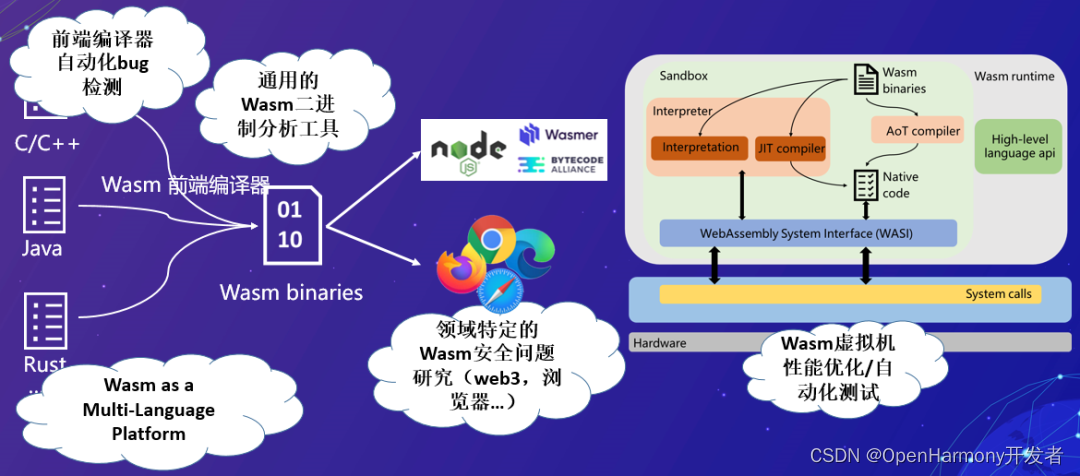
👀Spring Boot Starter Security 中文文档
- Spring Security中文文档
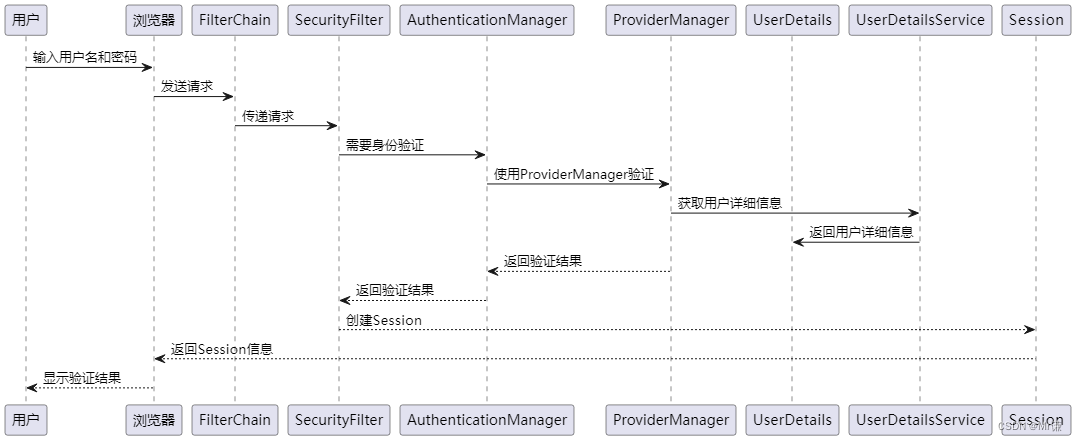
👀Spring Boot Starter Security 运行流程
当然可以。首先,我们会将用户存储和认证的流程融入整个Spring Boot Starter Security的使用流程中。以下是当你使用Spring Boot Starter Security时,背后发生的完整流程及其示例:
✌1. 添加依赖:
示例:在 pom.xml 中添加以下内容:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
✌2. 应用启动:
示例:启动你的 Spring Boot 应用,例如通过运行 SpringBootApplication 的 main 方法。
✌3. 默认认证:
示例:当你首次启动应用程序,控制台上会打印类似以下的内容:
Using generated security password: 78fa095d-3f4c-48b1-ad50-e24c31d5cf35
✌4. 请求过滤:
示例:使用浏览器访问你的应用,所有请求都会经过一系列过滤器,如 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter 来处理表单登录。
✌5. 访问决策:
示例:如果你尝试访问一个受保护的端点 /admin, 而没有 ADMIN 角色,你会被重定向到登录页面或收到一个权限不足的消息。
✌6. 用户存储和认证:
通常,你可以选择多种方式存储和认证用户,如内存存储、数据库、LDAP等。
示例:使用内存存储用户和密码。
@Autowired
public void configureGlobal(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth
.inMemoryAuthentication()
.withUser("user").password(passwordEncoder().encode("password")).roles("USER")
.and()
.withUser("admin").password(passwordEncoder().encode("admin")).roles("USER", "ADMIN");
}
✌7. 认证和授权:
示例:在默认的登录页面上输入用户名 user 和控制台上生成的密码,登录后你将被认证,并获得相应的权限。
✌8. 会话管理:
示例:登录成功后,浏览器会收到一个名为 JSESSIONID 的 cookie,用于识别已经认证的会话。
✌9. 方法级别的安全性:
示例:
@Service
public class BookService {
@PreAuthorize("hasRole('ADMIN')")
public void addBook(Book book) {
// ... 添加书籍的实现
}
}
✌10. 其他特性:
示例:为了启用 CSRF 保护,你只需在配置中加入:
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.csrf().enable();
}
✌11. 自定义:
示例:自定义安全配置以允许 /public 下的所有请求:
@Configuration
public class CustomSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/public/**").permitAll()
.anyRequest().authenticated();
}
}
通过上述流程,你可以更深入地了解Spring Boot Starter Security在应用中的实际应用流程以及如何使用。希望这能满足你的需求。
👀Spring Boot Starter Security 功能详解
Spring Boot Starter Security 是为基于 Spring 的应用提供的一个强大的认证和授权框架。通过这个启动器,可以快速整合 Spring Security,同时享受 Spring Boot 的自动配置。
