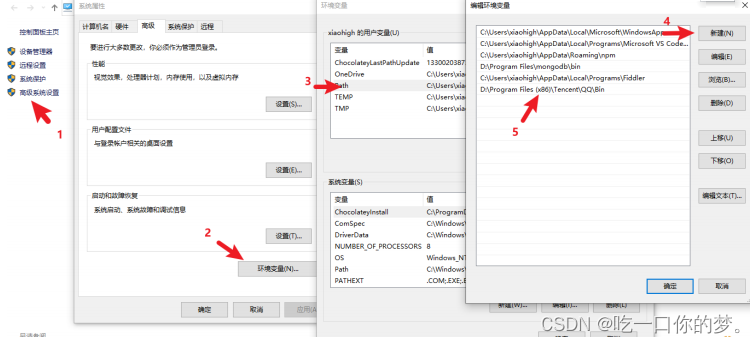
大家好,我是ST小智,今天给大家分享一下,u-boot的启动流程。

今天给大家全面的分析一下u-boot启动流程。整理这篇文章花费时间较长,中间很长时间未更新,希望这篇文章对大家有所帮助。
本章主要是详细的分析一下uboot的启动流程,理清uboot是如何启动的。通过对uboot启动流程的梳理,我们就可以掌握一些外设是在哪里被初始化的,这样当我们需要修改这些外设驱动的时候就会心里有数。另外,通过分析uboot的启动流程可以了解Linux内核是如何被启动的。
在看本章之前,个人建议先去看一下前几篇文章。对u-boot的开发环境搭建、u-boot整体移植和u-boot下网络调试有一点了解后,再来看本篇文章,这样可能比较容易看明白。
本章主要是详细的分析一下uboot的启动流程,理清uboot是如何启动的。通过对uboot启动流程的梳理,我们就可以掌握一些外设是在哪里被初始化的,这样当我们需要修改这些外设驱动的时候就会心里有数。另外,通过分析uboot的启动流程可以了解Linux内核是如何被启动的。
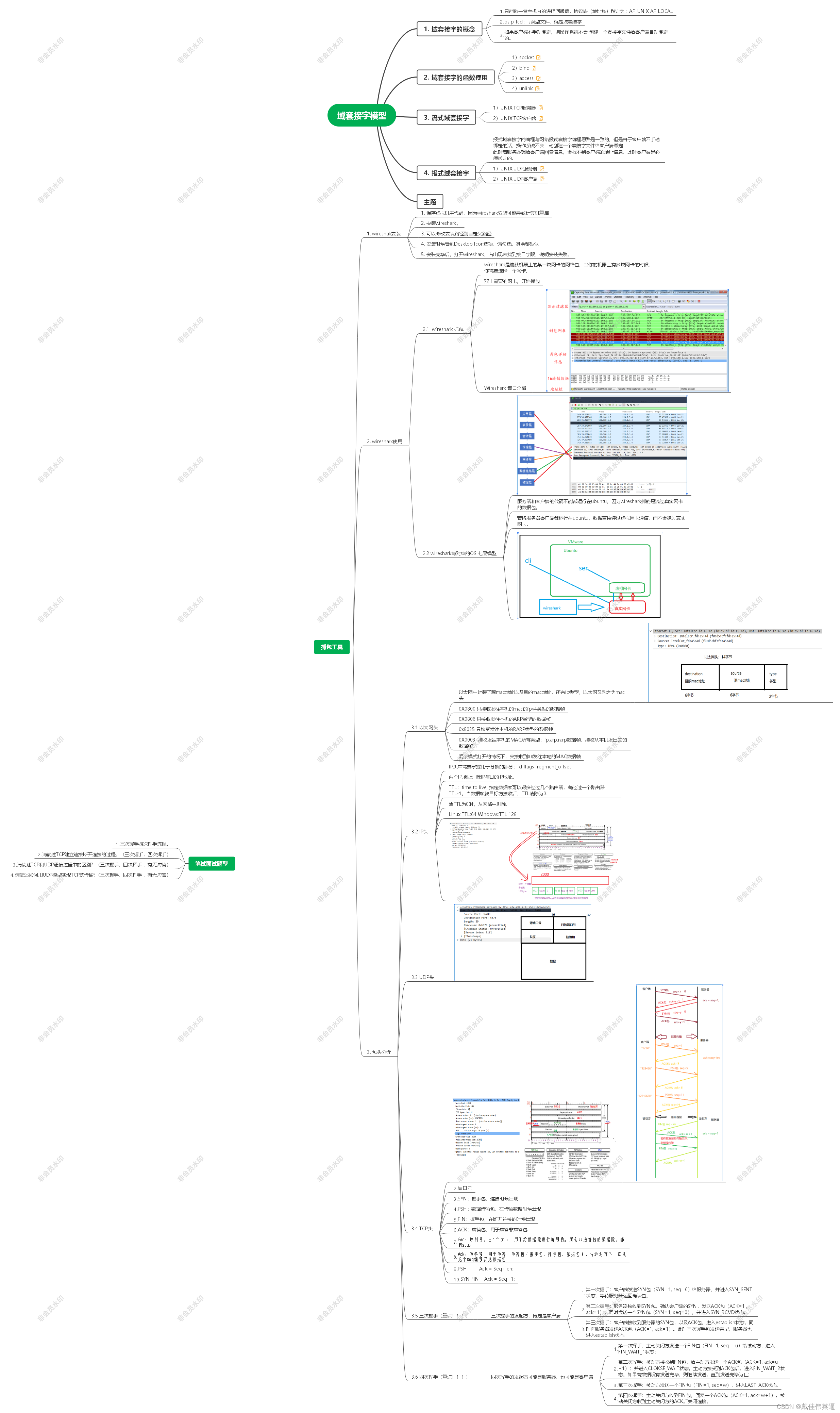
一、u-boot启动详细函数调用流程
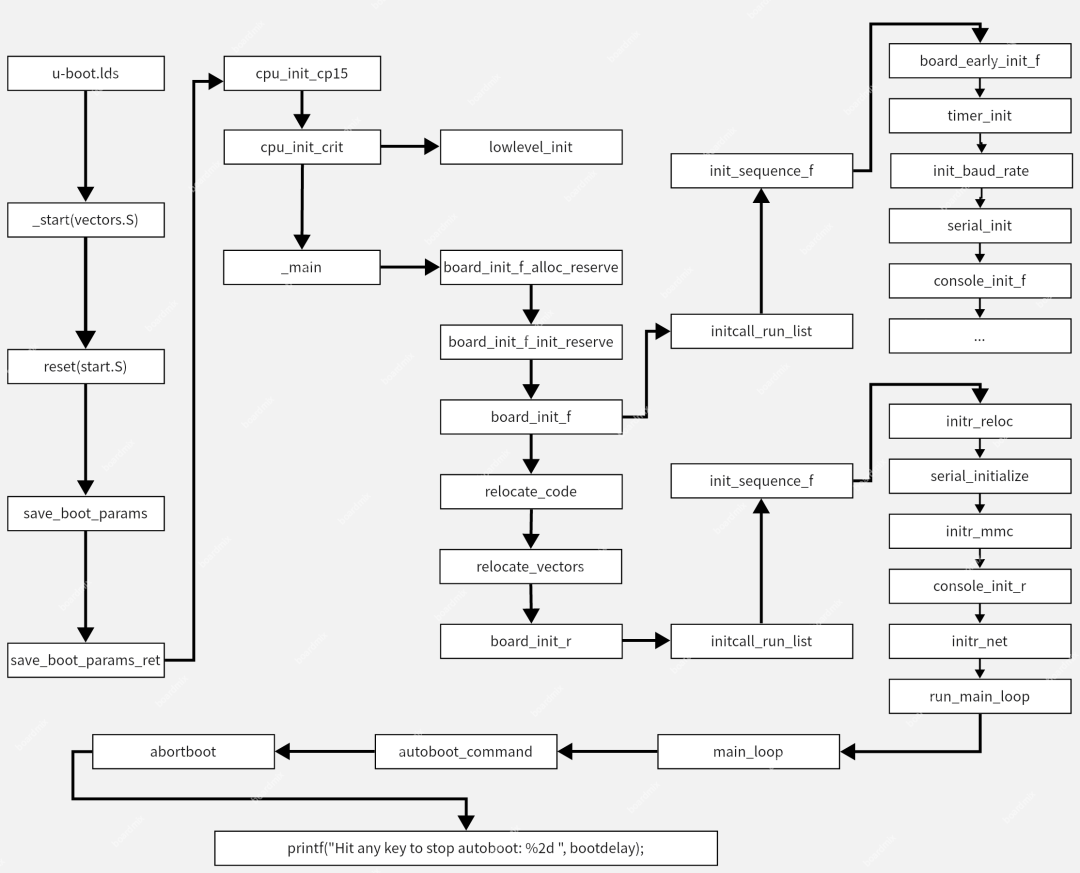
首先给大家先看一下,u-boot启动从入口函数到启动内核的详细函数调用流程的层级关系图,对u-boot启动的整体有一个快速了解,后面会详细介绍各个函数的作用。
u-boot:启动详细的代码调用流程
u-boot.lds:(arch/arm/cpu/u-boot.lds)
|-->_start:(arch/arm/lib/vectors.S)
|-->reset(arch/arm/cpu/armv7/start.S)
|-->save_boot_params(arch/arm/cpu/armv7/start.S)/*将引导参数保存到内存中*/
|-->save_boot_params_ret(arch/arm/cpu/armv7/start.S)
|-->cpu_init_cp15(arch/arm/cpu/armv7/start.S)/*初始化*/
|-->cpu_init_crit(arch/arm/cpu/armv7/start.S)
|-->lowlevel_init(arch/arm/cpu/armv7/lowlevel_init.S)
|-->_main(arch/arm/lib/crt0.S)
|-->board_init_f_alloc_reserve(common/init/board_init.c)/*为u-boot的gd结构体分配空间*/
|-->board_init_f_init_reserve(common/init/board_init.c) /*将gd结构体清零*/
|-->board_init_f(common/board_f.c)
|-->initcall_run_list(include/initcall.h) /*初始化序列函数*/
|-->init_sequence_f[](common/board_f.c) /* 初始化序列函数数组 */
|-->board_early_init_f(board/freescale/mx6ull_toto/mx6ull_toto.c)/*初始化串口的IO配置*/
|-->timer_init(arch/arm/imx-common/timer.c) /*初始化内核定时器,为uboot提供时钟节拍*/
|-->init_baud_rate(common/board_f.c) /*初始化波特率*/
|-->serial_init(drivers/serial/serial.c) /*初始化串口通信设置*/
|-->console_init_f(common/console.c) /*初始化控制台*/
|-->...
