Codeforces Round 560 (Div. 3)
Dashboard - Codeforces Round 560 (Div. 3) - Codeforces
A. Remainder(模拟)

思路:模拟取余操作 , 只需考虑数字的后 x 位变成要变成的数字即可。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fi first
#define se second
#define IOS std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
#define int long long
const int N = 2e6 + 10;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
typedef pair<int,int>PII;
int n , x , y;
int a[N] , res;
signed main(){
cin >> n >> x >> y;
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++) scanf("%01d" , &a[i]);
reverse(a + 1 , a + 1 + n);
y += 1;
for(int i = 1 ; i <= x ; i ++){
if(i == y){
if(a[i] == 0) res += 1;
}else{
if(a[i] == 1) res += 1;
}
}
cout << res;
return 0;
}
//freopen("文件名.in","r",stdin);
//freopen("文件名.out","w",stdout);
B. Polycarp Training(排序)

思路:对比赛按照从小到大排序 , 贪心的去训练。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fi first
#define se second
#define IOS std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
#define int long long
const int N = 2e6 + 10;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
typedef pair<int,int>PII;
int n , a[N];
signed main(){
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++) cin >> a[i];
sort(a + 1 , a + 1 + n);
int now = 0;
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++){
if(a[i] >= (now + 1)) now += 1;
}
cout << now;
return 0;
}
//freopen("文件名.in","r",stdin);
//freopen("文件名.out","w",stdout);
C. Good String(模拟)

思路:手模了一下 ,没什么性质 , 直接模拟即可 , 这里我每个字符串去匹配下一个与其不同的字符串 , 加到答案中即可。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fi first
#define se second
#define IOS std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
#define int long long
const int N = 2e6 + 10;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
typedef pair<int,int>PII;
/*
ooa
*/
int n , cnt;
string s , ans;
signed main(){
cin >> n >> s;
s = '~' + s;
int now = 0;
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i = now + 1){
ans += s[i];
cnt += 1;
bool tag = 0;
for(int j = i + 1 ; j <= n ; j ++){
if(s[j] != s[i]){
tag = 1;
now = j;
break;
}
}
if(!tag) break;
ans += s[now];
cnt += 1;
}
if(cnt & 1) cnt -= 1;
cout << n - cnt << "\n";
for(int i = 0 ; i < cnt ; i ++) cout << ans[i];
cout << "\n";
return 0;
}
//freopen("文件名.in","r",stdin);
//freopen("文件名.out","w",stdout);
D. Almost All Divisors(思维 + 数论)

思路:首先想到的就是分奇偶 , 奇数会比偶数多一个平方因子 , 然后把所有因子排序后 , 要判断对应位置相乘是否都相等。还有一个坑点 , 就是要求这 n 个数要是(所有因子) , 因此如果满足上面条件 , 还要额外检查因子是否全 , 因为即使因子不全也满足对应位置相乘都相等。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fi first
#define se second
#define IOS std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
#define int long long
const int N = 2e6 + 10;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
typedef pair<int,int>PII;
/*
12
1 2 3 4 6 12
*/
int n , t , a[N];
map<int,int>all;
bool judge(){
map<int,int>mp;
if(n & 1){
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n / 2 + 1 ; i ++){
mp[a[i] * a[n + 1 - i]] += 1;
}
}else{
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n / 2 ; i ++){
mp[a[i] * a[n + 1 - i]] += 1;
}
}
return mp.size() == 1;
}
bool judge1(int x){
for(int i = 2 ; i * i <= x ; i ++){
if(x % i == 0){
if(!all[i]) return 0;
if(!all[x / i]) return 0;
}
}
return 1;
}
signed main(){
IOS
cin >> t;
while(t --){
cin >> n;
all.clear();
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++) cin >> a[i] , all[a[i]] += 1;
sort(a + 1 , a + 1 + n);
//第一次判断
if(!judge()){
cout << "-1\n";
}else{
int now = 0;
if(n & 1){
now = a[(n + 1) / 2];
now = now * now;
}else{
now = a[1] * a[n];
}
//第二次判断
if(judge1(now)){
cout << now << "\n";
}else{
cout << "-1\n";
}
}
}
return 0;
}
//freopen("文件名.in","r",stdin);
//freopen("文件名.out","w",stdout);
E. Two Arrays and Sum of Functions(思维 + 排序)

