一、说明
Python是唯一有习语(idioms)的语言。这增强了它的可读性,也许还有它的美感。装饰师遵循Python的禅宗,又名“Pythonic”方式。装饰器从 Python 2.2 开始可用。PEP318增强了它们。下面是一个以初学者为中心的教程,介绍如何使用装饰器。如果您希望自己运行代码示例,请继续阅读!
二、装饰
A(不要与装饰器模式混淆)是一种在不更改原始函数的情况下添加/更改函数行为的方法。在 Python 中,装饰器是一种设计模式,允许您通过将函数包装在另一个函数中来修改函数的功能。外部函数称为装饰器,它将原始函数作为参数并返回修改后的版本。decorator
让我们以身作则。在这里,我们声明一个装饰器。它有助于打印函数的输出,而不是添加打印命令,打印命令后来变得笨拙,有时删除起来非常乏味。debug
def debug(function):
def wrapper(name, address):
print ('Debugging:')
func = function(name, address)
print (func)
return wrapper
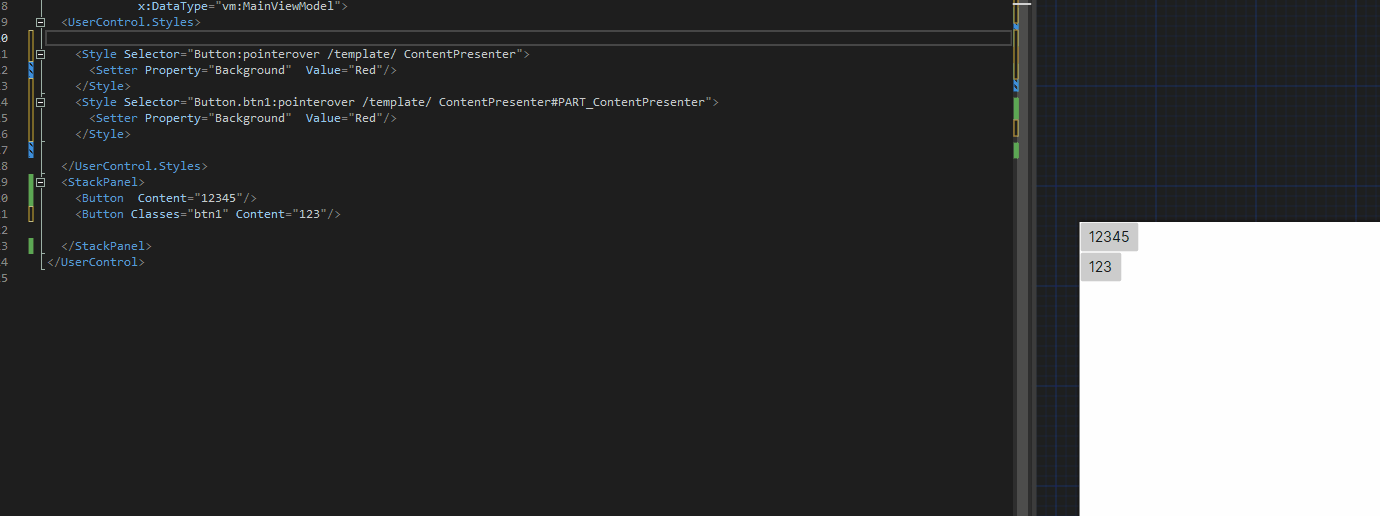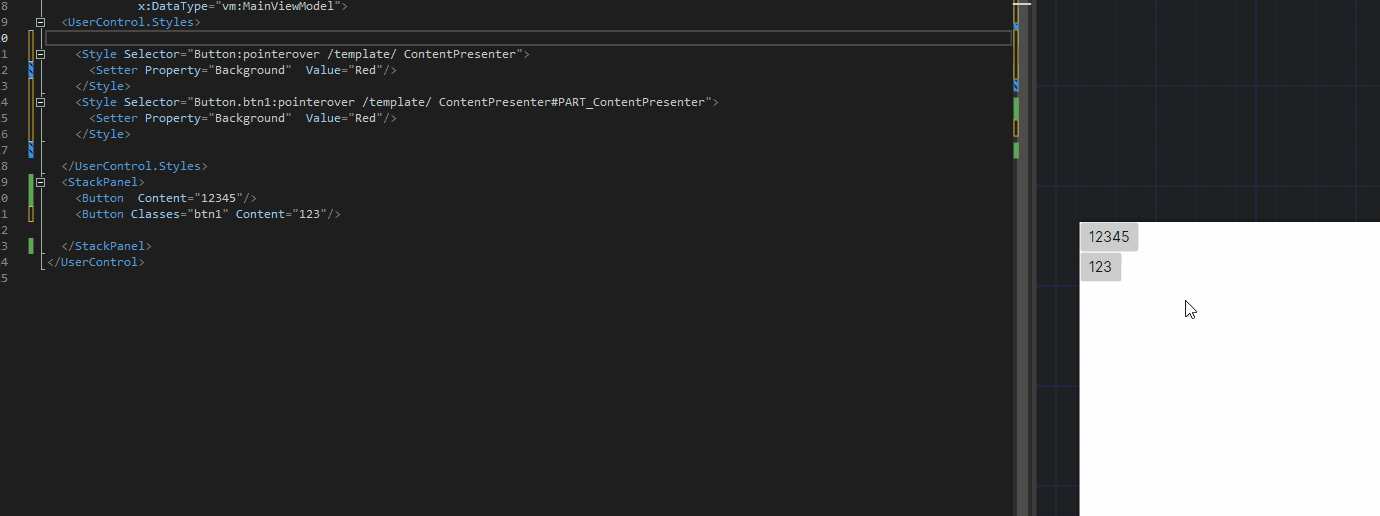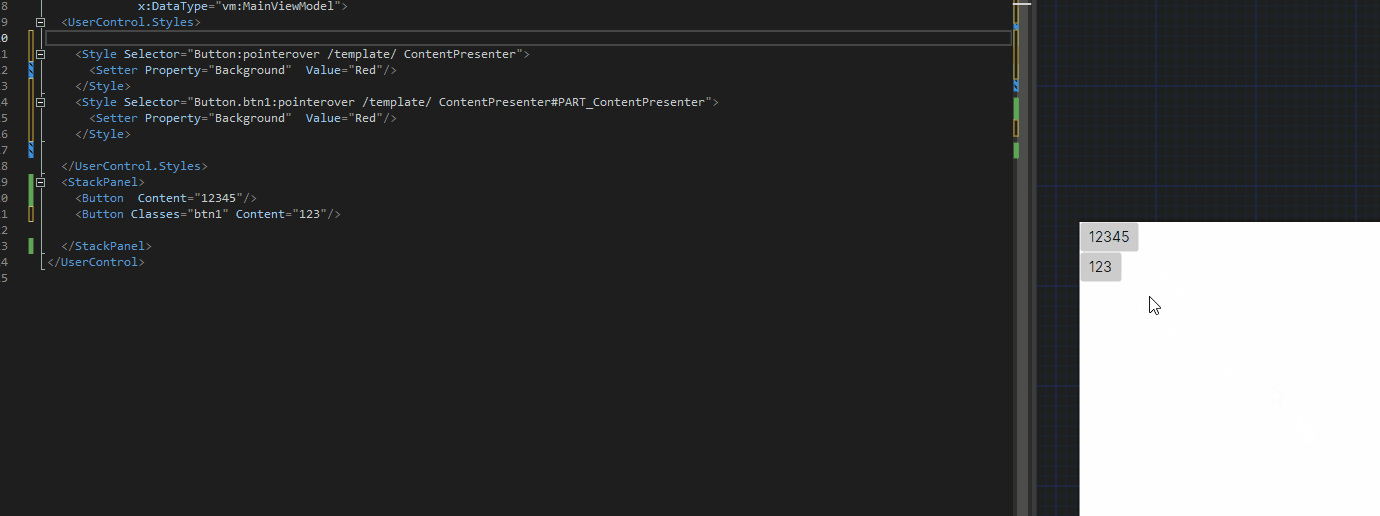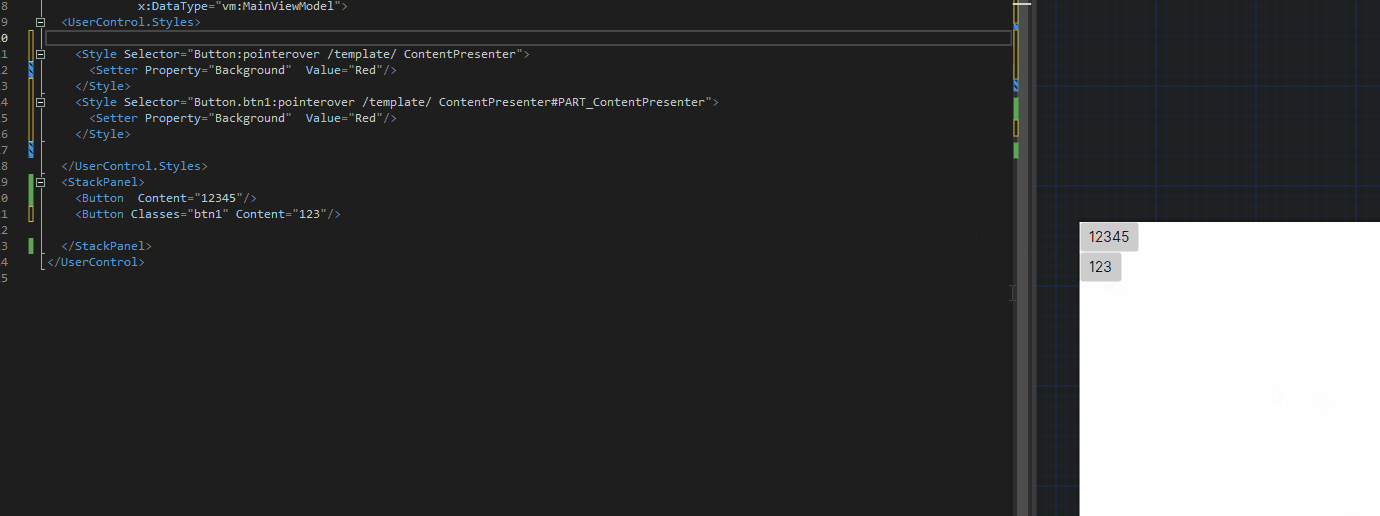
@debug
def typical_crunching_function(name, city):
return 'You are '+ name + ' from '+ city
typical_crunching_function('John','Los Angeles')输出:
Debugging:
You are John from Los Angeles 在这里,我们定义了装饰器,并使用@语法应用于函数。line 1-6typical_crunching_function line 8
三、Python 类装饰器
类装饰器于 PEP3129 年引入。这是在社区的很多阻力之后,他们更喜欢.主要目的是将装饰函数的能力扩展到类。metaclasses
下面是一个增强函数功能的类装饰器示例。
class Accolade:
def __init__(self, function):
self.function = function
def __call__ (self, name):
# Adding Excellency before name
name = "Excellency " + name
