文章目录
- 1. 682 棒球比赛
- 2. 71 简化路径
- 3. 388 文件的最长绝对路径
- 4. 150 逆波兰表达式求值
- 5. 227. 基本计算器II
- 6. 224. 基本计算器
- 7. 20. 有效的括号
- 8. 636. 函数的独占时间
- 9. 591. 标签验证器
- 10. 32.最长有效括号
- 12. 341. 扁平化嵌套列表迭代器
- 13. 394.字符串解码
1. 682 棒球比赛



解法:
使用变长数组对栈进行模拟。
如果操作是 +,那么访问数组的后两个得分,将两个得分之和加到总得分,并且将两个得分之和入栈。
如果操作是D,那么访问数组的最后一个得分,将得分乘以 2 加到总得分,并且将得分乘以 2 入栈。
如果操作是C,那么访问数组的最后一个得分,将总得分减去该得分,并且将该得分出栈。
如果操作是整数,那么将该整数加到总得分,并且将该整数入栈。
时间复杂度:O(n),其中 n为数组 ops 的大小。遍历整个ops 需要 O(n)。
空间复杂度:O(n)。变长数组最多保存O(n) 个元素。
class Solution {
public:
int calPoints(vector<string>& operations) {
int sum=0;
int tmp=0;
vector<int>top;
for(int i=0;i< operations.size();i++){
if(operations[i]=="+"){
int n=top.size();
tmp= top[n-1]+top[n-2];
top.emplace_back(tmp);
}
else if(operations[i]=="C"){
top.pop_back();
}
else if(operations[i]=="D"){
int n=top.size();
tmp=top[n-1]*2;
top.emplace_back(tmp);
}
else{
tmp=atoi(operations[i].c_str());
top.emplace_back(tmp);
}
}
for(auto item:top){
sum+=item;
}
return sum;
}
};
2. 71 简化路径

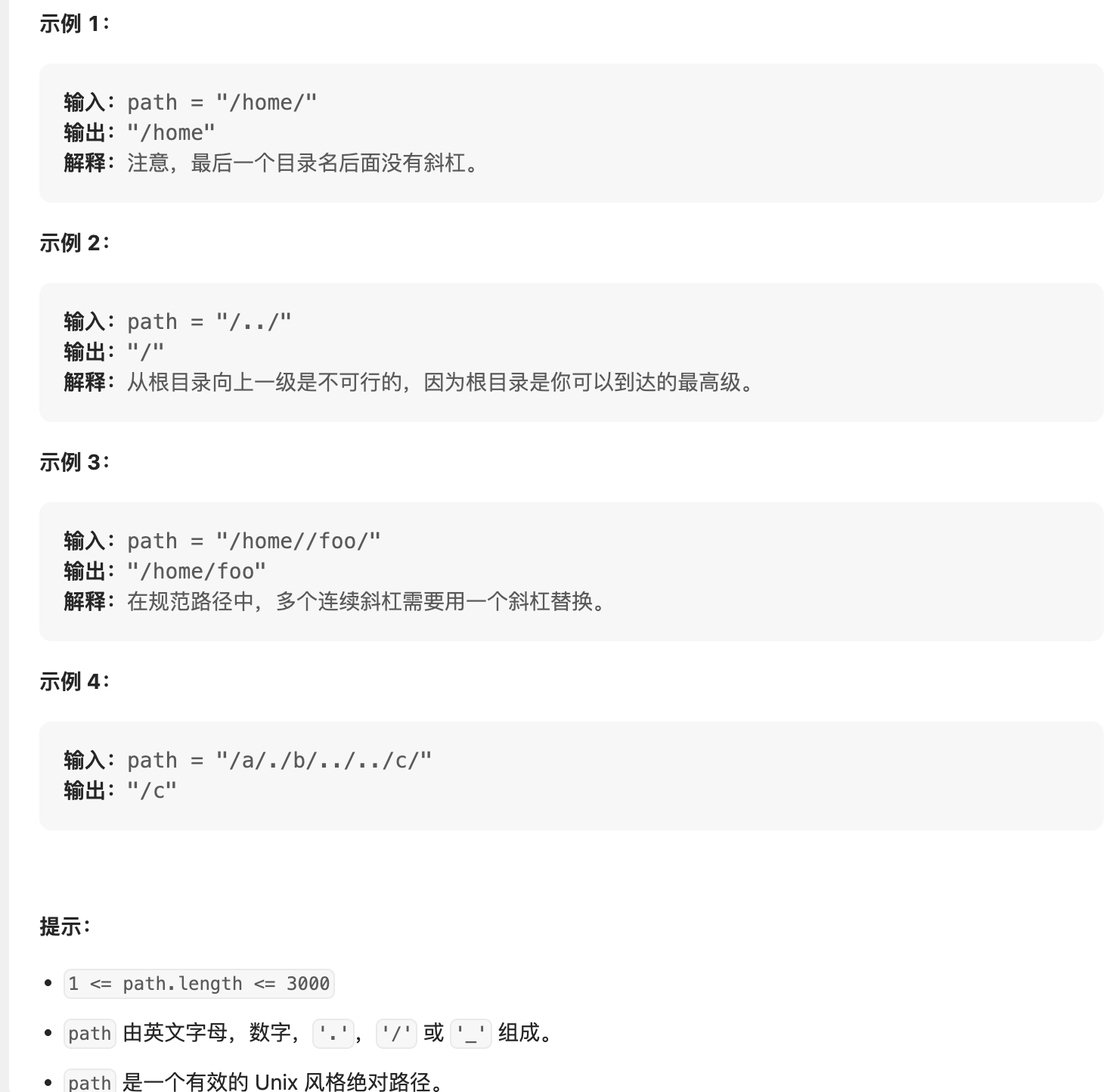
解法:使用栈来解决,首先将path根据/分隔为由若干个字符串组成的列表,因为多个/最终也表示/。但是由于c++没有split函数,因此要自己手动实现一个split方法。之后对于vector内的元素,如果是一个点,保持不变,两个点目录切换到上一级,对应弹栈,若都不是,代表目录名,则入栈。
最后将目录名用“/”连接输出即可
class solution62 {
public:
string simplifyPath(string path) {
vector<string>result;
int n=path.length();
//split path by /
for(int i=0;i<n;){
if(path[i]=='/')
{
i++;
if(i==n)
break;
string tmp="";
while(path[i]!='/'&&i<n){
tmp+=path[i];
i++;
}
if(!tmp.empty())
{
result.emplace_back(tmp);
}
}
}
vector<string>last;
for(auto r:result){
if(r==".")
continue;
else if(r=="..")