|-->relocate_code(arch/arm/lib/relocate.S) /*主要完成镜像拷贝和重定位*/
|-->relocate_vectors(arch/arm/lib/relocate.S)/*重定位向量表*/
|-->board_init_r(common/board_r.c)/*板级初始化*/
|-->initcall_run_list(include/initcall.h)/*初始化序列函数*/
|-->init_sequence_r[](common/board_f.c)/*序列函数*/
|-->initr_reloc(common/board_r.c) /*设置 gd->flags,标记重定位完成*/
|-->serial_initialize(drivers/serial/serial-uclass.c)/*初始化串口*/
|-->serial_init(drivers/serial/serial-uclass.c) /*初始化串口*/
|-->initr_mmc(common/board_r.c) /*初始化emmc*/
|-->mmc_initialize(drivers/mmc/mmc.c)
|-->mmc_do_preinit(drivers/mmc/mmc.c)
|-->mmc_start_init(drivers/mmc/mmc.c)
|-->console_init_r(common/console.c) /*初始化控制台*/
|-->interrupt_init(arch/arm/lib/interrupts.c) /*初始化中断*/
|-->initr_net(common/board_r.c) /*初始化网络设备*/
|-->eth_initialize(net/eth-uclass.c)
|-->eth_common_init(net/eth_common.c)
|-->phy_init(drivers/net/phy/phy.c)
|-->uclass_first_device_check(drivers/core/uclass.c)
|-->uclass_find_first_device(drivers/core/uclass.c)
|-->device_probe(drivers/core/device.c)
|-->device_of_to_plat(drivers/core/device.c)
|-->drv->of_to_plat
|-->fecmxc_of_to_plat(drivers/net/fec_mxc.c)/*解析设备树信息*/
|-->device_get_uclass_id(drivers/core/device.c)
|-->uclass_pre_probe_device(drivers/core/uclass.c)
|-->drv->probe(dev)
/*drivers/net/fec_mxc.c*/
U_BOOT_DRIVER(fecmxc_gem) = {
.name = "fecmxc",
.id = UCLASS_ETH,
.of_match = fecmxc_ids,
.of_to_plat = fecmxc_of_to_plat,
.probe = fecmxc_probe,
.remove = fecmxc_remove,
.ops = &fecmxc_ops,
.priv_auto = sizeof(struct fec_priv),
.plat_auto = sizeof(struct eth_pdata),
};
|-->fecmxc_probe(drivers/net/fec_mxc.c)/*探测和初始化*/
|-->fec_get_miibus(drivers/net/fec_mxc.c)
|-->mdio_alloc(drivers/net/fec_mxc.c)
|-->bus->read = fec_phy_read;
|-->bus->write = fec_phy_write;
|-->mdio_register(common/miiphyutil.c)
|-->fec_mii_setspeed(drivers/net/fec_mxc.c)
|-->fec_phy_init(drivers/net/fec_mxc.c)
|-->device_get_phy_addr(drivers/net/fec_mxc.c)
|-->phy_connect(drivers/net/phy/phy.c)
|-->phy_find_by_mask(drivers/net/phy/phy.c)
|-->bus->reset(bus)
|-->get_phy_device_by_mask(drivers/net/phy/phy.c)
|-->create_phy_by_mask(drivers/net/phy/phy.c)
|-->phy_device_create(drivers/net/phy/phy.c)
|-->phy_probe(drivers/net/phy/phy.c)
|-->phy_connect_dev(drivers/net/phy/phy.c)
|-->phy_reset(drivers/net/phy/phy.c)
|-->phy_config(drivers/net/phy/phy.c)
|-->board_phy_config(drivers/net/phy/phy.c)
|-->phydev->drv->config(phydev)
/*drivers/net/phy/smsc.c*/
static struct phy_driver lan8710_driver = {
.name = "SMSC LAN8710/LAN8720",
.uid = 0x0007c0f0,
.mask = 0xffff0,
.features = PHY_BASIC_FEATURES,
.config = &genphy_config_aneg,
.startup = &genphy_startup,
.shutdown = &genphy_shutdown,
};
|-->genphy_config_aneg(drivers/net/phy/phy.c)
|-->phy_reset(需要手动调用)(drivers/net/phy/phy.c)
|-->genphy_setup_forced(drivers/net/phy/phy.c)
|-->genphy_config_advert(drivers/net/phy/phy.c)
|-->genphy_restart_aneg(drivers/net/phy/phy.c)
|-->uclass_post_probe_device(drivers/core/uclass.c)
|-->uc_drv->post_probe(drivers/core/uclass.c)
/*net/eth-uclass.c*/
UCLASS_DRIVER(ethernet) = {
.name = "ethernet",
.id = UCLASS_ETH,
.post_bind = eth_post_bind,
.pre_unbind = eth_pre_unbind,
.post_probe = eth_post_probe,
.pre_remove = eth_pre_remove,
.priv_auto = sizeof(struct eth_uclass_priv),
.per_device_auto = sizeof(struct eth_device_priv),
.flags = DM_UC_FLAG_SEQ_ALIAS,
};
|-->eth_post_probe(net/eth-uclass.c)
|-->eth_write_hwaddr(drivers/core/uclass.c)
|-->...
