使用管道时,一个进程的输出可成为另外一个进程的输入。
命名管道(Named pipe或FIFO)是一种类似于管道的特殊文件,但在文件系统上有一个名称,它允许以先进先出(FIFO, first in, first out)的方式存储有限数量的数据。它的使用类似于消息传递,其中一个进程发送一条信息,其它进程接收它。数据以FIFO方式以高吞吐速度进入管道。但是,队列一次可以容纳的最大数据大小为16页(pages)或65536字节。它实际上使用了一块内核内存。
命名管道是在文件系统中作为一个特殊的设备文件而存在。不同祖先的进程之间可以通过命名管道共享数据。当共享命名管道的进程执行完所有的I/O操作以后,命名管道将继续保存在文件系统中,以便以后使用,除非调用unlink。通过命名管道,不相关的进程也能交换数据。一旦已经用mkfifo函数创建了一个FIFO,就可用open打开它。实际上,一般的文件I/O函数(close、read、write、unlink等)都可用于FIFO。
只要FIFO有空间,write函数就是非阻塞的,但read会阻塞当前线程。
命名管道总结:
(1).同步(用于单向管道);
(2).队列大小为16页(page),每页4096字节。只要数据消耗足够快,数据大小就没有限制;
(3).单个管道的单向通信;
(4).以线性方式读写;
(5).自动内存管理。
注:以上内容主要来自网络整理。
如果父进程和子进程之间互相发送接收数据,需要两根管道,如以下测试代码:
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <error.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <cctype>
typedef struct message {
int pid;
char ch;
} message;
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
const char *named_pipe1 = "/tmp/named_pipe1", *named_pipe2 = "/tmp/named_pipe22";
unlink(named_pipe1); // deletes a name from the file system
unlink(named_pipe2);
if (mkfifo(named_pipe1, 0666) < 0 || mkfifo(named_pipe2, 0666) < 0) { // make a FIFO special file(a named pipe), if the file exists, the call will fail
fprintf(stderr, "fail to mkfifo: %s\n", strerror(errno));
return -1;
}
struct stat buffer1, buffer2;
if (stat(named_pipe1, &buffer1) != 0 || stat(named_pipe1, &buffer2) != 0) { // retrieve information about the file pointed to by pathname
fprintf(stderr, "fail to stat: %s\n", strerror(errno));
return -1;
}
pid_t pid = fork();
if (pid < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "fail to fork\n");
return -1;
}
if (pid == 0) { // child process
auto fd1 = open(named_pipe1, O_RDONLY); // read only
auto fd2 = open(named_pipe2, O_WRONLY); // write only
if (fd1 < 0 || fd2 < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "fail to open: %d, %s\n", pid, strerror(errno));
exit(1);
}
for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i) {
message msg;
auto ret = read(fd1, &msg, sizeof(msg));
if (ret < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "fail to read: %d, %d %s\n", pid, i, strerror(errno));
exit(1);
}
msg.ch = std::toupper(msg.ch);
ret = write(fd2, &msg, sizeof(msg));
if (ret < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "fail to write: %d, %d, %s\n", pid, i, strerror(errno));
exit(1);
}
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(100));
}
close(fd1);
close(fd2);
exit(0);
}
if (pid > 0) { // parent process
auto fd1 = open(named_pipe1, O_WRONLY); // write only
auto fd2 = open(named_pipe2, O_RDONLY); // read only
if (fd1 < 0 || fd2 < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "fail to open: %d, %s\n", pid, strerror(errno));
exit(1);
}
for (unsigned char i = 0; i < 5; ++i) {
message msg = {pid, 'a'+i};
auto ret = write(fd1, &msg, sizeof(msg));
if (ret < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "fail to write: %d, %d, %s\n", pid, i, strerror(errno));
exit(1);
}
fprintf(stdout, "src char: %c\n", msg.ch);
ret = read(fd2, &msg, sizeof(msg));
if (ret < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "fail to read: %d, %d, %s\n", pid, i, strerror(errno));
exit(1);
}
fprintf(stdout, "dst char: %c\n", msg.ch);
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(100));
}
close(fd1);
close(fd2);
int status;
auto pid2 = wait(&status); // system call suspends execution of the calling thread until one of its children terminates
fprintf(stdout, "process ID of the terminated child: %d\n", pid2);
if (WIFEXITED(status)) { // returns true if the child terminated normally
fprintf(stdout, "child process ended with: exit(%d)\n", WEXITSTATUS(status));
}
if (WIFSIGNALED(status)) { // returns true if the child process was terminated by a signal
fprintf(stderr, "child process ended with: kill -%d\n", WTERMSIG(status));
}
}
unlink(named_pipe1); // deletes a name from the file system
unlink(named_pipe2);
fprintf(stdout, "====== test finish ======\n");
return 0;
}build.sh内容如下:
#! /bin/bash
if [ -d build ]; then
echo "build directory already exists, it does not need to be created again"
else
mkdir -p build
fi
cd build
cmake ..
make
rc=$?
if [[ ${rc} != 0 ]];then
echo "#### ERROR: please check ####"
exit ${rc}
fi
echo "==== build finish ===="CMakeLists.txt内容如下:
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.22)
project(samples_multi_process)
set(CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE Release) # only works under linux
set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "${CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS} -Wall -O2 -std=c++17")
file(GLOB samples ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/test_*.cpp)
#message(STATUS "samples: ${samples}")
foreach(sample ${samples})
string(REGEX MATCH "[^/]+$" name ${sample})
string(REPLACE ".cpp" "" exec_name ${name})
#message(STATUS "exec name: ${exec_name}")
add_executable(${exec_name} ${sample})
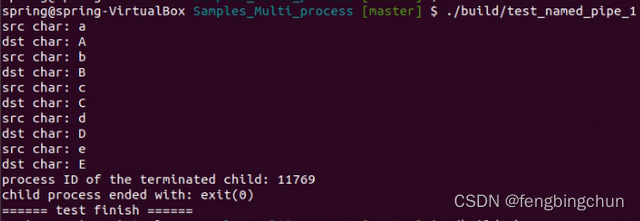
endforeach()执行结果如下图所示:
GitHub:https://github.com/fengbingchun/Linux_Code_Test