这个文本显示组件应该是我们最常用的组件,下面会非常细
归纳
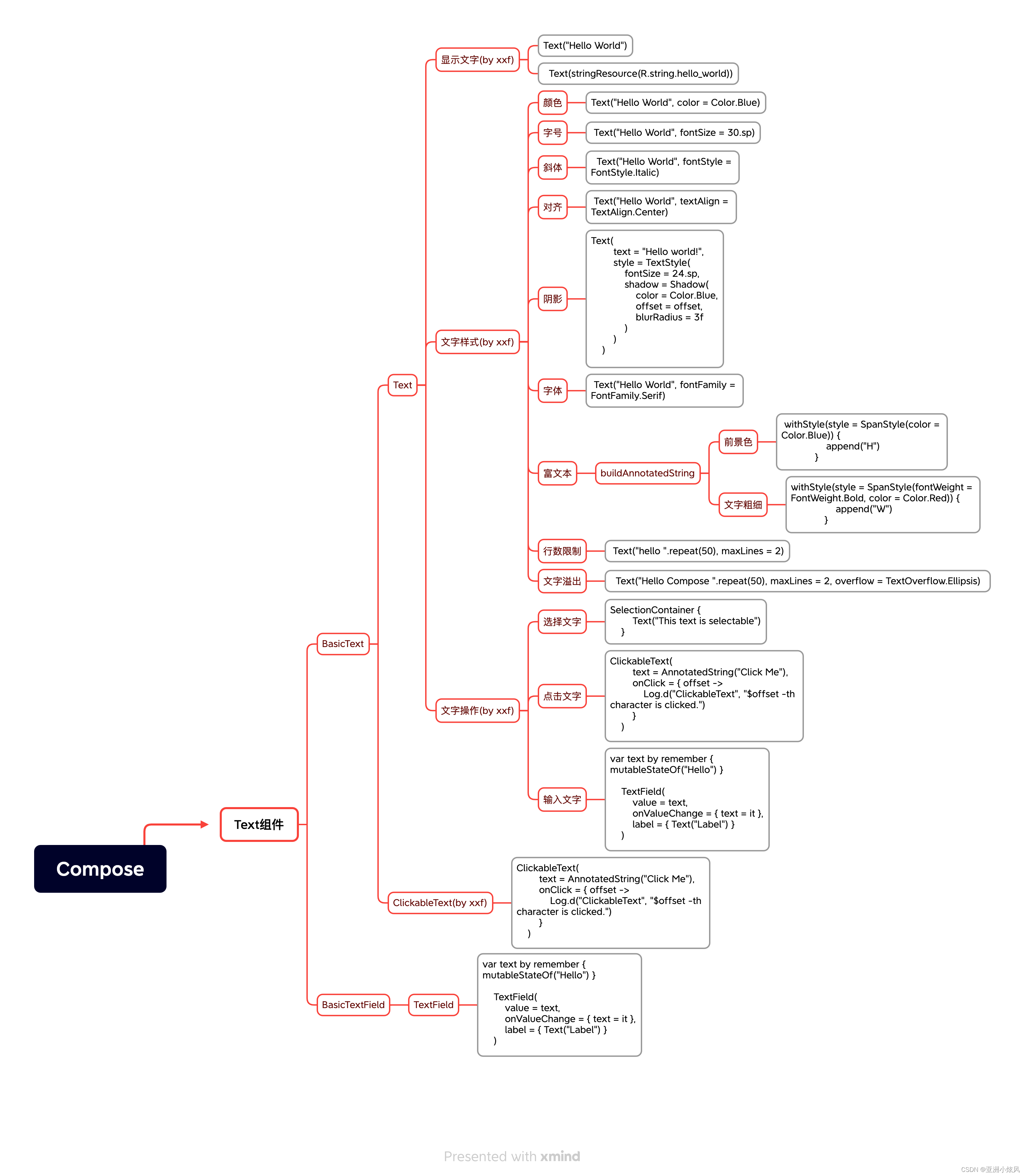
实例
下面一一演示这些属性与控制逻辑
文本的展示
Text组件 所有构造方法都是text:String,要想用string.xml里面的字符串资源 得使用
stringResource方法,其相似方法如下
/*
* Copyright 2019 The Android Open Source Project
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package androidx.compose.ui.res
import androidx.annotation.ArrayRes
import androidx.annotation.PluralsRes
import androidx.annotation.StringRes
import androidx.compose.runtime.Composable
import androidx.compose.runtime.ReadOnlyComposable
/**
* Load a string resource.
*
* @param id the resource identifier
* @return the string data associated with the resource
*/
@Composable
@ReadOnlyComposable
fun stringResource(@StringRes id: Int): String {
val resources = resources()
return resources.getString(id)
}
/**
* Load a string resource with formatting.
*
* @param id the resource identifier
* @param formatArgs the format arguments
* @return the string data associated with the resource
*/
@Composable
@ReadOnlyComposable
fun stringResource(@StringRes id: Int, vararg formatArgs: Any): String {
val resources = resources()
return resources.getString(id, *formatArgs)
}
/**
* Load a string resource.
*
* @param id the resource identifier
* @return the string data associated with the resource
*/
@Composable
@ReadOnlyComposable
fun stringArrayResource(@ArrayRes id: Int): Array<String> {
val resources = resources()
return resources.getStringArray(id)
}
/**
* Load a plurals resource.
*
* @param id the resource identifier
* @param count the count
* @return the pluralized string data associated with the resource
*/
@Composable
@ReadOnlyComposable
fun pluralStringResource(@PluralsRes id: Int, count: Int): String {
val resources = resources()
return resources.getQuantityString(id, count)
}
/**
* Load a plurals resource with provided format arguments.