self.function(name)
# Saluting after the name
print("Thanks "+ name+ " for gracing the occasion")
@Accolade
def simple_function(name):
print (name)
simple_function('John McKinsey')输出:
Excellency John McKinsey
Thanks Excellency John McKinsey for gracing the occasion 这里定义了类,可用于对simple_function执行预处理和后处理。在此示例中,我们只是添加到字符串中,并在打印名称后,感谢他们为这个场合增光添彩。这个简单的例子演示了我们可以使用类装饰器轻松地对函数参数执行预处理和后处理。这些预处理任务可以是以下任何一项,但不限于这些。CleanerExcellencyname,
- 添加计时信息
- 连接到数据库
- 关闭连接
- 记忆存储
示例2:
class Decorator(object):
def __init__(self, fget=None, fset=None, fdel=None, doc=None):
self.fget = fget
self.fset = fset
self.fdel = fdel
self.__doc__ = doc
def __get__(self, instance, owner):
if instance is None:
return self
return self.fget(instance)
def __set__(self, instance, value):
self.fset(instance, value)
def __delete__(self, instance):
self.fdel(instance)
def getter(self, fget):
return Decorator(fget, self.fset, self.fdel, self.__doc__)
def setter(self, fset):
return Decorator(self.fget, fset, self.fdel, self.__doc__)
def deleter(self, fdel):
return Decorator(self.fget, self.fset, fdel, self.__doc__)
class Target(object):
desc = "Amazing pyhton"
def __init__(self, attr=5):
