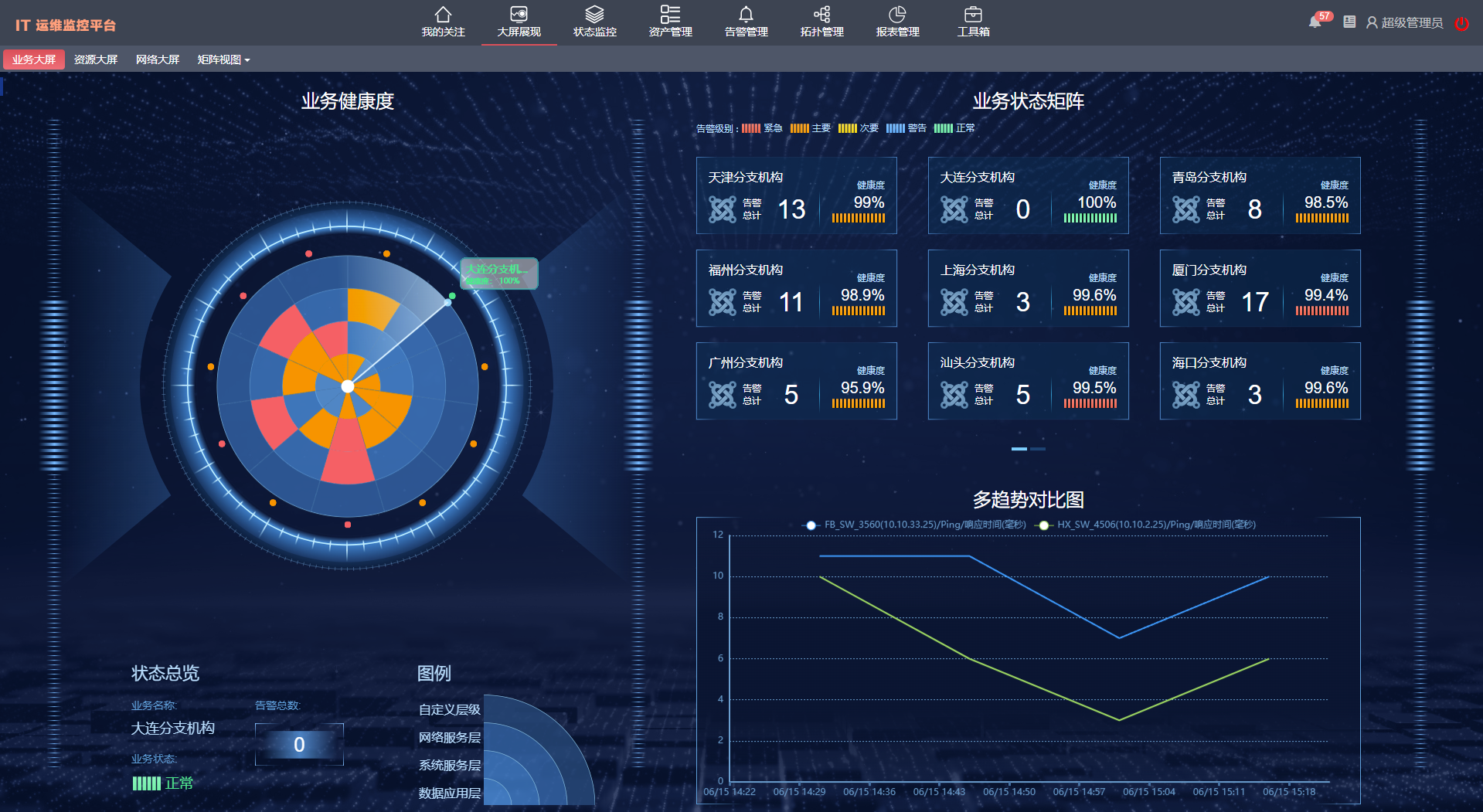
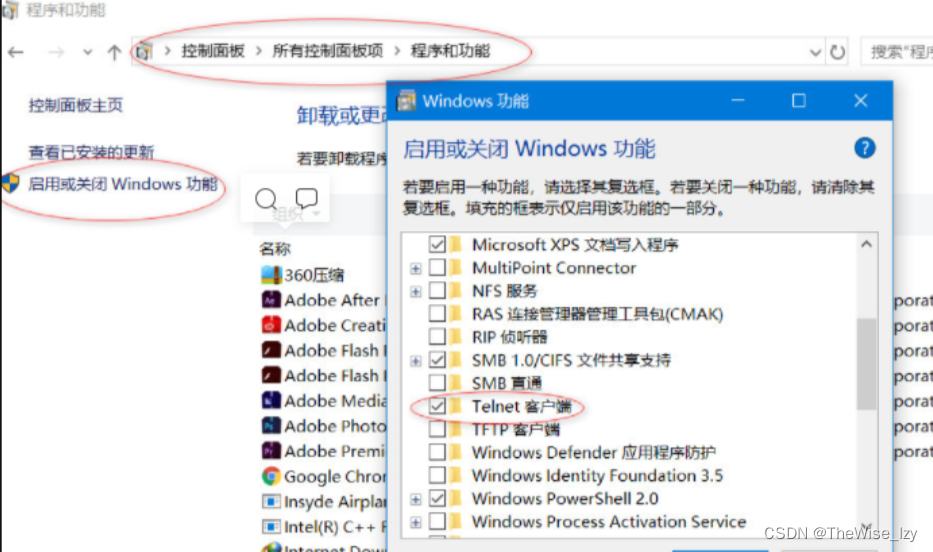
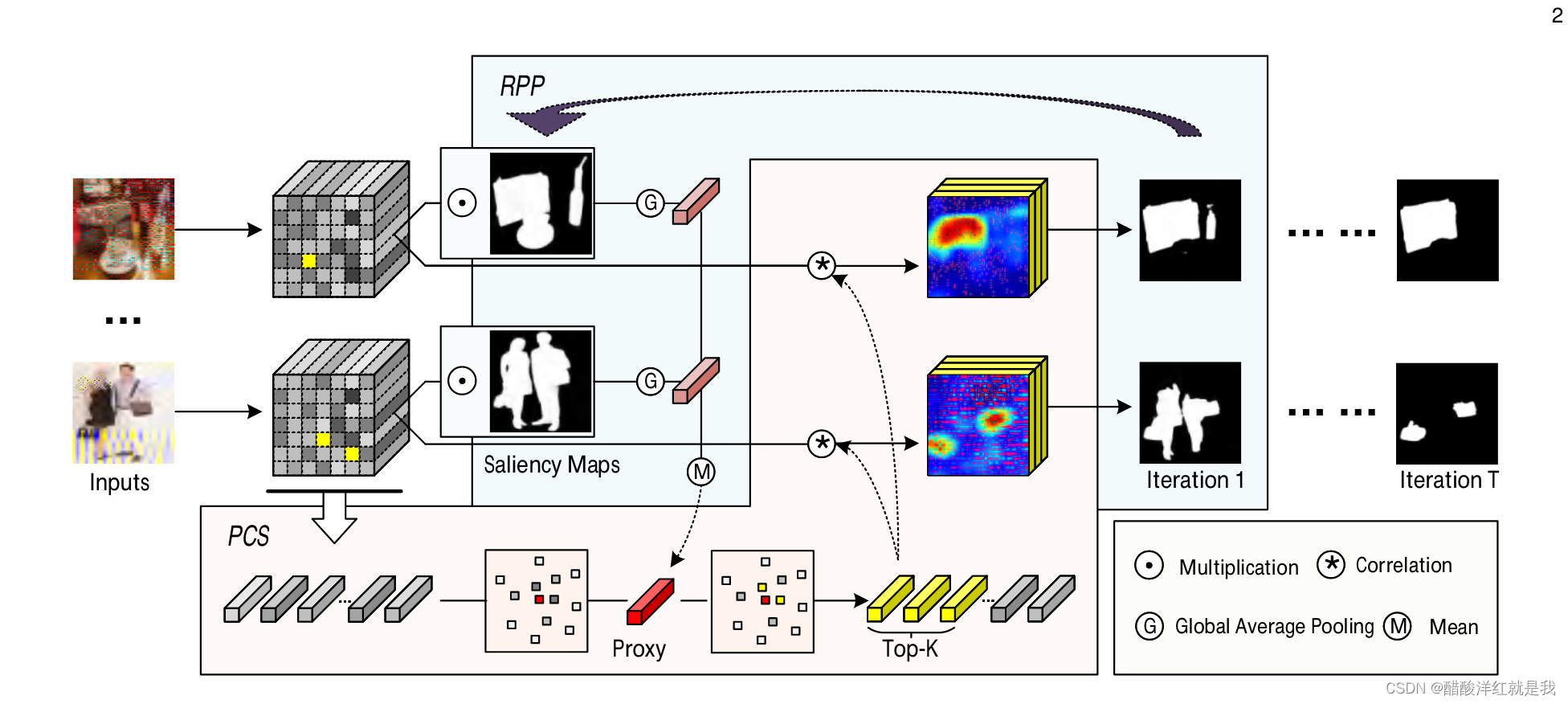
目录
- 1. pcl中的矩阵变换是什么
- 2. 举例:如何做矩阵变换
1. pcl中的矩阵变换是什么
通过激光传感器等设备获得的3d点云在拼接成更大场景时,需要对点云数据进行旋转和平移操作。而旋转和平移操作,就可以通过矩阵变换来实现。
- 点的表示
对于点云中的一个点
p
p
p,其表示为
p
=
[
x
y
z
1
]
p=\begin{bmatrix} x \\ y \\ z \\ 1 \\ \end{bmatrix}
p=
xyz1
这里,
(
x
,
y
,
z
)
(x, y, z)
(x,y,z)为点的空间坐标,第4维的1是什么?其实第4维是人为设置的,方便后面用矩阵乘法表示平移操作。
- 点的平移
如将上面的
p
p
p点沿着x轴远离原点平移8个单位,直观上就可以得到平移后的结果
p
′
p^{\prime}
p′
p
′
=
[
x
+
8
y
z
1
]
p^{\prime}=\begin{bmatrix} x+8 \\ y \\ z \\ 1 \\ \end{bmatrix}
p′=
x+8yz1
其实等价于下面的矩阵乘法
p
′
=
A
⋅
p
=
[
1
0
0
a
0
1
0
b
0
0
1
c
0
0
0
1
]
⋅
[
x
y
z
1
]
=
[
x
+
a
y
+
b
z
+
c
1
]
p^{\prime}=A\cdot p= \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0& 0& a \\ 0 & 1& 0& b\\ 0& 0& 1& c \\ 0& 0& 0& 1 \\ \end{bmatrix}\cdot \begin{bmatrix} x \\ y \\ z \\ 1 \\ \end{bmatrix}= \begin{bmatrix} x+a \\ y+b \\ z+c \\ 1 \\ \end{bmatrix}
p′=A⋅p=
100001000010abc1
⋅
xyz1
=
x+ay+bz+c1
