1. 数据存储
1.1 知识点
(1)掌握Android数据存储的分类;
(2)可以使用SharedPreferences存储数据。
1.2 具体内容
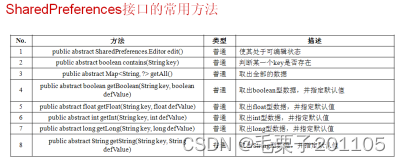
对于我们数据的存储而言,Android一共提供了5个数据存储的方式:SharedPreferences存储、文件存储方式、Sqlite存储、Content Provider存储、网络存储。


在Android之中操作,都需要使用Activity程序进行支持,本次课程我们只关注操作方法,所有不做过多的页面展示。
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal"
>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="请输入键:"
/>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/usernameKey"
android:layout_width="200px"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal"
>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="请输入值:"
/>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/username"
android:layout_width="200px"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
</LinearLayout>
<Button
android:id="@+id/mybut"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="保存"
/>
</LinearLayout>
现在的关键问题就在于编写Activity程序。
package com.example.sharedpreferences;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.SharedPreferences;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class SharedPreferencesActivity extends Activity {
private TextView username = null;
private TextView age = null;
public static final String FILMNAME = "wanczy";
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
super.setContentView(R.layout.activity_shared_preferences);
this.age = (TextView) super.findViewById(R.id.age);
this.username = (TextView) super.findViewById(R.id.username);
SharedPreferences share = super.getSharedPreferences(FILMNAME, Activity.MODE_PRIVATE);
this.username.setText("用户名:"+ share.getString("username", "无所谓默认值"));//根据键取得值并放入到TextView中
this.age.setText("年龄:"+ share.getInt("年龄",0));
}
}
和在Java中使用属性存储操作上有相似之处,但是Java中的属性存储已经过时,现在存储比较流行的是xml存储。此时程序就已经完成了,默认情况下,存储文件都会保存在手机里面,后缀为.xml,现在程序已经可以保存,当然也可以读取咯。
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<TextView
android:id="@+id/username"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/age"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
</LinearLayout>package com.example.sharedpreferences;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.SharedPreferences;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class SharedPreferencesActivity extends Activity {
private TextView username = null;
private TextView age = null;
public static final String FILMNAME = "wanczy";
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
super.setContentView(R.layout.activity_shared_preferences);
this.age = (TextView) super.findViewById(R.id.age);
this.username = (TextView) super.findViewById(R.id.username);
SharedPreferences share = super.getSharedPreferences(FILMNAME, Activity.MODE_PRIVATE);
this.username.setText("用户名:"+ share.getString("username", "无所谓默认值"));//根据键取得值并放入到TextView中
this.age.setText("年龄:"+ share.getInt("age",0));
}
}
对于SharedPreferences存储而言,并没有太多复杂操作,实际应用当中,使用SharedPreferences可以保存一些配置信息:例如,你正在看小说,希望关闭之后,下次打开能够在你最后浏览的进度点,那么这种情况下就可以使用SharedPreferences进行保存 。
1.3 小结
(1)SharedPreferences可以实现简单的数据存储功能实现,可以利用super.getSharedPreferences()方法取得实例;
2. 文件存储
2.1 知识点
(1)掌握Activity对文件存储的若干操作;
(2)可以实现文件的保存和读取操作。
2.2 具体内容
对于文件存储这块,必须要先掌握IO的基本操作,InputStream,OutputStream。
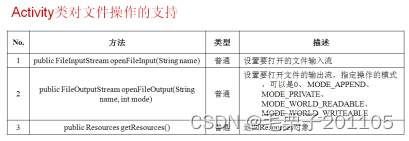
了解一下IO流对文件的操作:
·使用File找到一个指定的文件
·使用字节流或者字符流的子类为父类进行实例化
·完成输入/输出的操作
·关闭流
举例:向文件中写入内容—输出,我们的输入输出是对于程序而言。
范例:本次还是以文件保存为主,不再进行页面的编写。
package com.example.filesave;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.PrintStream;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
public class FileSaveActivity extends Activity {
public static final String FILENAME = "wanczy.txt";
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
super.setContentView(R.layout.activity_file_save);
FileOutputStream output = null;
PrintStream out = null;
try {
output = super.openFileOutput(FILENAME, Activity.MODE_PRIVATE);//使用Activity提供的方法创建了一个文件字节输出流
//在IO操作中,打印流操作是最方便的
out = new PrintStream(output);
out.print("姓名:毛栗子");
out.print("年龄:30");
out.print("地址:兰州市庆阳路128号");
} catch (Exception e) {
} finally{
out.close();
}
}
}那么现在既然可以写入内容到文件,当然我们也可以将内容从文件中拿出来,那么对于读取文件,那肯定需要将文件内容放入到TextView中显示。
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/msg"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"/>
</LinearLayout>
以后的读取的内容就放在msg这个文本显示组件上,如果大家学习过Java的话,应该很清楚,使用PrintStream对于输出来说很方便,对于输入呢,使用什么最方便呢?使用扫描类肯定是最方便的,就是Scanner
package com.example.filesave;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.util.Scanner;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class FileSaveActivity extends Activity {
private static final String FILENAME = "wanczy.txt";
private TextView msg = null;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
super.setContentView(R.layout.activity_file_save);
this.msg = (TextView) super.findViewById(R.id.msg);
FileInputStream input = null;
Scanner sc = null;
try {
input = super.openFileInput(FILENAME);//使用Activity提供的方法创建了一个文件字节输出流
//在IO操作中,打印流操作是最方便的
sc = new Scanner(input);
String content = sc.next();//读取数据
this.msg.setText("读取的信息为:"+content);
} catch (Exception e) {
} finally{
sc.close();
}
}
}以上的这种写法就是比较标准的程序。