✌1. 依赖管理:
作用: 快速集成 Spring Security 到 Spring Boot 项目中
使用场景: 新项目或需要为现有项目添加安全性的情况
在 pom.xml 文件中添加依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
✌2. 默认安全配置:
作用: 自动添加最基本的安全性设置
使用场景: 快速搭建原型或测试项目时
只需添加上述依赖,Spring Boot 会提供 HTTP Basic 认证,并生成默认用户名(“user”)和密码,应用启动时会打印在控制台。
✌3. 自定义安全配置:
作用: 根据项目需求定制访问权限
使用场景: 生产环境中根据业务逻辑定制权限
✍1. 继承 WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter
要自定义安全配置,首先需要创建一个类,继承 WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter,并使用 @Configuration 注解标记它。
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
// 配置内容将放在这里
}
✍2. 定义授权策略
使用 configure(HttpSecurity http) 方法,你可以定义哪些 URL 需要被保护、哪些不需要被保护、需要哪种角色等。
例如:
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/public/**").permitAll() // 公共路径,任何人都可以访问
.antMatchers("/admin/**").hasRole("ADMIN") // 只有ADMIN角色的用户可以访问/admin/路径下的所有资源
.anyRequest().authenticated() // 任何请求都需要经过身份验证
.and()
.formLogin() // 使用默认的登录表单
.and()
.httpBasic(); // 启用 HTTP Basic 认证
}
✍3. 自定义登录页面
你可能不希望使用 Spring Security 默认提供的登录页面。你可以定义自己的登录页面:
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.formLogin()
.loginPage("/customLogin") // 自定义登录页面的 URL
.loginProcessingUrl("/authenticateUser") // 登录表单的 action URL
.permitAll(); // 允许所有用户都能访问登录页面
}
✍4. 处理注销
注销功能也是 Spring Security 自带的,但可以进行定制:
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.logout()
.logoutUrl("/customLogout") // 自定义注销URL
.logoutSuccessUrl("/afterLogout") // 注销成功后跳转的URL
.invalidateHttpSession(true); // 注销时使当前会话无效
}
✍5. CSRF保护
🎷什么是 CSRF(Cross-Site Request Forgery)?
CSRF 是一种网络攻击技术,攻击者诱导用户点击一个链接或加载一个页面,从而在未经用户同意的情况下,以用户的身份对一个已认证的网站进行恶意操作。因为在浏览器中,用户可能已经登录并保存了网站的登录态,这使得攻击成为可能。
🎷Spring Security 中的 CSRF 保护
为了防止 CSRF 攻击,Spring Security 提供了内置的 CSRF 保护。默认情况下,该功能是启用的。其工作原理基于一个同步令牌模式:当用户访问一个表单页面时,Spring Security 将在该页面上生成一个 CSRF 令牌,并在后续的 POST 请求中要求该令牌与其存储的版本相匹配。
🎷如何工作?