{
if(!last.empty())
last.pop_back();
}
else
last.emplace_back(r);
}
string lastreuslt="/";
int m=last.size();
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
lastreuslt+=last[i];
if(i!=m-1){
lastreuslt+="/";
}
}
return lastreuslt;
}
};
时间复杂度:O(n),其中 n 是字符串path 的长度。
空间复杂度:O(n)。我们需要 O(n) 的空间存储names 中的所有字符串。
3. 388 文件的最长绝对路径



解法:hash表+前缀和
文件系统可以的最长绝对路径,即文件系统按照层次便利的最长路径,遍历的终点为一个文件。
题目中的制表符\t的个数为深度,根目录的深度为0。因此可以以\n来划分文件字符串,设置指针i和j,i指向首位置,j指向下一个\n的位置,因此j-i为两个\n之间的长度,包含了\t,因为文件总长度不包含\t。因此若为文件夹,该L层的长度为
j-i+levelLen[L-1]+1-cnt; 其中levelLen[L-1]是上一层的长度,cnt为\t个数,1表示“/”
若为文件,总长度为:
j-i+levelLen[L-1]-cnt; 其中levelLen[L-1]是上一层的长度,cnt为\t个数
最长长度一直从文件长度中取最大值。
代码:
class solution63 {
public:
int lengthLongestPath(string input) {
int n=input.size();
unordered_map<int,int>leveltoLen;
int ans=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
int j=i;
int cnt=0;
bool isFile=false;
while(j<n&&input[j]!='\n'){
if(input[j]=='\t')
cnt++;
else if(input[j]=='.')
{
isFile= true;
}
j++;
}
int len;
if(isFile){
len=j-i+leveltoLen[cnt-1]-cnt;
ans=max(ans,len);
}
else{
len=j-i+leveltoLen[cnt-1]+1-cnt;
}
leveltoLen[cnt]=len;
i=j;
}
return ans;
}
};
时间复杂度:O(n) n为字符串长度
空间复杂度:O(n) 哈希表空间
4. 150 逆波兰表达式求值
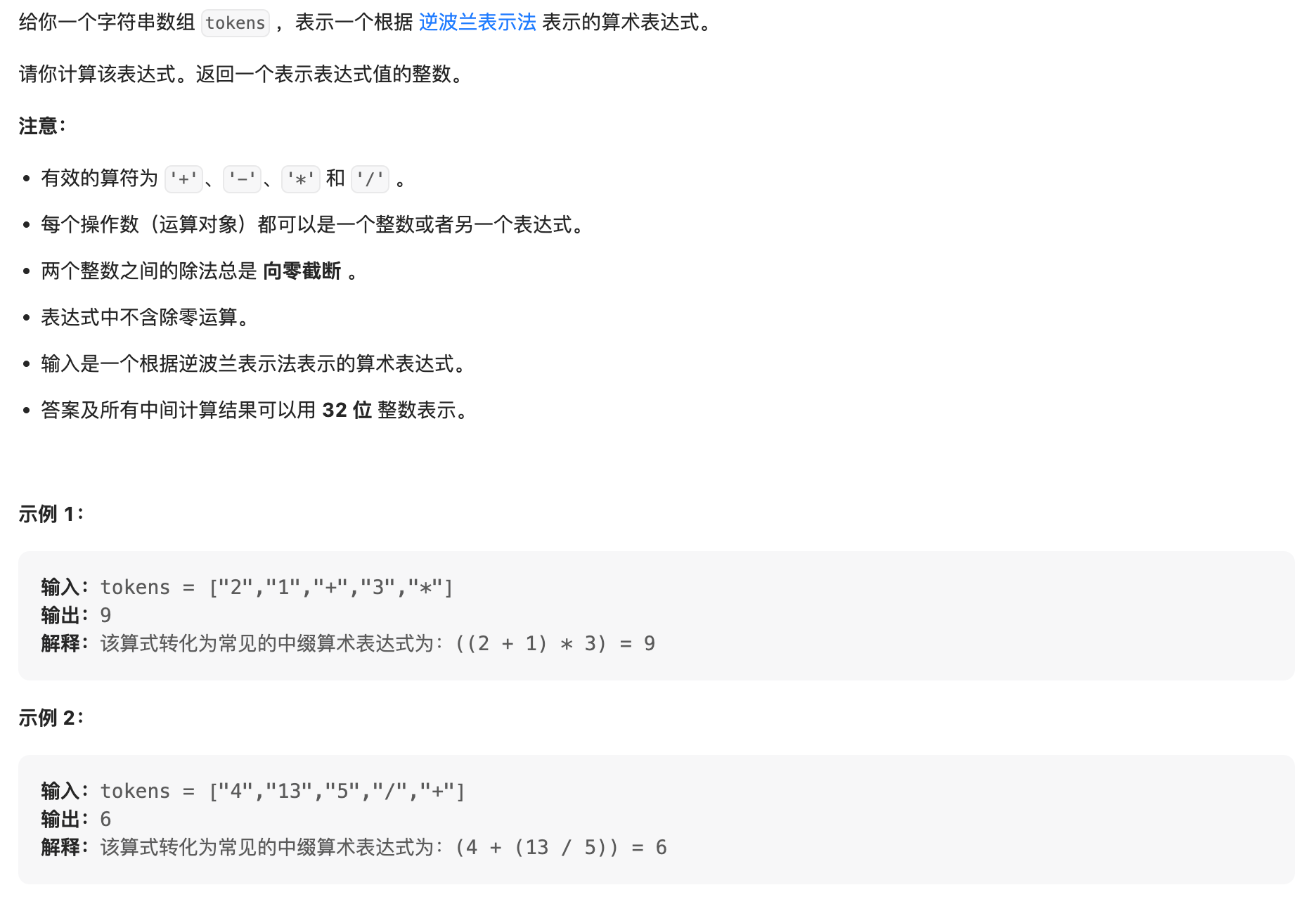

解法:中缀表达式可以使用栈来维护,首先遍历算数表达式,如果遇到数字入栈,如果遇到符号,则出栈两个数字,并且与符号相作用然后入栈,最后栈中剩余的唯一数字则为最后结果。
代码:
class solution64 {
public:
int evalRPN(vector<string>& tokens) {
vector<int>stacks;
for(auto item:tokens){
if(item=="+"){
int t1=stacks.back();
stacks.pop_back();
int t2=stacks.back();
stacks.pop_back();
int tmp=t2+t1;
stacks.emplace_back(tmp);
}
else if(item=="-"){
int t1=stacks.back();
stacks.pop_back();
int t2=stacks.back();
stacks.pop_back();
int tmp=t2-t1;
stacks.emplace_back(tmp);
}
else if(item=="*"){
int t1=stacks.back();
stacks.pop_back();
int t2=stacks.back();
stacks.pop_back();
int tmp=t2*t1;
stacks.emplace_back(tmp);
}
else if(item=="/"){
int t1=stacks.back();
stacks.pop_back();
int t2=stacks.back();
stacks.pop_back();
int tmp=t2/t1;
stacks.emplace_back(tmp);
}
else{
int t= std::atoi(item.c_str());
stacks.emplace_back(t);
}
}
return stacks.back();
}
};
时间复杂度:O(n),其中 n 是数组 tokens 的长度。需要遍历数组 tokens 一次,计算逆波兰表达式的值。
空间复杂度:O(n),其中 n是数组tokens 的长度。使用栈存储计算过程中的数,栈内元素个数不会超过逆波兰表达式的长度。
5. 227. 基本计算器II

解法:
这题没有括号实现计算器,可以使用双栈的思路,一个栈存储数字,另一个栈存储运算符,注意到*/的运算符优先级相同,±运算符优先级相同,乘除的优先级高于加减。因此当运算符a入栈时,需要判断栈顶元素,如果a为+或者-号,则栈内所有其他运算符必须先和数字占进行结合计算。如果a为乘号或者除号,则栈顶元素为“+”或者“-”可以直接入栈。
