基本使用
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor继承自ThreadPoolExecutor。它主要用来在给定的延迟之后运行任务,或者定期执行任务。
public class ScheduledThreadPoolExecutorTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(2);
threadPoolExecutor.scheduleAtFixedRate(() -> System.out.println(1), 2, 3, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
}

上述代码会延迟2秒每隔3秒在控制台打印1。
原理解析
1.延迟队列介绍
看源码之前,先看看延迟队列,延迟任务。
DelayQueue是一个支持延时获取元素的无界阻塞队列。队列使用PriorityQueue来实现。队列中的元素必须实现Delayed接口,在创建元素时可以指定多久才能从队列中获取当前元素。只有在延迟期满时才能从队列中提取元素。
实现Delayed接口,延迟任务
class MyDelayedTask implements Delayed {
// 当前任务创建时间
private long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 延时时间
private long time;
// 初始化
public MyDelayedTask(long time) {
this.time = time;
}
/**
* 需要实现的接口,获得延迟时间(用过期时间-当前时间)
*/
@Override
public long getDelay(TimeUnit unit) {
return unit.convert((start + time) - System.currentTimeMillis(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
/**
* 用于延迟队列内部比较排序(当前时间的延迟时间 - 比较对象的延迟时间)
*/
@Override
public int compareTo(Delayed o) {
return (int) (this.getDelay(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS) - o.getDelay(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS));
}
}
任务生产者向延迟队列中添加任务,消费线程向队列中拉取任务,(比较延迟时间)消费任务。
2.线程池核心原理

- 当前的线程池个数小于核心线程数,直接添加核心线程即可
- 当前的线程池个数大于等于核心线程数,将任务添加至阻塞队列中
- 如果添加阻塞队列失败(队列满了),则需要添加非核心线程数处理任务
- 如果添加非核心线程数失败(线程池满了),执行拒绝策略
3.定时执行原理
3.1构造器
public ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize) {
super(corePoolSize, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 0, NANOSECONDS,
new DelayedWorkQueue());
}
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue) {
this(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue,
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), defaultHandler);
}
阻塞队列DelayedWorkQueue,有界队列
static class DelayedWorkQueue extends AbstractQueue<Runnable>
implements BlockingQueue<Runnable> {
private static final int INITIAL_CAPACITY = 16;
private RunnableScheduledFuture<?>[] queue =
new RunnableScheduledFuture<?>[INITIAL_CAPACITY];
// ...
}
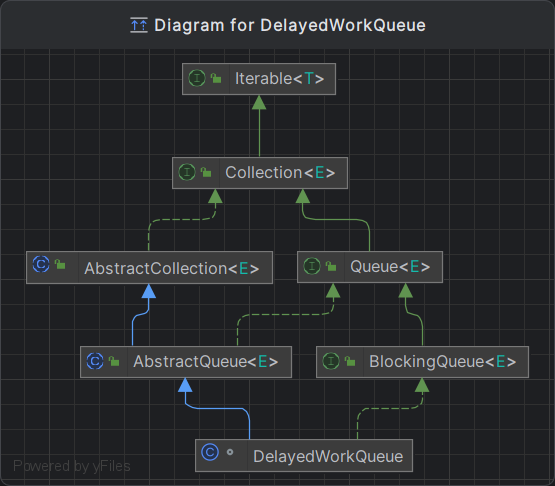
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor内部自定义阻塞队列
3.2周期执行
public ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleAtFixedRate(Runnable command,
long initialDelay,
long period,
TimeUnit unit) {
if (command == null || unit == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
