一、场景:
二、结论:
1. 四种方法耗时
三、代码:
一、场景:
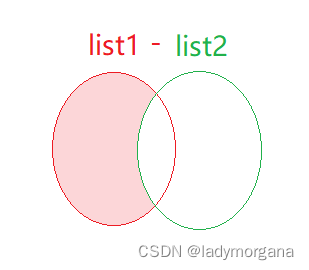
- 求差集 List1 - Lsit2
二、结论:
1. 四种方法耗时
| 初始条件 | 方法名 | 方法思路 | 耗时 | |
| List1.size=319418 List2.size=284900 | List..removeAll(Lsit2) | 1036987ms | ||
| removeAll_01 | List.contains() | 614859ms | ||
| removeAll_02 | 运用Set | 150ms | 推荐 | |
| removeAll_03 | 用Set.contains()再优化 | 112ms | 推荐 |
三、代码:
package com.privatecloud.core.util.collections;
import com.alibaba.fastjson2.JSON;
import com.privatecloud.core.util.file.FileIOUtil;
import com.privatecloud.core.util.file.FilesReadUtil;
import com.privatecloud.core.util.file.FilesUtil;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.*;
@Slf4j
public class ListUtils<T> {
public List<T> removeAll_01(List<T> source, List<T> destination) {
List<T> result = new LinkedList<T>();
for (T t : source) {
if (!destination.contains(t)) {
result.add(t);
}
}
return result;
}
/**
* 2,运用Set可以去重这一特性。效率有明显提升
*
* @param source
* @param destination
* @return
*/
public List<T> removeAll_02(List<T> source, List<T> destination) {
List<T> result = new LinkedList<T>();
Map<T, Integer> sourceMap = new HashMap<T, Integer>();
for (T t : source) {
if (sourceMap.containsKey(t)) { //原集合中的重复值
sourceMap.put(t, sourceMap.get(t) + 1);
} else {
sourceMap.put(t, 1);
}
}
Set<T> all = new HashSet<T>(destination);
for (Map.Entry<T, Integer> entry : sourceMap.entrySet()) {
T key = entry.getKey();
Integer value = entry.getValue();
if (all.add(key)) {
for (int i = 0; i < value; i++) {
result.add(key);
}
}
}
return result;
}
/**
* 3,用Set.contains()再优化
*
* @param source
* @param destination
* @return
*/
public List<T> removeAll_03(List<T> source, List<T> destination) {
List<T> result = new LinkedList<T>();
Set<T> destinationSet = new HashSet<T>(destination);
for (T t : source) {
if (!destinationSet.contains(t)) {
result.add(t);
}
}
return result;
}
}