文章目录
前言
Target Language Compiler(TLC)
C MEX S-Function模块
编写TLC文件
生成代码
Tips
分析和应用
总结
前言
见《开箱报告,Simulink Toolbox库模块使用指南(一)——powergui模块》
见《开箱报告,Simulink Toolbox库模块使用指南(二)——MATLAB Fuction模块》
见《开箱报告,Simulink Toolbox库模块使用指南(三)——Simscape 电路仿真模块》
见《开箱报告,Simulink Toolbox库模块使用指南(四)——S-Fuction模块》
见《开箱报告,Simulink Toolbox库模块使用指南(五)——S-Fuction模块(C MEX S-Function)》
Target Language Compiler(TLC)
目标语言编译器(Target Language Compiler)代码生成器的重要组成部分。Mathworks官方Help对该部分内容的说明如下所示。
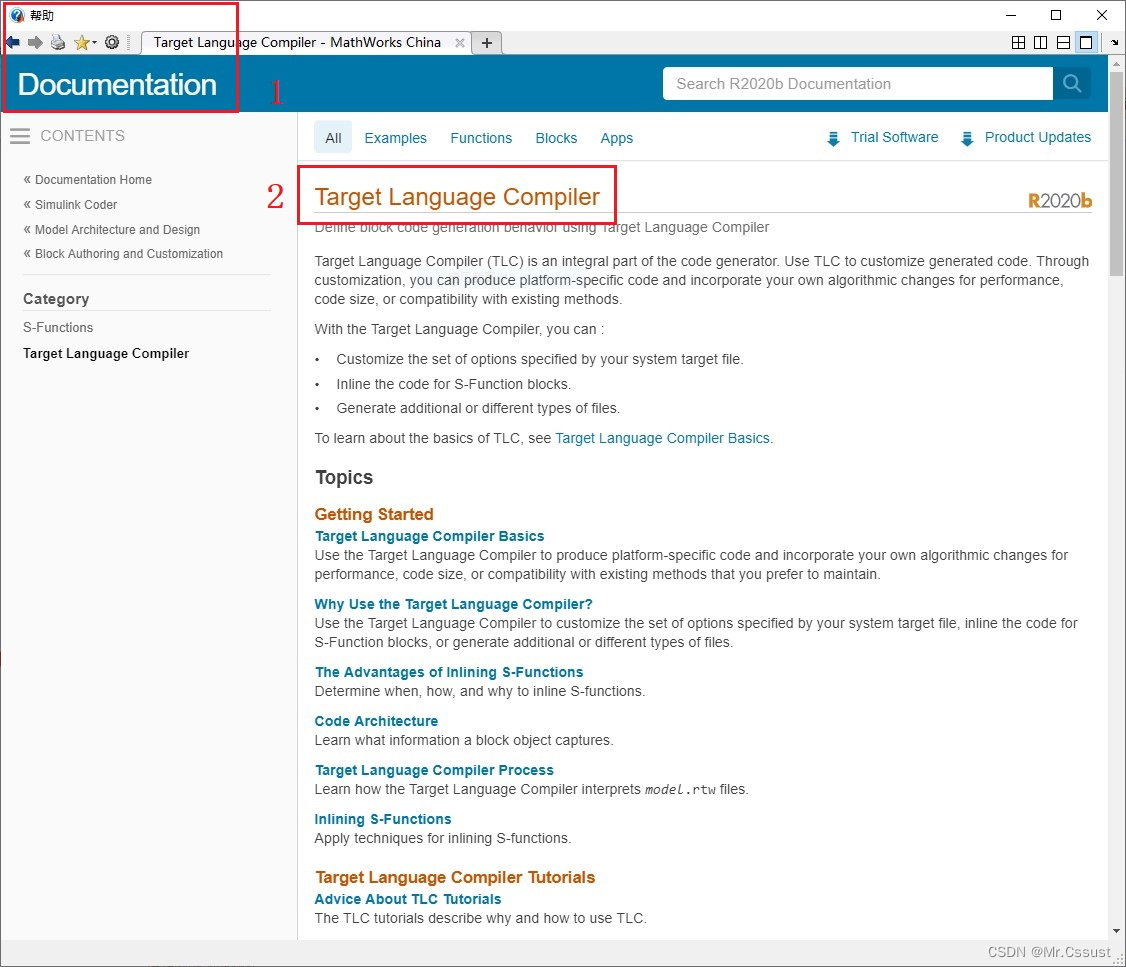
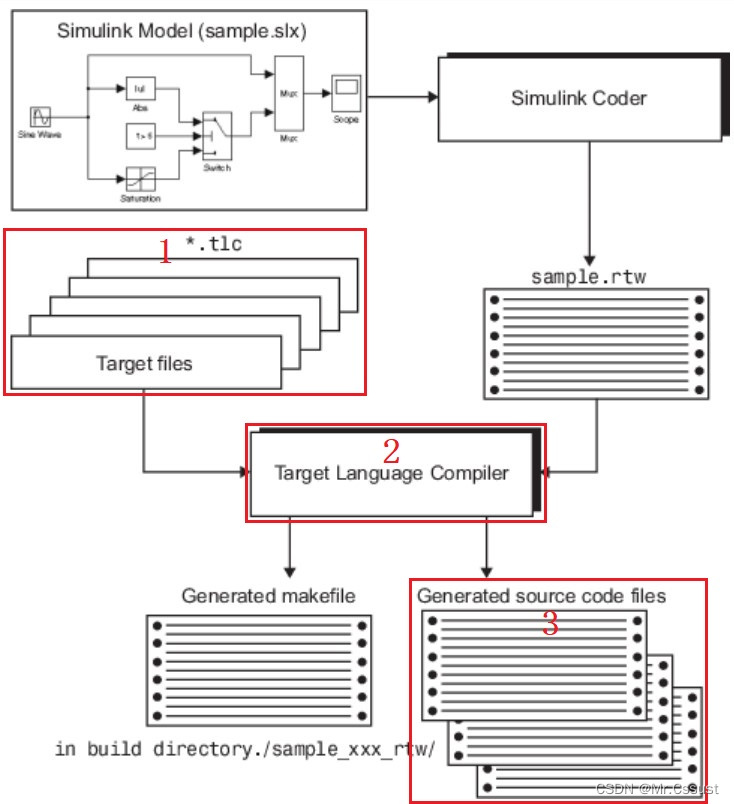
在使用Simulink自动生成代码时,Library中自带的模块可以顺利的生成代码,但是如果用户在Model中用到了自己开发的C MEX S-Function模块,Simulink就不知道这个模块如何生成代码了。TLC文件的作用就是,告诉Simulink自己想把C MEX S-Function模块生成一些什么样的代码,以及如何与Model中的其他内容互联融合。TLC及模型代码的生成过程如下图所示:
本文继续以DFT算法为例,介绍如何编写一个TLC文件,将C MEX S-Function模块生成代码。
