一、加载properties属性文件
目的:将数据库的连接参数抽取到一个单独的文件中,与Spring配置文件解耦
1. 编写jdbc.properties属性文件
jdbc.driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/spring_db
jdbc.username=root
jdbc.password=1234
2. 在applicationContext.xml中开启context命名空间
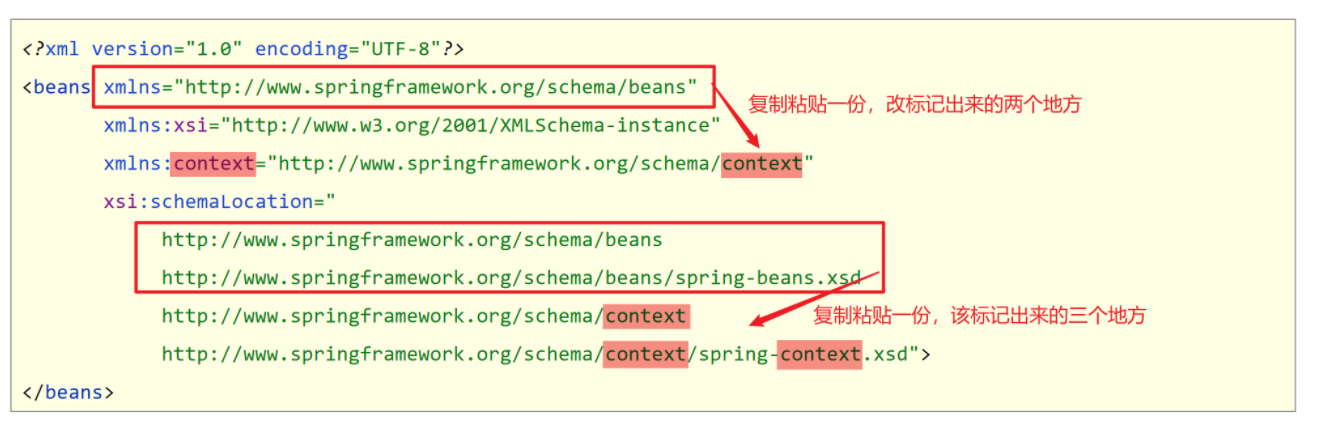
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
">
3. 加载jdbc.properties属性文件
<context:property-placeholder location="jdbc.properties"/>
4. 在配置连接池Bean的地方使用EL表达式获取jdbc.properties属性文件中的值
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driver}"></property>
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"></property>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>
</bean>
配置完成之后,运行之前的获取Druid连接池代码,可以获取到连接池对象就表示配置成功。
二、配置不加载系统属性
问题
如果属性文件中配置的不是jdbc.username,而是username=root666,那么使用${username}获取到的不是root666,而是计算机的名称。
原因
系统属性的优先级比我们属性文件中的高,替换了我们的username=root666。
解决
解决1:换一个名称,例如不叫username,叫jdbc.username。
解决2:使用system-properties-mode="NEVER"属性表示不使用系统属性。
<context:property-placeholder location="jdbc.properties" system-properties-mode="NEVER"/>
三、 加载properties文件写法
- 加载多个properties文件
<context:property-placeholder location="jdbc.properties,msg.properties"/>
- 加载所有properties文件
<context:property-placeholder location="*.properties"/>
- 加载properties文件**标准格式**
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:*.properties"/>
- 加载properties文件标准格式
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath*:*.properties"/>
ties文件标准格式
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath*:*.properties"/>


![【Spring]SpringMVC](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/25d9ee93503603196683ce9b9ae615a8.png)

![[附源码]计算机毕业设计Python-大学生健康档案管理(程序+源码+LW文档)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/12c6e7ff31674f48b067323ad24dc82c.png)