础上完成的,然后进行复用。
Date Date::operator+(int day) const { //法二:复用日期 += 天数 Date ret(*this); ret += day; return ret; }
日期+=天数
- 法一:
前面我们实现了日期+天数,下面我们看函数的第一行,我们就调用了一个拷贝构造:
Date ret(*this); //拷贝构造,拿d1去初始化ret这里调用拷贝构造是为了不在*this上面直接做改动,只在ret上面进行操作,其理由是日期+天数得到的还是另外一个日期,而不用拷贝构造直接在*this上面做改动只会导致原有的日期也发生变化,而这个变化也正是我日期+=天数的需求。
Date& Date::operator+=(int day) //传引用返回 { //如果day小于0,要单独处理 if (day < 0) { return *this -= -day; } _day += day; while (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month)) { _day -= GetMonthDay(_year, _month); _month++; if (_month == 13) { _year++; _month = 1; } } return *this; }这里我们用的是传引用返回,原因就在于我们返回的*this是全局的,出了作用域还在。
- 法二:复用日期+天数
Date& Date::operator+=(int day) { //法二:复用 * this = *this + day; return *this; }⭐:法一和法二那个更优呢?
答案:法一。讨论这个问题的本质就是去分析用+去复用+=好还是用+=复用+好。答案是用+去复用+=好,因为+有两次拷贝,而+=没有拷贝,所以实现+=,并且用+去复用+=效率更高。
日期-=天数
- 思路:
日期-=天数得到的还是一个日期。日期减去天数后要分析day是否大于0,只要大于0就没问题,如果小于0就需要借位。所以我们就需要进行讨论:
- 当减的天数为负数,则调用+=
- 若减后的day<0,则从月借位
- 若月为0,则从年借位,月重置为12
- 代码如下:
Date& Date::operator-=(int day) { //如果减去的天数是负数,要单独处理,直接调用+=运算符重载 if (day < 0) { return *this += -day; } _day -= day; while (_day <= 0) { --_month; if (_month == 0) { _month = 12; --_year; } _day += GetMonthDay(_year, _month); } return *this; }
日期-天数
日期-天数我们直接复用日期-=天数即可:
//日期 - 天数 Date Date::operator-(int day) const { Date ret(*this); ret -= day; return ret; }
前置++&&后置++
- 思路:
C++里面有前置++和后置++,这也就导致了一个问题,我们该如何区别它们呢?C++规定:无参的为前置++,有参的为后置。
- 前置++
//前置++ Date& Date::operator++() //无参的为前置 { *this += 1; //直接复用+= return *this; }
- 后置++
//后置++ Date Date::operator++(int i) //有参数的为后置 { Date tmp(*this); *this += 1; //复用+= return tmp; }
前置--&&后置--
思路:
前置--和后置--思路和前置++后置++一样。
- 前置--
//前置-- Date& Date::operator--() //无参的为前置 { *this -= 1; //直接复用-= return *this; }
- 后置--
//后置-- Date Date::operator--(int i) //有参数的为后置 { Date tmp(*this); *this -= 1; return tmp; }
日期-日期
- 思路:
日期 - 日期得到的是天数,首先我们得判断两个日期的大小,用min和max分别代表小的和大的日期,随后,算出min和max之间的差距,若min!=max,则min就++,随即定义变量n也自增++,最后返回n(注意符号)
- 代码如下:
//日期 - 日期 int Date::operator-(const Date& d) const { int flag = 1; //方便后续计算正负 Date max = *this; Date min = d; if (*this < d) { min = *this; max = d; flag = -1; //计算正负 } //确保max是大的,min是小的 int n = 0; while (min != max) { min++; n++; }//算出min和max之间绝对值差距 return n * flag; //如果d1大,结果为正,d2大结果为负 }
三、总代码
Date.h文件
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <assert.h>
using std::cout;
using std::cin;
using std::endl;
class Date
{
public:
bool isLeapYear(int year) //判断是否为闰年
{
return (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || (year % 400 == 0);
}
int GetMonthDay(int year, int month);//获取某年某月天数
//构造函数
Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1);
//打印
void Print() const
{
cout << _year << "-" << _month << "-" << _day << endl;
}
//<运算符重载
bool operator<(const Date& d) const;
//==运算符重载
bool operator==(const Date& d)const;
//<=运算符重载
bool operator<=(const Date& d)const
{
return *this < d || *this == d;