思路:很经典的一道题 , 首先我们考虑每个位置 i 被覆盖的次数应该是 cnt[i] = i * (n + 1 - i); 就是左边可选的端点数乘右边的端点数。
这样我们可以把答案表示成下面这个形式。
a n s = ∑ 1 n c n t [ i ] ∗ a [ i ] ∗ b [ i ] ans=\sum_{1}^{n}cnt[i] *a[i]*b[i] ans=1∑ncnt[i]∗a[i]∗b[i]
现在 cnt[i] 与 a[i] 已知 , 要重排b数组最小化 ans ,只要贪心的让大的数去配对小的数就好了。
注意会有一些小的实现细节。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fi first
#define se second
#define IOS std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
#define int long long
const int N = 2e6 + 10;
const int mod = 998244353;
typedef pair<int,int>PII;
int a[N] , b[N] , n , cnt[N] , res;
signed main(){
IOS
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++) cin >> a[i];
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++) cin >> b[i];
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++) cnt[i] = i * (n - i + 1);
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++) a[i] = a[i] * cnt[i];
sort(a + 1 , a + 1 + n ,
[&](int a , int b){
return a > b;
}
);
sort(b + 1 , b + 1 + n ,
[&](int a , int b){
return a < b;
}
);
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++){
res = (res + a[i] % mod * b[i] % mod) % mod;
}
cout << res ;
return 0;
}
//freopen("文件名.in","r",stdin);
//freopen("文件名.out","w",stdout);
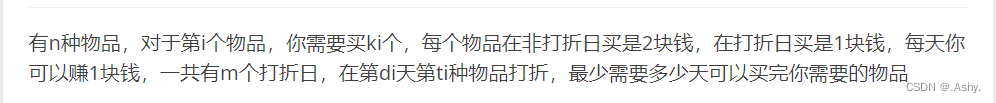
F. Microtransactions(二分 + 贪心)
思路:显然时间是满足二分性的 , 考虑去二分答案 。 那么如何二分答案呢 , 我们可以观察到一个商品是可以有很多个打折时间的 , 那么我们在二分答案的时候选择哪一个打折时间去购买呢 ? 这里我们要用到贪心的思想 ,对于一个商品的多个打折时间 , 我们选择满足条件的最靠后的打折时间去购买 , 这样能最大化的利用资源。
注意细节即可。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fi first
#define se second
#define IOS std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
#define int long long
const int N = 2e6 + 10;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
typedef pair<int,int>PII;
int n , m;
int cnt[N] , sum , cnt_1[N];
map<int , vector<int>>mp;//某个商品的所有打折时间
map<int , vector<int>>ed;//某个时间可以处理的商品
bool judge(int t){
//处理每个商品的最晚打折时间
ed.clear();
for(auto [x , y] : mp){
int res = 0;
for(auto v : y) if(v <= t) res = max(res , v);
ed[res].push_back(x);
}
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++) cnt_1[i] = cnt[i];
int need = 0;
for(auto [x , y] : ed){
int now = (x - need);//当前时刻的可用资源
for(auto v : y){
if(cnt_1[v] <= now){
now -= cnt_1[v];
need += cnt_1[v];
cnt_1[v] = 0;
}else{
cnt_1[v] -= now;
need += now;
break;
}
}
}
//未打折使用的资源
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++) need += cnt_1[i] * 2;
return need <= t;
}
signed main(){
IOS
cin >> n >> m;
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++) cin >> cnt[i];
for(int i = 1 ; i <= m ; i ++){
int x , y;
cin >> x >> y;
mp[y].push_back(x);
}
int l = 0 , r = 4e5;
while(l < r){
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if(judge(mid)) r = mid;
else l = mid + 1;
}
cout << l << "\n";
return 0;
}
//freopen("文件名.in","r",stdin);
//freopen("文件名.out","w",stdout);