-
令牌生成:当你的应用显示一个表单时,Spring Security 会自动包含一个隐藏的 CSRF 令牌字段。这是一个随机生成的、不可预测的值。
-
令牌验证:当表单提交时,Spring Security 过滤器会检查请求中的 CSRF 令牌与服务器端存储的版本是否匹配。如果不匹配或缺失令牌,请求将被拒绝。
-
令牌存储:默认情况下,令牌是在用户的会话中存储的。
🎷如何启用和禁用?
在 Spring Security,CSRF 保护默认是启用的。如果你需要关闭(尽管不推荐),可以使用以下配置:
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.csrf().disable();
}
🎷如何定制?
-
自定义令牌仓库:你可以使用
csrfTokenRepository方法定制令牌的存储方式。例如,如果你想使用 Cookie 而不是会话来存储令牌:http .csrf() .csrfTokenRepository(CookieCsrfTokenRepository.withHttpOnlyFalse()); -
自定义请求匹配:你也可以为 CSRF 保护指定特定的请求匹配器。例如,只为某些URL启用 CSRF 保护:
http .csrf() .requireCsrfProtectionMatcher(new AntPathRequestMatcher("/secure/**"));
✌4. 用户存储和认证:
作用: 定义用户、角色和密码
使用场景: 当需要预定义几个用户或从数据库、LDAP获取用户时
当涉及到 web 安全,尤其是使用 Spring Security,用户存储和认证是最核心的部分。这部分涉及如何管理和验证尝试访问应用程序的用户的身份。
✍ 用户存储
用户存储通常是一个数据库、LDAP 服务器或其他存储机制,其中包含了用户的凭证(例如用户名和密码)及其权限。
Spring Security 支持多种用户存储:
- 内存存储:适用于简单应用或初步开发阶段。
- JDBC 存储:使用关系型数据库存储用户凭证。
- LDAP 存储:用于连接到 LDAP 服务器。
- 自定义 UserDetailsService:允许你连接到任何你想要的用户存储。
✍ 认证
认证是验证用户提供的凭证的过程。
在 Spring Security 中,这通过 AuthenticationManager 接口来完成,它有一个实现方法:authenticate(Authentication auth)。
✍ 示例和详细解析
-
内存认证:
适用于简单的使用场景或开发/测试环境。
@Configuration @EnableWebSecurity public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter { @Override protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception { auth.inMemoryAuthentication() .withUser("user").password("{noop}password").roles("USER") .and() .withUser("admin").password("{noop}admin").roles("ADMIN"); } }分析:
inMemoryAuthentication()方法启用了内存中的用户存储。{noop}是密码编码的前缀,表示使用无操作的密码编码器。实际生产中,你会想使用一个强加密的密码编码器,例如BCryptPasswordEncoder。
-
JDBC 认证:
使用关系型数据库验证用户。需要提供一个
DataSource。@Autowired private DataSource dataSource; @Override protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception { auth.jdbcAuthentication().dataSource(dataSource) .usersByUsernameQuery("select username, password, enabled from users where username = ?") .authoritiesByUsernameQuery("select username, authority from authorities where username = ?"); }分析:
jdbcAuthentication()方法启用了 JDBC 认证。usersByUsernameQuery和authoritiesByUsernameQuery用于指定获取用户凭证和权限的 SQL 查询。
-
LDAP 认证:
使用 LDAP 服务器进行认证。
@Override protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception { auth.ldapAuthentication() .userDnPatterns("uid={0},ou=people") .groupSearchBase("ou=groups") .contextSource() .url("ldap://localhost:8389/dc=springframework,dc=org") .and() .passwordCompare() .passwordEncoder(new BCryptPasswordEncoder()) .passwordAttribute("userPassword"); }分析:
ldapAuthentication()方法启用了 LDAP 认证。userDnPatterns和groupSearchBase用于指定如何在 LDAP 服务器中查找用户和组。contextSource()定义了连接到 LDAP 服务器的方式。passwordCompare()用于密码的比较。