遍历完式子之后,如果符号栈为空,返回数字栈中的数字,如果符号栈不为空,则按照符号栈的顺序弹栈并且与数字栈结合计算返回结果。
注意两点:c++的isdigit函数可以判断字符串是否为数字,且数字为非负整数,不止是一位数,因此需要对数字进行转换。
并且s[i]-'0’需要用int进行强制类型转换,因为减法运算可能导致溢出或者不确定的结构,使得ascii为负数。
代码可能比较冗余,但逻辑是清晰的。
代码:
class solution65 {
public:
int calculate(string s) {
vector<int>num;
vector<char>op;
int n=s.size();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
if(s[i]==' ')
continue;
else if(s[i]=='*'){
int tmp;
while(!op.empty()){
if(op.back()=='/'){
int t1=num.back();
num.pop_back();
int t2=num.back();
num.pop_back();
tmp=t2/t1;
num.emplace_back(tmp);
}
else if(op.back()=='*'){
int t1=num.back();
num.pop_back();
int t2=num.back();
num.pop_back();
tmp=t2*t1;
num.emplace_back(tmp);
}
else{
break;
}
op.pop_back();
}
op.emplace_back(s[i]);
}
else if(s[i]=='/'){
int tmp;
while(!op.empty()){
if(op.back()=='/'){
int t1=num.back();
num.pop_back();
int t2=num.back();
num.pop_back();
tmp=t2/t1;
num.emplace_back(tmp);
}
else if(op.back()=='*'){
int t1=num.back();
num.pop_back();
int t2=num.back();
num.pop_back();
tmp=t2*t1;
num.emplace_back(tmp);
}
else{
break;
}
op.pop_back();
}
op.emplace_back(s[i]);
}
else if(s[i]=='+'||s[i]=='-'){
int t1,t2,tmp;
while(!op.empty()){
if(op.back()=='+'){
t1=num.back();
num.pop_back();
t2=num.back();
num.pop_back();
tmp=t2+t1;
num.emplace_back(tmp);
}
else if(op.back()=='-'){
t1=num.back();
num.pop_back();
t2=num.back();
num.pop_back();
tmp=t2-t1;
num.emplace_back(tmp);
}
else if(op.back()=='*'){
t1=num.back();
num.pop_back();
t2=num.back();
num.pop_back();
tmp=t2*t1;
num.emplace_back(tmp);
}
else if(op.back()=='/'){
t1=num.back();
num.pop_back();
t2=num.back();
num.pop_back();
tmp=t2/t1;
num.emplace_back(tmp);
}
op.pop_back();
}
op.emplace_back(s[i]);
}
else{
int n=0;
while(isdigit(s[i])){
n=n*10+s[i]-'0';
i++;
}
num.emplace_back(n);
i--;
}
}
int t1,t2,tmp;
while(!op.empty()){
char o=op.back();
op.pop_back();
t1=num.back();
num.pop_back();
t2=num.back();
num.pop_back();
if(o=='*'){
tmp=t2*t1;
}
else if(o=='/'){
tmp=t2/t1;
}
else if(o=='+'){
tmp=t2+t1;
}
else{
tmp=t2-t1;
}
num.emplace_back(tmp);
}
return num.back();
}
};
时间复杂度:O(n),其中n 为字符串 s的长度。需要遍历字符串 s 一次,计算表达式的值。
空间复杂度:O(n),其中 n 为字符串 s 的长度。空间复杂度主要取决于栈的空间,栈的元素个数不超过 n。
6. 224. 基本计算器

解法:使用两个栈 num 和 op 。
num: 存放所有的数字 op :存放所有的数字以外的操作。(±)