self._x = attr
@Decorator
def show(self):
return self._x
@show.setter
def show(self, value):
self._x = value
@show.deleter
def show(self):
del self._x
四、一些内置的类装饰器
下面是一些内置的类装饰器。
4.1 缓存/记忆
请注意,它仅在Python >= 3.9中可用。这允许缓存以前的值并重用它们,而不是重新计算它们。
from functools import cache
@cache
def factorial(n):
return n * factorial(n-1) if n else 1
print(factorial(10))输出:
36288004.2 属性property
property的意义
@property把一个类的getter方法变成属性,如果还有setter方法,就在setter方法前面加上@method.setter。使用类属性=property(getx,setx,delx,desc)也是可以的。
实现很简单,那么它背后的原理是什么呢?
Property类的伪代码如下,里面涉及了__get__、__set__、__delete__魔法方法。Decorator类是装饰器类,Target是目标类。当你设置装饰器类的实例对象为目标类的x属性后,当试图访问目标类的x属性会触发装饰器类的__get__方法;当为目标类的x属性赋值时,会触发装饰器类的__setter__方法;尝试删除目标类的x属性时,会触发装饰器类的__delete__方法。当访问Target.x.__doc__,可以打印出装饰器类的描述文档。事实上这种装饰器类也被称为描述符类。描述符类就是将一个特殊类的实例指派给一个类的属性。
类属性实现方式:
示例1:
这个装饰器允许将 setter 和 getter 函数添加到类中的属性。
class Pencil:
def __init__(self, count):
self._counter=count
@property
def counter(self):
return self._counter
@counter.setter
def counter(self, count):
self._counter = count
@counter.getter
def counter(self):
return self._counter
HB = Pencil(100)
print (HB.counter)
HB.counter = 20
print (HB.counter)输出:
