1. 背景说明
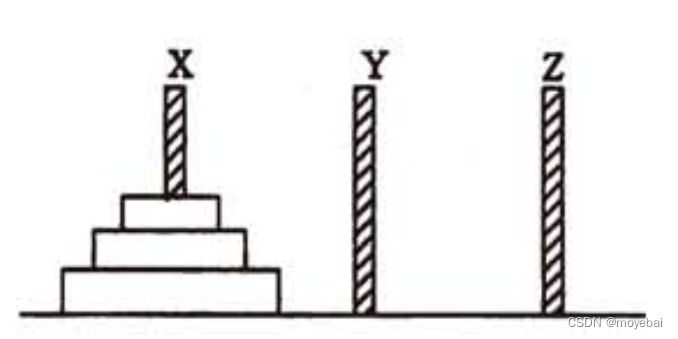
假设有 3 个分别命名为 X、Y 和 Z 的塔座,在塔座 X 上插有 n 个直径大小各不相同、依小到大编号为 1, 2,…,n 的圆盘。
现要求将 X 轴上的 n 个圆盘移至塔座 Z 上并仍按同样顺序叠排,圆盘移动时必须遵循下列规则:
(1) 每次只能移动一个圆盘;
(2) 圆盘可以插在 X、Y 和 Z 中的任一塔座上;
(3) 任何时刻都不能将一个较大的圆盘压在较小的圆盘之上。
2. 示例代码
1)hanoi.h
/* 汉诺塔定义头文件 */
#ifndef HANOI_H
#define HANOI_H
#define N 4 /* 初始汉诺塔层数 */
#define SIZE 3 /* 塔基个数 */
typedef struct {
int **plates;
int high[3];
} Tower;
void Init(int n, Tower *T);
void DestroyHanoi(Tower *T);
void PrintGraph(char t1, int n, char t2, Tower *T);
/* 算法 3.5, 将塔座 x 上按直径由小到大且自上而下编号为 1 至 n 的 n 个圆盘
按规则搬到塔座 z 上。y 可用作辅助塔座 */
void Hanoi(int n, char x, char y, char z, Tower *T, int *step);
#endif // !HANOI_H2) hanoi.c
/* 汉诺塔实现源文件 */
#include "hanoi.h"
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
void Init(int n, Tower *T)
{
/* Apply for a memory to storage the pointer of int */
T->plates = (int **)malloc(SIZE * sizeof(int *));
/* Apply for a memory to storage the information of the blocks */
for (int i = 0; i < SIZE; ++i) {
T->plates[i] = (int*)malloc(n * sizeof(int));
}
/* Initial the plate information */
T->high[0] = n;
T->high[1] = 0;
T->high[2] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
T->plates[0][i] = n - i;
T->plates[1][i] = 0;
T->plates[2][i] = 0;
}
}
void DestroyHanoi(Tower *T)
{
for (int i = 0; i < SIZE; ++i) {
free(T->plates[i]);
}
free(T->plates);
}
/* Show move n th block from plate t1 to plate t2 */
void PrintGraph(char t1, int n, char t2, Tower *T)
{
/* Check the parameters */
if ((t1 == t2) && (t1 != '\0')) {
printf("Error: Can not move block for the same plate to the same plate.\n");
return;
}
/* Move from */
if (t1 == 'x') {
T->plates[0][T->high[0] - 1] = 0;
--T->high[0];
}
else if (t1 == 'y') {
T->plates[1][T->high[1] - 1] = 0;
--T->high[1];
}
else if (t1 == 'z') {
T->plates[2][T->high[2] - 1] = 0;
--T->high[2];
}
/* Move to */
if (t2 == 'x') {
T->plates[0][T->high[0]] = n;
++T->high[0];
}
else if (t2 == 'y') {
T->plates[1][T->high[1]] = n;
++T->high[1];
}
else if (t2 == 'z') {
