Apache APISIX
https://apisix.apache.org/
功能比nginx-ingress更强
本文采用2.5.0版本
https://apisix.apache.org/zh/docs/apisix/2.15/getting-started/
概述内容来源于官方,学习于马士兵云原生课程
概述
Apache APISIX 是什么?
Apache APISIX 是 Apache 软件基金会下的云原生 API 网关,它兼具动态、实时、高性能等特点,提供了负载均衡、动态上游、灰度发布(金丝雀发布)、服务熔断、身份认证、可观测性等丰富的流量管理功能。我们可以使用 Apache APISIX 来处理传统的南北向流量,也可以处理服务间的东西向流量。同时,它也支持作为 K8s Ingress Controller 来使用。
主要特性
- 多平台支持:APISIX 提供了多平台解决方案,它不但支持裸机运行,也支持在 Kubernetes 中使用,还支持与 AWS Lambda、Azure Function、Lua 函数和 Apache OpenWhisk 等云服务集成。
- 全动态能力:APISIX 支持热加载,这意味着你不需要重启服务就可以更新 APISIX 的配置。请访问为什么 Apache APISIX 选择 Nginx + Lua 这个技术栈?以了解实现原理。
- 精细化路由:APISIX 支持使用 NGINX 内置变量做为路由的匹配条件,你可以自定义匹配函数来过滤请求,匹配路由。
- 运维友好:APISIX 支持与以下工具和平台集成:HashiCorp Vault、Zipkin、Apache SkyWalking、Consul、Nacos、Eureka。通过 APISIX Dashboard,运维人员可以通过友好且直观的 UI 配置 APISIX。
- 多语言插件支持:APISIX 支持多种开发语言进行插件开发,开发人员可以选择擅长语言的 SDK 开发自定义插件。
主要概念
| 概念/组件 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| Route | 通过路由定义规则来匹配客户端请求,根据匹配结果加载并执行相应的插件,最后把请求转发给到指定的上游应用。 |
| Upstream | 上游的作用是按照配置规则对服务节点进行负载均衡,它的地址信息可以直接配置到路由或服务上。 |