*
* @param id the resource identifier
* @param count the count
* @param formatArgs arguments used in the format string
* @return the pluralized string data associated with the resource
*/
@Composable
@ReadOnlyComposable
fun pluralStringResource(@PluralsRes id: Int, count: Int, vararg formatArgs: Any): String {
val resources = resources()
return resources.getQuantityString(id, count, *formatArgs)
}
| 作用 | 方法 |
|---|---|
stringResource(@StringRes id: Int) | 获取xml指定id字符串资源 |
stringResource(@StringRes id: Int, vararg formatArgs: Any) | 获取xml指定id字符串资源,且格式化占位符号 |
stringArrayResource(@ArrayRes id: Int) | 获取xml指定id字符串资源数组,返回是数组 <string-array name="xxx"... |
pluralStringResource(@PluralsRes id: Int, count: Int) | 根据数字的不同自动选择不同的字符串显示,特别是单复数。 特别是不同国家的语言对应不同的单复数。 |
pluralStringResource(@PluralsRes id: Int, count: Int, vararg formatArgs: Any) | 根据数字的不同自动选择不同的字符串显示,特别是单复数。 |
@Composable
fun showXMLString(){
Text(text = stringResource(id = R.string.app_name))
}文字颜色
color属性,但是是Color对象,暂时没看到支持resource的 得转换,估计也是md设计的原因 希望使用CompositionLocal来嫁接,其内置了很多常用色
@Composable
fun showTextColor(){
Text(text = stringResource(id = R.string.app_name), color = Color.Yellow)
}文字大小
fontSize:UnitType类型
UnitType 支持sp 和em,app一般用sp,em 网页用得多,估计是为跨平台考虑,kotlin在数字上的拓展转化单位
@Composable
fun showTextSize(){
Text(text = stringResource(id = R.string.app_name), fontSize =30.sp )
}
文字粗细
fontWeight属性
类型是FontWeight,已经提前预置了很多static常量,当然也可以自己new,常用的
FontWeight.Bold
FontWeight.Medium
FontWeight.Normal
class FontWeight(val weight: Int) : Comparable<FontWeight> {
companion object {
/** [Thin] */
@Stable
val W100 = FontWeight(100)
/** [ExtraLight] */
@Stable
val W200 = FontWeight(200)
/** [Light] */
@Stable
val W300 = FontWeight(300)
/** [Normal] / regular / plain */
@Stable
val W400 = FontWeight(400)
/** [Medium] */
@Stable
val W500 = FontWeight(500)
/** [SemiBold] */
@Stable
val W600 = FontWeight(600)
/** [Bold] */
@Stable