-
自定义 UserDetailsService:
当标准的解决方案不满足你的需求时,你可以提供一个自定义的
UserDetailsService实现。@Service public class CustomUserDetailsService implements UserDetailsService { // ... load user by username logic }然后在你的安全配置中,你可以这样做:
@Autowired private CustomUserDetailsService userDetailsService; @Override protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception { auth.userDetailsService(userDetailsService); }分析:
UserDetailsService是 Spring Security 用于加载用户特定数据的核心接口。其主要操作是loadUserByUsername方法,根据用户名加载用户。- 使用
userDetailsService()方法,你可以指定自己的用户详情服务。
✍ 结论
用户存储和认证是 Spring Security 中的两个核心概念。根据应用的需求和复杂性,可以选择不同的认证策略。无论选择哪种方式,Spring Security 都为你提供了一套完整、可扩展的解决方案。
✌5. 方法级别的安全性:
作用: 在方法级别控制访问权限
使用场景: 当某些特定的业务方法需要特定的角色才能访问
在许多应用程序中,除了在入口点(例如 HTTP 请求)上进行安全检查之外,还需要在应用的内部进行更细粒度的安全检查,特别是在方法调用时。这种安全性通常称为“方法级别的安全性”。
Spring Security 提供了对方法级别安全性的支持,允许开发者通过注解或 XML 配置为特定的方法添加安全约束。
✍ 启用方法级别的安全性
首先,你需要在配置中启用它。以下是 Java 配置和 XML 配置的示例:
Java配置:
@Configuration
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = true, securedEnabled = true)
public class MethodSecurityConfig extends GlobalMethodSecurityConfiguration {
// ... 其他配置
}
XML配置:
<global-method-security pre-post-annotations="enabled" secured-annotations="enabled"/>
✍ 常用的安全注解
-
@PreAuthorize:
这个注解允许你在进入方法之前基于表达式的计算结果来决定是否可以调用此方法。
@PreAuthorize("hasRole('ADMIN')") public void deleteAllUsers() { // ... 删除所有用户的逻辑 } -
@PostAuthorize:
允许你在方法执行后基于方法的返回值检查权限。此检查只在方法成功返回后执行。
@PostAuthorize("returnObject.ownerName == authentication.name") public Document getUserDocument(Long documentId) { // ... 返回用户的文档 } -
@Secured:
这是一个简单的注解,允许你指定必须拥有的角色列表才能访问方法。
@Secured("ROLE_ADMIN") public void updateUser(User user) { // ... 更新用户的逻辑 } -
@PostFilter 和 @PreFilter:
这些注解允许你对集合或数组进行过滤,以删除或包含只有特定用户可以看到的项目。
@PostFilter("filterObject.ownerName == authentication.name") public List<Document> getAllDocuments() { // ... 返回所有文档的逻辑 }
✍ 表达式基础
Spring Security 提供了一组有用的方法和关键字,你可以在 @PreAuthorize 和 @PostAuthorize 注解中使用这些方法和关键字。例如:
hasRole('ROLE_ADMIN'):用户必须具有 ADMIN 角色。hasAnyRole('ROLE_ADMIN', 'ROLE_USER'):用户必须具有 ADMIN 或 USER 角色之一。permitAll():任何人都可以访问。denyAll():没有人可以访问。isAuthenticated():用户必须被验证。isAnonymous():用户必须是匿名的。
✍ 结论
方法级别的安全性为 Spring Security 提供了一个强大的机制,使得开发者可以对应用程序内的方法调用进行精细的访问控制。通过组合多种注解和表达式,你可以为你的应用创建复杂而强大的安全策略。
✌6. 其他特性:
- CSRF 保护: 默认启用,用于保护跨站请求伪造攻击。
- CORS 配置: 可以为您的应用配置跨域资源共享策略。
- OAuth2: Spring Security 提供对 OAuth2 的支持,允许您的应用作为 OAuth2 的客户端或提供者。
- JWT: 可以与 JWT (JSON Web Tokens) 结合,提供无状态的身份验证和授权。
✌7. 结论:
spring-boot-starter-security 提供了简便的方式,使得 Spring Boot 应用程序能够方便地集成安全性。它具有许多默认配置,同时也提供了丰富的自定义配置选项。结合 Spring Security 的其他模块,可以为应用程序提供全方位的安全解决方案。