一、简介
JdbcTemplate是Spring提供的⼀个JDBC模板类,是对JDBC的封装,简化JDBC代码。 当然,你也可以不⽤,可以让Spring集成其它的ORM框架,例如:MyBatis、Hibernate等。
第一步:引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>6.0.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.13.2</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.30</version>
</dependency>
<!--新增的依赖:spring jdbc,这个依赖中有JdbcTemplate-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>6.0.2</version>
</dependency>二、整合JdbcTemplate
第二步:编写Spring配置⽂件
JdbcTemplate是Spring提供好的类,这类的完整类名是: org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate 我们怎么使⽤这个类呢?new对象就可以了。怎么new对象,Spring最在⾏了。直接将这个类配置到 Spring配置⽂件中,纳⼊Bean管理即可。
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate"></bean>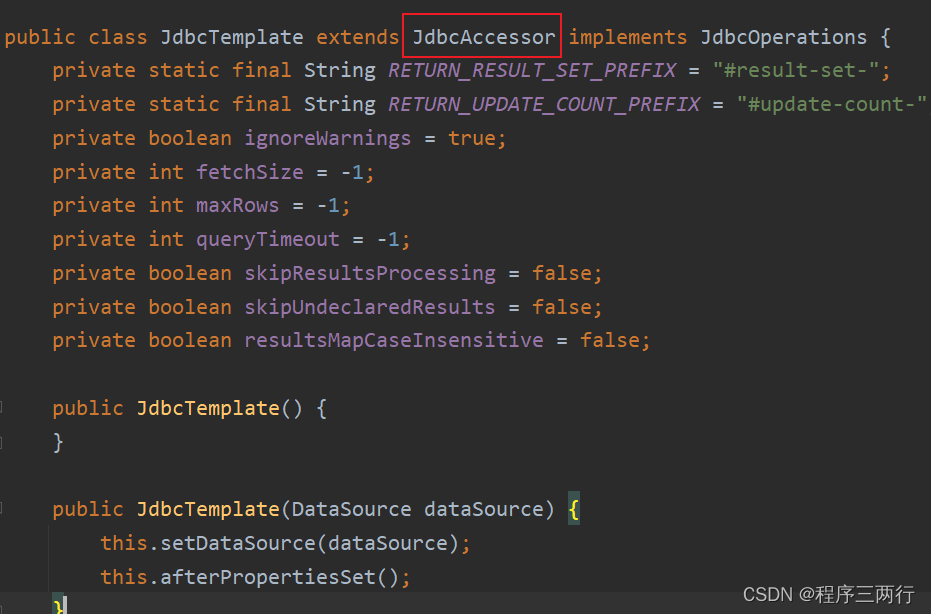
可以看到JdbcTemplate中有⼀个DataSource属性,这个属性是数据源,我们都知道连接数据库需要 Connection对象,⽽⽣成Connection对象是数据源负责的。
所以我们需要给JdbcTemplate设置数据源 属性。 所有的数据源都是要实现javax.sql.DataSource接⼝的。这个数据源可以⾃⼰写⼀个,也可以⽤写好的, ⽐如:阿⾥巴巴的德鲁伊连接池,c3p0,dbcp等。我们这⾥⾃⼰先⼿写⼀个数据源。
public class MyDataSource implements DataSource {
// 添加4个属性
private String driver;
private String url;
private String username;
private String password;
// 提供4个setter⽅法
public void setDriver(String driver) {
this.driver = driver;
}
public void setUrl(String url) {
this.url = url;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
// 重点写怎么获取Connection对象就⾏。其他⽅法不⽤管。
@Override
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
try {
Class.forName(driver);
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
return conn;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
@Override
public Connection getConnection(String username, String password) throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public PrintWriter getLogWriter() throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public void setLogWriter(PrintWriter out) throws SQLException {
}
@Override
public void setLoginTimeout(int seconds) throws SQLException {
}
@Override
public int getLoginTimeout() throws SQLException {
return 0;
}
@Override
public Logger getParentLogger() throws SQLFeatureNotSupportedException {
return null;
}
@Override
public <T> T unwrap(Class<T> iface) throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public boolean isWrapperFor(Class<?> iface) throws SQLException {
return false;
}
}写完数据源,我们需要把这个数据源传递给JdbcTemplate。因为JdbcTemplate中有⼀个DataSource属 性:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<bean id="myDataSource" class="com.springcode.example.entity.MyDataSource">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring6"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="root"/>
</bean>
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="myDataSource"/>
</bean>
</beans>三、增删改查
1、增加
public class SpringTest {
@Test
public void test(){
// 获取JdbcTemplate对象
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = applicationContext.getBean("jdbcTemplate", JdbcTemplate.class);
/*注意:insert delete update的sql语句,都是执⾏update⽅法。update⽅法有两个参数:
第⼀个参数:要执⾏的SQL语句。(SQL语句中可能会有占位符 ? )
第⼆个参数:可变⻓参数,参数的个数可以是0个,也可以是多个。⼀般是SQL语句中有⼏个问号,
则对应⼏个参数。*/
String sql = "insert into t_user(id,real_name,age) values(?,?,?)";
int count = jdbcTemplate.update(sql, null, "张三", 30);
System.out.println("插⼊的记录条数:" + count);
}
}2、修改
public class SpringTest {
@Test
public void test(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = applicationContext.getBean("jdbcTemplate", JdbcTemplate.class);
// 执⾏更新操作
String sql = "update t_user set real_name = ?, age = ? where id = ?";
int count = jdbcTemplate.update(sql, "张三丰", 55, 1);
System.out.println("更新的记录条数:" + count);
}
}3、删除
public class SpringTest {
@Test
public void test(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = applicationContext.getBean("jdbcTemplate", JdbcTemplate.class);
// 执⾏delete
String sql = "delete from t_user where id = ?";
int count = jdbcTemplate.update(sql, 1);
System.out.println("删除了⼏条记录:" + count);
}
}4、查询一个对象
public class SpringTest {
@Test
public void test(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = applicationContext.getBean("jdbcTemplate", JdbcTemplate.class);
// 执⾏select
String sql = "select id, real_name, age from t_user where id = ?";
/*
queryForObject⽅法三个参数:
第⼀个参数:sql语句