C MEX S-Function模块
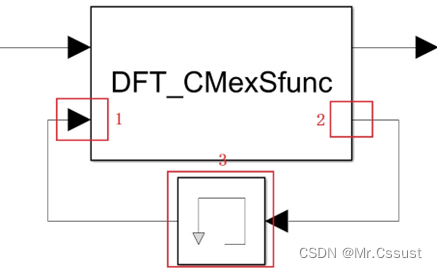
DFT算法的原理讲解和C MEX S-Function模块的开发在上一篇文章中已经完成了,见 《开箱报告,Simulink Toolbox库模块使用指南(五)——S-Fuction模块(C MEX S-Function)》。到这里仅仅是在Simulink中仿真时可以使用这样一个算法模块,本文是要把他生成C代码。由于算法中涉及了4个状态变量,对应到C语言中就要定义一组全局变量,这在TLC文件中实现会稍微麻烦一些。为了简化该过程,让大家更好地理解TLC,笔者对原有的C MEX S-Function模块进行了一些调整,将全局变量的定义放到了模块外面。如下图所示:
DFT_CMexSfunc.c中对应代码的调整如下:
//增加一个输入端口
if (!ssSetNumInputPorts(S, 2)) return;
ssSetInputPortWidth(S, 0, 1);
ssSetInputPortWidth(S, 1, 4); //新增的输入端口有4个信号
//增加一个输出端口
if (!ssSetNumOutputPorts(S, 2)) return;
ssSetOutputPortWidth(S, 0, 1);
ssSetOutputPortWidth(S, 1, 4); //新增的输处端口有4个信号
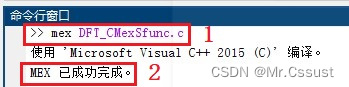
DFT_CMexSfunc.c调整后需要用mex命令重新编译,如下图所示:
编写TLC文件
在Model的Workspace文件夹下,新建一个DFT_CMexSfunc.tlc文件,编写tlc代码。写好后的完整内容如下,各部分代码的解释,以注释形式标注在对应位置。