|-->run_main_loop(common/board_r.c)/*主循环,处理命令*/
|-->main_loop(common/main.c)
|-->bootdelay_process(common/autoboot.c) /*读取环境变量bootdelay和bootcmd的内容*/
|-->autoboot_command(common/autoboot.c) /*倒计时按下执行,没有操作执行bootcmd的参数*/
|-->abortboot(common/autoboot.c)
|-->printf("Hit any key to stop autoboot: %2d ", bootdelay);
/*到这里就是我们看到uboot延时3s启动内核的地方*/
|-->cli_loop(common/cli.c) /*倒计时按下space键,执行用户输入命令*/
二、程序入口
U-Boot 源码文件众多,我们如何知道最开始的启动文件(程序入口)是哪个呢?程序的链接是由链接脚本来决定的,所以通过链接脚本可以找到程序的入口,链接脚本为arch/arm/cpu/u-boot.lds,它描述了如何生成最终的二进制文件,其中就包含程序入口。
三、链接脚本 u-boot.lds 详解
1.u-boot.lds
u-boot.lds,文件所在位置arch/arm/cpu/u-boot.lds
/* SPDX-License-Identifier: GPL-2.0+ */
/*
* Copyright (c) 2004-2008 Texas Instruments
*
* (C) Copyright 2002
* Gary Jennejohn, DENX Software Engineering, <garyj@denx.de>
*/
#include <config.h>
#include <asm/psci.h>
/* 指定输出可执行文件: "elf 32位 小端格式 arm指令" */
OUTPUT_FORMAT("elf32-littlearm", "elf32-littlearm", "elf32-littlearm")
/* 指定输出可执行文件的目标架构:"arm" */
OUTPUT_ARCH(arm)
/* 指定输出可执行文件的起始地址为:"_start" */
ENTRY(_start)
SECTIONS
{
#ifndef CONFIG_CMDLINE
/DISCARD/ : { *(__u_boot_list_2_cmd_*) }
#endif
#if defined(CONFIG_ARMV7_SECURE_BASE) && defined(CONFIG_ARMV7_NONSEC)
/*
* If CONFIG_ARMV7_SECURE_BASE is true, secure code will not
* bundle with u-boot, and code offsets are fixed. Secure zone
* only needs to be copied from the loading address to
* CONFIG_ARMV7_SECURE_BASE, which is the linking and running
* address for secure code.
*
* If CONFIG_ARMV7_SECURE_BASE is undefined, the secure zone will
* be included in u-boot address space, and some absolute address
* were used in secure code. The absolute addresses of the secure
* code also needs to be relocated along with the accompanying u-boot
* code.
*
* So DISCARD is only for CONFIG_ARMV7_SECURE_BASE.
*/
/DISCARD/ : { *(.rel._secure*) }
#endif
/*
* 指定可执行文件(image)的全局入口地址,通常都放在ROM(flash)0x0位置
* 设置 0 的原因是 arm 内核的处理器,上电后默认是从 0x00000000 处启动
*/
. = 0x00000000;
. = ALIGN(4); ``````````/* 中断向量表 */
.text :
{
*(.__image_copy_start) /* u-boot 的设计中需要将 u-boot 的镜像拷贝到 ram(sdram,ddr....)中执行,这里表示复制的开始地址 */
*(.vectors) /* 中断向量表 */
CPUDIR/start.o (.text*) /* CPUDIR/start.o 中的所有.text 段 */
}
/* This needs to come before *(.text*) */
.__efi_runtime_start : {
*(.__efi_runtime_start)
}
.efi_runtime : {
*(.text.efi_runtime*)
*(.rodata.efi_runtime*)
*(.data.efi_runtime*)
}
.__efi_runtime_stop : {
*(.__efi_runtime_stop)
}
.text_rest :
{
*(.text*)
}
#ifdef CONFIG_ARMV7_NONSEC
/* Align the secure section only if we're going to use it in situ */
.__secure_start
#ifndef CONFIG_ARMV7_SECURE_BASE
ALIGN(CONSTANT(COMMONPAGESIZE))
#endif
: {
KEEP(*(.__secure_start))
}
#ifndef CONFIG_ARMV7_SECURE_BASE
#define CONFIG_ARMV7_SECURE_BASE
#define __ARMV7_PSCI_STACK_IN_RAM
#endif
.secure_text CONFIG_ARMV7_SECURE_BASE :
AT(ADDR(.__secure_start) + SIZEOF(.__secure_start))
{
*(._secure.text)
}
.secure_data : AT(LOADADDR(.secure_text) + SIZEOF(.secure_text))
{
*(._secure.data)
}
#ifdef CONFIG_ARMV7_PSCI
.secure_stack ALIGN(ADDR(.secure_data) + SIZEOF(.secure_data),
CONSTANT(COMMONPAGESIZE)) (NOLOAD) :
#ifdef __ARMV7_PSCI_STACK_IN_RAM
AT(ADDR(.secure_stack))
#else
AT(LOADADDR(.secure_data) + SIZEOF(.secure_data))
#endif
{
KEEP(*(.__secure_stack_start))
/* Skip addreses for stack */
. = . + CONFIG_ARMV7_PSCI_NR_CPUS * ARM_PSCI_STACK_SIZE;
/* Align end of stack section to page boundary */
. = ALIGN(CONSTANT(COMMONPAGESIZE));
KEEP(*(.__secure_stack_end))
#ifdef CONFIG_ARMV7_SECURE_MAX_SIZE
/*
* We are not checking (__secure_end - __secure_start) here,
* as these are the load addresses, and do not include the
* stack section. Instead, use the end of the stack section
* and the start of the text section.
*/
ASSERT((. - ADDR(.secure_text)) <= CONFIG_ARMV7_SECURE_MAX_SIZE,
"Error: secure section exceeds secure memory size");
#endif
}
#ifndef __ARMV7_PSCI_STACK_IN_RAM
/* Reset VMA but don't allocate space if we have secure SRAM */
. = LOADADDR(.secure_stack);
#endif
#endif
.__secure_end : AT(ADDR(.__secure_end)) {
*(.__secure_end)
LONG(0x1d1071c); /* Must output something to reset LMA */
}
#endif
/*
* .rodata 段,确保是以4字节对齐
*/
. = ALIGN(4);
.rodata : { *(SORT_BY_ALIGNMENT(SORT_BY_NAME(.rodata*))) }
/*
* data段,确保是以4字节对齐
*/
. = ALIGN(4);
.data : {
*(.data*)
}
. = ALIGN(4);
. = .;
/*
* u_boot_list 段,确保是以 4 字节对齐
* 这里存放的都是 u_boot_list 中的函数
*/
. = ALIGN(4);
__u_boot_list : {
KEEP(*(SORT(__u_boot_list*)));
}
. = ALIGN(4);
.efi_runtime_rel_start :
{
*(.__efi_runtime_rel_start)
}
.efi_runtime_rel : {
*(.rel*.efi_runtime)
*(.rel*.efi_runtime.*)
}
.efi_runtime_rel_stop :
{
*(.__efi_runtime_rel_stop)
}
/*
* __image_copy_end 也是个符号表示一个结束地址,确保是以4字节对齐
*/
. = ALIGN(4);
.image_copy_end : /* u-boot 的设计中需要将 u-boot 的镜像拷贝到ram(sdram,ddr....)中执行,这里表示复制的结束地址 */
{
*(.__image_copy_end)
}
.rel_dyn_start : /* .rel.dyn 段起始地址 */
{
*(.__rel_dyn_start)
}
.rel.dyn : {
*(.rel*)
}
.rel_dyn_end : /* .rel.dyn 段结束地址 */
{
*(.__rel_dyn_end)
}
.end :
{
*(.__end)
}
_image_binary_end = .; /* bin文件结束地址 */
/*
* Deprecated: this MMU section is used by pxa at present but
* should not be used by new boards/CPUs.