1.首先预处理字符串,将所有空格去掉。
2.然后对于所有的"("直接放入符号栈
3.如果有新的符号入栈,且不是")“,可以将当前栈内可以计算的符号进行计算,避免在通过”)"进行判断计算的时候,将(-+)操作顺序变换导致出错。
4.如果遇到")“将当前”("前的所有符号都计算,并且弹出左括号,计算结果加入num
时刻注意一些细节:由于第一个数可能是负数,如“-2+1”,为了减少边界判断,先往 nums 添加一个 0;
为防止 () 内出现的首个字符为运算符如(-2)(+2),如果遇到(-,(+,在num中添加0
代码:
class solution66 {
public:
int calculate(string s) {
vector<int>num;
//为了防止第一个数是负数
num.emplace_back(0);
vector<char>op;
bool flag=false;
string ns="";
for(int i=0;i<s.size();i++){
if(s[i]==' ')
continue;
ns+=s[i];
}
int n=ns.size();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
if(ns[i]=='('){
if(ns[i+1]=='-'||ns[i+1]=='+'){
num.emplace_back(0);
}
op.emplace_back(ns[i]);
}
else{
if(isdigit(ns[i])){
int m=0;
while(isdigit(ns[i])){
m=m*10+int(ns[i]-'0');
i++;
}
num.emplace_back(m);
i--;
}
else if(ns[i]=='+'||ns[i]=='-'){
//将栈内能算的先算,避免之后算让如(-+)操作的+号运算比-前
int t1,t2,tmp;
while(!op.empty()&&op.back()!='('){
t1=num.back();
num.pop_back();
t2=num.back();
num.pop_back();
char o=op.back();
op.pop_back();
if(o=='+')
tmp=t2+t1;
else if(o=='-')
tmp=t2-t1;
num.emplace_back(tmp);
}
op.emplace_back(ns[i]);
}
else if(ns[i]==')'){
int t1,t2,tmp;
while(op.back()!='('){
t1=num.back();
num.pop_back();
t2=num.back();
num.pop_back();
char o=op.back();
op.pop_back();
if(o=='+')
tmp=t2+t1;
else if(o=='-')
tmp=t2-t1;
num.emplace_back(tmp);
}
op.pop_back();
}
}
}
int t1,t2,tmp;
while(!op.empty()){
char o=op.back();
op.pop_back();
t1=num.back();
num.pop_back();
t2=num.back();
num.pop_back();
if(o=='+')
tmp=t2+t1;
else if(o=='-')
tmp=t2-t1;
num.emplace_back(tmp);
}
return num.back();
}
};
时间复杂度:o(n)
空间复杂度:o(n)
7. 20. 有效的括号

解法:利用栈来解决,首先字符串为空或者长度为1,一定返回false;
然后便利字符串中的括号,如果是左括号则入栈,如果碰到右括号,如果栈中非空,并且栈顶有对应的左括号与其匹配,则弹栈;否则将右括号入栈;
最后如果栈为空,说明匹配,否则不匹配
class solution67 {
public:
bool isValid(string s) {
vector<char>stack;
if(s.empty()||s.size()==1)
return false;
for( auto item:s){
if(item=='('||item=='['||item=='{')
stack.emplace_back(item);
else if(item==')'){
if(stack.empty()||stack.back()!='(')
stack.emplace_back(item);
else
stack.pop_back();
}
else if(item==']'){
if(stack.empty()||stack.back()!='[')
stack.emplace_back(item);
else
stack.pop_back();
}
else if(item=='}'){
if(stack.empty()||stack.back()!='{')
stack.emplace_back(item);
else
stack.pop_back();
}
}
return stack.empty();
}
};
时间复杂度:O(n)
空间复杂度:O(n)
8. 636. 函数的独占时间
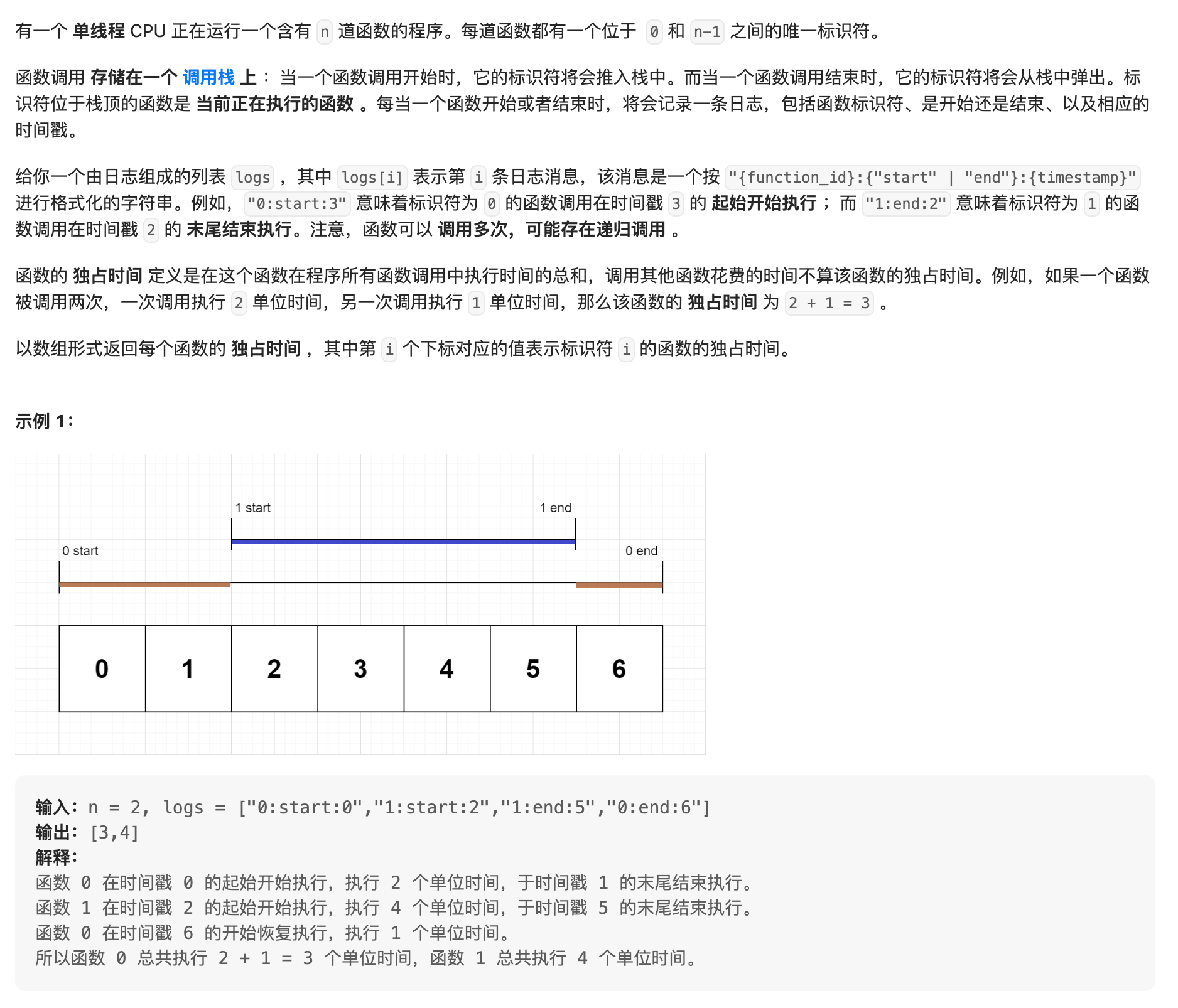