if (period <= 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
// 初始化任务
ScheduledFutureTask<Void> sft =
new ScheduledFutureTask<Void>(command,
null,
triggerTime(initialDelay, unit),
unit.toNanos(period));
RunnableScheduledFuture<Void> t = decorateTask(command, sft);
sft.outerTask = t;
// 添加任务,创建线程处理
delayedExecute(t);
return t;
}
private void delayedExecute(RunnableScheduledFuture<?> task) {
// 将当前任务添加至延时队列
super.getQueue().add(task);
// 创建核心线程并启动
ensurePrestart();
}
// 触发时间延时实现
private long triggerTime(long delay, TimeUnit unit) {
return now() + delay;
}
队列任务RunnableScheduledFuture
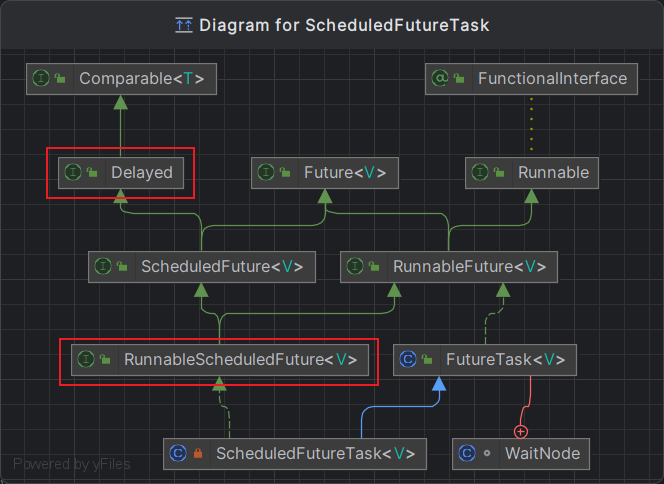
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor内部自定义延时任务
定时线程池通过延时队列来达到定时的目的。
仅仅使用延迟队列是无法到达定时执行的目的,因此看从阻塞队列获取任务以及启动线程执行任务代码。
获取任务
for (;;) {
// 从延时队列中获取任务
Runnable r = workQueue.take();
}
public RunnableScheduledFuture<?> take(){
// 死循环获取任务
for (;;) {
// 获取队列第一个任务
RunnableScheduledFuture<?> first = queue[0];
// 如果当前队列任务为空,则等待
if (first == null){
available.await();
}
// 获取当前任务的时间
long delay = first.getDelay(NANOSECONDS);
// 到延迟时间
if (delay <= 0){
// 弹出当前任务【数组头任务】
return finishPoll(first);
}
}
}
// 延迟时间减去当前时间
public long getDelay(TimeUnit unit) {
return unit.convert(time - now(), NANOSECONDS);
}
执行任务
当拿到任务(ScheduledFutureTask)之后,会执行任务:task.run()【ThreadPoolExecutor#runWorker】
public void run() {
// 执行当前的任务
if (ScheduledFutureTask.super.runAndReset()) {
setNextRunTime();
reExecutePeriodic(outerTask);
}
}
protected boolean runAndReset() {
if (state != NEW){
return false;
}
int s = state;
try {
Callable<V> c = callable;
if (c != null && s == NEW) {
try {
// 执行任务
c.call();
// 【重点】如果任务正常执行成功的话,这里会将ran置为true
// 如果任务执行期间发生异常,会被下面直接捕捉到,不会将此处的ran置为true
ran = true;
} catch (Throwable ex) {
// 出现异常会将state置为EXCEPTIONAL
// 标记当前任务执行失败并将异常赋值到结果
setException(ex);
}finally {
s = state;
}
}
}
// ran:当前任务是否执行成功
// s:当前任务状态
// ran为false:当前任务执行失败
// s == NEW = false:当前任务状态出现异常
return ran && s == NEW;
}
如果定时任务执行发送异常, runAndReset 返回 false,无法继续执行:
if (ScheduledFutureTask.super.runAndReset()) {
// 重置下一次任务执行时间
setNextRunTime();
// 将任务重新丢进队列
reExecutePeriodic(outerTask);
}
小结
1.执行任务发生异常会影响定时线程池?
不会。任务执行异常不会影响线程池,只是线程池将当前任务给丢失,没有继续放到队列中(该任务后续就不会执行),线程池仍一直处于运行状态。
2.定时线程池实现原理
线程池 + 延迟队列
3.使用注意事项
使用定时线程池,定时任务一定要加Try Catch
![[Java]异常](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/7ad858ba0dd84be9a7cc38624ba8ca67.png)