%implements "DFT_CMexSfunc" "C"//与C MEX S-Function模块相对应
%% Function: Outputs
%function Outputs(block, system) Output//定义一个输出函数
%assign u = LibBlockInputSignal(0,"","",0)//获取输入信号
%assign u_count = LibBlockInputSignal(1,"","",0)
%assign u_t = LibBlockInputSignal(1,"","",1)
%assign u_cos_integ = LibBlockInputSignal(1,"","",2)
%assign u_sin_integ = LibBlockInputSignal(1,"","",3)
%assign y = LibBlockOutputSignal(0,"","",0) //获取输出信号
%assign y_count = LibBlockOutputSignal(1,"","",0)
%assign y_t = LibBlockOutputSignal(1,"","",1)
%assign y_cos_integ = LibBlockOutputSignal(1,"","",2)
%assign y_sin_integ = LibBlockOutputSignal(1,"","",3)
/%下面是要为C MEX S-Function模块生成的代码%/
if(%<u_count> < 5e3)//为了降低TLC复杂度,将常量L的值5e3直接写出来
{
%<y_cos_integ> = %<u_cos_integ> + %<u>*cos(2*3.14 * 50*%<u_t>);//将常量Freq的值50直接写出来
%<y_sin_integ> = %<u_sin_integ> + %<u>*sin(2*3.14 * 50*%<u_t>);
%<y_t> = %<u_t> + 1/10e3; //将常量Fs的值10e3直接写出来
%<y_count> = %<u_count> + 1;
}
else if(%<u_count> == 5e3)
{
%<y> = sqrt((%<u_cos_integ>/L*2)^2 + (%<u_sin_integ>/L*2)^2); //将过程变量real和imag用对应公式直接写出来
%<y_count> = %<u_count> + 1;//避免无效运行消耗资源
}
else
{}
%endfunction//结束函数定义
DFT_CMexSfunc.tlc文件保存在对应的路径下即可,不需要做额外的编译操作。
生成代码
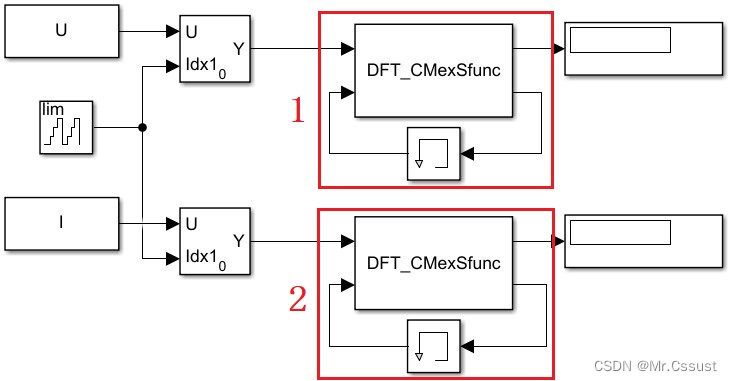
C MEX S-Function模块调整后对应的完整模型如下:
点击代码生成按钮 ,可以看到如下过程提示:
,可以看到如下过程提示:
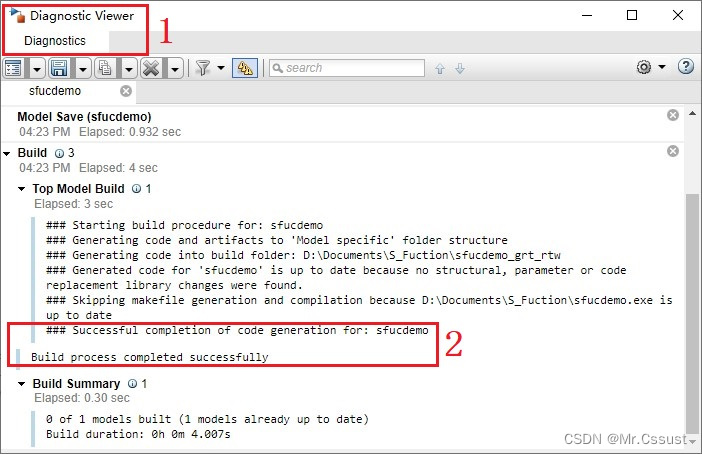
点击打开报告按钮 ,可以看到如下生成报告:
,可以看到如下生成报告:
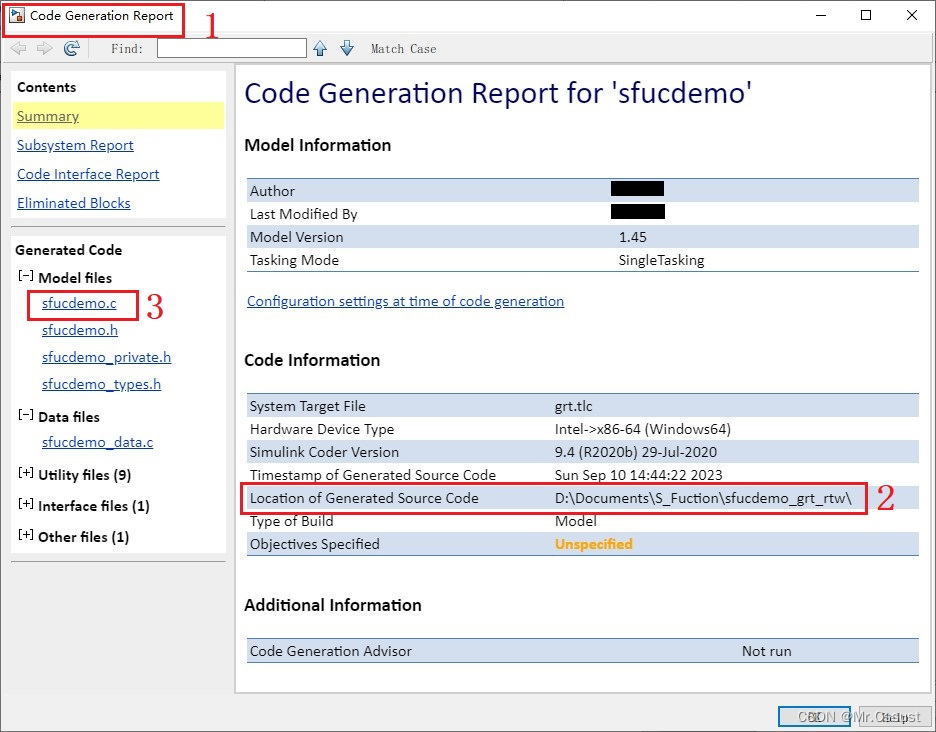
点击左侧的sfucdemo.c超链接,可以看到如下生成的代码,其中30行到140行是该模型主要功能的代码,40行到53行是与我们C MEX S-Function模块直接相关的代码。
File: sfucdemo.c
1 /*
2 * sfucdemo.c
3 *
4 * Code generation for model "sfucdemo".