*/
. = ALIGN(4096);
.mmutable : {
*(.mmutable)
}
/*
* Compiler-generated __bss_start and __bss_end, see arch/arm/lib/bss.c
* __bss_base and __bss_limit are for linker only (overlay ordering)
*/
.bss_start __rel_dyn_start (OVERLAY) : { /* .bss段起始地址 */
KEEP(*(.__bss_start));
__bss_base = .;
}
.bss __bss_base (OVERLAY) : {
*(.bss*)
. = ALIGN(4);
__bss_limit = .;
}
.bss_end __bss_limit (OVERLAY) : { /* .bss段结束地址 */
KEEP(*(.__bss_end));
}
.dynsym _image_binary_end : { *(.dynsym) }
.dynbss : { *(.dynbss) }
.dynstr : { *(.dynstr*) }
.dynamic : { *(.dynamic*) }
.plt : { *(.plt*) }
.interp : { *(.interp*) }
.gnu.hash : { *(.gnu.hash) }
.gnu : { *(.gnu*) }
.ARM.exidx : { *(.ARM.exidx*) }
.gnu.linkonce.armexidx : { *(.gnu.linkonce.armexidx.*) }
}
通过上面的分析可以看出:由于在链接脚本中规定了文件start.o(对应于start.S)作为整个uboot的起始点,因此启动uboot时会执行首先执行start.S。一般来说,内存空间可分为代码段、数据段、全局变量段、未初始化变量区、栈区、堆区等.其中,栈区由指针SP决定,堆区实质上是由C代码实现的,其它段则由编译器决定.从上面的分析可以看出,从0x00000000地址开始,编译器首先将代码段放在最开始的位置,然后是数据段,然后是bss段(未初始化变量区)。
2.u-boot.map
u-boot.map 是uboot的映射文件,可以从此文件看到某个文件或者函数链接到了哪个地址,下面打开 u-boot.map,查看各个段的起始地址和结束分别是多少;
内存配置
名称 来源 长度 属性
*default* 0x00000000 0xffffffff
链结器命令稿和内存映射
段 .text 的地址设置为 0x87800000
0x00000000 . = 0x0
0x00000000 . = ALIGN (0x4)
.text 0x87800000 0x3a8
*(.__image_copy_start)
.__image_copy_start
0x87800000 0x0 arch/arm/lib/sections.o
0x87800000 __image_copy_start
*(.vectors)
.vectors 0x87800000 0x2e8 arch/arm/lib/vectors.o
0x87800000 _start
0x87800020 _undefined_instruction
0x87800024 _software_interrupt
0x87800028 _prefetch_abort
0x8780002c _data_abort
0x87800030 _not_used
0x87800034 _irq
0x87800038 _fiq
0x87800040 IRQ_STACK_START_IN
arch/arm/cpu/armv7/start.o(.text*)
.text 0x878002e8 0xc0 arch/arm/cpu/armv7/start.o
0x878002e8 reset
0x878002ec save_boot_params_ret
0x87800328 c_runtime_cpu_setup
0x87800338 save_boot_params
0x8780033c cpu_init_cp15
0x8780039c cpu_init_crit
...
从u-boot.map映射文件种,可以知道__image_copy_start为0x87800000,而.text的起始地址也是0x87800000,.vectors 段的起始地址也是0x87800000,可以得出各个段的地址关系表,如下;
| 变量名 | 地址 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| __image_copy_start | 0x87800000 | u-boot拷贝的起始地址 |
| __image_copy_end | 0x87850ff0 | u-boot拷贝的结束地址 |
| .vectors | 0x87800000 | 中断向量表的起始地址 |
| .text | 0x878002e8 | .text段的起始地址 |
| __rel_dyn_start | 0x87850ff0 | .rel_dyn段的起始地址 |
| __rel_dyn_end | 0x8785cf30 | .rel_dyn段的结束地址 |
| _image_binary_end | 0x8785cf30 | 镜像结束地址 |
| __bss_start | 0x87850ff0 | .bss段的起始地址 |
| __bss_end | 0x878585c0 | .bss段的结束地址 |
注:表中的变量除了__image_copy_start以外,其他的变量值每次编译的时候可能会变化。修改uboot 代码、配置等都会影响到这些值。所以,一切以实际值为准!
四、_start函数详解
从链接文件(u-boot.lds) 中知道了程序入口是 _start,_start 在文件 arch/arm/lib/vectors.S 中有定义,具体代码如下;
/*
*************************************************************************
*
* Symbol _start is referenced elsewhere, so make it global
*
*************************************************************************
*/
.globl _start
/*
*************************************************************************
*
* Vectors have their own section so linker script can map them easily
*
*************************************************************************
*/
.section ".vectors", "ax"
#if defined(CONFIG_ENABLE_ARM_SOC_BOOT0_HOOK)
/*
* Various SoCs need something special and SoC-specific up front in
* order to boot, allow them to set that in their boot0.h file and then
* use it here.
*
* To allow a boot0 hook to insert a 'special' sequence after the vector
* table (e.g. for the socfpga), the presence of a boot0 hook supresses
* the below vector table and assumes that the vector table is filled in
* by the boot0 hook. The requirements for a boot0 hook thus are:
* (1) defines '_start:' as appropriate
* (2) inserts the vector table using ARM_VECTORS as appropriate
*/
#include <asm/arch/boot0.h>
#else
/*
*************************************************************************
*
* Exception vectors as described in ARM reference manuals
*
* Uses indirect branch to allow reaching handlers anywhere in memory.
*
*************************************************************************
*/
_start:
#ifdef CONFIG_SYS_DV_NOR_BOOT_CFG
.word CONFIG_SYS_DV_NOR_BOOT_CFG
#endif
ARM_VECTORS
#endif /* !defined(CONFIG_ENABLE_ARM_SOC_BOOT0_HOOK) */
#if !CONFIG_IS_ENABLED(SYS_NO_VECTOR_TABLE)
/*
*************************************************************************
*
* Indirect vectors table
*
* Symbols referenced here must be defined somewhere else
*
*************************************************************************
*/
.globl _reset
.globl _undefined_instruction /* 未定义指令异常 */
.globl _software_interrupt /* 软中断异常 */
.globl _prefetch_abort /* 预取异常 */
.globl _data_abort /* 数据异常 */
.globl _not_used /* 未使用 */
.globl _irq /* 外部中断请求IRQ */
.globl _fiq /* 快束中断请求FIQ */
...
从u-boot.map映射文件可以得出.vectors段的最开始就是_start,而从_start定义我们可以知道首先是跳转到reset函数,再设置中断向量表。
五、reset函数详解
1.reset函数讲解
从程序入口_start定义中得出,_start中首先是跳转到reset函数,reset函数在文件arch/arm/cpu/armv7/start.S中有定义,具体代码如下;
/*************************************************************************
*
* Startup Code (reset vector)
*
* Do important init only if we don't start from memory!
* Setup memory and board specific bits prior to relocation.
* Relocate armboot to ram. Setup stack.
*
*************************************************************************/
.globl reset
.globl save_boot_params_ret
.type save_boot_params_ret,%function
#ifdef CONFIG_ARMV7_LPAE
.global switch_to_hypervisor_ret
#endif
reset:
/* Allow the board to save important registers */
b save_boot_params
save_boot_params_ret:
...
reset函数只有一句跳转语句,直接跳转到了save_boot_params函数,而save_boot_params函数同样定义在start.S里面,定义如下:
/*************************************************************************
*
* void save_boot_params(u32 r0, u32 r1, u32 r2, u32 r3)
* __attribute__((weak));
*
* Stack pointer is not yet initialized at this moment
* Don't save anything to stack even if compiled with -O0
*
*************************************************************************/
ENTRY(save_boot_params)
b save_boot_params_ret @ back to my caller
####2.save_boot_params_ret函数讲解
同样save_boot_params函数也是只有一句跳转语句,跳转到save_boot_params_ret函数save_boot_params_ret 函数代码如下:
save_boot_params_ret:
#ifdef CONFIG_POSITION_INDEPENDENT
/*
* Fix .rela.dyn relocations. This allows U-Boot to loaded to and
* executed at a different address than it was linked at.