可以看到,通过给三维点坐标增加一维,可以非常方便的通过矩阵乘法实现点的平移操作。注意到,这里的矩阵 A A A总是 4 × 4 4\times4 4×4方阵。
- 点的旋转
这里指的是点按照某个方向围绕原点旋转
θ
\theta
θ角度。比如,三维坐标系里绕着x轴逆时针旋转,如下所示(可参考博客《PCL点云库——旋转平移矩阵》)
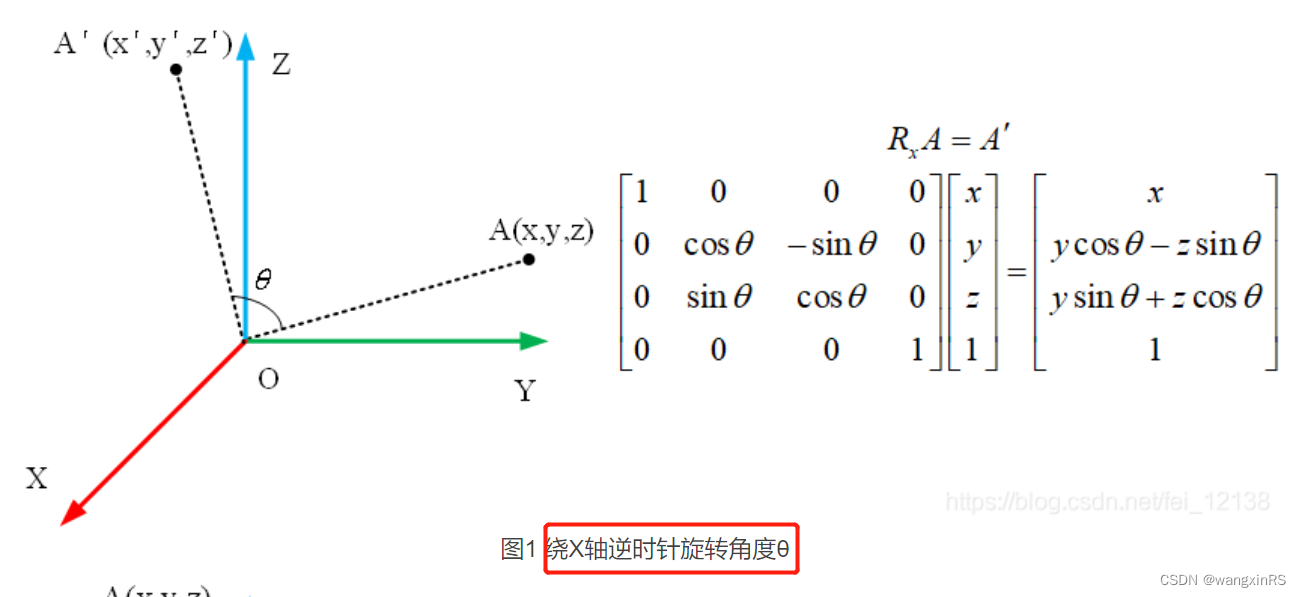
任意方向旋转任意角度,可通过绕着x轴旋转、绕着y轴旋转、绕着z轴旋转等三个基本旋转操作组合而成。而绕着x轴旋转、绕着y轴旋转、绕着z轴旋转可分别通过矩阵表示。
记绕着x轴逆时针旋转
θ
\theta
θ角度的操作为
R
x
(
θ
)
R_x(\theta)
Rx(θ),则该操作对应的矩阵为
p
′
=
R
x
(
θ
)
⋅
p
=
[
1
0
0
0
0
c
o
s
θ
−
s
i
n
θ
0
0
s
i
n
θ
c
o
s
θ
0
0
0
0
1
]
⋅
[
x
y
z
1
]
=
[
x
y
⋅
c
o
s
θ
−
z
⋅
s
i
n
θ
y
⋅
s
i
n
θ
+
z
⋅
c
o
s
θ
1
]
p^{\prime}=R_x(\theta)\cdot p= \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0& 0& 0 \\ 0 & cos\theta& -sin\theta& 0\\ 0& sin\theta& cos\theta& 0 \\ 0& 0& 0& 1 \\ \end{bmatrix}\cdot \begin{bmatrix} x \\ y \\ z \\ 1 \\ \end{bmatrix}= \begin{bmatrix} x \\ y \cdot cos\theta-z\cdot sin\theta \\ y \cdot sin\theta+z\cdot cos\theta \\ 1 \\ \end{bmatrix}
p′=Rx(θ)⋅p=
10000cosθsinθ00−sinθcosθ00001
⋅
xyz1
=
xy⋅cosθ−z⋅sinθy⋅sinθ+z⋅cosθ1
记绕着y轴逆时针旋转
θ
\theta
θ角度的操作为
R
y
(
θ
)
R_y(\theta)
Ry(θ),则该操作对应的矩阵为
p
′
=
R
y
(
θ
)
⋅
p
=
[
c
o
s
θ
0
s
i
n
θ
0
0
1
0
0