5 *
6 * Model version : 1.45
7 * Simulink Coder version : 9.4 (R2020b) 29-Jul-2020
8 * C source code generated on : Sun Sep 10 14:44:22 2023
9 *
10 * Target selection: grt.tlc
11 * Note: GRT includes extra infrastructure and instrumentation for prototyping
12 * Embedded hardware selection: Intel->x86-64 (Windows64)
13 * Code generation objectives: Unspecified
14 * Validation result: Not run
15 */
16
17 #include "sfucdemo.h"
18 #include "sfucdemo_private.h"
19
20 /* Block signals (default storage) */
21 B_sfucdemo_T sfucdemo_B;
22
23 /* Block states (default storage) */
24 DW_sfucdemo_T sfucdemo_DW;
25
26 /* Real-time model */
27 static RT_MODEL_sfucdemo_T sfucdemo_M_;
28 RT_MODEL_sfucdemo_T *const sfucdemo_M = &sfucdemo_M_;
29
30 /* Model step function */
31 void sfucdemo_step(void)
32 {
33 /* Selector: '<Root>/Selector2' incorporates:
34 * Constant: '<Root>/Constant2'
35 * UnitDelay: '<S1>/Output'
36 */
37 sfucdemo_B.Selector2 =
38 sfucdemo_ConstP.Constant2_Value[sfucdemo_DW.Output_DSTATE];
39
40 /* S-Function (DFT_CMexSfunc): '<Root>/S-Function3' */
41 if (sfucdemo_B.Memory[0] < 5e3) {
42 sfucdemo_B.SFunction3_o2[2] = sfucdemo_B.Memory[2] + sfucdemo_B.Selector2*
43 cos(2*3.14 * 50*sfucdemo_B.Memory[1]);
44 sfucdemo_B.SFunction3_o2[3] = sfucdemo_B.Memory[3] + sfucdemo_B.Selector2*
45 sin(2*3.14 * 50*sfucdemo_B.Memory[1]);
46 sfucdemo_B.SFunction3_o2[1] = sfucdemo_B.Memory[1] + 1/10e3;
47 sfucdemo_B.SFunction3_o2[0] = sfucdemo_B.Memory[0] + 1;
48 } else if (sfucdemo_B.Memory[0] == 5e3) {
49 sfucdemo_B.SFunction3_o1 = sqrt((sfucdemo_B.Memory[2]/L*2)^2 +
50 (sfucdemo_B.Memory[3]/L*2)^2);
51 sfucdemo_B.SFunction3_o2[0] = sfucdemo_B.Memory[0] + 1;
52 } else {
53 }
54
55 /* Selector: '<Root>/Selector3' incorporates:
56 * Constant: '<Root>/Constant3'
57 * UnitDelay: '<S1>/Output'
58 */
59 sfucdemo_B.Selector3 =
60 sfucdemo_ConstP.Constant3_Value[sfucdemo_DW.Output_DSTATE];
61
62 /* S-Function (DFT_CMexSfunc): '<Root>/S-Function4' */
63 if (sfucdemo_B.Memory1[0] < 5e3) {
64 sfucdemo_B.SFunction4_o2[2] = sfucdemo_B.Memory1[2] + sfucdemo_B.Selector3*
65 cos(2*3.14 * 50*sfucdemo_B.Memory1[1]);
66 sfucdemo_B.SFunction4_o2[3] = sfucdemo_B.Memory1[3] + sfucdemo_B.Selector3*
67 sin(2*3.14 * 50*sfucdemo_B.Memory1[1]);
68 sfucdemo_B.SFunction4_o2[1] = sfucdemo_B.Memory1[1] + 1/10e3;
69 sfucdemo_B.SFunction4_o2[0] = sfucdemo_B.Memory1[0] + 1;
70 } else if (sfucdemo_B.Memory1[0] == 5e3) {
71 sfucdemo_B.SFunction4_o1 = sqrt((sfucdemo_B.Memory1[2]/L*2)^2 +
72 (sfucdemo_B.Memory1[3]/L*2)^2);
73 sfucdemo_B.SFunction4_o2[0] = sfucdemo_B.Memory1[0] + 1;
74 } else {
75 }
76
77 /* Switch: '<S3>/FixPt Switch' incorporates:
78 * Constant: '<S2>/FixPt Constant'
79 * Sum: '<S2>/FixPt Sum1'
80 * UnitDelay: '<S1>/Output'
81 */
82 if ((uint16_T)(sfucdemo_DW.Output_DSTATE + 1U) > 4999) {