100
20 示例2:
class Decorator(object):
def __init__(self, fget=None, fset=None, fdel=None, doc=None):
self.fget = fget
self.fset = fset
self.fdel = fdel
self.__doc__ = doc
def __get__(self, instance, owner):
if instance is None:
return self
return self.fget(instance)
def __set__(self, instance, value):
self.fset(instance, value)
def __delete__(self, instance):
self.fdel(instance)
def getter(self, fget):
return Decorator(fget, self.fset, self.fdel, self.__doc__)
def setter(self, fset):
return Decorator(self.fget, fset, self.fdel, self.__doc__)
def deleter(self, fdel):
return Decorator(self.fget, self.fset, fdel, self.__doc__)
class Target(object):
desc = "Amazing pyhton"
def __init__(self, attr=5):
self._x = attr
def getx(self):
return self._x
def setx(self, value):
self._x = value
def delx(self):
del self._x
x = Decorator(getx,setx,delx,desc)
4.3 缓存属性cached_property
此修饰器允许缓存类的属性。这等于嵌套两个装饰器。
@cached
@property
def counter:
return self._counter五、结论
装饰器是非常方便和优雅的工具,但是,它们也很容易出错。因此,应非常小心地使用它们。查看下面的课程,获得 Python 装饰器的实践经验! 教育团队



![[学习笔记]DeepWalk图神经网络论文精读](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/95ff673399934b85b341c704794d8e45.png)