*/
pie_fixup:
/* 获取标号reset的运行地址到r0 */
adr r0, reset /* r0 <- Runtime value of reset label */
/* 获取标号reset的链接地址到r0 */
ldr r1, =reset /* r1 <- Linked value of reset label */
/* 计算运行地址和link地址的偏移 */
subs r4, r0, r1 /* r4 <- Runtime-vs-link offset */
/* 如果为0,说明link地址和运行地址一致,不需要重定位直接退出 */
beq pie_fixup_done
/*
* 下面几行代码的作用是计算运行时rel.dyn段在内存中实际地址,只有获取这个段的
* 真实的起使地址才能依据其中的信息进行重定位。
*/
//获取pie_fixup标号的运行地址
adr r0, pie_fixup
//_rel_dyn_start_ofs链接时rel.dyn段相对pie_fixup标号的偏移
ldr r1, _rel_dyn_start_ofs
add r2, r0, r1 /* r2 <- Runtime &__rel_dyn_start */
//计算rel.dyn运行时起始地址
ldr r1, _rel_dyn_end_ofs
//计算rel.dyn运行结束地址
add r3, r0, r1 /* r3 <- Runtime &__rel_dyn_end */
pie_fix_loop:
//获取rel.dyn段地址中的内容
ldr r0, [r2] /* r0 <- Link location */
//获取rel.dyn段地址接下来4个字节中的内容
ldr r1, [r2, #4] /* r1 <- fixup */
//如果r1等于23则执行重定位
cmp r1, #23 /* relative fixup? */
bne pie_skip_reloc
/* relative fix: increase location by offset */
add r0, r4
ldr r1, [r0]
add r1, r4
str r1, [r0]
str r0, [r2]
add r2, #8
pie_skip_reloc:
//判断是否所有表项都修改完成,没完成则循环操作
cmp r2, r3
blo pie_fix_loop
pie_fixup_done:
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_ARMV7_LPAE
/*
* check for Hypervisor support
*/
mrc p15, 0, r0, c0, c1, 1 @ read ID_PFR1
and r0, r0, #CPUID_ARM_VIRT_MASK @ mask virtualization bits
cmp r0, #(1 << CPUID_ARM_VIRT_SHIFT)
beq switch_to_hypervisor
switch_to_hypervisor_ret:
#endif
/*
* disable interrupts (FIQ and IRQ), also set the cpu to SVC32 mode,
* except if in HYP mode already
*/
/* 将程序状态寄存器读取到通用寄存器R0 */
mrs r0, cpsr
and r1, r0, #0x1f @ mask mode bits
teq r1, #0x1a @ test for HYP mode
/* 清除当前的工作模式 */
bicne r0, r0, #0x1f @ clear all mode bits
/* 设置SVC模式,即超级管理员权限 */
orrne r0, r0, #0x13 @ set SVC mode
/* 失能中断FIQ和IRQ */
orr r0, r0, #0xc0 @ disable FIQ and IRQ
msr cpsr,r0
#if !CONFIG_IS_ENABLED(SYS_NO_VECTOR_TABLE)
/*
* Setup vector:
*/
/* Set V=0 in CP15 SCTLR register - for VBAR to point to vector */
mrc p15, 0, r0, c1, c0, 0 @ Read CP15 SCTLR Register
bic r0, #CR_V @ V = 0
mcr p15, 0, r0, c1, c0, 0 @ Write CP15 SCTLR Register
#ifdef CONFIG_HAS_VBAR
/* Set vector address in CP15 VBAR register */
ldr r0, =_start
mcr p15, 0, r0, c12, c0, 0 @Set VBAR
#endif
#endif
/* the mask ROM code should have PLL and others stable */
#if !CONFIG_IS_ENABLED(SKIP_LOWLEVEL_INIT)
#ifdef CONFIG_CPU_V7A
bl cpu_init_cp15
#endif
#if !CONFIG_IS_ENABLED(SKIP_LOWLEVEL_INIT_ONLY)
bl cpu_init_crit
#endif
#endif
bl _main
save_boot_params_ret函数主要的操作如下:
-
1.如果定义宏CONFIG_POSITION_INDEPENDENT,则进行修正重定位的问题(pie_fixup、pie_fix_loop、pie_skip_reloc);
-
2.如果定义宏CONFIG_ARMV7_LPAE,LPAE(Large Physical Address Extensions)是ARMv7系列的一种地址扩展技术,可以让32位的ARM最大能支持到1TB的内存空间,由于嵌入式ARM需求的内存空间一般不大,所以一般不使用LPAE技术;
-
3.设置CPU为SVC32模式,除非已经处于HYP模式,同时禁止中断(FIQ和IRQ);
-
4.设置中断向量表地址为_start函数的地址,在map文件中可以看到,为0x87800000;
-
5.进行CPU初始化,调用函数cpu_init_cp15和cpu_init_crit分别初始化CP15和CRIT;
-
6.最后跳转到_main函数。
3.cpu_init_cp15函数讲解
cpu_init_cp15函数,在文件arch/arm/cpu/armv7/start.S中定义,具体代码如下;
/*************************************************************************
*
* cpu_init_cp15
*
* Setup CP15 registers (cache, MMU, TLBs). The I-cache is turned on unless
* CONFIG_SYS_ICACHE_OFF is defined.
*
*************************************************************************/
ENTRY(cpu_init_cp15)
#if CONFIG_IS_ENABLED(ARMV7_SET_CORTEX_SMPEN)
/*
* The Arm Cortex-A7 TRM says this bit must be enabled before
* "any cache or TLB maintenance operations are performed".
*/
mrc p15, 0, r0, c1, c0, 1 @ read auxilary control register
orr r0, r0, #1 << 6 @ set SMP bit to enable coherency
mcr p15, 0, r0, c1, c0, 1 @ write auxilary control register
#endif
/*
* Invalidate L1 I/D
*/
mov r0, #0 @ set up for MCR
mcr p15, 0, r0, c8, c7, 0 @ invalidate TLBs
mcr p15, 0, r0, c7, c5, 0 @ invalidate icache
mcr p15, 0, r0, c7, c5, 6 @ invalidate BP array
mcr p15, 0, r0, c7, c10, 4 @ DSB
mcr p15, 0, r0, c7, c5, 4 @ ISB
/*
* disable MMU stuff and caches
*/
mrc p15, 0, r0, c1, c0, 0
bic r0, r0, #0x00002000 @ clear bits 13 (--V-)
bic r0, r0, #0x00000007 @ clear bits 2:0 (-CAM)
orr r0, r0, #0x00000002 @ set bit 1 (--A-) Align
orr r0, r0, #0x00000800 @ set bit 11 (Z---) BTB
...
cpu_init_cp15函数主要的操作如下:
-
1.失效 L1 I/D Cache;
-
2.禁用MMU和缓存。
4.cpu_init_crit函数讲解
cpu_init_crit在文件arch/arm/cpu/armv7/start.S中定义,具体代码如下;
/*************************************************************************
*
* CPU_init_critical registers
*
* setup important registers
* setup memory timing
*
*************************************************************************/
ENTRY(cpu_init_crit)
/*
* Jump to board specific initialization...
* The Mask ROM will have already initialized
* basic memory. Go here to bump up clock rate and handle
* wake up conditions.
*/
b lowlevel_init @ go setup pll,mux,memory
ENDPROC(cpu_init_crit)
#endif
可以看到函数cpu_init_crit内部又只是一句跳转语句,调用了函数lowlevel_init,接下来就是详细的分析一下lowlevel_init和_main这两个函数。
六、lowlevel_init函数详解
lowlevel_init函数,在文件arch/arm/cpu/armv7/lowlevel_init.S中有定义,具体代码如下;
WEAK(lowlevel_init)
/*
* Setup a temporary stack. Global data is not available yet.
*/
#if defined(CONFIG_SPL_BUILD) && defined(CONFIG_SPL_STACK)
ldr sp, =CONFIG_SPL_STACK
#else
ldr sp, =SYS_INIT_SP_ADDR
#endif
bic sp, sp, #7 /* 8-byte alignment for ABI compliance */
#ifdef CONFIG_SPL_DM
mov r9, #0
#else
/*
* Set up global data for boards that still need it. This will be
* removed soon.
*/
#ifdef CONFIG_SPL_BUILD
ldr r9, =gdata
#else
sub sp, sp, #GD_SIZE
bic sp, sp, #7
mov r9, sp
#endif
#endif
/*
* Save the old lr(passed in ip) and the current lr to stack
*/
push {ip, lr}
/*
* Call the very early init function. This should do only the
* absolute bare minimum to get started. It should not:
*
* - set up DRAM
* - use global_data
* - clear BSS
* - try to start a console
*
* For boards with SPL this should be empty since SPL can do all of
* this init in the SPL board_init_f() function which is called
* immediately after this.
*/
bl s_init
pop {ip, pc}
ENDPROC(lowlevel_init)
lowlevel_init函数主要的操作如下:
-
1.设置SP指针为CONFIG_SYS_INIT_SP_ADDR
-
2.对sp指针做8字节对齐处理
-
3.SP减去#GD_SIZE = 248,GD_SIZE同样在generic-asm-offsets.h 中定了
-
4.对 sp 指针做8字节对齐处理
-
5.将SP保存到R9,ip和lr入栈,程序跳转到s_init(对于I.MX6ULL来说,s_init 就是个空函数)
-
6.函数一路返回,直到_main,s_init函数-->函数lowlevel_ini-->cpu_init_crit-->save_boot_params_ret-->_main。
七、_main函数详解
_main函数在文件 arch/arm/lib/crt0.S中有定义 _main函数执行可以大致分为如下4个部分:
-
设置初始化C运行环境并调用board_init_f函数
-
设置新的sp指针和gd指针,设置中间环境位,调用代码重定位
-
重定位向量表
-
设置最后的运行环境并调用board_init_r函数
1.设置初始化C运行环境并调用board_init_f函数
代码部分,具体如下;
/*
* entry point of crt0 sequence
*/
ENTRY(_main)
/* Call arch_very_early_init before initializing C runtime environment. */
#if CONFIG_IS_ENABLED(ARCH_VERY_EARLY_INIT)
bl arch_very_early_init
#endif
/*
* Set up initial C runtime environment and call board_init_f(0).
