1. 说明
在执行C++代码时,有时希望知道当前代码所在的文件名、函数名和对应行号位置信息,方便快速定位到代码所在处。想要获取这些信息,可以使用C++提供的一些宏进行获取。
2. 简单说明
__FILE__ : 用于获取当前语句所在源文件的文件名
——func__ : 用于获取当前语句所在的函数名
__LINE__ : 用于获取当前语句所在的行号位置
使用时只需要将上述三个标识符当作参数进行传递即可,示例代码如下:
// 先定义一个函数
void selfTest(int a, int b, const std::string &file, const std::string &func,int line){
std::cout << "a + b: " << a + b << " => " << file << ":" << func << ":" << line << std::endl;
}
// 然后在mian函数中调用
int main() {
// 调用时直接将标识符当作参数进行传递即可
selfTest(3,8,__FILE__,__func__,__LINE__);
}
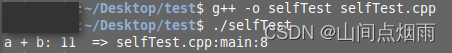
在linux终端编译文件并执行,结果如下:
3. 简化写法
上述方式在每次调用函数时都需要将参数传递进去,写法比较繁琐,也可采用下述方法进行简化
3.1 单独封装成函数
将输出相关信息的函数单独封装成一个函数,在需要输出位置信息时直接调用这个函数即可,示例代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
void logInfo(const string file,const string func,const int line){
cout << "File: " << file << " Func: " << func << " Line: " << line << endl;
}
void selfTest(int a,int b){
logInfo(__FILE__,__func__,__LINE__);
cout << "a + b: " << a + b << endl;
}
int main(){
selfTest(3,8);
}
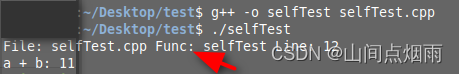
编译结果如下:
3.2 使用宏定义和可变参数
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <cstdarg>
using namespace std;
void selfTest(int a,int b,const string &file,const string &func,const int &line){
cout << "File: " << file << ", Func: " << func << ", Line: " << line << endl;
cout << "a + b: " << a + b << endl;
}
// 使用的...符号是可变参函数传参的写法,可以使用__VA_ARGS__接收参数
#define selfTest(...) selfTest(__VA_ARGS__,__FILE__,__func__,__LINE__)
int main(){
selfTest(3,8);//上面进行宏定义后,此行代码相当于selfTest(3,8,__FILE__,__func__,__LINE__)
}