前言:
本篇涉及的题目都与10 二叉树的层序遍历有关,共九道题
- 107.二叉树的层次遍历II medium
- 199.二叉树的右视图 medium
- 637.二叉树的层平均值 easy
- 429.N叉树的前序遍历 medium
- 515.在每个树行中找最大值 medium
- 116.填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针 medium
- 117.填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针II medium
- 104.二叉树的最大深度 easy
- 111.二叉树的最小深度 easy
正文
107 二叉树的层序遍历II medium
给定一个二叉树,返回其节点值自底向上的层次遍历。
和上一题相比,只是需要翻转一下最后结果而已,代码如下:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrderBottom(TreeNode* root) {
queue<TreeNode*> que;
vector<vector<int>> res;
if (root) que.push(root);
while (!que.empty()) {
int size = que.size();
vector<int> vec;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode *temp = que.front();
que.pop();
vec.push_back(temp->val);
if (temp->left) que.push(temp->left);
if (temp->right) que.push(temp->right);
}
res.push_back(vec);
}
reverse(res.begin(), res.end());
return res;
}
199 二叉树的右视图 medium
做这道题首先要知道什么叫做二叉树的右视图,理解起来也简单,和初中学三视图的时候没什么两样,如下图所示,站在二叉树的右边,返回右侧能看到的所有值。
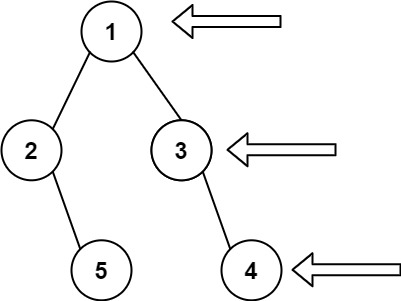
此处就要明确,如果当前层最右边有结点,如上图的结点4,将4加入结果就可以了。但如果没有呢?就需要将5加入节点,基于此要做一个判断。
那么怎么判断呢?其实也不难,当我们把每一层都加入队列后,最后一个元素,就是改层最右边的值,也是右视图能看见的值。
其余的和普通的层序遍历没有什么区别,代码如下:
vector<int> rightSideView(TreeNode* root) {
queue<TreeNode*> que;
vector<int> res;
if (root) que.push(root);
while (!que.empty()) {
int size = que.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode *temp = que.front();
que.pop();
if (i == (size - 1)) res.push_back(temp->val);
if (temp->left) que.push(temp->left);
if (temp->right) que.push(temp->right);
}
}
return res;
}
637 二叉树的层平均值 easy
这,没什么可说的了,就是做一次普通的层序遍历,然后求一下每层的平均值而已。
代码如下:
vector<double> averageOfLevels(TreeNode* root) {
queue<TreeNode*> que;
vector<double> res;
if (root) que.push(root);
while (!que.empty()) {
int size = que.size();
double sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <size; i++) {
TreeNode *temp = que.front();
que.pop();
sum += temp->val;
if (temp->left) que.push(temp->left);
if (temp->right) que.push(temp->right);
}
res.push_back(sum / size);
}
return res;
}
429 N叉树的层序遍历 medium
不同之处在于,遍历子结点的时候,要用循环处理,其余和二叉树的层序遍历没什么区别,代码如下:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(Node* root) {
queue<Node*> que;
vector<vector<int>> res;
if (root) que.push(root);
while (!que.empty()) {
int size = que.size();
vector<int> vec;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
Node *cur = que.front();
que.pop();
vec.push_back(cur->val);
// 此处为不同之处
for (int j = 0; j < cur->children.size(); j++) {
if (cur->children[j]) que.push(cur->children[j]);
}
}
res.push_back(vec);
}
return res;
}
515 在每个树行中找最大值 medium
层序遍历,取每一层的最大值
vector<int> largestValues(TreeNode* root) {
queue<TreeNode*> que;
if (root != NULL) que.push(root);
vector<int> result;
while (!que.empty()) {
int size = que.size();
int maxValue = INT_MIN; // 取每一层的最大值
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode* node = que.front();
que.pop();
maxValue = node->val > maxValue ? node->val : maxValue;
if (node->left) que.push(node->left);
if (node->right) que.push(node->right);