val W700 = FontWeight(700)
/** [ExtraBold] */
@Stable
val W800 = FontWeight(800)
/** [Black] */
@Stable
val W900 = FontWeight(900)
/** Alias for [W100] */
@Stable
val Thin = W100
/** Alias for [W200] */
@Stable
val ExtraLight = W200
/** Alias for [W300] */
@Stable
val Light = W300
/** The default font weight - alias for [W400] */
@Stable
val Normal = W400
/** Alias for [W500] */
@Stable
val Medium = W500
/** Alias for [W600] */
@Stable
val SemiBold = W600
/**
* A commonly used font weight that is heavier than normal - alias for [W700]
*/
@Stable
val Bold = W700
/** Alias for [W800] */
@Stable
val ExtraBold = W800
/** Alias for [W900] */
@Stable
val Black = W900
/** A list of all the font weights. */
internal val values: List<FontWeight> = listOf(
W100,
W200,
W300,
W400,
W500,
W600,
W700,
W800,
W900
)
}
init {
require(weight in 1..1000) {
"Font weight can be in range [1, 1000]. Current value: $weight"
}
}
}
@Composable
fun showFontWeight(){
Text(text = stringResource(id = R.string.app_name), fontWeight = FontWeight.Bold )
}
文字对齐方式
textAlign属性,类型TextAlign对象,固定五6个常量对象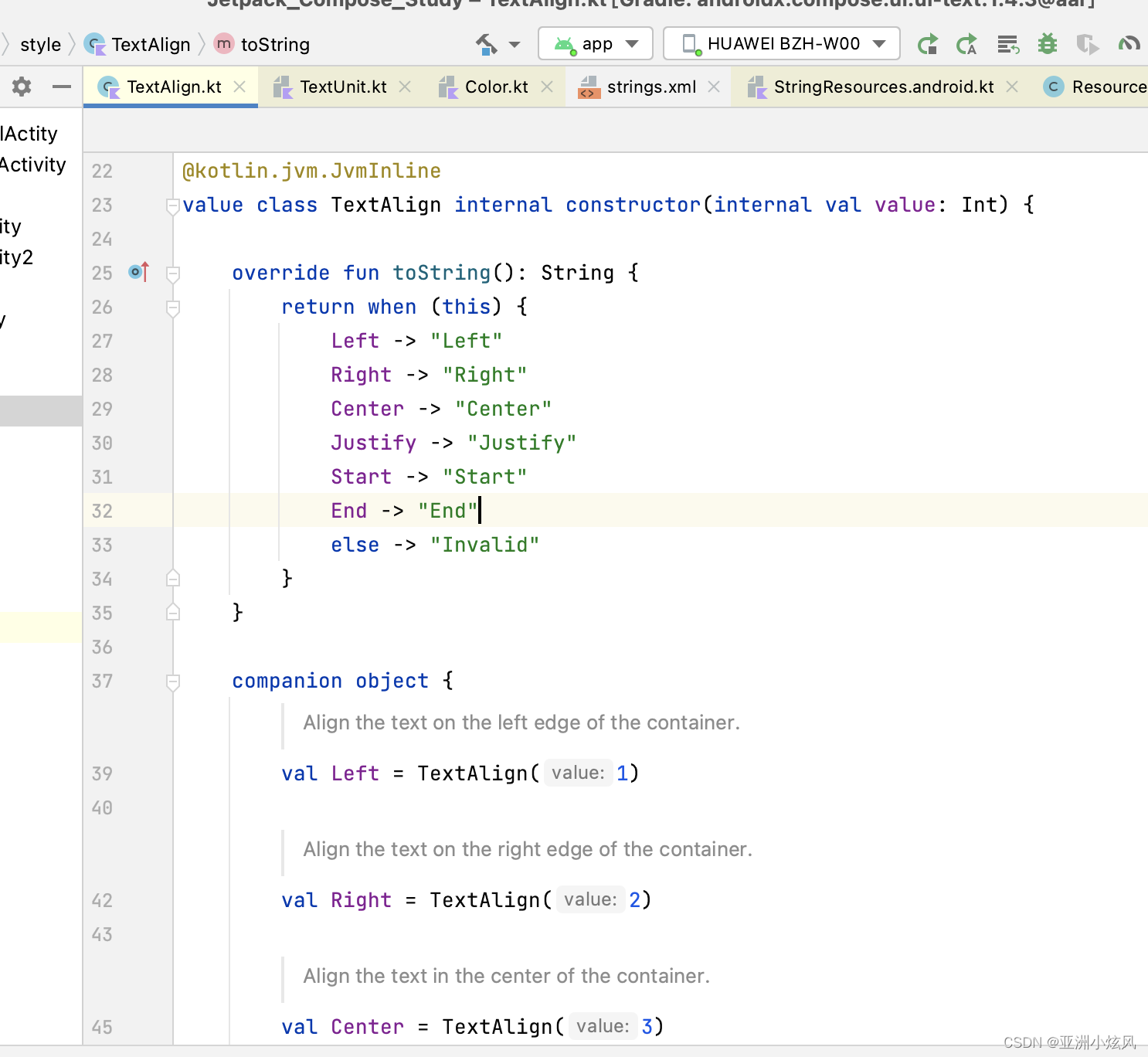
文字居中实例
@Composable
fun showTextAlign(){
Text(text = "textAlign", textAlign = TextAlign.Center, modifier = Modifier.width(150.dp).background(Color.Blue))
}
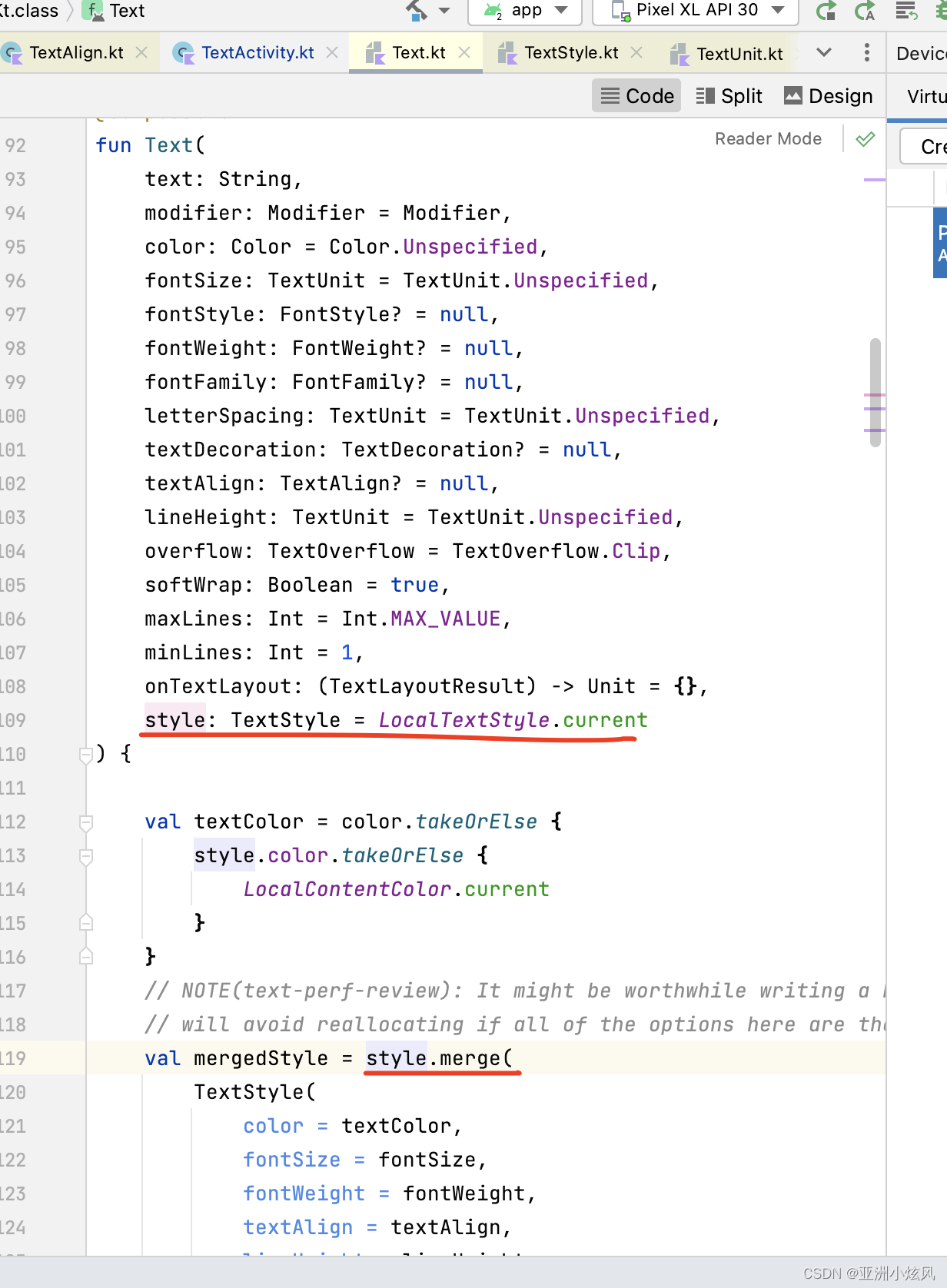
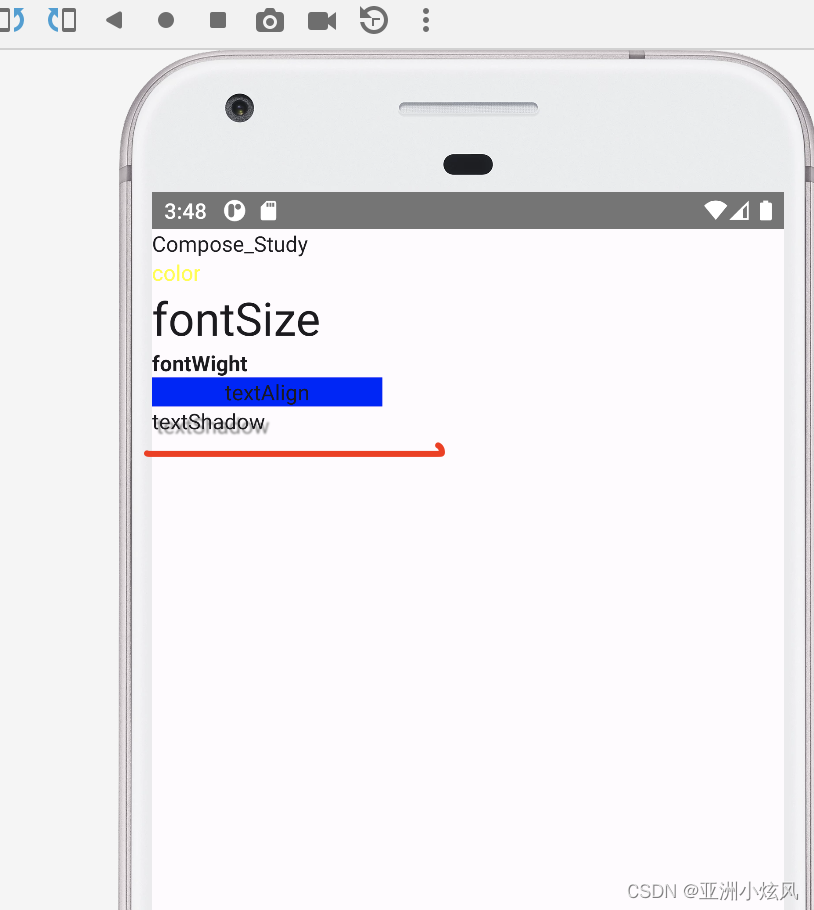
文字阴影
文字阴影没有一级属性,估计也是不常用,放在了style里面,style的类型是TextStyle,其实所有控制样式的一级属性最后都会merge到TextStyle对象里面,所以能通过一级属性控制的 也基本能通过TextStyle来控制
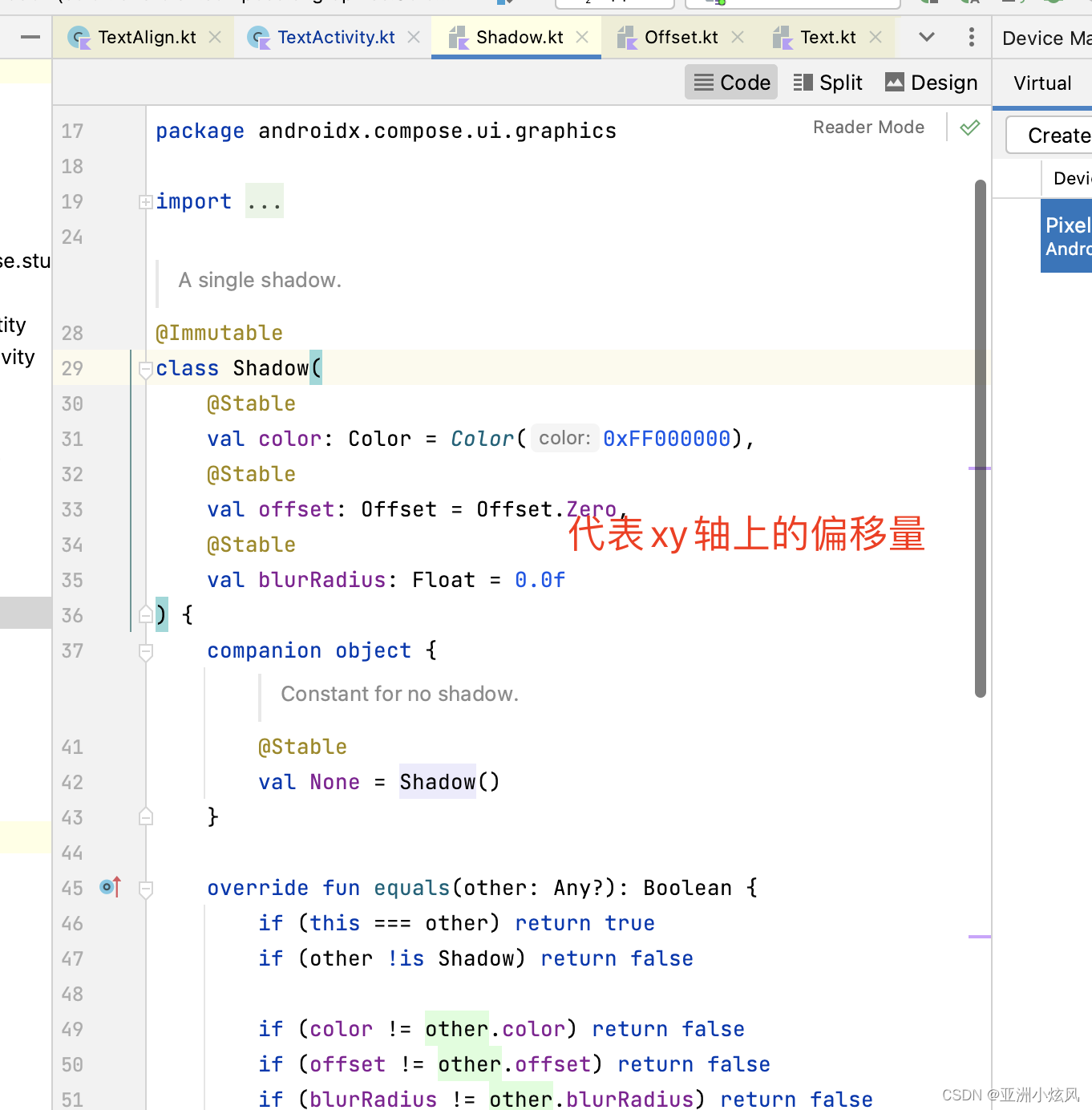
@Composable
fun showTextShadow(){
Text(text = "textShadow",
style = TextStyle(shadow = Shadow(color = Color.Gray,
offset = Offset(10.0f,10.0f),
blurRadius=3f)))
}
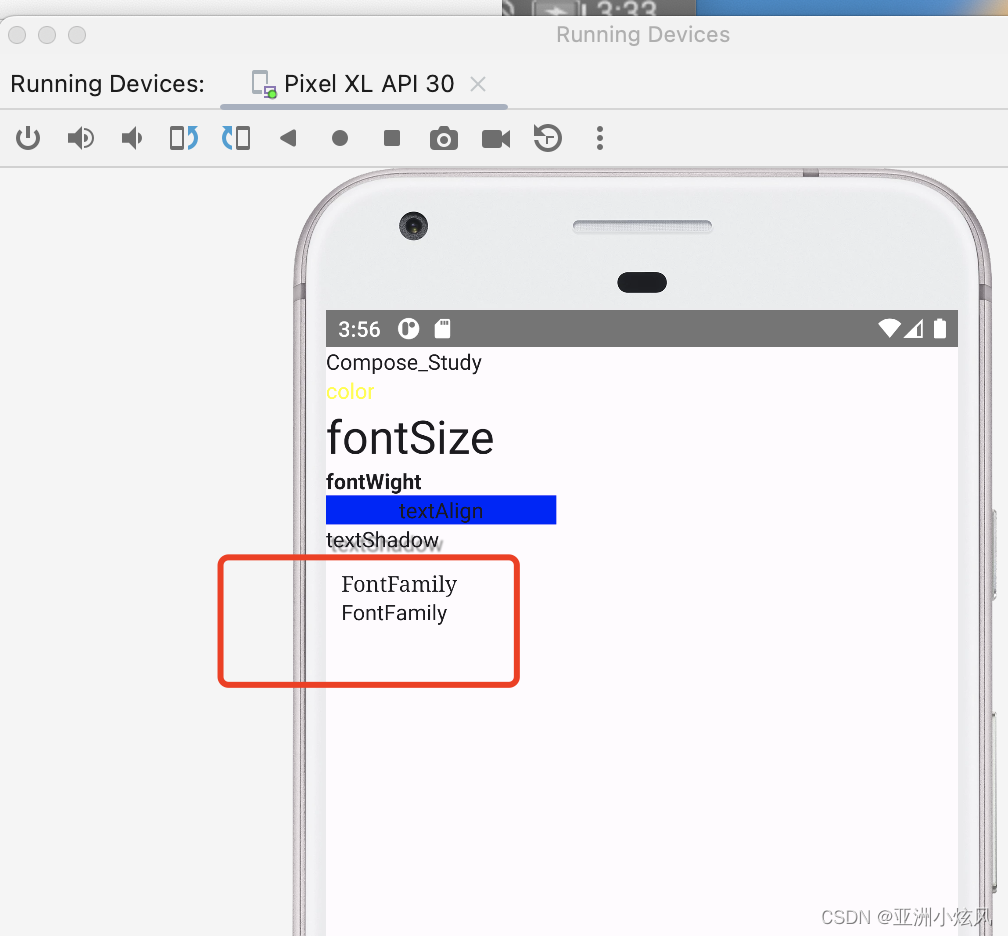
文字字体
fontFamily属性,内置了6种字体
@Composable
fun showFontFamily(){
Column(modifier = Modifier.padding(10.dp)) {
Text(text = "FontFamily", fontFamily = FontFamily.Serif)