解法:因为每个函数都有对应的start和end;即栈中记录函数的id号和开始时间戳;result记录每个函数的累积执行时间,
1.若为起始函数,直接入栈;
2.若有新的函数为start,则入栈,栈顶的函数s的运行时间是当前新函数的时间戳timestamp2-栈顶时间戳timestamp1;累加到result[s]中,且需要将栈顶函数的其实时间改为新函数的其实时间。
3.如果新函数为end,那么会弹出栈顶函数s,栈顶函数的运行时间为当新函数的时间戳timestamps2-栈顶时间戳+1;此时pop栈顶函数;同时若栈顶不为空的话,新的栈顶函数的时间戳为timestamp2+1
最后栈为空,返回result
代码:
class solution68 {
public:
vector<int> exclusiveTime(int n, vector<string>& logs) {
vector<int>result(n,0);
vector<pair<int,int>>stack;
for(auto log:logs){
int pos1=log.find(":");
int pos2=log.rfind(":");
int id=std::atoi(log.substr(0,pos1).c_str());
string status=log.substr(pos1+1,pos2-pos1-1);
int timestamp=std::atoi(log.substr(pos2+1,log.size()).c_str());
pair<int,int>item= make_pair(id, timestamp);
if(status=="start"){
if(!stack.empty()){
result[stack.back().first]+=timestamp-stack.back().second;
stack.back().second=timestamp;
}
stack.emplace_back(item);
}
else{
result[id]+=timestamp-stack.back().second+1;
stack.pop_back();
if(!stack.empty()){
stack.back().second=timestamp+1;
}
}
}
return result;
}
};
时间复杂度:O(n)),其中 n 为全部日志 logs 的数量,n 条日志信息对应总共 n 次入栈和出栈操作。
空间复杂度:O(n),其中 n 为全部日志logs 的数量,n 条日志信息对应n/2次入栈操作,最坏的情况下全部 n/2 条日志入栈后才会依次弹栈。
c++函数使用:注意substr函数的形式为s.substr(pos, n),
需要两个参数,第一个是开始位置,第二个是获取子串的长度。
函数可以从一个字符串中获取子串,返回一个string,包含s中从pos开始的n个字符的拷贝(pos的默认值是0,n的默认值是s.size() - pos,即不加参数会默认拷贝整个s)。官方解法中给出了一个按照冒号分割字符串的新方式:
char type[10];
int idx, timestamp;
在C++中,你可以使用
sscanf函数来按照指定的格式从一个C风格的字符串中读取数据。这个函数的原型为:int sscanf(const char* str, const char* format, ...);它的工作方式类似于
scanf函数,但是不是从标准输入读取,而是从给定的字符串中读取数据。在你提供的代码中,
sscanf函数的格式字符串是"%d:%[^:]:%d"。这个格式字符串指示sscanf从log.c_str()这个字符串中按照以下规则读取数据:
%d:读取一个整数,赋值给idx。::读取一个冒号,但不存储。%[^:]:读取一个非冒号的字符串,赋值给type。这个格式说明符%[^:]使用了[^:]表达式,它表示匹配除冒号外的任意字符,这样可以读取type的值。::读取一个冒号,但不存储。%d:读取一个整数,赋值给timestamp。所以,当
sscanf函数调用时,它会根据给定的格式字符串解析log.c_str()中的内容,并将解析出的值存储到相应的变量。需要注意的是,虽然在C++中可以使用
sscanf进行字符串解析,但这通常不是最安全的方法,因为它对于输入数据的格式和边界条件的检查相对较弱。在实际应用中,更推荐使用更安全的字符串解析方法,比如使用std::istringstream或者字符串分割库来处理字符串。
9. 591. 标签验证器



解法:栈模拟
字符串模拟,假设字符串 s 长度为 n,当前处理到的位置为 i,根据以下优先级进行检查:
优先尝试检查以 i 为开始的连续段是否为 CDATA,若能匹配到开头,则尝试匹配到 CDATA 的结尾处,并更新 i,若无法找到结尾,返回 False;
1.尝试匹配 s[i] <,若满足,则根据 s[i+1] 是否为 / 来判断当前 TAG_NAME 是处于右边还是左边,然后将 TAG_NAME 取出,记为 tag,判断 tag 长度是否合法,不合法返回 False,合法则根据是左边还是右边的 TAG_NAME 分情况讨论:
2.位于左边的 TAG_NAME:将其加入栈中,等待右边的 TAG_NAME 与其匹配;
位于右边的 TAG_NAME:将其与当前栈顶的元素进行匹配,若栈为空或匹配不上,返回 False.