T->plates[2][T->high[2]] = n;
++T->high[2];
}
/* Initialize the block string graphic */
char **s = (char **)malloc((N + 2) * sizeof(char *));
for (int i = 0, j; i < N + 2; ++i) {
s[i] = (char *)malloc((N + 1) * sizeof(char));
for (j = 0; j < i; ++j) {
if (i == N + 1) {
s[i][j] = '-';
}
else {
s[i][j] = '*';
}
}
if (i == N + 1) {
s[i][j - 1] = '\0';
}
else {
s[i][j] = '\0';
}
}
// Eg: N = 2
// s[0][0] = '\0'
// s[1][0] = '*', s[1][1] = '\0'
// s[2][0] = '*', s[2][1] = '*', s[2][2] = '\0'
// s[3][0] = '-', s[3][1] = '-', s[3][2] = '-', s[3][2] = '\0'
for (int i = N - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
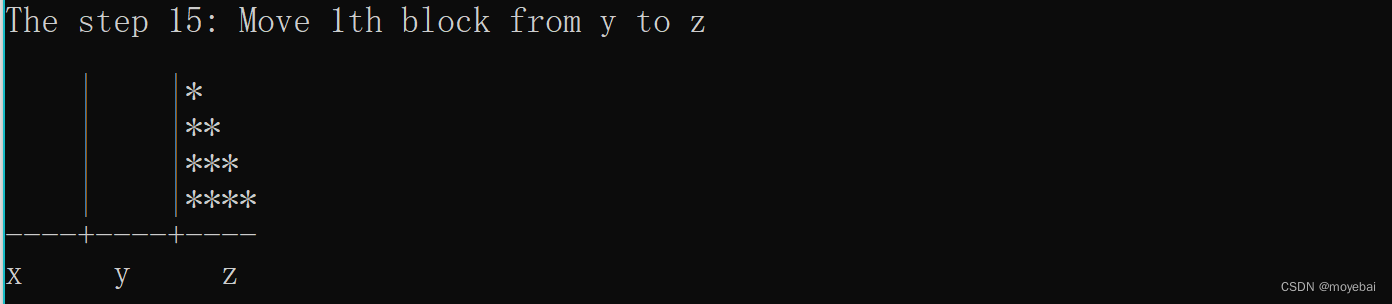
printf("%-*s|%-*s|%-*s\n", N, s[T->plates[0][i]], N, s[T->plates[1][i]], N, s[T->plates[2][i]]);
}
printf("%-*s+%-*s+%-*s\n", N, s[N + 1], N, s[N + 1], N, s[N + 1]);
printf("%-*s%-*s%-*s\n", N + 2, "x", N + 2, "y", N + 2, "z"); /* use "" not the '' */
for (int i = 0; i < N + 2; ++i) {
free(s[i]);
}
free(s);
}
static void Move(char x, int n, char z, Tower *T, int *step)
{
/* If use (*step)++, do not forget add() cause the priority of the ++ is higher than *
You can also not add the() instead use ++*step, no problem but bad reading */
++(*step);
printf("The step %2d: Move %dth block from %c to %c\n\n", *step, n, x, z);
PrintGraph(x, n, z, T);
printf("\n");
}
/* 算法 3.5, 将塔座 x 上按直径由小到大且自上而下编号为 1 至 n 的 n 个圆盘
按规则搬到塔座 z 上。y 可用作辅助塔座 */
void Hanoi(int n, char x, char y, char z, Tower *T, int *step)
{
if (n == 1) {
Move(x, 1, z, T, step);
}
else {
Hanoi(n - 1, x, z, y, T, step);
Move(x, n, z, T, step);
Hanoi(n - 1, y, x, z, T, step);
}
}3) main.c
/* 汉诺塔主函数源文件 */
/* Note: Consider use stack to storage the information of the hanoi tower */
#include "hanoi.h"
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
char x = 'x', y = 'y', z = 'z';
printf("Initialize the %d layers hanoi tower:\n\n", N);
Tower T = { 0 };
Init(N, &T);
PrintGraph('\0', 0, '\0', &T);
printf("\n");
int step = 0;
Hanoi(N, x, y, z, &T, &step);
DestroyHanoi(&T);
return 0;
}3. 输出示例