Text(text = "FontFamily", fontFamily = FontFamily.SansSerif)
}
}
您可以使用 fontFamily 属性来处理 res/font 文件夹中定义的自定义字体和字型:
font 文件夹的图示" class="l10n-absolute-url-src screenshot" l10n-attrs-original-order="src,alt,width,class" src="https://developer.android.com/static/images/jetpack/compose/text-font-folder.png" width="400" />
此示例展示了如何根据这些字体文件以及使用 Font 函数定义 fontFamily:
val firaSansFamily = FontFamily(
Font(R.font.firasans_light, FontWeight.Light),
Font(R.font.firasans_regular, FontWeight.Normal),
Font(R.font.firasans_italic, FontWeight.Normal, FontStyle.Italic),
Font(R.font.firasans_medium, FontWeight.Medium),
Font(R.font.firasans_bold, FontWeight.Bold)
)富文本样式
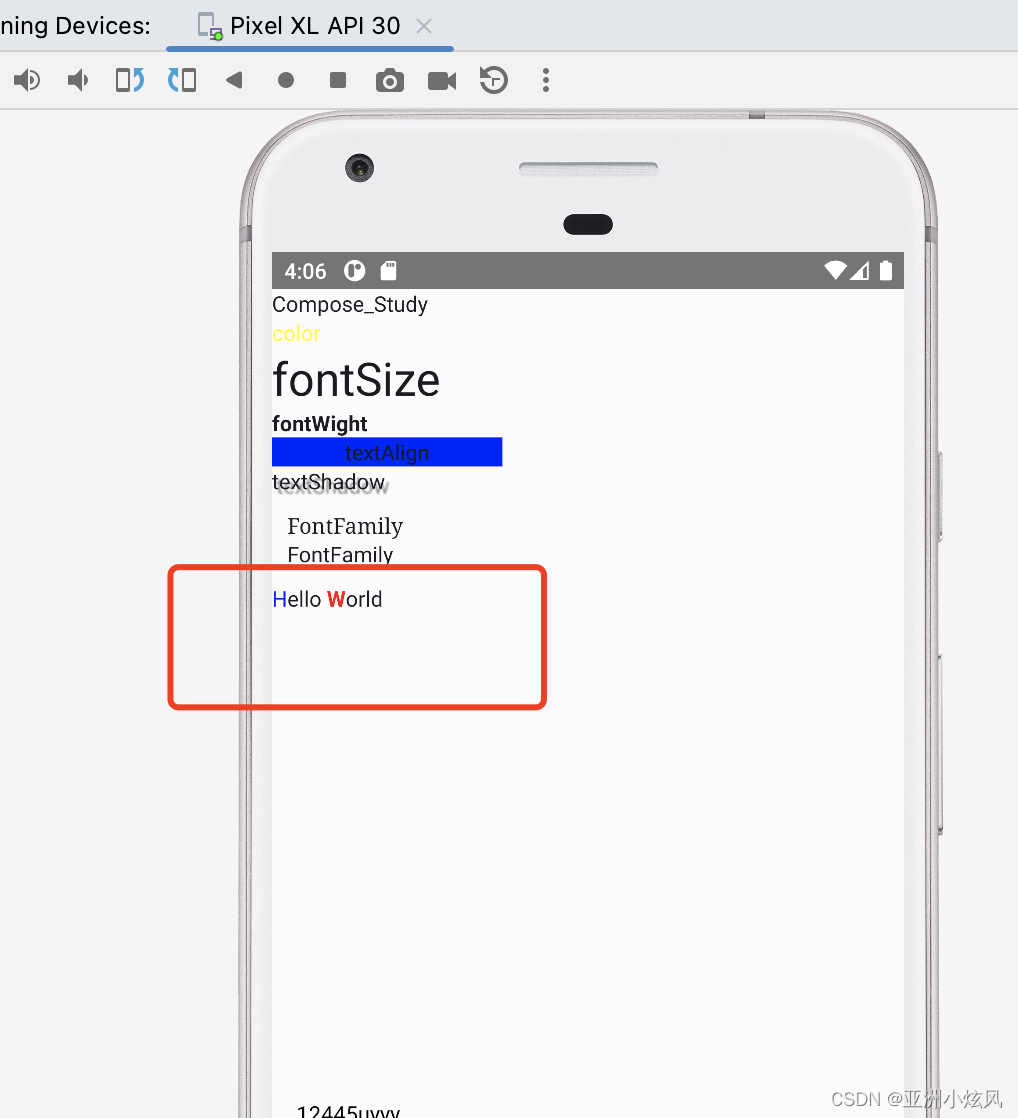
AnnotatedString类型,类型Android spanString,ios attributeString
通过spanStyle 来可以控制文字样式 字重 颜色,背景色等等
@Composable
fun MultipleStylesInText() {
Text(
buildAnnotatedString {
withStyle(style = SpanStyle(color = Color.Blue)) {
append("H")
}
append("ello ")