3.其余情况则为普通字符。
最后由于整个 s 应当被一对 TAG_NAME 所包裹,因此当 i=0时,不能是情况 1和情况 3,需要特判一下。
注意细节:因为题目中说到代码必须被合法的闭合标签包围,因此当字符串未遍历完成,stack不能为空;所以对于pop标签后,若是栈为空,且没有遍历完字符串,则返回false,如“
<A></A><B></B>” 情况,此时A标签pop时候,stack已经为空。同理当为其他字符时,必须保证stack内有标签存在
代码:
class solution69 {
public:
string findTagName(string &s,int index,int&end){
int i=index;
string reuslt="";
int n=s.size();
while(i<n&&isupper(s[i])){
reuslt+=s[i];
i++;
}
end=i;
if(i==n){
return "";
}
if(s[i]=='>'){
return reuslt;
}
else{
return "";
}
}
bool isCdata(string &s,int index,int &end){
int i=index;
int n=s.size();
string c="[CDATA[";
int cnt=0;
for( i=index;i<n;i++){
if(s[i]!=c[cnt]){
return false;
}
cnt++;
if(cnt==c.size()){
break;
}
}
i++;
while(i<n){
if(s[i]==']'){
if(i+2<n&&s[i+1]==']'&&s[i+2]=='>'){
end=i+2;
return true;
}
}
i++;
}
return false;
}
bool isValid(string code) {
vector<string>stack;
int n=code.size();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
int end;
if(code[i]=='<'){
if(i+1<n&&code[i+1]=='/'){
//end标签
string s= findTagName(code,i+2,end);
if(stack.empty())
return false;
string start=stack.back();
if(s.empty()||s!=start){
return false;
}
stack.pop_back();
if(stack.empty()&&end!=n-1)
return false;
}
else if(i+1<n&&code[i+1]=='!'){
bool flag= isCdata(code,i+2,end);
if(!flag){
return false;
}
if(stack.empty()&&end!=n-1)
return false;
}
else{
string s= findTagName(code,i+1,end);
if(s.empty()||s.size()>9||s.size()<1)
return false;
stack.emplace_back(s);
}
i=end;
}
else{
if(stack.empty())
return false;
}
}
return stack.empty();
}
};
时间复杂度:O(n)
空间复杂度:O(n)
10. 32.最长有效括号

解法:
我们定义 dp[i] 表示以下标 i 字符结尾的最长有效括号的长度。我们将dp 数组全部初始化为 0 。显然有效的子串一定以 ‘)’ 结尾,因此我们可以知道以 ‘(’ 结尾的子串对应的dp 值必定为 0 ,我们只需要求解 ‘‘)’ 在 dp 数组中对应位置的值。
-
我们从前往后遍历字符串求解 dp 值,我们每两个字符检查一次:s[i−1]=‘(’,也就是字符串形如 “……()”,我们可以推出:
dp[i]=dp[i−2]+2
我们可以进行这样的转移,是因为结束部分的 “()” 是一个有效子字符串,并且将之前有效子字符串的长度增加了 2 2 2 。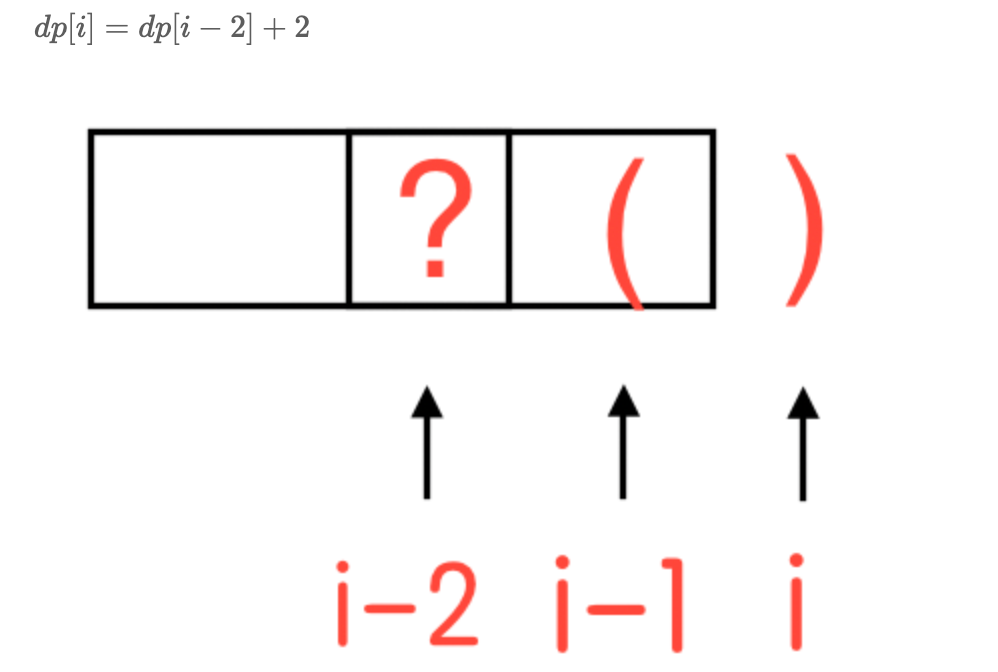
-
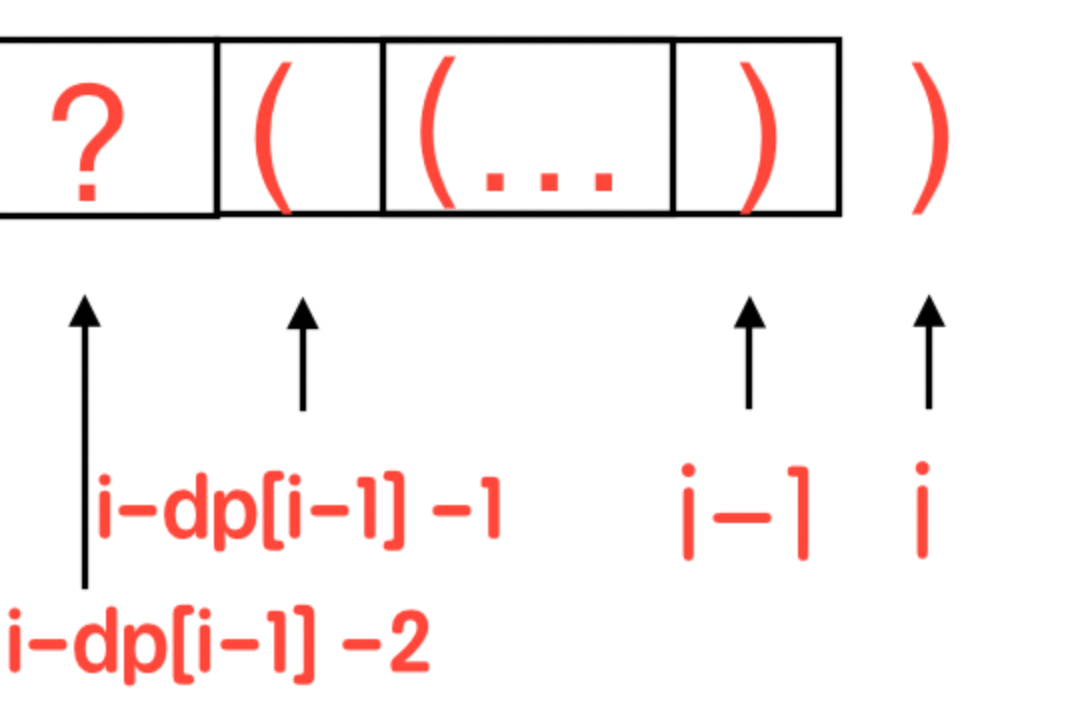
s[i−1]== ′)’
这种情况下,如果前面有和s[i]组成有效括号对的字符,即形如 ((…)),这样的话,就要求s[i−1]位置必然是有效的括号对,否则s[i]s[i]s[i]无法和前面对字符组成有效括号对。
这时,我们只需要找到和s[i]配对对位置,并判断其是否是 ( 即可。和其配对位置为:i-dp[i-1]+1.