}
result.push_back(maxValue); // 把最大值放进数组
}
return result;
}
116 填充每个节点的下一个右侧结点指针 medium
(这道题的题目给我一种日式轻小说的错觉
首先要明白题意,在这道题下,每个节点有一个next指针,需要让该指针指向右侧的结点,如下图所示:
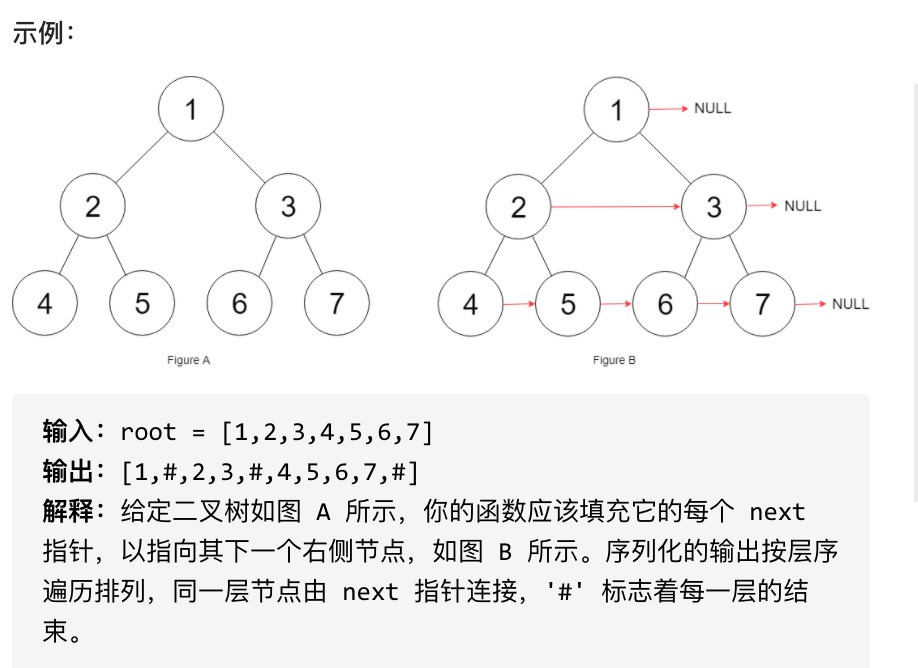
本质还是层序遍历,但需要用每一层的第一个节点,并且记录上一个结点,令其指向当前结点,代码如下:
Node* connect(Node* root) {
queue<Node*> que;
if (root) que.push(root);
while (!que.empty()) {
int size = que.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
Node* node = que.front();
que.pop();
// 如果不是本层的最后一个
if (i != size -1) {
// 当前结点指向本层的下一个结点
node->next = que.front();
} else
node->next = NULL;
if (node->left) que.push(node->left);
if (node->right) que.push(node->right);
}
}
return root;
}
其实这道题,如果用递归来做,会简洁很多,LeetCode官方版代码如下:
private:
void traversal(Node* cur) {
if (cur == NULL) return;
// 中
if (cur->left) cur->left->next = cur->right; // 操作1
if (cur->right) {
if (cur->next) cur->right->next = cur->next->left; // 操作2
else cur->right->next = NULL;
}
traversal(cur->left); // 左
traversal(cur->right); // 右
}
public:
Node* connect(Node* root) {
traversal(root);
return root;
}
117 填充每个节点下一个右侧节点指针II medium
和116的区别在于,这道题说的不是完全二叉树了,官方示例见下图:
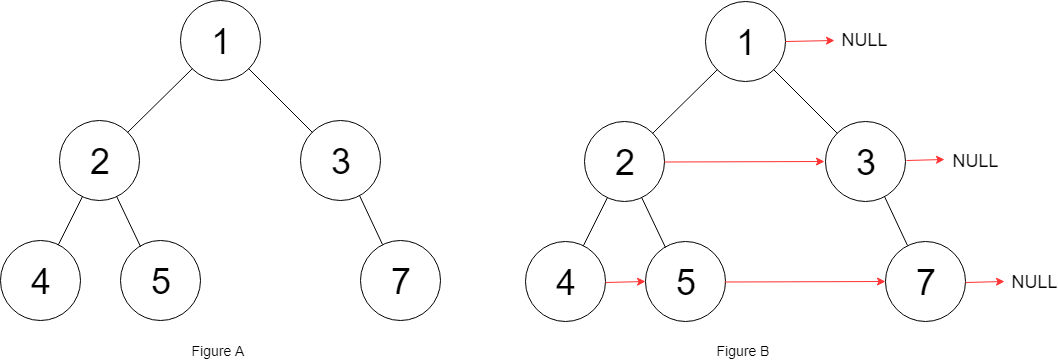
但是思想还是一致的,我们直接用116的题解,就可以通过(LeetCode你有些偷懒啊)
代码如下,还是放一遍吧:
Node* connect(Node* root) {
queue<Node*> que;
if (root) que.push(root);
while (!que.empty()) {
int size = que.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
Node* node = que.front();
que.pop();
// 如果不是本层的最后一个
if (i != size -1) {
// 当前结点指向本层的下一个结点
node->next = que.front();
} else
node->next = NULL;
if (node->left) que.push(node->left);
if (node->right) que.push(node->right);
}
}
return root;
}
104 二叉树的最大深度 easy
本质还是层序遍历,记录一共遍历了多少层就行,代码如下:
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) return 0;
int depth = 0;
queue<TreeNode*> que;
que.push(root);
while (!que.empty()) {
int size = que.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode *node = que.front();
que.pop();
if (node->left) que.push(node->left);
if (node->right) que.push(node->right);
}
depth++;
}
return depth;
}
111 二叉树的最小深度 easy
还是层序遍历,但是要注意一点,如果某个结点的左右子树都为空,就说明已经达到最小深度的那一层了,多了一个判断,代码如下:
int minDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) return 0;
int depth = 0;
queue<TreeNode*> que;
que.push(root);
while(!que.empty()) {
int size = que.size();
depth++; // 记录最小深度
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode* node = que.front();
que.pop();
if (node->left) que.push(node->left);
if (node->right) que.push(node->right);
if (!node->left && !node->right) {
return depth;
}
}
}
return depth;
}
这道题也可以用递归来做,代码如下:
int minDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) return 0;
if (root->left == NULL && root->right != NULL) {
return 1 + minDepth(root->right);
}
if (root->left != NULL && root->right == NULL) {
return 1 + minDepth(root->left);
}
// 相当于左右子树都是空的
return 1 + min(minDepth(root->left), minDepth(root->right));
}








![行为树 --- [7] BehaviorTree.CPP 4.x版本的编译及使用](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/d48351ae319b4135b20b789b3cd827b5.png)