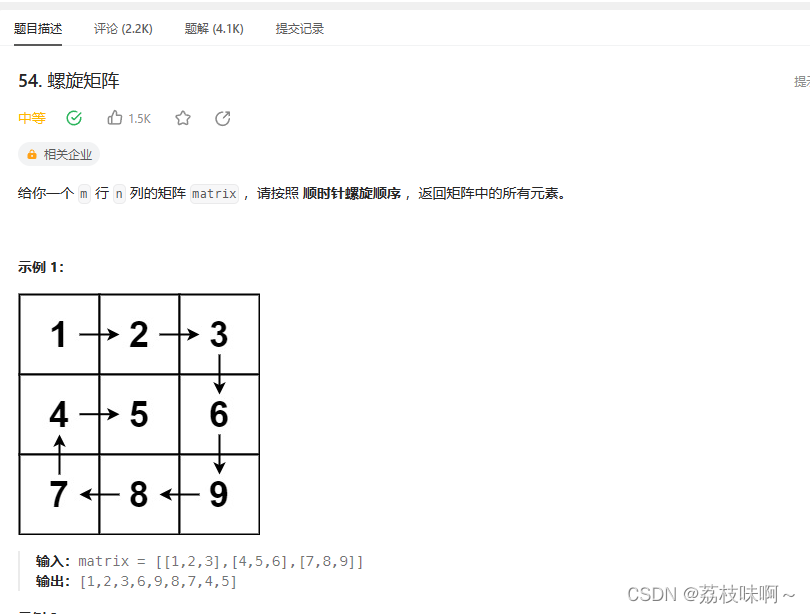
这道题一看好像在哪做过一样,好像是写剑指offer里面的状态机的时候写过类似的,就是定义4个方向,它就是按右,下,左,上的规律螺旋的,所以只要拿4个方向给他循环就可以,我是用一个表示方向的二维数组来表示方向
int[][] direct = new int[][]{{0,1},{1,0},{0,-1},{-1,0}};然后用一个corDir表示当前行进的方向,然后是用一个index来在方向数组里面循环的,它要变换为下一个方向的时候corDir=direct[index++],但是要做到循环就要让index等于4的时候给他赋值为0,这样当前方向就能在方向数组里面循环起来,
int index=0;
int[] corDir = direct[index];当你遍历到一个元素matrix[i][j]的时候,你要遍历他的下一个元素,就要用i+=corDir[0];j+=corDir[1],但是你还要判断一下i和j是不是大于等于0小于数组长度,并且还要判断这个元素是不是已经访问过,所以我们还要创建一个与matrix等大的bool数组visited,它表示对应矩阵位置中的元素是不是被访问过,这些条件只要有一个不满足我们就要换方向,变成下一个方向,然后重新计算i和j
int corI = i+corDir[0]; int corJ=j+corDir[1];
if(corI>=0 && corI<row && corJ>=0 && corJ<clown && !visited[corI][corJ]){
i=corI;j=corJ;
}else{
index++;
if(index==4)index=0;
corDir = direct[index];
i+=corDir[0];j+=corDir[1];
}把这些操作放到一个循环里面,每遍历一个元素就把它放进答案并且把它对应的visited改为true,但是如何终止循环呢,通过记录访问到的元素的个数,如果等于矩阵中的元素的个数就退出循环,以下是我的代码
class Solution {
public List<Integer> spiralOrder(int[][] matrix) {
List<Integer> ans= new ArrayList<>();
int row = matrix.length;
int clown = matrix[0].length;
boolean[][] visited = new boolean[row][clown];
int i=0,j=0;
int[][] direct = new int[][]{{0,1},{1,0},{0,-1},{-1,0}};
int index=0;
int[] corDir = direct[index];
int visitedNum=0;
while(visitedNum != row*clown){
ans.add(matrix[i][j]);
visited[i][j]=true;
visitedNum++;
int corI = i+corDir[0]; int corJ=j+corDir[1];
if(corI>=0 && corI<row && corJ>=0 && corJ<clown && !visited[corI][corJ]){
i=corI;j=corJ;
}else{
index++;
if(index==4)index=0;
corDir = direct[index];
i+=corDir[0];j+=corDir[1];
}
}
return ans;
}
}看看题解做法,题解的第一种做法和我的完全一样,看来我算法写的越来越官方了,以下是题解第一种做法代码:
class Solution {
public List<Integer> spiralOrder(int[][] matrix) {
List<Integer> order = new ArrayList<Integer>();
if (matrix == null || matrix.length == 0 || matrix[0].length == 0) {
return order;
}