若:s[i-dp[i-1]-1]==‘(’:
有效括号长度新增长度 2,i位置对最长有效括号长度为 i-1位置的最长括号长度加上当前位置新增的 2,那么有:
dp[i]=dp[i−1]+2
值得注意的是,i−dp[i−1]−1 和 i 组成了有效括号对,这将是一段独立的有效括号序列,如果之前的子序列是形如 (…) 这种序列,那么当前位置的最长有效括号长度还需要加上这一段。所以:
dp[i]=dp[i−1]+dp[i−dp[i−1]−2]+2;
这个地方很容易遗漏,因为如用例)()(()),如果直接dp[i]=dp[i-1]+2就很容易遗漏。
代码:
class solution70 {
public:
int longestValidParentheses(string s) {
int n=s.size();
int *dp=new int[n];
std::fill(dp,dp+n,0);
int result=0;
for(int i=1;i<s.size();i++){
if(s[i]‘)’)
{
if(s[i-1]‘(’)
{
if(i-2>=0)
dp[i]=dp[i-2]+2;
else
dp[i]=2;
}
else{
if(i-dp[i-1]>0&&s[i-dp[i-1]-1]==‘(’){
dp[i]=dp[i-1]+2;
int pre=i-dp[i-1]-2>=0?dp[i-dp[i-1]-2]:0;
dp[i]+=pre;
}
}
}
result=max(result,dp[i]);
}
delete []dp;
return result;
}
};
时间复杂度: O(n),其中 n 为字符串的长度。我们只需遍历整个字符串一次,即可将 dp 数组求出来。
空间复杂度: O(n)】。我们需要一个大小为 n 的 dp 数组。
### 11. 385.迷你语法分析器

解法:
这道题用栈来解决,主要是要读懂辅助结构NestedInteger的几个函数的意思。
1. `NestedInteger();` :Constructor initializes an empty nested list. (构造函数初始化一个空的嵌套列表。)
2. `NestedInteger(int value);` :Constructor initializes a single integer.(构造函数初始化一个整数。)
3. `void add(const NestedInteger &ni);` :Set this NestedInteger to hold a nested list and adds a nested integer to it.(设置这个NestedInteger保存一个嵌套的列表,并向它添加一个嵌套的整数。)
3个方法的具体效果如下:
```csharp
NestedInteger ans = NestedInteger(); // ans = []
ans.add(NestedInteger(789)); // ans = [789]
NestedInteger temp = NestedInteger(); // temp = []
temp.add(NestedInteger(456)); // temp = [456]
temp.add(ans); // temp = [456, [789]]
NestedInteger res = NestedInteger(); // res = []
res.add(NestedInteger(123)); // res = [123]
res.add(temp); // res = [123, [456, [789]]]
因此利用栈来遍历字符串,如果遇到‘[’,则表示一个新的NestedInteger对象,将其入栈,如果遇到的是“,“或者”]",则表示一个数字,或者一个NestedInteger对象的结束,需要将这个数字添加到栈顶的对象中去。
以下又可以分成两种情况:若"]"或“,”左边是数字,说明是独立的对象,因此将数字加入栈顶对象中;
若“]”的左边是“]”带边对象的嵌入,因此当前栈顶的对象应该嵌入到它的上一个对象中,如789嵌入到456对象中
其中还需要注意一些特殊情况,若不以“[”开头,则说明只包含一个数字对象;而且注意可能有负数,需要判断
代码:
/**
* // This is the interface that allows for creating nested lists.
* // You should not implement it, or speculate about its implementation
* class NestedInteger {
* public:
* // Constructor initializes an empty nested list.
* NestedInteger();
*
* // Constructor initializes a single integer.
* NestedInteger(int value);
*
* // Return true if this NestedInteger holds a single integer, rather than a nested list.
* bool isInteger() const;
*
* // Return the single integer that this NestedInteger holds, if it holds a single integer
* // The result is undefined if this NestedInteger holds a nested list
* int getInteger() const;
*
* // Set this NestedInteger to hold a single integer.
* void setInteger(int value);
*
* // Set this NestedInteger to hold a nested list and adds a nested integer to it.
* void add(const NestedInteger &ni);
*
* // Return the nested list that this NestedInteger holds, if it holds a nested list
* // The result is undefined if this NestedInteger holds a single integer
* const vector<NestedInteger> &getList() const;
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
NestedInteger deserialize(string s) {
if(s[0]!='[')
return NestedInteger(atoi(s.c_str()));
vector<NestedInteger>stack;
int num=0;
bool flag=false;
for(int i=0;i<s.size();i++){
char c=s[i];
if(c=='-'){
flag=true;
continue;
}
else if(isdigit(c)){
num=num*10+int(c-'0');
}
//检测到左括号,同步往栈中添加对象
else if(c=='[')
stack.emplace_back(NestedInteger());
else if (c==','||c==']'){
//如果其左边是整数,说明它是一个对象,如果c为逗号,说明其对象有其他嵌套对象,为]说明为完整对象
if(isdigit(s[i-1])){
if(flag){
num*=-1;
}
stack.back().add(NestedInteger(num));
}
num=0;
flag=false;
if(c==']'&&stack.size()>1){
//将其和上一个对象合并
NestedInteger n=stack.back();
stack.pop_back();
stack.back().add(n);
}
}
}
return stack.back();
}
};
时间复杂度:O(n),其中 n是 s 的长度。我们需要遍历 s 的每一位来解析。
空间复杂度:O(n),其中 n 是 s 的长度。栈的深度最多为 O(n)。
12. 341. 扁平化嵌套列表迭代器

解法一:递归
注意,递归是最简单的方法,但是在面试过程中,面试官可能想考察的不会是递归的方法,而是迭代的方法
因为整个nestedList结构可看成树形结构的一种表达形式,树上的叶子结点就是一个正数,而非叶子结点就是一个列表。
因此我们可以对这个nestedList结构进行深搜,在深搜的过程中,将最终结果存入数组。
如上述的例子 n e x t e d L i s t = [ [ 1 , 1 ] , 2 , [ 1 , 1 ] ] nextedList=[[1,1],2,[1,1]] nextedList=[[1,1],2,[1,1]]那么通过dfs将结果存入 r e s u l t result result得到 [ 1 , 1 , 2 , 1 , 1 ] [1,1,2,1,1] [1,1,2,1,1]
所以 h a s n e x t hasnext hasnext即判断 r e s u l t result result中是否有整数, n e x t next next则是返回 r e s u l t result result中的整数.
