0.前言

1.for_each
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// 常用遍历算法 for_each
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
//普通函数
void print01(int val)
{
cout << val << " ";
}
//仿函数
class Print02
{
public:
void operator()(int val)
{
cout << val << " ";
}
};
void test01()
{
vector<int>v;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
v.push_back(i);
}
//遍历算法
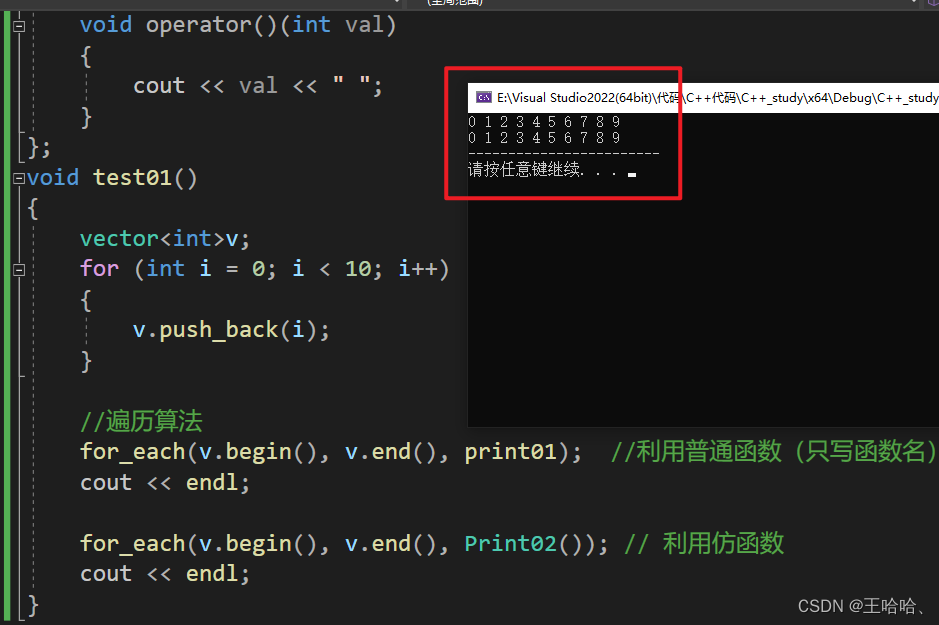
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print01); //利用普通函数(只写函数名)
cout << endl;
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), Print02()); // 利用仿函数
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
cout << "------------------------" << endl;
//test02();
//cout << "------------------------" << endl << endl;
//test03();
//**************************************
system("pause");
return 0;
}
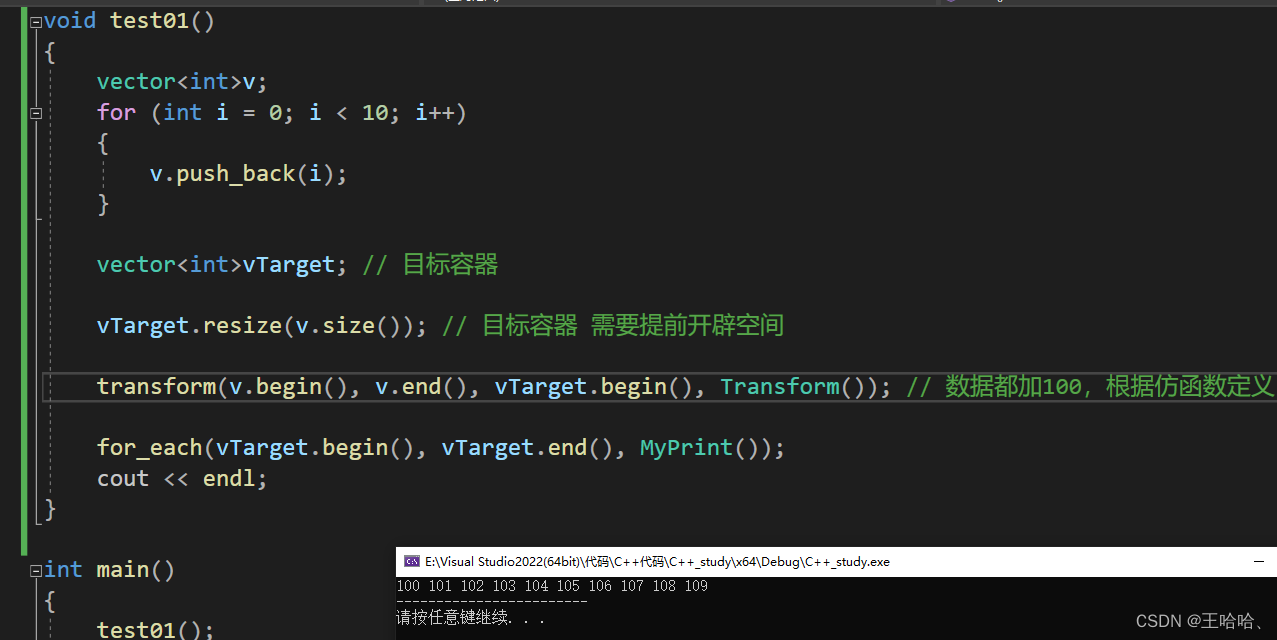
2.transform
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// 常用遍历算法 transform
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
//仿函数
class Transform
{
public:
int operator()(int val)
{
return val + 100;
}
};
//打印输出
class MyPrint
{
public:
void operator()(int val)
{
cout << val << " ";
}
};
void test01()
{
vector<int>v;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
v.push_back(i);
}
vector<int>vTarget; // 目标容器
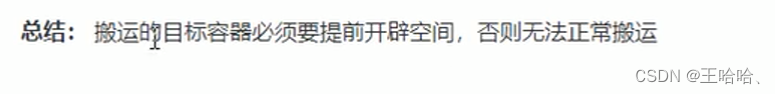
vTarget.resize(v.size()); // 目标容器 需要提前开辟空间
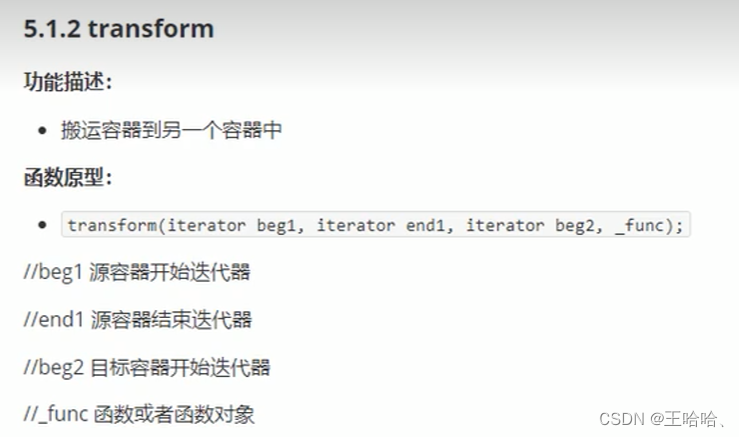
transform(v.begin(), v.end(), vTarget.begin(), Transform()); // 数据都加100,根据仿函数定义
for_each(vTarget.begin(), vTarget.end(), MyPrint());
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
cout << "------------------------" << endl;
//test02();
//cout << "------------------------" << endl << endl;
//test03();
//**************************************
system("pause");
return 0;
}