withStyle(style = SpanStyle(fontWeight = FontWeight.Bold, color = Color.Red)) {
append("W")
}
append("orld")
}
)
}
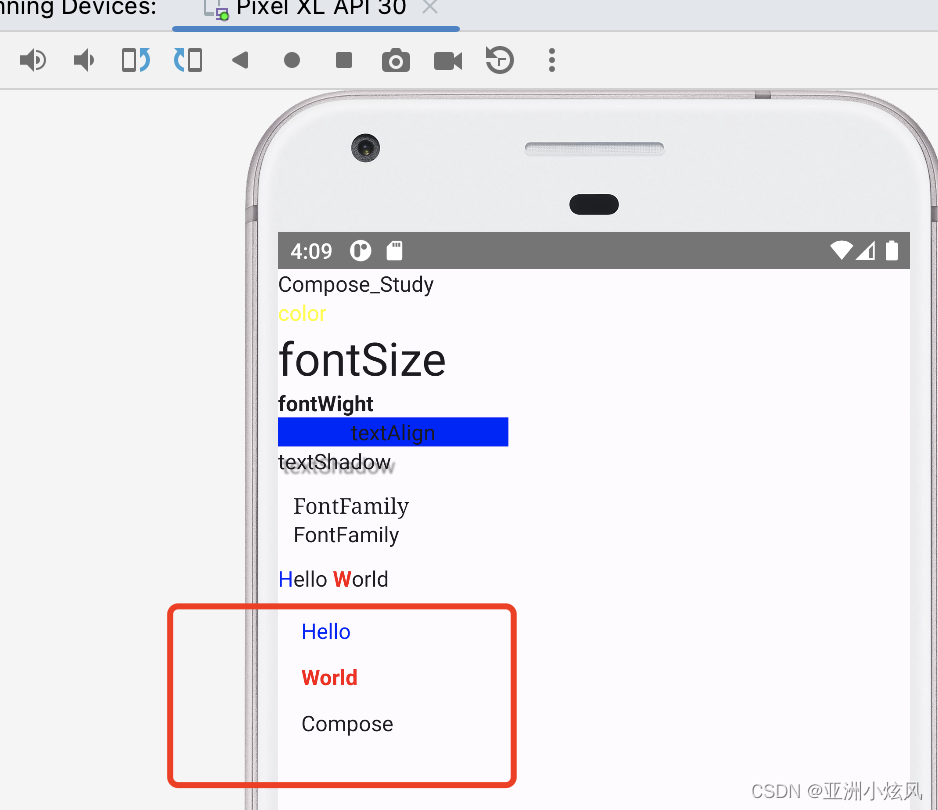
还可以设置段落样式,如下设置段落间距
@Composable
fun ParagraphStyleDemo() {
Text(
buildAnnotatedString {
withStyle(style = ParagraphStyle(lineHeight = 30.sp)) {
withStyle(style = SpanStyle(color = Color.Blue)) {
append("Hello\n")
}
withStyle(
style = SpanStyle(
fontWeight = FontWeight.Bold,
color = Color.Red
)
) {
append("World\n")
}
append("Compose")
}
}
)
}
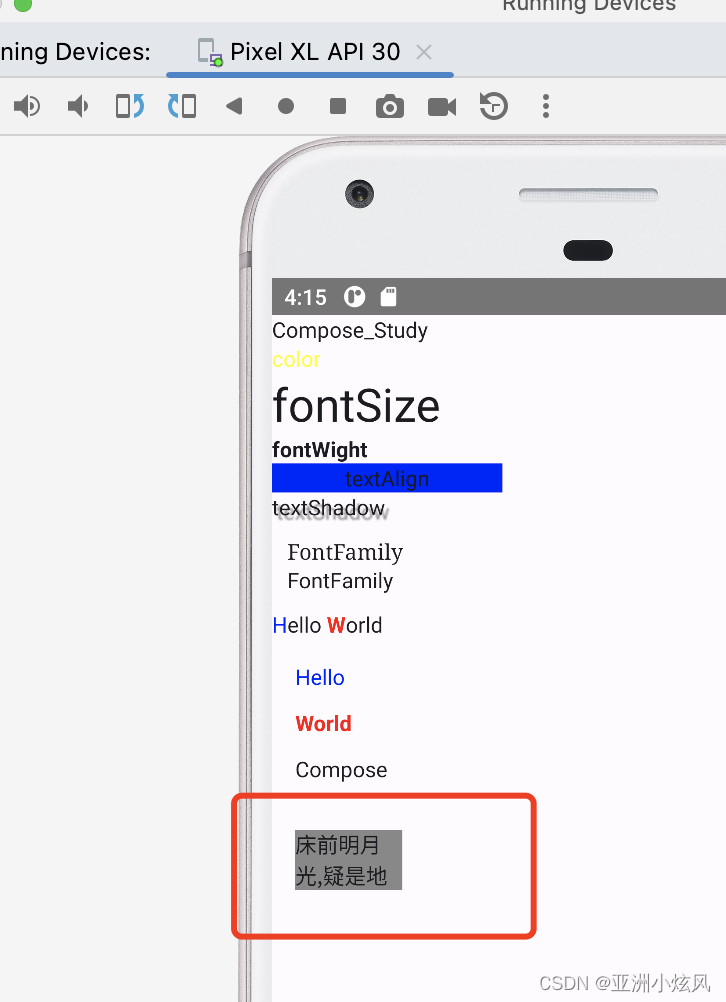
行数限制
maxLines,android 开发用得比较常见,不多说,看效果
@Composable
fun showMaxLine(){
Box(modifier = Modifier.width(100.dp)) {
Text("床前明月光,疑是地上双,举头望明月,低头思故乡", maxLines = 2, modifier = Modifier
.padding(15.dp)
.background(Color.Gray))
}
}
文字溢出
用于控制文字截断得时候表现形式,如尾部三个点 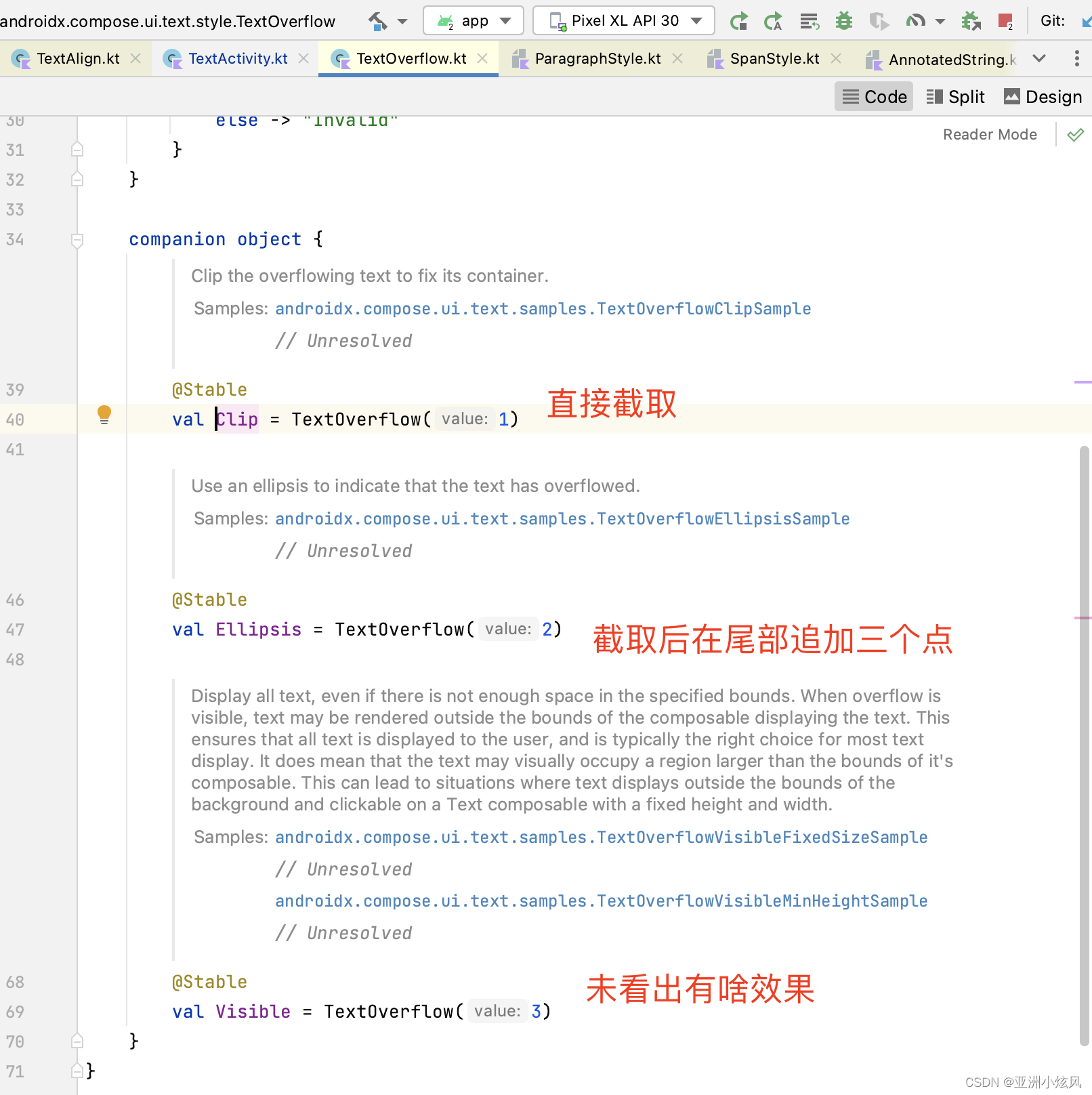
相比于Android 还是特别少
Text("床前明月光,疑是地上双,举头望明月,低头思故乡",
maxLines = 2,
overflow = TextOverflow.Ellipsis,
modifier = Modifier
.padding(15.dp)