}
//>运算符重载
bool operator>(const Date& d)const
{
return !(*this <= d);
}
//>=运算符重载
bool operator>=(const Date& d)const
{
return !(*this < d);
}
//!=运算符重载
bool operator!=(const Date& d)const
{
return !(*this == d);
}
Date& operator+=(int day);
Date operator+(int day) const;
Date& operator-=(int day);
Date operator-(int day) const;
//前置++
Date& operator++() //无参的为前置
{
*this += 1; //直接复用+=
return *this;
}
//后置++
Date operator++(int i) //有参数的为后置
{
Date tmp(*this);
*this += 1; //复用+=
return tmp;
}
//前置--
Date& operator--() //无参的为前置
{
*this -= 1; //直接复用-=
return *this;
}
//后置--
Date operator--(int i) //有参数的为后置
{
Date tmp(*this);
*this -= 1;
return tmp;
}
int operator-(const Date& d) const;
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};Date.cpp文件
#include "Date.h"
//<运算符重载
bool Date::operator<(const Date& d)const
{
if (_year < d._year ||
_year == d._year && _month < d._month ||
_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day < d._day)
return true;
else
return false;
}
//==运算符重载
bool Date::operator==(const Date& d)const
{
return _year == d._year &&
_month == d._month &&
_day == d._day;
}
//获取某年某月天数
int Date::GetMonthDay(int year, int month)
{
assert(year >= 0 && month > 0 && month < 13);
static int monthDayArray[13] = { 0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31 };
if (month == 2 && isLeapYear(year))
{
return 29;
}
else
{
return monthDayArray[month];
}
}
//构造函数
Date::Date(int year, int month, int day)
{
if (year >= 1 &&
month <= 12 && month >= 1 &&
day >= 1 && day <= GetMonthDay(year, month))
{
_year = year;
_month = month;
_day = day;
}
else
{
cout << "日期非法" << endl;
}
}
Date& Date::operator+=(int day) //传引用返回
{
if (day < 0)
{
return *this -= -day;
}
_day += day;
while (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month))
{
_day -= GetMonthDay(_year, _month);
_month++;
if (_month == 13)
{
_year++;
_month = 1;
}
}
return *this;
}
Date Date::operator+(int day) const
{
//法二:复用日期 += 天数
Date ret(*this);
ret += day;
return ret;
}
//日期 -=天数 d1-=100
Date& Date::operator-=(int day)
{
//如果减去的天数是负数,要单独处理,直接调用+=运算符重载
if (day < 0)
{
return *this += -day;
}
_day -= day;
while (_day <= 0)
{
--_month;
if (_month == 0)
{
_month = 12;
--_year;
}
_day += GetMonthDay(_year, _month);
}
return *this;
}
//日期 - 天数
Date Date::operator-(int day) const
{
Date ret(*this);
ret -= day;
return ret;
}
//日期 - 日期
int Date::operator-(const Date& d) const
{
int flag = 1; //方便后续计算正负
Date max = *this;
Date min = d;
if (*this < d)
{
min = *this;
max = d;
flag = -1; //计算正负
} //确保max是大的,min是小的
int n = 0;
while (min != max)
{
min++;
n++;
}//算出min和max之间绝对值差距
return n * flag; //如果d1大,结果为正,d2大结果为负
}
![[附源码]Python计算机毕业设计Django校园疫情防范管理系统](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/5d9b52770fd846928d3cdf89478dff5d.png)




![[附源码]计算机毕业设计Python的物品交换平台(程序+源码+LW文档)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/0debc74d2bec4a17ad5ee521cdd62c22.png)