*/
#if defined(CONFIG_TPL_BUILD) && defined(CONFIG_TPL_NEEDS_SEPARATE_STACK)
ldr r0, =(CONFIG_TPL_STACK)
#elif defined(CONFIG_SPL_BUILD) && defined(CONFIG_SPL_STACK)
ldr r0, =(CONFIG_SPL_STACK)
#else
ldr r0, =(SYS_INIT_SP_ADDR)
#endif
bic r0, r0, #7 /* 8-byte alignment for ABI compliance */
mov sp, r0
bl board_init_f_alloc_reserve
mov sp, r0
/* set up gd here, outside any C code */
mov r9, r0
bl board_init_f_init_reserve
#if defined(CONFIG_DEBUG_UART) && CONFIG_IS_ENABLED(SERIAL)
bl debug_uart_init
#endif
#if defined(CONFIG_SPL_BUILD) && defined(CONFIG_SPL_EARLY_BSS)
CLEAR_BSS
#endif
mov r0, #0
bl board_init_f
-
1.设置sp指针为 CONFIG_SYS_INIT_SP_ADDR;
-
2.对sp指针做8字节对齐处理;
-
3.读取sp到寄存器r0里面;
-
4.调用函数board_init_f_alloc_reserve;
-
5.调用函数board_init_f_init_reserve;
-
6.调用函数board_init_f。
1.board_init_f_alloc_reserve函数
board_init_f_alloc_reserve函数,在common/init/board_init.c文件中定义,如下;
ulong board_init_f_alloc_reserve(ulong top)
{
/* Reserve early malloc arena */
#ifndef CONFIG_MALLOC_F_ADDR
#if CONFIG_VAL(SYS_MALLOC_F_LEN)
top -= CONFIG_VAL(SYS_MALLOC_F_LEN);
#endif
#endif
/* LAST : reserve GD (rounded up to a multiple of 16 bytes) */
top = rounddown(top-sizeof(struct global_data), 16);
return top;
}
board_init_f_alloc_reserve函数的作用是根据传入参数是栈顶地址,计算出预留空间的底部,并将其返回。主要是留出早期的 malloc 内存区域和gd内存区域。如果宏CONFIG_MALLOC_F_ADDR没有被定义,则为malloc预留部分内存空间,大小为CONFIG_SYS_MALLOC_F_LEN;其次为GD变量(global_data结构体类型)预留空间,并且对齐到16个字节的倍数。
2.board_init_f_init_reserve函数
board_init_f_init_reserve函数,在common/init/board_init.c文件中定义,如下;
void board_init_f_init_reserve(ulong base)
{
struct global_data *gd_ptr;
/*
* clear GD entirely and set it up.
* Use gd_ptr, as gd may not be properly set yet.
*/
gd_ptr = (struct global_data *)base;
/* zero the area */
memset(gd_ptr, '\0', sizeof(*gd));
/* set GD unless architecture did it already */
#if !defined(CONFIG_ARM)
arch_setup_gd(gd_ptr);
#endif
if (CONFIG_IS_ENABLED(SYS_REPORT_STACK_F_USAGE))
board_init_f_init_stack_protection_addr(base);
/* next alloc will be higher by one GD plus 16-byte alignment */
base += roundup(sizeof(struct global_data), 16);
/*
* record early malloc arena start.
* Use gd as it is now properly set for all architectures.
*/
#if CONFIG_VAL(SYS_MALLOC_F_LEN)
/* go down one 'early malloc arena' */
gd->malloc_base = base;
#endif
if (CONFIG_IS_ENABLED(SYS_REPORT_STACK_F_USAGE))
board_init_f_init_stack_protection();
}
board_init_f_init_reserve函数的作用:
初始化gd,其实就是清零处理;设置了gd->malloc_base为gd基地址+gd 大小,并做16字节对齐处理。
2.设置新的sp指针和gd指针,调用重定位代码,调用代码重定位
代码部分,具体如下;
#if ! defined(CONFIG_SPL_BUILD)
/*
* Set up intermediate environment (new sp and gd) and call
* relocate_code(addr_moni). Trick here is that we'll return
* 'here' but relocated.
*/
ldr r0, [r9, #GD_START_ADDR_SP] /* sp = gd->start_addr_sp */
bic r0, r0, #7 /* 8-byte alignment for ABI compliance */
mov sp, r0
ldr r9, [r9, #GD_NEW_GD] /* r9 <- gd->new_gd */
adr lr, here
#if defined(CONFIG_POSITION_INDEPENDENT)
adr r0, _main
ldr r1, _start_ofs
add r0, r1
ldr r1, =CONFIG_SYS_TEXT_BASE
sub r1, r0
add lr, r1
#endif
ldr r0, [r9, #GD_RELOC_OFF] /* r0 = gd->reloc_off */
add lr, lr, r0
#if defined(CONFIG_CPU_V7M)
orr lr, #1 /* As required by Thumb-only */
#endif
ldr r0, [r9, #GD_RELOCADDR] /* r0 = gd->relocaddr */
b relocate_code
-
1.设置新的栈顶指针为sp = gd->start_addr_sp;
-
2.设置新的gd指针为r9 <- gd->new_gd;
-
3.设置新r0指针为r0 = gd->reloc_off;
-
4.设置r0寄存器的值为gd->relocaddr,跳转到代码重定位relocate_code。
3.重定位向量表
代码部分,具体如下;
here:
/*
* now relocate vectors
*/
bl relocate_vectors
代码重定位后返回到here标号处,调用relocate_vectors函数,对中断向量表做重定位。
4.设置最后的运行环境并调用board_init_r函数
代码部分,具体如下;
/* Set up final (full) environment */
bl c_runtime_cpu_setup /* we still call old routine here */
#endif
#if !defined(CONFIG_SPL_BUILD) || CONFIG_IS_ENABLED(FRAMEWORK)
#if !defined(CONFIG_SPL_BUILD) || !defined(CONFIG_SPL_EARLY_BSS)
CLEAR_BSS
#endif
# ifdef CONFIG_SPL_BUILD
/* Use a DRAM stack for the rest of SPL, if requested */
bl spl_relocate_stack_gd
cmp r0, #0
movne sp, r0
movne r9, r0
# endif
#if ! defined(CONFIG_SPL_BUILD)
bl coloured_LED_init
bl red_led_on
#endif
/* call board_init_r(gd_t *id, ulong dest_addr) */
mov r0, r9 /* gd_t */
ldr r1, [r9, #GD_RELOCADDR] /* dest_addr */
/* call board_init_r */
#if CONFIG_IS_ENABLED(SYS_THUMB_BUILD)
ldr lr, =board_init_r /* this is auto-relocated! */
bx lr
#else
ldr pc, =board_init_r /* this is auto-relocated! */
#endif
/* we should not return here. */
#endif
ENDPROC(_main)
board_init_r函数主要工作:
-
1.调用函数c_runtime_cpu_setup,失效I-cache;
-
2.清除BSS段;
-
3.设置函数board_init_r的两个参数;
-
4.调用函数board_init_r。
八、board_init_f 函数详解
board_init_f函数,在common/board_f.c文件定义,具体代码如下;
void board_init_f(ulong boot_flags)
{
gd->flags = boot_flags;
gd->have_console = 0;
if (initcall_run_list(init_sequence_f))
hang();
#if !defined(CONFIG_ARM) && !defined(CONFIG_SANDBOX) && \
!defined(CONFIG_EFI_APP) && !CONFIG_IS_ENABLED(X86_64) && \
!defined(CONFIG_ARC)
/* NOTREACHED - jump_to_copy() does not return */
hang();
#endif
}
board_init_f函数主要有两个工作:
-
1.初始化gd的各个成员变量
-
2.调用函数initcall_run_list,初始化序列init_sequence_f里面的一系列函数,来初始化一系列外设,比如串口、定时器,或者打印一些消息等。
init_sequence_f数组,在common/board_f.c文件中定义,如下,初始化函数表省略其中部分代码;
static const init_fnc_t init_sequence_f[] = {
setup_mon_len,
fdtdec_setup,
trace_early_init,
initf_malloc,
log_init,
initf_bootstage, /* uses its own timer, so does not need DM */
event_init,
bloblist_init,
setup_spl_handoff,
console_record_init,
arch_fsp_init,
arch_cpu_init, /* basic arch cpu dependent setup */
mach_cpu_init, /* SoC/machine dependent CPU setup */
initf_dm,
board_early_init_f,
get_clocks, /* get CPU and bus clocks (etc.) */
timer_init, /* initialize timer */
board_postclk_init,
env_init, /* initialize environment */
init_baud_rate, /* initialze baudrate settings */
serial_init, /* serial communications setup */
console_init_f, /* stage 1 init of console */
display_options, /* say that we are here */
display_text_info, /* show debugging info if required */
checkcpu,
print_resetinfo,
print_cpuinfo, /* display cpu info (and speed) */
embedded_dtb_select,
show_board_info,
INIT_FUNC_WATCHDOG_INIT
misc_init_f,
INIT_FUNC_WATCHDOG_RESET
init_func_i2c,
init_func_vid,
announce_dram_init,
dram_init, /* configure available RAM banks */
post_init_f,
INIT_FUNC_WATCHDOG_RESET
testdram,
INIT_FUNC_WATCHDOG_RESET
init_post,
INIT_FUNC_WATCHDOG_RESET
setup_dest_addr,
fix_fdt,
reserve_pram,
...