第⼆个参数:Bean属性值和数据库记录⾏的映射对象。在构造⽅法中指定映射的对象类型。
第三个参数:可变⻓参数,给sql语句的占位符问号传值。
*/
User user = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, new BeanPropertyRowMapper<>(User.class), 2);
System.out.println(user);
}
}5、查询多个对象
public class SpringTest {
@Test
public void test(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = applicationContext.getBean("jdbcTemplate", JdbcTemplate.class);
// 执⾏select
String sql = "select id, real_name, age from t_user";
List<User> users = jdbcTemplate.query(sql, new BeanPropertyRowMapper<>(User.class));
System.out.println(users);
}
}6、查询⼀个值
public class SpringTest {
@Test
public void test(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = applicationContext.getBean("jdbcTemplate", JdbcTemplate.class);
// 执⾏select
String sql = "select count(1) from t_user";
Integer count = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, int.class); // 这⾥⽤Integer.class也可以
System.out.println("总记录条数:" + count);
}
}7、批量添加
public class SpringTest {
@Test
public void test(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = applicationContext.getBean("jdbcTemplate", JdbcTemplate.class);
// 批量添加
String sql = "insert into t_user(id,real_name,age) values(?,?,?)";
Object[] objs1 = {null, "⼩花", 20};
Object[] objs2 = {null, "⼩明", 21};
Object[] objs3 = {null, "⼩刚", 22};
List<Object[]> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(objs1);
list.add(objs2);
list.add(objs3);
int[] count = jdbcTemplate.batchUpdate(sql, list);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(count));
}
}8、批量修改
public class SpringTest {
@Test
public void test(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = applicationContext.getBean("jdbcTemplate", JdbcTemplate.class);
// 批量修改
String sql = "update t_user set real_name = ?, age = ? where id = ?";
Object[] objs1 = {"⼩花11", 10, 2};
Object[] objs2 = {"⼩明22", 12, 3};
Object[] objs3 = {"⼩刚33", 9, 4};
List<Object[]> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(objs1);
list.add(objs2);
list.add(objs3);
int[] count = jdbcTemplate.batchUpdate(sql, list);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(count));
}
}9、批量删除
public class SpringTest {
@Test
public void test(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = applicationContext.getBean("jdbcTemplate", JdbcTemplate.class);
// 批量删除
String sql = "delete from t_user where id = ?";
Object[] objs1 = {2};
Object[] objs2 = {3};
Object[] objs3 = {4};
List<Object[]> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(objs1);
list.add(objs2);
list.add(objs3);
int[] count = jdbcTemplate.batchUpdate(sql, list);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(count));
}
}10、使⽤回调函数
public class SpringTest {
@Test
public void test(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = applicationContext.getBean("jdbcTemplate", JdbcTemplate.class);
String sql = "select id, real_name, age from t_user where id = ?";
User user = jdbcTemplate.execute(sql, new PreparedStatementCallback<User>() {
@Override
public User doInPreparedStatement(PreparedStatement ps) throws SQLException, DataAccessException {
User user = null;
ps.setInt(1, 5);
ResultSet rs = ps.executeQuery();
if (rs.next()) {
user = new User();
user.setId(rs.getInt("id"));
user.setRealName(rs.getString("real_name"));
user.setAge(rs.getInt("age"));
}
return user;
}
});
System.out.println(user);
}
}四、使⽤德鲁伊连接池
上面数据源是⽤我们⾃⼰写的。也可以使⽤别⼈写好的。例如⽐较⽜的德鲁伊连接池。
第⼀步:引⼊德鲁伊连接池的依赖。
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.1.8</version>
</dependency>
第⼆步:将德鲁伊中的数据源配置到spring配置⽂件中。和配置我们⾃⼰写的⼀样。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<bean id="druidDataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring6"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="root"/>
</bean>
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="druidDataSource"/>
</bean>
</beans>测试
public class SpringTest {
@Test
public void test(){
// 获取JdbcTemplate对象
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = applicationContext.getBean("jdbcTemplate", JdbcTemplate.class);
String sql = "insert into t_user(id,real_name,age) values(?,?,?)";
int count = jdbcTemplate.update(sql, null, "张三", 30);
System.out.println("插⼊的记录条数:" + count);
}
}