83 /* Update for UnitDelay: '<S1>/Output' incorporates:
84 * Constant: '<S3>/Constant'
85 */
86 sfucdemo_DW.Output_DSTATE = 0U;
87 } else {
88 /* Update for UnitDelay: '<S1>/Output' */
89 sfucdemo_DW.Output_DSTATE++;
90 }
91
92 /* End of Switch: '<S3>/FixPt Switch' */
93
94 /* Memory: '<Root>/Memory' */
95 sfucdemo_B.Memory[0] = sfucdemo_DW.Memory_PreviousInput[0];
96
97 /* Memory: '<Root>/Memory1' */
98 sfucdemo_B.Memory1[0] = sfucdemo_DW.Memory1_PreviousInput[0];
99
100 /* Update for Memory: '<Root>/Memory' */
101 sfucdemo_DW.Memory_PreviousInput[0] = sfucdemo_B.SFunction3_o2[0];
102
103 /* Update for Memory: '<Root>/Memory1' */
104 sfucdemo_DW.Memory1_PreviousInput[0] = sfucdemo_B.SFunction4_o2[0];
105
106 /* Memory: '<Root>/Memory' */
107 sfucdemo_B.Memory[1] = sfucdemo_DW.Memory_PreviousInput[1];
108
109 /* Memory: '<Root>/Memory1' */
110 sfucdemo_B.Memory1[1] = sfucdemo_DW.Memory1_PreviousInput[1];
111
112 /* Update for Memory: '<Root>/Memory' */
113 sfucdemo_DW.Memory_PreviousInput[1] = sfucdemo_B.SFunction3_o2[1];
114
115 /* Update for Memory: '<Root>/Memory1' */
116 sfucdemo_DW.Memory1_PreviousInput[1] = sfucdemo_B.SFunction4_o2[1];
117
118 /* Memory: '<Root>/Memory' */
119 sfucdemo_B.Memory[2] = sfucdemo_DW.Memory_PreviousInput[2];
120
121 /* Memory: '<Root>/Memory1' */
122 sfucdemo_B.Memory1[2] = sfucdemo_DW.Memory1_PreviousInput[2];
123
124 /* Update for Memory: '<Root>/Memory' */
125 sfucdemo_DW.Memory_PreviousInput[2] = sfucdemo_B.SFunction3_o2[2];
126
127 /* Update for Memory: '<Root>/Memory1' */
128 sfucdemo_DW.Memory1_PreviousInput[2] = sfucdemo_B.SFunction4_o2[2];
129
130 /* Memory: '<Root>/Memory' */
131 sfucdemo_B.Memory[3] = sfucdemo_DW.Memory_PreviousInput[3];
132
133 /* Memory: '<Root>/Memory1' */
134 sfucdemo_B.Memory1[3] = sfucdemo_DW.Memory1_PreviousInput[3];
135
136 /* Update for Memory: '<Root>/Memory' */
137 sfucdemo_DW.Memory_PreviousInput[3] = sfucdemo_B.SFunction3_o2[3];
138
139 /* Update for Memory: '<Root>/Memory1' */
140 sfucdemo_DW.Memory1_PreviousInput[3] = sfucdemo_B.SFunction4_o2[3];
141
142 /* Matfile logging */
143 rt_UpdateTXYLogVars(sfucdemo_M->rtwLogInfo, (&sfucdemo_M->Timing.taskTime0));
144
145 /* signal main to stop simulation */
146 { /* Sample time: [0.001s, 0.0s] */
147 if ((rtmGetTFinal(sfucdemo_M)!=-1) &&
148 !((rtmGetTFinal(sfucdemo_M)-sfucdemo_M->Timing.taskTime0) >
149 sfucdemo_M->Timing.taskTime0 * (DBL_EPSILON))) {
150 rtmSetErrorStatus(sfucdemo_M, "Simulation finished");
151 }
152 }
153
154 /* Update absolute time for base rate */
155 /* The "clockTick0" counts the number of times the code of this task has
156 * been executed. The absolute time is the multiplication of "clockTick0"
157 * and "Timing.stepSize0". Size of "clockTick0" ensures timer will not
158 * overflow during the application lifespan selected.
