文章目录
- 一、vector 类的模拟实现

vector 是一个动态增长的数组,可以存储任意类型
模板参数 T 表示存储元素的类型,Alloc 是空间配置器,一般不用传
vector 的接口使用和 string 类似,参考 string
一、vector 类的模拟实现
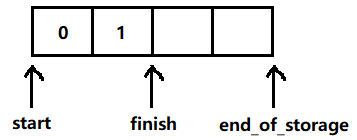
vector 类中成员的意义:
- start:指向动态数组第一个元素
- finish:指向动态数组最后一个元素的下一个位置
- end_of_storage:指向动态数组已开辟空间的最后一个空间的下一个位置
vector 类常用接口模拟实现:
//test.cpp
#include "vector.h"
int main()
{
starrycat::vector_test4();
return 0;
}
//vector.h
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <assert.h>
#include <algorithm>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
namespace starrycat
{
template<class T>
class vector
{
public:
typedef T* iterator;
typedef const T* const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return start;
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
return start;
}
iterator end()
{
return finish;
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return finish;
}
//默认构造函数
vector<T>()
{}
//n 个 value 构造
//const 引用会延长匿名对象的生命周期
vector<T>(size_t n, const T& value = T())
{
reserve(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
start[i] = value;
}
finish = start + n;
}
//避免内置类型构造时调用迭代器区间构造
//当第一个参数为整形家族时,需要重载函数
vector<T>(int n, const T& value = T())
{
reserve(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
start[i] = value;
}
finish = start + n;
}
//迭代器区间构造
template<class InputIterator>
vector<T>(InputIterator first, InputIterator last)
{
while (first != last)
{
push_back(*first);
++first;
}
}
//拷贝构造
//vector<T>(const vector<T>& v)
//{
// //开空间
// reserve(v.capacity());
// //深拷贝 vector 数据
// for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); ++i)
// {
// start[i] = v.start[i];
// }
// finish = start + v.size();
// end_of_storage = start + v.capacity();
//}
//现代写法
vector<T>(const vector<T>& v)
{
vector<T> tmp(v.begin(), v.end());
swap(tmp);
}
//赋值重载
//vector<T>& operator=(const vector<T>& v)
//{
// if (this != &v)
// {
// T* tmp = new T[v.capacity() == 0 ? 4 : v.capacity()];
// //深拷贝数据
// for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); ++i)
// {
// tmp[i] = v.start[i];
// }
// delete[] start;
// start = tmp;
// finish = start + v.size();
// end_of_storage = start + v.capacity();
// }
// return *this;
//}
//现代写法
vector<T>& operator=(vector<T> v)
{
swap(v);
return *this;
}
void swap(vector<T>& v)
{
std::swap(start, v.start);
std::swap(finish, v.finish);
std::swap(end_of_storage, v.end_of_storage);
}
//析构函数
~vector<T>()
{
delete[] start;
start = nullptr;
finish = nullptr;
end_of_storage = nullptr;
}
size_t size() const
{
return finish - start;
}
size_t capacity() const
{
return end_of_storage - start;
}
T& operator[](size_t pos)
{
assert(pos < size());
return start[pos];
}
const T& operator[](size_t pos) const
{
assert(pos < size());
return start[pos];
}
void reserve(size_t n)
{
if (n > capacity())
{
//深拷贝
T* tmp = new T[n];
//vector 中如果是自定义类型,也需要深拷贝
//需要提前保存 sz,否则释放空间后 finish 位置就不对了
const size_t sz = size();
for (int i = 0; i < sz; ++i)
{
tmp[i] = start[i];
}
delete[] start;
start = tmp;
finish = start + sz;
end_of_storage = start + n;
}
}
void resize(size_t n, T value = T())
{
if (n < size())
{
finish = start + n;
}
else
{
if (n > capacity())
{
reserve(n);
}
while (finish != start + n)
{
*finish = value;
++finish;
}
}
}
bool empty() const
{
return start == finish;
}
void push_back(const T& x)
{
//扩容
//if (finish == end_of_storage)
//{
// reserve(capacity() == 0 ? 4 : 2 * capacity());
//}
插入数据
//*finish = x;
//++finish;
insert(end(), x);
}
void pop_back()
{
//assert(!empty());
//--finish;
erase(end() - 1);
}
iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& value)
{
assert(pos <= finish);
//扩容
if (finish == end_of_storage)
{