int rows = matrix.length, columns = matrix[0].length;
boolean[][] visited = new boolean[rows][columns];
int total = rows * columns;
int row = 0, column = 0;
int[][] directions = {{0, 1}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {-1, 0}};
int directionIndex = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < total; i++) {
order.add(matrix[row][column]);
visited[row][column] = true;
int nextRow = row + directions[directionIndex][0], nextColumn = column + directions[directionIndex][1];
if (nextRow < 0 || nextRow >= rows || nextColumn < 0 || nextColumn >= columns || visited[nextRow][nextColumn]) {
directionIndex = (directionIndex + 1) % 4;
}
row += directions[directionIndex][0];
column += directions[directionIndex][1];
}
return order;
}
}
题解第二种做法是按层模拟,看完第二个题解我想起来了,我做过这道题剑指offer29.顺时针打印矩阵_荔枝味啊~的博客-CSDN博客
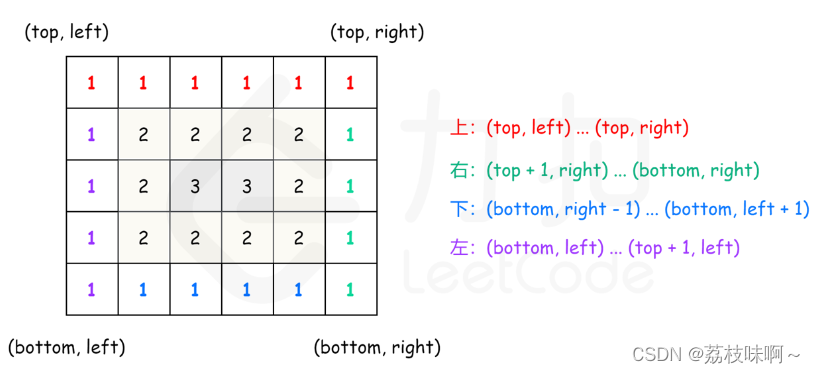
这种方法就是从外向内,一层一层遍历,定义一个top,bottom,right,left,4条边,每一层都是先遍历上面这条边,然后右边然后下边,然后左边,遍历完一层之后,top++,right--,bottom--,left++,循环的终止条件是左边大于了右边或者下边大于了上边,它也用用一个visited数组来记录访问过的元素,以下是题解第二种做法代码:
class Solution {
public List<Integer> spiralOrder(int[][] matrix) {
List<Integer> order = new ArrayList<Integer>();
if (matrix == null || matrix.length == 0 || matrix[0].length == 0) {
return order;
}
int rows = matrix.length, columns = matrix[0].length;
int left = 0, right = columns - 1, top = 0, bottom = rows - 1;
while (left <= right && top <= bottom) {
for (int column = left; column <= right; column++) {
order.add(matrix[top][column]);
}
for (int row = top + 1; row <= bottom; row++) {
order.add(matrix[row][right]);
}
if (left < right && top < bottom) {
for (int column = right - 1; column > left; column--) {
order.add(matrix[bottom][column]);
}
for (int row = bottom; row > top; row--) {
order.add(matrix[row][left]);
}
}
left++;
right--;
top++;
bottom--;
}
return order;
}
}