#if !defined(CONFIG_ARM) && !defined(CONFIG_SANDBOX) && \
!CONFIG_IS_ENABLED(X86_64)
jump_to_copy,
#endif
NULL,
};
其中比较重要的一些初始化函数如下:
-
1.setup_mon_len函数:设置gd的mon_len成员变量,也就是整个代码的长度;
-
2.initf_malloc函数:设置gd中和malloc有关的成员变量;
-
3.board_early_init_f函数:用来初始化串口的IO配置,在board/freescale/mx6ull_toto/mx6ull_toto.c文件中定义;
-
4.timer_init函数:初始化内核定时器,为uboot提供时钟节拍,在arch/arm/imx-common/timer.c文件中定义;
-
5.get_clocks函数:获取了SD卡外设的时钟(sdhc_clk),在arch/arm/imx-common/speed.c文件中定义;
-
6.init_baud_rate函数:初始化波特率,在common/board_f.c文件中定义;
-
7.serial_init函数:初始化串口通信设置,在drivers/serial/serial.c文件中定义;
-
8.console_init_f函数:初始化控制台,在common/console.c文件中定义:
-
9.display_options函数:打印uboot版本信息和编译信息,在lib/display_options.c文件中定义;
-
10.print_cpuinfo函数:用来显示CPU信息和主频,在arch/arm/imx-common/cpu.c文件中定义;
-
11.show_board_info函数:打印开发板信息,在common/board_info.c文件中定义;
-
12.init_func_i2c函数:用于初始化I2C;
-
13.announce_dram_init函数:此函数很简单,就是输出字符串“DRAM:”;
-
14.dram_init函数:并非真正的初始化DDR,只是设置gd->ram_size的值。
九、relocate_code函数详解
relocate_code函数,在arch/arm/lib/relocate.S文件定义,具体代码如下;
/*
* void relocate_code(addr_moni)
*
* This function relocates the monitor code.
*
* NOTE:
* To prevent the code below from containing references with an R_ARM_ABS32
* relocation record type, we never refer to linker-defined symbols directly.
* Instead, we declare literals which contain their relative location with
* respect to relocate_code, and at run time, add relocate_code back to them.
*/
ENTRY(relocate_code)
relocate_base:
adr r3, relocate_base
ldr r1, _image_copy_start_ofs
add r1, r3 /* r1 <- Run &__image_copy_start */
subs r4, r0, r1 /* r4 <- Run to copy offset */
beq relocate_done /* skip relocation */
ldr r1, _image_copy_start_ofs
add r1, r3 /* r1 <- Run &__image_copy_start */
ldr r2, _image_copy_end_ofs
add r2, r3 /* r2 <- Run &__image_copy_end */
copy_loop:
ldmia r1!, {r10-r11} /* copy from source address [r1] */
stmia r0!, {r10-r11} /* copy to target address [r0] */
cmp r1, r2 /* until source end address [r2] */
blo copy_loop
/*
* fix .rel.dyn relocations
*/
ldr r1, _rel_dyn_start_ofs
add r2, r1, r3 /* r2 <- Run &__rel_dyn_start */
ldr r1, _rel_dyn_end_ofs
add r3, r1, r3 /* r3 <- Run &__rel_dyn_end */
fixloop:
ldmia r2!, {r0-r1} /* (r0,r1) <- (SRC location,fixup) */
and r1, r1, #0xff
cmp r1, #R_ARM_RELATIVE
bne fixnext
/* relative fix: increase location by offset */
add r0, r0, r4
ldr r1, [r0]
add r1, r1, r4
str r1, [r0]
fixnext:
cmp r2, r3
blo fixloop
relocate_done:
#ifdef __XSCALE__
/*
* On xscale, icache must be invalidated and write buffers drained,
* even with cache disabled - 4.2.7 of xscale core developer's manual
*/
mcr p15, 0, r0, c7, c7, 0 /* invalidate icache */
mcr p15, 0, r0, c7, c10, 4 /* drain write buffer */
#endif
/* ARMv4- don't know bx lr but the assembler fails to see that */
#ifdef __ARM_ARCH_4__
mov pc, lr
#else
bx lr
#endif
ENDPROC(relocate_code)
relocate_code此函数作用:
完成镜像拷贝和重定位,镜像地址从__image_copy_start开始,到__image_copy_end结束,拷贝的目标地址由参数传进来,也就是r0寄存器的值。重定位的原理此处不展开,需要了解的自行去学习。
十、relocate_vectors函数详解
relocate_vectors函数,在arch/arm/lib/relocate.S文件定义,具体代码如下;
ENTRY(relocate_vectors)
#ifdef CONFIG_CPU_V7M
/*
* On ARMv7-M we only have to write the new vector address
* to VTOR register.
*/
ldr r0, [r9, #GD_RELOCADDR] /* r0 = gd->relocaddr */
ldr r1, =V7M_SCB_BASE
str r0, [r1, V7M_SCB_VTOR]
#else
#ifdef CONFIG_HAS_VBAR
/*
* If the ARM processor has the security extensions,
* use VBAR to relocate the exception vectors.
*/
ldr r0, [r9, #GD_RELOCADDR] /* r0 = gd->relocaddr */
mcr p15, 0, r0, c12, c0, 0 /* Set VBAR */
#else
/*
* Copy the relocated exception vectors to the
* correct address
* CP15 c1 V bit gives us the location of the vectors:
* 0x00000000 or 0xFFFF0000.
*/
ldr r0, [r9, #GD_RELOCADDR] /* r0 = gd->relocaddr */
mrc p15, 0, r2, c1, c0, 0 /* V bit (bit[13]) in CP15 c1 */
ands r2, r2, #(1 << 13)
ldreq r1, =0x00000000 /* If V=0 */
ldrne r1, =0xFFFF0000 /* If V=1 */
ldmia r0!, {r2-r8,r10}
stmia r1!, {r2-r8,r10}
ldmia r0!, {r2-r8,r10}
stmia r1!, {r2-r8,r10}
#endif
#endif
bx lr
ENDPROC(relocate_vectors)
relocate_vectors函数作用:
用于重定位向量表,只有一步操作比较重要,就是将uboot重定位完之后的地址,装载到CP15的VBAR寄存器中设置向量表偏移,该寄存器自行去学习。
十一、board_init_r函数详解
board_init_r函数,在common/board_r.c文件定义,具体代码如下;
void board_init_r(gd_t *new_gd, ulong dest_addr)
{
/*
* Set up the new global data pointer. So far only x86 does this
* here.