159 * Timer of this task consists of two 32 bit unsigned integers.
160 * The two integers represent the low bits Timing.clockTick0 and the high bits
161 * Timing.clockTickH0. When the low bit overflows to 0, the high bits increment.
162 */
163 if (!(++sfucdemo_M->Timing.clockTick0)) {
164 ++sfucdemo_M->Timing.clockTickH0;
165 }
166
167 sfucdemo_M->Timing.taskTime0 = sfucdemo_M->Timing.clockTick0 *
168 sfucdemo_M->Timing.stepSize0 + sfucdemo_M->Timing.clockTickH0 *
169 sfucdemo_M->Timing.stepSize0 * 4294967296.0;
170 }
171
172 /* Model initialize function */
173 void sfucdemo_initialize(void)
174 {
175 /* Registration code */
176
177 /* initialize non-finites */
178 rt_InitInfAndNaN(sizeof(real_T));
179
180 /* initialize real-time model */
181 (void) memset((void *)sfucdemo_M, 0,
182 sizeof(RT_MODEL_sfucdemo_T));
183 rtmSetTFinal(sfucdemo_M, 10.0);
184 sfucdemo_M->Timing.stepSize0 = 0.001;
185
186 /* Setup for data logging */
187 {
188 static RTWLogInfo rt_DataLoggingInfo;
189 rt_DataLoggingInfo.loggingInterval = NULL;
190 sfucdemo_M->rtwLogInfo = &rt_DataLoggingInfo;
191 }
192
193 /* Setup for data logging */
194 {
195 rtliSetLogXSignalInfo(sfucdemo_M->rtwLogInfo, (NULL));
196 rtliSetLogXSignalPtrs(sfucdemo_M->rtwLogInfo, (NULL));
197 rtliSetLogT(sfucdemo_M->rtwLogInfo, "tout");
198 rtliSetLogX(sfucdemo_M->rtwLogInfo, "");
199 rtliSetLogXFinal(sfucdemo_M->rtwLogInfo, "");
200 rtliSetLogVarNameModifier(sfucdemo_M->rtwLogInfo, "rt_");
201 rtliSetLogFormat(sfucdemo_M->rtwLogInfo, 0);
202 rtliSetLogMaxRows(sfucdemo_M->rtwLogInfo, 0);
203 rtliSetLogDecimation(sfucdemo_M->rtwLogInfo, 1);
204 rtliSetLogY(sfucdemo_M->rtwLogInfo, "");
205 rtliSetLogYSignalInfo(sfucdemo_M->rtwLogInfo, (NULL));
206 rtliSetLogYSignalPtrs(sfucdemo_M->rtwLogInfo, (NULL));
207 }
208
209 /* block I/O */
210 (void) memset(((void *) &sfucdemo_B), 0,
211 sizeof(B_sfucdemo_T));
212
213 /* states (dwork) */
214 (void) memset((void *)&sfucdemo_DW, 0,
215 sizeof(DW_sfucdemo_T));
216
217 /* Matfile logging */
218 rt_StartDataLoggingWithStartTime(sfucdemo_M->rtwLogInfo, 0.0, rtmGetTFinal
219 (sfucdemo_M), sfucdemo_M->Timing.stepSize0, (&rtmGetErrorStatus(sfucdemo_M)));