范例:向SD卡上保存文件
package com.example.filesave;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.PrintStream;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
public class FileSaveActivity extends Activity {
public static final String FILENAME = "/mnt/sdcard/wanczy/jjm/wanczy.txt";
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
super.setContentView(R.layout.activity_file_save);
FileOutputStream output = null;
PrintStream out = null;
try {
File file = new File(FILENAME);
if(!file.getParentFile().exists()){//如果文件夹不存在
file.mkdirs();
}
output = new FileOutputStream(file,true);//表示创建了一个文件的字节输出流 ,这种写法不能进行文件内容的追加
//在IO操作中,打印流操作是最方便的
out = new PrintStream(output);
out.print("姓名:毛栗子");
out.print("年龄:30");
out.print("地址:兰州市庆阳路128号");
} catch (Exception e) {
} finally{
if(null != out){
out.close();
}
}
}
}
范例:向SD卡上保存文件
现在虽然程序写好了,既然是对SD card的操作,那么一定需要具备操作sdcard的权限。
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE"/>
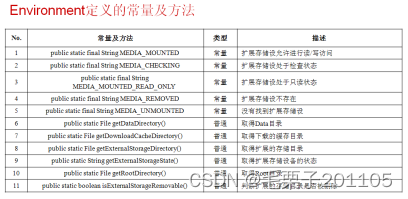
现在我们只需要使用此类去判断sdcard是否存在。
if(Environment.getExternalStorageState().equals(Environment.MEDIA_MOUNTED)){//表示存储目录能够进行你读写操作
System.out.println("表示sdcard存在");
}package com.example.filesave;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.PrintStream;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.Environment;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class FileSaveActivity extends Activity {
public static final String FILENAME = "/mnt/sdcard/wanczy/jjm/wanczy.doc";
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
super.setContentView(R.layout.activity_file_save);
if (Environment.getExternalStorageState().equals(
Environment.MEDIA_MOUNTED)) {// 表示存储目录能够进行你读写操作
FileOutputStream output = null;
PrintStream out = null;
try {
File file = new File(FILENAME);
if (!file.getParentFile().exists()) {// 如果文件夹不存在
file.mkdirs();
}
output = new FileOutputStream(file, true);// 表示创建了一个文件的字节输出流
// ,这种写法不能进行文件内容的追加
// 在IO操作中,打印流操作是最方便的
out = new PrintStream(output);
out.print("《幽窗小记》 宠若不惊 闲看庭前花开花落 去留无意 漫随天外云卷云舒");
} catch (Exception e) {
} finally {
if (null != out) {
out.close();
}
}
}else{
Toast.makeText(this, "sdcard不存在,请使用其他保存路径", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}
}
这个程序更加适合在真机上进行操作。现在已经完成输出的功能,现在进行一些输入的显示。
package com.example.filesave;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.util.Scanner;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.Environment;
import android.widget.TextView;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class FileSaveActivity extends Activity {
private static final String FILENAME = "wanczy.doc";
private static final String DIR = "CSDN/mlz";
private TextView msg = null;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
super.setContentView(R.layout.activity_file_save);
this.msg = (TextView) super.findViewById(R.id.msg);
if (Environment.getExternalStorageState().equals(
Environment.MEDIA_MOUNTED)) {
FileInputStream input = null;
Scanner sc = null;
try {
File file = new File(Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory().toString()+File.separator+DIR+File.separator+FILENAME);
input = new FileInputStream(file);
sc = new Scanner(input);
while(sc.hasNext()){
this.msg.append( sc.next());
}
} catch (Exception e) {
} finally {
sc.close();
}
}else{
Toast.makeText(this, "sdcard不存在,请使用其他保存路径", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}
}
以上保存在sdcard的程序与之前的不保存在sdcard并没有本质的区别。

package com.example.filesave;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.Scanner;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.res.Resources;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class FileSaveActivity extends Activity {
private TextView msg = null;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
super.setContentView(R.layout.activity_file_save);
this.msg = (TextView) super.findViewById(R.id.msg);
Resources res = super.getResources();//取得Resources对象
InputStream in = res.openRawResource(R.raw.wanczy);//将资源文件加入到字节输入流、
Scanner sc = null;
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
try {
sc = new Scanner(in);
while(sc.hasNext()){
sb.append(sc.next()+"\n");
}
}catch(Exception e){
}finally{
sc.close();
}
this.msg .setText(sb.toString());
}
}
2.3 小结
(1)使用文件存储可以保存更加丰富的数据;
(2)在Android之中可以使用XML的DOM和SAX解析方式进行文件操作;
(3)在Android之中提供了PULL解析用于完成XML解析;
(4)JSON可以进行简便的信息传送,性能更高;
(5)可以将要读取的文件配置到项目的res文件目录之中,这样可以采用Resource直接进行资源文件的读取。




![java八股文面试[数据库]——行溢出](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/27961e3c45d3379bbc7b7e726a057b91.png)