.background(Color.Gray))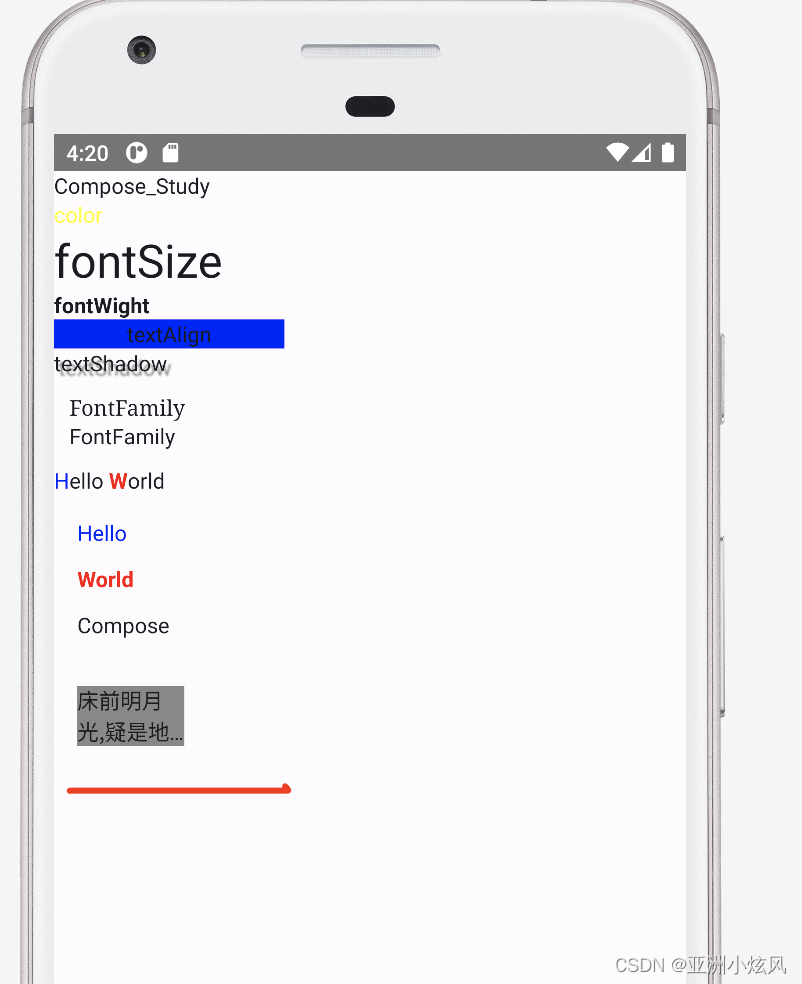
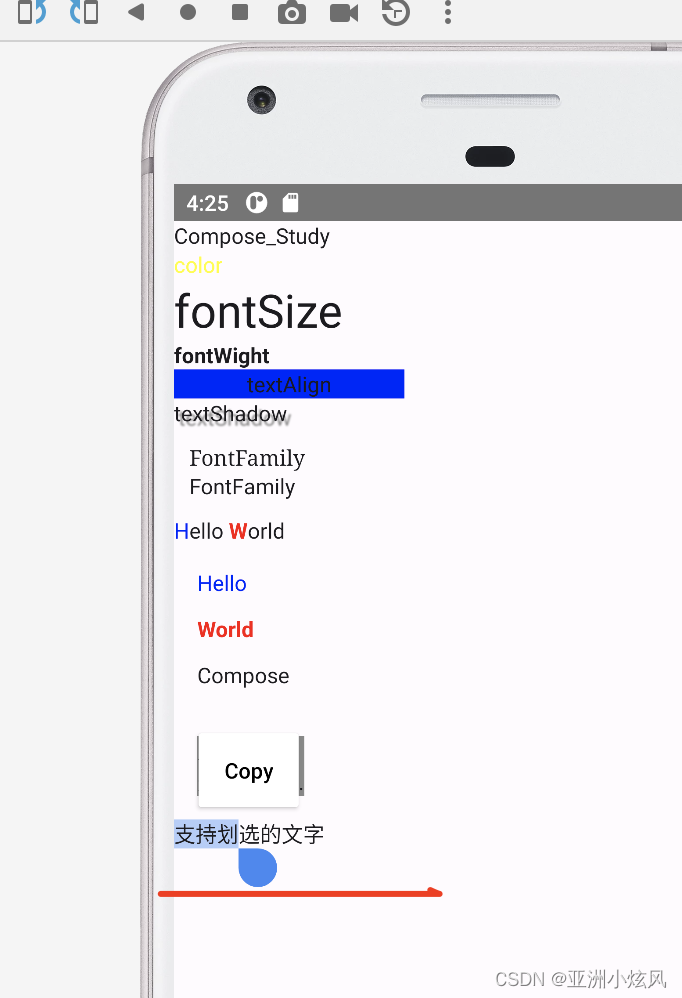
文字选中
compose 需要套一个SelectionContainer才能实现长按划选文字
@Composable
fun showSelectableText() {
SelectionContainer {
Text("支持划选的文字")
}
}
而且还支持多个Text组件实现划选
@Composable
fun showMutiSelectableText() {
SelectionContainer(modifier = Modifier.padding(10.dp)) {
Column {
Text("支持划选的文字第一个")
Text("支持划选的文字第二个")
Text("支持划选的文字第三个")
}
}
}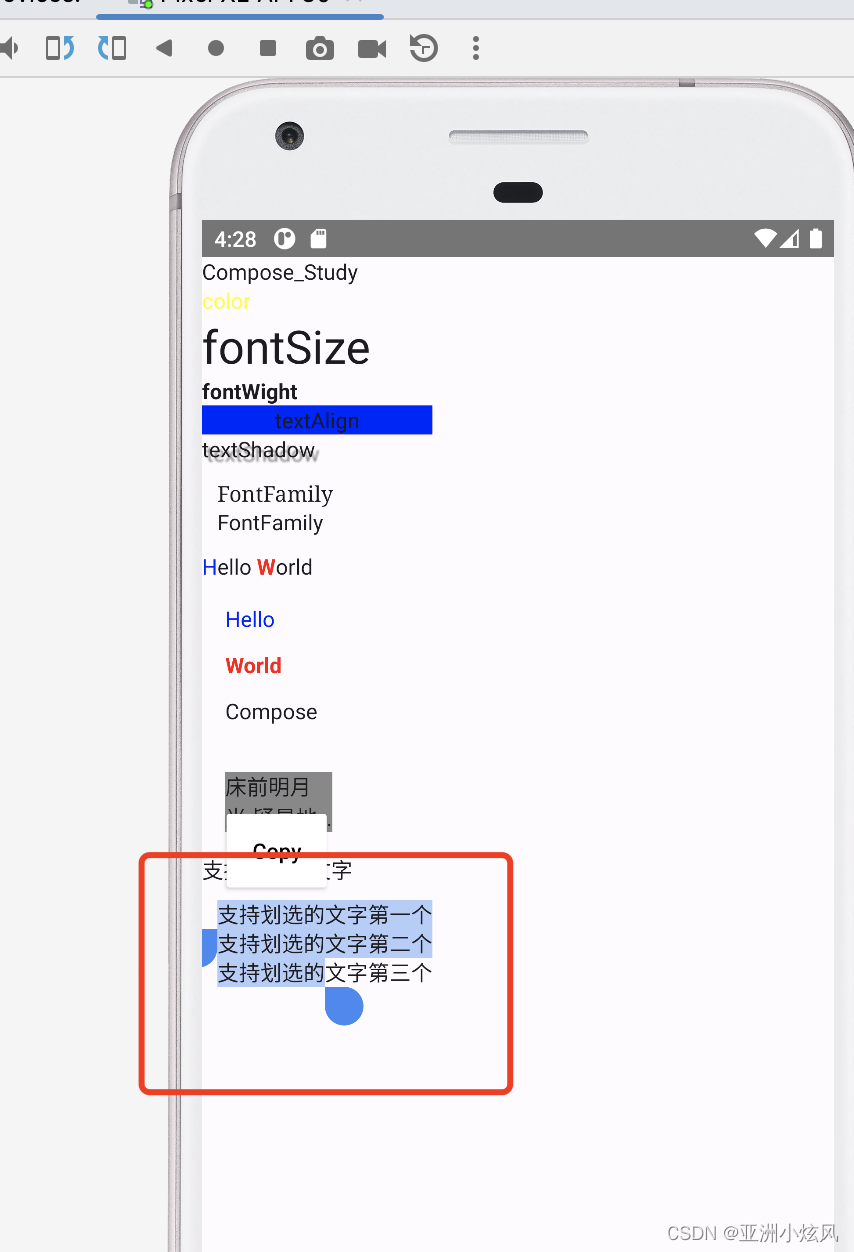
当然也支持局部屏蔽 不让划选
@Composable
fun showMutiSelectableText() {
SelectionContainer(modifier = Modifier.padding(10.dp)) {
Column {
Text("支持划选的文字第一个")
DisableSelection {
Text("支持划选的文字第二个")
}
Text("支持划选的文字第三个")
}
}
}
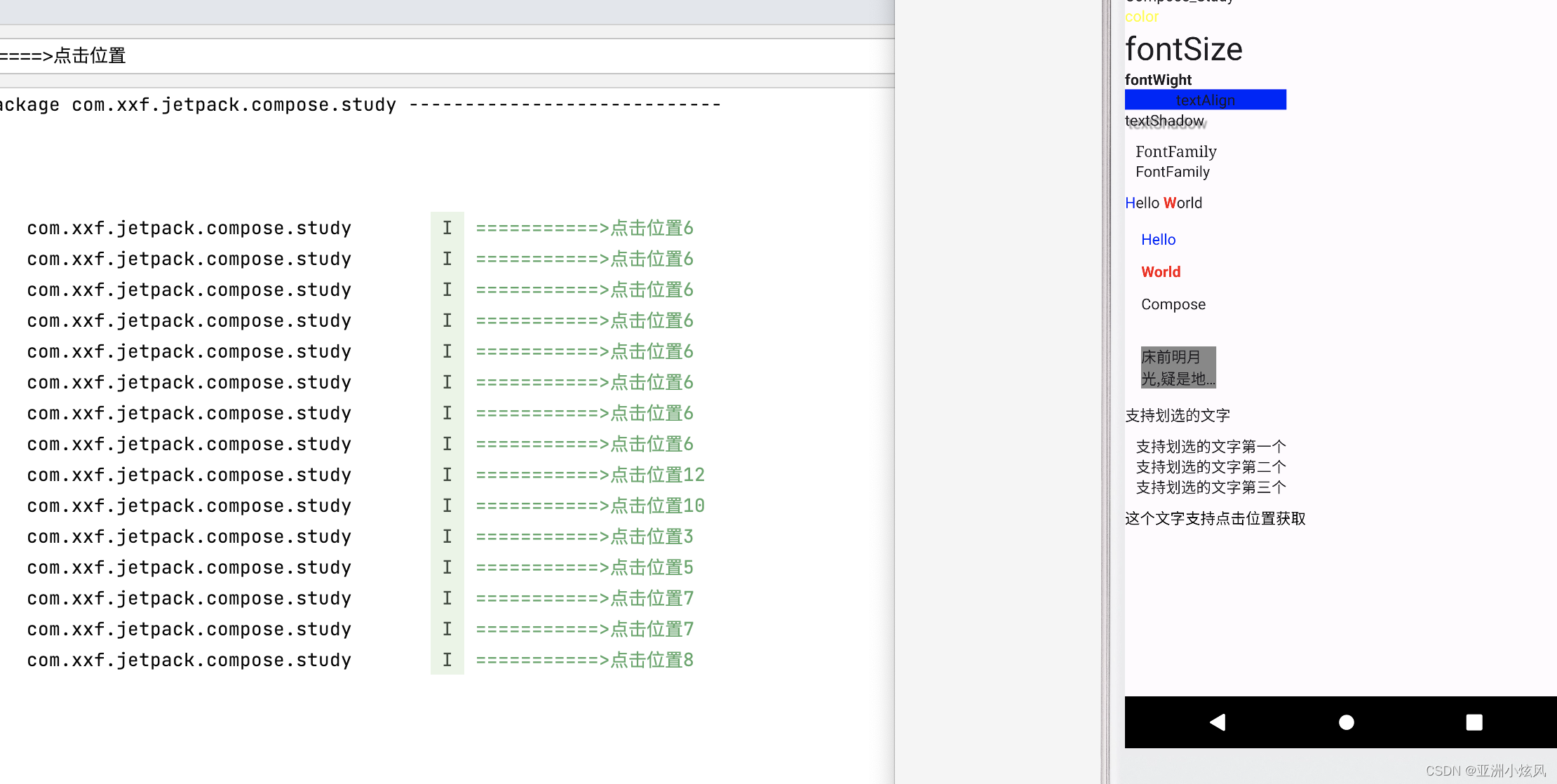
点击文字的位置
ClickableText可以获取点击文字的位置
@Composable
fun showClickableText(){
ClickableText(text = AnnotatedString("这个文字支持点击位置获取"), onClick ={ offset->
println("===========>点击位置${offset}");
Toast.makeText(this,"点击未知${offset}",Toast.LENGTH_SHORT);
})
}
所有实例demo地址