−
s
i
n
θ
0
c
o
s
θ
0
0
0
0
1
]
⋅
[
x
y
z
1
]
=
[
x
⋅
c
o
s
θ
+
z
⋅
s
i
n
θ
y
−
x
⋅
s
i
n
θ
+
z
⋅
c
o
s
θ
1
]
p^{\prime}=R_y(\theta)\cdot p= \begin{bmatrix} cos\theta & 0& sin\theta& 0 \\ 0 & 1&0 & 0\\ -sin\theta&0 & cos\theta& 0 \\ 0& 0& 0& 1 \\ \end{bmatrix}\cdot \begin{bmatrix} x \\ y \\ z \\ 1 \\ \end{bmatrix}= \begin{bmatrix} x \cdot cos\theta+z\cdot sin\theta \\ y \\ -x \cdot sin\theta+z\cdot cos\theta \\ 1 \\ \end{bmatrix}
p′=Ry(θ)⋅p=
cosθ0−sinθ00100sinθ0cosθ00001
⋅
xyz1
=
x⋅cosθ+z⋅sinθy−x⋅sinθ+z⋅cosθ1
记绕着z轴逆时针旋转
θ
\theta
θ角度的操作为
R
z
(
θ
)
R_z(\theta)
Rz(θ),则该操作对应的矩阵为
p
′
=
R
z
(
θ
)
⋅
p
=
[
c
o
s
θ
−
s
i
n
θ
0
0
s
i
n
θ
c
o
s
θ
0
0
0
0
1
0
0
0
0
1
]
⋅
[
x
y
z
1
]
=
[
x
⋅
c
o
s
θ
−
y
⋅
s
i
n
θ
x
⋅
s
i
n
θ
+
y
⋅
c
o
s
θ
z
1
]
p^{\prime}=R_z(\theta)\cdot p= \begin{bmatrix} cos\theta & -sin\theta& 0& 0 \\ sin\theta & cos\theta&0& 0\\ 0& 0& 1& 0 \\ 0& 0& 0& 1 \\ \end{bmatrix}\cdot \begin{bmatrix} x \\ y \\ z \\ 1 \\ \end{bmatrix}= \begin{bmatrix} x \cdot cos\theta-y\cdot sin\theta \\ x \cdot sin\theta+y\cdot cos\theta \\ z \\ 1 \\ \end{bmatrix}