/**
* // This is the interface that allows for creating nested lists.
* // You should not implement it, or speculate about its implementation
* class NestedInteger {
* public:
* // Return true if this NestedInteger holds a single integer, rather than a nested list.
* bool isInteger() const;
*
* // Return the single integer that this NestedInteger holds, if it holds a single integer
* // The result is undefined if this NestedInteger holds a nested list
* int getInteger() const;
*
* // Return the nested list that this NestedInteger holds, if it holds a nested list
* // The result is undefined if this NestedInteger holds a single integer
* const vector<NestedInteger> &getList() const;
* };
*/
class NestedIterator {
public:
vector<int>result;
vector<int>::iterator iters;
void dfs(const vector<NestedInteger> &nestedList){
for(auto &nest:nestedList){
if(nest.isInteger()){
result.emplace_back(nest.getInteger());
}
else{
dfs(nest.getList());
}
}
}
NestedIterator(vector<NestedInteger> &nestedList) {
dfs(nestedList);
iters=result.begin();
}
int next() {
return *iters++;
}
bool hasNext() {
return iters!=result.end();
}
};
/**
* Your NestedIterator object will be instantiated and called as such:
* NestedIterator i(nestedList);
* while (i.hasNext()) cout << i.next();
*/
时间复杂度:初始化O(n),next 和 hasNext 为O(1)。其中 n 是嵌套的整型列表中的元素个数。
空间复杂度:O(n)。需要一个数组存储嵌套的整型列表中的所有元素。
解法二:迭代
基于迭代的方式,利用栈来模拟递归的过程,
-
初始化的时候,由于栈是先进先出的,可以利用vector模拟栈,将所有元素逆序加入栈中。
-
在hasNext()方法中,判断栈顶是否为int
-
若为ints说明有下一个元素,返回true,next()函数被调用,此时弹出栈顶元素
-
如果是list就将当前列表的各个元素再放入栈中【逆序】
使用栈的好处:就是不用一开始就展开所有元素,只在需要展开的时候展开
代码:
/**
* // This is the interface that allows for creating nested lists.
* // You should not implement it, or speculate about its implementation
* class NestedInteger {
* public:
* // Return true if this NestedInteger holds a single integer, rather than a nested list.
* bool isInteger() const;
*
* // Return the single integer that this NestedInteger holds, if it holds a single integer
* // The result is undefined if this NestedInteger holds a nested list
* int getInteger() const;
*
* // Return the nested list that this NestedInteger holds, if it holds a nested list
* // The result is undefined if this NestedInteger holds a single integer
* const vector<NestedInteger> &getList() const;
* };
*/
class NestedIterator {
public:
vector<NestedInteger>result;
NestedIterator(vector<NestedInteger> &nestedList) {
for(int i=nestedList.size()-1;i>=0;i--){
result.push_back(nestedList[i]);
}
}
int next() {
int next=result.back().getInteger();
result.pop_back();
return next;
}
bool hasNext() {
if(result.empty()){
return false;
}
auto item=result.back();
if(item.isInteger()){
return true;
}
else{
//此时展开NestedInteger 利用hasnext判断
//注意必须为逆序放入,不然弹出顺序又问题
auto num=item.getList();
result.pop_back();
for(int i=num.size()-1;i>=0;i--){
result.push_back(num[i]);
}
return hasNext();
}
}
};
/**
* Your NestedIterator object will be instantiated and called as such:
* NestedIterator i(nestedList);
* while (i.hasNext()) cout << i.next();
*/
时间复杂度:初始化和 =next 为 O(1),hasNext 为均摊 O(1)。
空间复杂度:O(n)。最坏情况下嵌套的整型列表是一条链,我们需要一个O(n) 大小的栈来存储链上的所有元素。
13. 394.字符串解码


解法1:辅助栈
- 首先创建两个栈,数字栈nums和字符串栈str
- 遍历该字符串s,对于其中一个字符c,若为数字,则入数字栈;若为字符[a-z,A-Z],则继续遍历,知道该位置不为字符类型,将其拼接成字符串,入str栈;
- 若c为"[“,则入str栈,若c为”]"。那么str栈不断弹栈,直到遇到“[”。此时栈中的字符串必须按照逆序拼接组成新的字符串。
- 然后取得数字栈顶数字n,将该字符串重复n次后,加入str栈中
“[”必定和数字配对,因此若出现“[”,数字栈顶必有数字 - 最后遍历结束后,将str栈中元素顺序拼接就能得到结果
代码:
class solution72 {
public:
vector<int>nums;
vector<string>str;
string laststr="";
string decodeString(string s) {
int i=0;
while(i<s.size()){
int num=0;
int flag=0;
while(isdigit(s[i])){
num=(s[i]-'0')+10*num;
i++;
flag=1;
}
if(flag)
nums.emplace_back(num);
string c="";
flag=0;
while(isalpha(s[i])){
c+=s[i];
i++;
flag=1;
}
if(flag)
str.emplace_back(c);
if(s[i]=='['){
str.emplace_back(string(1,s[i]));
i++;
}
if(s[i]==']'){
int num=nums.back();
nums.pop_back();
string s="";
while(str.back()!="["){
s.insert(0,str.back());
str.pop_back();
}
str.pop_back();
string top="";
for(int i=0;i<num;i++){
top+=s;
}
str.emplace_back(top);
i++;
}
}
for(auto s:str){
laststr+=s;
}
return laststr;
}
};
时间复杂度:O(S)
空间复杂度:O(S)
解法2:递归
见官方题解:[394. 字符串解码 - 力扣(LeetCode)](