* TODO(sjg@chromium.org): Consider doing this for all archs, or
* dropping the new_gd parameter.
*/
if (CONFIG_IS_ENABLED(X86_64) && !IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_EFI_APP))
arch_setup_gd(new_gd);
#if !defined(CONFIG_X86) && !defined(CONFIG_ARM) && !defined(CONFIG_ARM64)
gd = new_gd;
#endif
gd->flags &= ~GD_FLG_LOG_READY;
if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_NEEDS_MANUAL_RELOC)) {
for (int i = 0; i < ARRAY_SIZE(init_sequence_r); i++)
MANUAL_RELOC(init_sequence_r[i]);
}
if (initcall_run_list(init_sequence_r))
hang();
/* NOTREACHED - run_main_loop() does not return */
hang();
}
board_init_f函数中,会初始化一些外设和gd的成员变量,但并没有初始化所有的外设,还需要一些后续工作,这些工作就是由board_init_r函数完成的,调用initcall_run_list函数执行初始化序列init_sequence_r。
init_sequence_r是一个函数表,也定义在该文件中,部分代码如下;
static init_fnc_t init_sequence_r[] = {
initr_trace,
initr_reloc,
event_init,
initr_caches,
initr_reloc_global_data,
initr_barrier,
initr_malloc,
log_init,
initr_bootstage,
console_record_init,
initr_of_live,
board_init, /* Setup chipselects */
stdio_init_tables,
serial_initialize,
initr_announce,
INIT_FUNC_WATCHDOG_RESET
INIT_FUNC_WATCHDOG_RESET
power_init_board,
initr_flash,
initr_nand,
initr_mmc,
initr_env,
INIT_FUNC_WATCHDOG_RESET
cpu_secondary_init_r,
INIT_FUNC_WATCHDOG_RESET
stdio_add_devices,
jumptable_init,
console_init_r, /* fully init console as a device */
interrupt_init,
board_late_init,
INIT_FUNC_WATCHDOG_RESET
initr_net,
run_main_loop,
};
其中比较重要的一些初始化函数如下:
-
1.initr_caches函数:初始化cache,使能cache;
-
2.board_init函数:FEC初始化,在board/freescale/mx6ull_toto/mx6ull_toto.c文件中定义;
-
3.initr_mmc函数:初始化emmc,在common/board_r.c文件中定义;
-
4.iinitr_env函数:初始化环境变量;
-
5.console_init_r函数:初始化控制台,在common/console.c文件中定义;
-
6.interrupt_init函数和initr_enable_interrupts函数:初始化中断并使能中断;在arch/arm/lib/interrupts.c文件中定义;
-
7.initr_ethaddr函数:初始化网络地址,获取MAC地址,读取环境变量ethaddr的值;
-
8.initr_net函数:初始化网络设备,函 数 调 用 顺 序 为 :initr_net->eth_initialize->board_eth_init(),在common/board_r.c文件中定义;
-
9.run_main_loop函数:主循环,处理命令。
十二、run_main_loop函数详解
run_main_loop函数,在common/board_r.c文件定义,具体代码如下;
static int run_main_loop(void)
{
#ifdef CONFIG_SANDBOX
sandbox_main_loop_init();
#endif
/* main_loop() can return to retry autoboot, if so just run it again */
for (;;)
main_loop();
return 0;
}
uboot启动以后会进入3秒倒计时,如果在3秒倒计时结束之前按下按下回车键,那么就会进入uboot的命令模式,如果倒计时结束以后都没有按下回车键,那么就会自动启动Linux内核,这个功能就是由run_main_loop函数来完成的。
main_loop函数,在common/main.c文件中定义,具体代码如下;
/* We come here after U-Boot is initialised and ready to process commands */
void main_loop(void)
{
const char *s;
bootstage_mark_name(BOOTSTAGE_ID_MAIN_LOOP, "main_loop");
if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_VERSION_VARIABLE))
env_set("ver", version_string); /* set version variable */
cli_init();
if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_USE_PREBOOT))
run_preboot_environment_command();
if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_UPDATE_TFTP))
update_tftp(0UL, NULL, NULL);
if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_EFI_CAPSULE_ON_DISK_EARLY)) {
/* efi_init_early() already called */
if (efi_init_obj_list() == EFI_SUCCESS)
efi_launch_capsules();
}
s = bootdelay_process();
if (cli_process_fdt(&s))
cli_secure_boot_cmd(s);
autoboot_command(s);
cli_loop();
panic("No CLI available");
}
main_loop函数主要工作:
-
1.调用bootstage_mark_name函数,打印出启动进度
-
2.如果宏CONFIG_VERSION_VARIABLE定义了就会执行函数setenv,设置换将变量ver的值为version_string,也就是设置版本号环境变量;
-
3.调用cli_init函数,初始化hushshell相关的变量
-
4.调用bootdelay_process函数,此函数会读取环境变量bootdelay和bootcmd的内容,然后将bootdelay的值赋值给全局变量stored_bootdelay,返回值为环境变量bootcmd的值。
-
5.autoboot_command函数,此函数就是检查倒计时是否结束?倒计时结束之前有没有被打断?
autoboot_command函数,在文件common/autoboot.c文件中定义,具体代码如下;
void autoboot_command(const char *s)
{
debug("### main_loop: bootcmd=\"%s\"\n", s ? s : "<UNDEFINED>");
if (s && (stored_bootdelay == -2 ||
(stored_bootdelay != -1 && !abortboot(stored_bootdelay)))) {
bool lock;
int prev;
lock = autoboot_keyed() &&
!IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_AUTOBOOT_KEYED_CTRLC);
if (lock)
prev = disable_ctrlc(1); /* disable Ctrl-C checking */
run_command_list(s, -1, 0);
if (lock)
disable_ctrlc(prev); /* restore Ctrl-C checking */
}
if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_AUTOBOOT_USE_MENUKEY) &&
menukey == AUTOBOOT_MENUKEY) {
s = env_get("menucmd");
if (s)
run_command_list(s, -1, 0);
}
}
abortboot函数,在文件common/autoboot.c文件中定义,具体代码如下;
static int abortboot(int bootdelay)
{
int abort = 0;
if (bootdelay >= 0) {
if (autoboot_keyed())
abort = abortboot_key_sequence(bootdelay);
else
abort = abortboot_single_key(bootdelay);
}
if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_SILENT_CONSOLE) && abort)
gd->flags &= ~GD_FLG_SILENT;
return abort;
}
在倒计时结束之前有按键按下则执行函数 abortboot_single_key,abortboot_single_key函数在common/autoboot.c文件中定义,具体代码如下;
static int abortboot_single_key(int bootdelay)
{
int abort = 0;
unsigned long ts;
printf("Hit any key to stop autoboot: %2d ", bootdelay);
/*
* Check if key already pressed
*/
if (tstc()) { /* we got a key press */
getchar(); /* consume input */
puts("\b\b\b 0");
abort = 1; /* don't auto boot */
}
while ((bootdelay > 0) && (!abort)) {
--bootdelay;
/* delay 1000 ms */
ts = get_timer(0);
do {
if (tstc()) { /* we got a key press */
int key;
abort = 1; /* don't auto boot */
bootdelay = 0; /* no more delay */
key = getchar();/* consume input */
if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_AUTOBOOT_USE_MENUKEY))
menukey = key;
break;
}
udelay(10000);
} while (!abort && get_timer(ts) < 1000);
printf("\b\b\b%2d ", bootdelay);
}
putc('\n');
return abort;
}
abortboot_single_key函数主要工作:
-
1.倒计时的具体实现;
-
2.判断键盘是否有按下,也就是是否打断了倒计时,如果键盘按下的话就执行相应的分支。比如设置abort为 1,设置 bootdelay为0等,最后跳出倒计时循环;
-
3.返回abort的值,如果倒计时自然结束,没有被打断abort就为0,否则的话abort的值就为 1;
-
4.在autoboot_command函数中,如果倒计时自然结束那么就执行函数run_command_list,此函数会执行参数s指定的一系列命令,也就是环境变量bootcmd的命令,bootcmd里面保存着默认的启动命令,因此linux内核启动!
十三、u-boot启动函数调用流程框图
上面给大家详细的讲解了各个函数的作用,以及调用关系。现在给大家总结一下,以流程框图的形式,展示u-boot启动流程;
今天的内容到这就结束了,感谢大家的收看!