p′=Rz(θ)⋅p=
cosθsinθ00−sinθcosθ0000100001
⋅
xyz1
=
x⋅cosθ−y⋅sinθx⋅sinθ+y⋅cosθz1
2. 举例:如何做矩阵变换
只要实现矩阵变换,就可以做点云的旋转和平移。PCL库中做矩阵变换有两种方法,分别为Eigen::Matrix4f和Eigen::Affine3f。Eigen::Matrix4f需要手动构建旋转和平移矩阵,较易出错;Eigen::Affine3f则接近于人类操作步骤,将平移操作和旋转操作做成函数,调用即可。
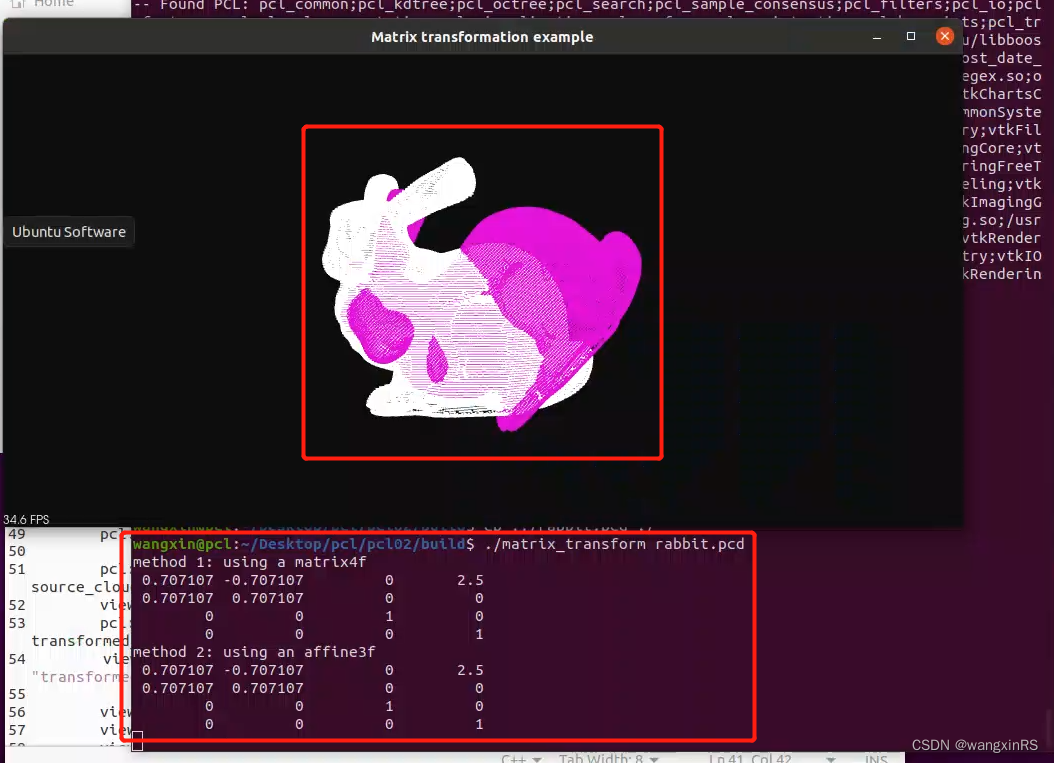
举例:将点云数据先沿着x轴平移2.5,然后绕着z轴逆时针旋转 π 4 \frac{\pi}{4} 4π的角度。
实现主要参考双愚的代码;兔子pcd数据从博客《PCL读取PCD文件的数据》中获取
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1v6mjPjwd7fIqUSjlIGTIGQ
提取码:zspx
- matrix_transform.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h>
#include <pcl/io/ply_io.h>
#include <pcl/point_cloud.h>
#include <pcl/console/parse.h>
#include <pcl/common/transforms.h>
#include <pcl/visualization/pcl_visualizer.h>
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr source_cloud(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>());
if (pcl::io::loadPCDFile(argv[1], *source_cloud) < 0)
{
std::cout << "Error loading point cloud " << argv[1] << std::endl;
return -1;
}
float theta = M_PI / 4; // 旋转角度