//需要更新 pos
size_t posIndex = pos - start;
reserve(capacity() == 0 ? 4 : 2 * capacity());
pos = start + posIndex;
}
//移动数据
iterator cur = end();
while (cur != pos)
{
*cur = *(cur - 1);
--cur;
}
*pos = value;
++finish;
return pos;
}
void erase(iterator pos)
{
assert(pos < finish);
iterator cur = pos + 1;
while (cur != end())
{
*(cur - 1) = *cur;
++cur;
}
--finish;
}
private:
iterator start = nullptr;
iterator finish = nullptr;
iterator end_of_storage = nullptr;
};
void Print(const vector<int>& v)
{
vector<int>::const_iterator it = v.begin();
while (it != v.end())
{
//(*it) *= 2;
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); ++i)
{
//v[i] *= 2;
cout << v[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void vector_test1()
{
vector<int> v;
v.push_back(1);
v.push_back(2);
v.push_back(3);
v.push_back(4);
v.push_back(5);
vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin();
while (it != v.end())
{
(*it) *= 10;
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
for (auto e : v)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); ++i)
{
v[i] = i;
cout << v[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
Print(v);
}
void vector_test2()
{
//3 个 1 构造
vector<int> v1(3, 1);
for (auto e : v1)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
vector<int> v2(3);
for (auto e : v2)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//3 个 "111" 构造
std::string s1 = "111";
vector<std::string> v3(3, s1);
for (const std::string& e : v3)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
vector<std::string> v4(3);
for (const std::string& e : v4)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//3 个 v1 构造
vector<vector<int>> v5(3, v1);
for (const vector<int>& e1 : v5)
{
for (auto e2 : e1)
{
cout << e2 << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
cout << endl;
//迭代器区间构造
std::string s2 = "abcde";
vector<int> v6(s2.begin(), s2.end());
for (auto e : v6)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
int arr[] = { 4, 2, 1, 5, 34, 9 };
vector<int> v7(arr + 1, arr + sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]));
for (auto e : v7)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//拷贝构造
vector<int> v8(v7);
for (auto e : v8)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void vector_test3()
{
vector<int> v;
v.push_back(1);
v.push_back(2);
v.push_back(3);
v.push_back(4);
v.push_back(5);
for (auto e : v)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
v.pop_back();
v.pop_back();
v.pop_back();
for (auto e : v)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
v.resize(10, 1);
for (auto e : v)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
v.resize(3);
for (auto e : v)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl << endl;
vector<std::string> vs;
vs.push_back("11111");
vs.push_back("22222");
vs.push_back("33333");
vs.push_back("44444");
vs.push_back("55555");
for (const std::string& e : vs)
{
cout << e << endl;
}
cout << endl;
vs.resize(10, "xxxxx");
for (const std::string& e : vs)
{
cout << e << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
void vector_test4()
{
vector<int> v;
v.push_back(1);
v.push_back(2);
v.push_back(3);
v.push_back(4);
//v.push_back(5);
for (auto e : v)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//如果插入时 vector 扩容了,则迭代器 pos 会失效
//如果还想使用 pos,则可以接收 insert 返回值
vector<int>::iterator pos = std::find(v.begin(), v.end(), 2);
v.insert(pos, 20);
for (auto e : v)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//如果 erase end() - 1 位置的数据,则迭代器失效
//因此认为 erase(pos) 后,迭代器 pos 失效
pos = v.end() - 1;
v.erase(pos);
for (auto e : v)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
}