220
221 /* InitializeConditions for UnitDelay: '<S1>/Output' */
222 sfucdemo_DW.Output_DSTATE = 0U;
223
224 /* InitializeConditions for Memory: '<Root>/Memory' */
225 sfucdemo_DW.Memory_PreviousInput[0] = 0.0;
226
227 /* InitializeConditions for Memory: '<Root>/Memory1' */
228 sfucdemo_DW.Memory1_PreviousInput[0] = 0.0;
229
230 /* InitializeConditions for Memory: '<Root>/Memory' */
231 sfucdemo_DW.Memory_PreviousInput[1] = 0.0;
232
233 /* InitializeConditions for Memory: '<Root>/Memory1' */
234 sfucdemo_DW.Memory1_PreviousInput[1] = 0.0;
235
236 /* InitializeConditions for Memory: '<Root>/Memory' */
237 sfucdemo_DW.Memory_PreviousInput[2] = 0.0;
238
239 /* InitializeConditions for Memory: '<Root>/Memory1' */
240 sfucdemo_DW.Memory1_PreviousInput[2] = 0.0;
241
242 /* InitializeConditions for Memory: '<Root>/Memory' */
243 sfucdemo_DW.Memory_PreviousInput[3] = 0.0;
244
245 /* InitializeConditions for Memory: '<Root>/Memory1' */
246 sfucdemo_DW.Memory1_PreviousInput[3] = 0.0;
247 }
248
249 /* Model terminate function */
250 void sfucdemo_terminate(void)
251 {
252 /* (no terminate code required) */
253 }
254
人工检查上述自动生成的C代码,可以实现该Simulink模型设计的功能。
至此,可以证明该TLC文件可以较好地生成C MEX S-Fuction模块的自动代码。
Tips
TLC的特殊性在于,它本身是一种编程语言,具有文本类编程语言的大部分特点,同时它要实现的功能又是控制C或C++另一种文本语言代码的生成,所以TLC的开发必须熟练掌握它特有的语法结构,常见的一些基础语法如下。
1、%,TLC指令开始的标志符。
2、%implements,一个模块的TLC文件要执行的第一条指令,不可省略。
3、%function,声明一个函数,要配合%endfunction使用。
4、%assign,创建变量。
5、函数LibBlockInputSignal(portIdx, "","",sigIdx),返回模块的输入信号,portIdx和sigIdx都从0开始计数。
6、函数LibBlockOutputSignal(portIdx, "","",sigIdx),返回模块的输出信号。
7、函数LibBlockParameterValue(param, elIdx),返回模块的参数值。
8、<>,TLC表达式的开始和结束。
9、%%和/% %/,注释。
分析和应用
本文上述内容中看到,TLC实现了C MEX S-Fuction模块的代码生成,但是进一步仔细研究发现,Library中自带的模块的代码生成也是由TLC实现的,甚至生成代码的总体结构也是由TLC实现的,这些模块的TLC文件就存放在Matlab的系统路径ProgramFiles\Matlab2020b\rtw\c\tlc下。
所以说Simulink的自动代码生成过程,并不是完全固定死的,当我们有特定需求时,可以通过调整TLC文件的内容来实现的。这样就给了代码开发工程师们在代码生成方面的灵活度和自由度,为Simulink的自动代码生成提供了无限可能。
总结
以上就是本人在使用TLC时,一些个人理解和分析的总结,首先介绍了TLC的背景知识,然后展示它的使用方法,最后分析了该模块的特点和适用场景。
后续还会分享另外几个最近总结的Simulink Toolbox库模块,欢迎评论区留言、点赞、收藏和关注,这些鼓励和支持都将成文本人持续分享的动力。
另外,上述例程使用的Demo工程,可以到笔者的主页查找和下载。
版权声明,原创文章,转载和引用请注明出处和链接,侵权必究!