//方法一: Matrix4f
Eigen::Matrix4f transform_1 = Eigen::Matrix4f::Identity();
transform_1(0, 0) = std::cos(theta);
transform_1(0, 1) = -std::sin(theta);
transform_1(1, 0) = std::sin(theta);
transform_1(1, 1) = std::cos(theta);
transform_1(0, 3) = 2.5;
printf("method 1: using a matrix4f\n");
std::cout << transform_1 << std::endl;
//方法二: Affine3f
Eigen::Affine3f transform_2 = Eigen::Affine3f::Identity();
transform_2.translation() << 2.5, 0.0, 0.0;
transform_2.rotate(Eigen::AngleAxisf(theta, Eigen::Vector3f::UnitZ()));
printf("method 2: using an affine3f\n");
std::cout << transform_2.matrix() << std::endl;
// excuting the transformation(执行平移和旋转操作)
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr transformed_cloud(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>());
pcl::transformPointCloud(*source_cloud, *transformed_cloud, transform_2);
// visualization(可视化)
pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer viewer("Matrix transformation example");
pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<pcl::PointXYZ> source_cloud_color_handler(source_cloud, 255, 255, 255);
viewer.addPointCloud(source_cloud, source_cloud_color_handler, "original_cloud");
pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<pcl::PointXYZ> transformed_cloud_color_handler(transformed_cloud, 230, 20, 220);
viewer.addPointCloud(transformed_cloud, transformed_cloud_color_handler, "transformed_cloud");
viewer.addCoordinateSystem(1.0, "cloud", 0);
viewer.setBackgroundColor(0.05, 0.05, 0.05, 0);
viewer.setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_POINT_SIZE, 2, "original_cloud");
viewer.setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_POINT_SIZE, 2, "transformed_cloud");
while (!viewer.wasStopped())
{
viewer.spinOnce();
}
return 0;
}
- CMakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.6 FATAL_ERROR)
project(pcl-matrix_transform)
find_package(PCL 1.7 REQUIRED)
add_executable (matrix_transform matrix_transform.cpp)
target_link_libraries (matrix_transform ${PCL_LIBRARIES})
- 运行
./matrix_transform rabbit.pcd