| Admin API | 用户可以通过 Admin API 控制 APISIX 实例。 |
部署
本次采用应用仓库部署
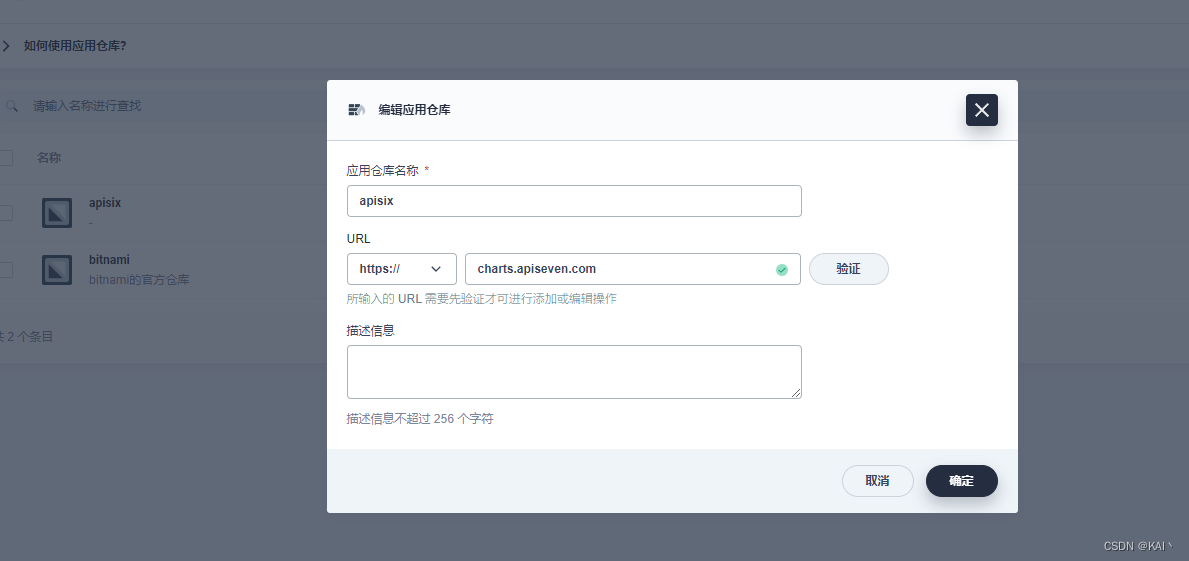
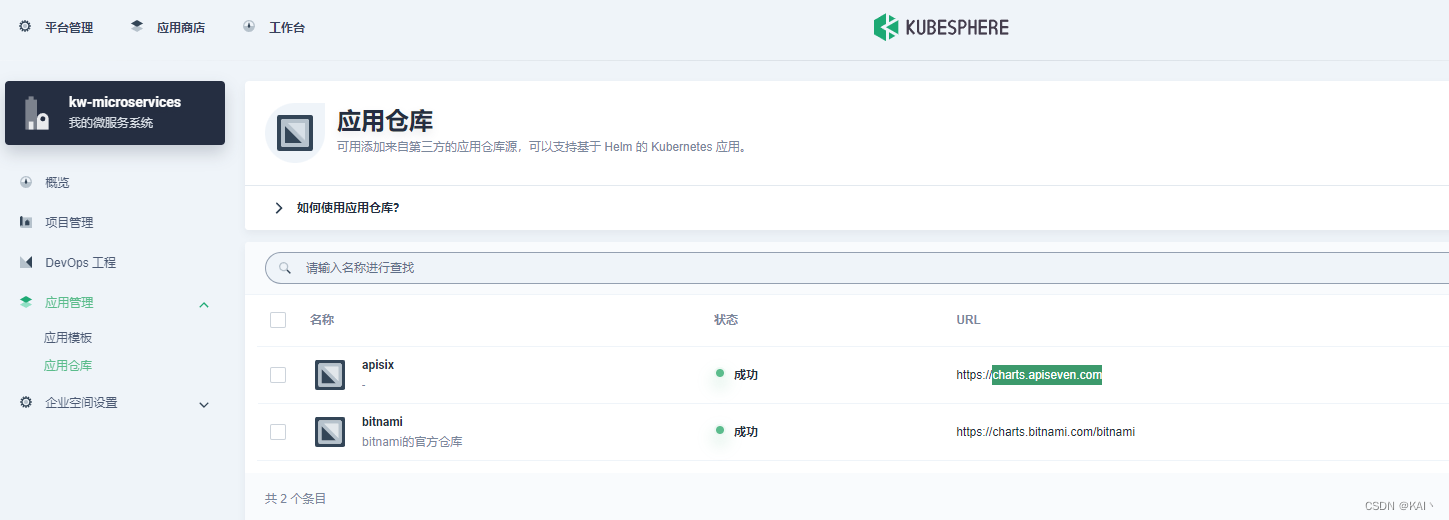
添加应用仓库
进入企业空间-应用管理-应用仓库
添加应用仓库charts.apiseven.com
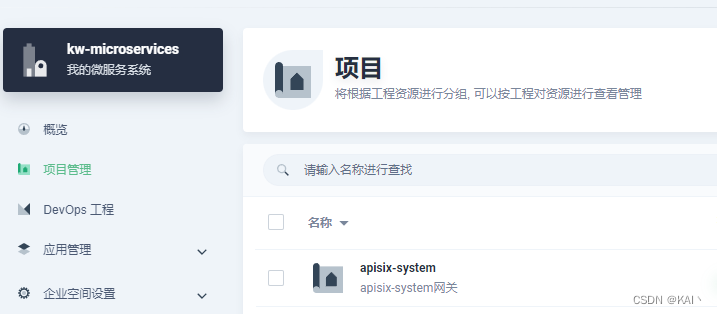
创建项目apisix-system
创建应用
进入项目控制台,应用负载-应用
部署新应用-选择应用模板,选择apisix,部署第三个
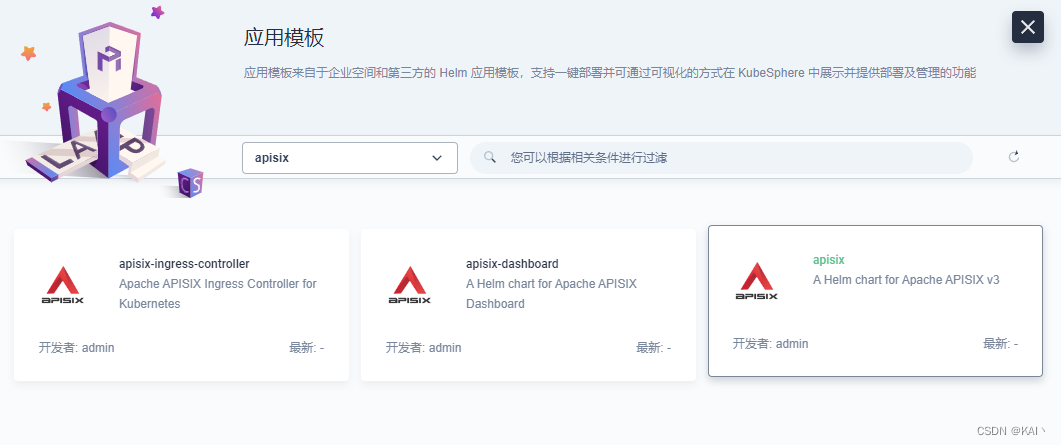
学习阶段,选择视频教程中的版本一致,0.11.2(2.5.0)
点击部署
下一步
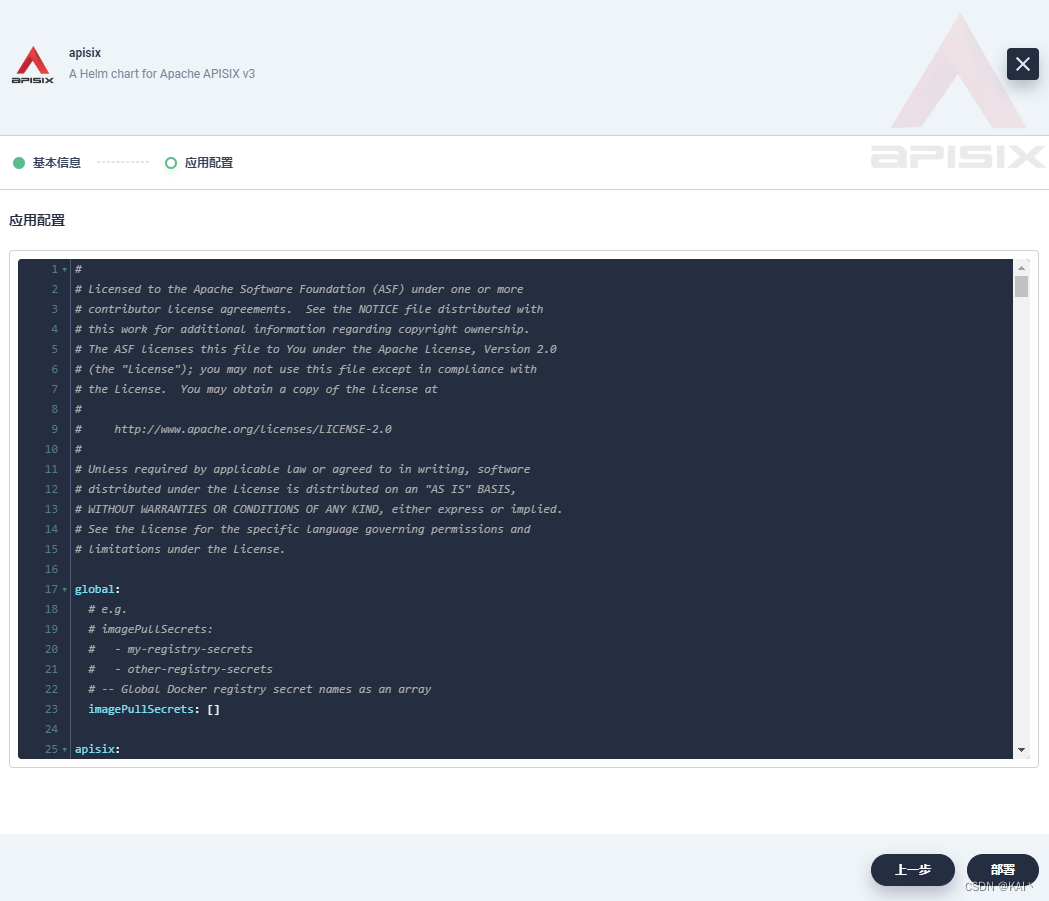
修改配置文件
改动了10处内容,标注了"改动"二字
复制下面内容,覆盖上面的配置即可
#
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
global:
# e.g.
# imagePullSecrets:
# - my-registry-secrets
# - other-registry-secrets
#
imagePullSecrets: []
apisix:
# Enable or disable Apache APISIX itself
# Set it to false and ingress-controller.enabled=true will deploy only ingress-controller
enabled: true
# Enable nginx IPv6 resolver
enableIPv6: true
# Whether the APISIX version number should be shown in Server header
enableServerTokens: true
# Use Pod metadata.uid as the APISIX id.
setIDFromPodUID: false
customLuaSharedDicts: []
# - name: foo
# size: 10k
# - name: bar
# size: 1m
luaModuleHook:
enabled: false
# extend lua_package_path to load third party code
luaPath: ""
# the hook module which will be used to inject third party code into APISIX
# use the lua require style like: "module.say_hello"
hookPoint: ""
# configmap that stores the codes
configMapRef:
name: ""
# mounts decides how to mount the codes to the container.
mounts:
- key: ""
path: ""
# Defines how apisix handles routing:
# - radixtree_uri: match route by uri(base on radixtree)
# - radixtree_host_uri: match route by host + uri(base on radixtree)
# - radixtree_uri_with_parameter: match route by uri with parameters
httpRouter: radixtree_uri
enableCustomizedConfig: false
customizedConfig: {}
image:
repository: apache/apisix
pullPolicy: IfNotPresent
# Overrides the image tag whose default is the chart appVersion.
tag: 2.15.0-alpine
# Use a `DaemonSet` or `Deployment`
kind: Deployment
# kind is DaemonSet, replicaCount not become effective
replicaCount: 1
priorityClassName: ""
podAnnotations: {}
podSecurityContext: {}
# fsGroup: 2000
securityContext: {}
# capabilities:
# drop:
# - ALL
# readOnlyRootFilesystem: true
# runAsNonRoot: true
# runAsUser: 1000
# See https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/run-application/configure-pdb/ for more details
podDisruptionBudget:
enabled: false
minAvailable: 90%
maxUnavailable: 1
resources: {}
# We usually recommend not to specify default resources and to leave this as a conscious
# choice for the user. This also increases chances charts run on environments with little
# resources, such as Minikube. If you do want to specify resources, uncomment the following
# lines, adjust them as necessary, and remove the curly braces after 'resources:'.
# limits:
# cpu: 100m
# memory: 128Mi
# requests:
# cpu: 100m
# memory: 128Mi
hostNetwork: false
nodeSelector: {}
tolerations: []
affinity: {}
# timezone is the timezone where apisix uses.
# For example: "UTC" or "Asia/Shanghai"
# This value will be set on apisix container's environment variable TZ.
# You may need to set the timezone to be consistent with your local time zone,
# otherwise the apisix's logs may used to retrieve event maybe in wrong timezone.
timezone: ""
# extraEnvVars An array to add extra env vars
# e.g:
# extraEnvVars:
# - name: FOO
# value: "bar"
# - name: FOO2
# valueFrom:
# secretKeyRef:
# name: SECRET_NAME
# key: KEY
extraEnvVars: []
nameOverride: ""
fullnameOverride: ""
serviceAccount:
create: false
annotations: {}
name: ""
rbac:
create: false
gateway:
type: NodePort #改动1 这里先不改,后面改为OpenELB,暴露外网访问
# If you want to keep the client source IP, you can set this to Local.
# ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/access-application-cluster/create-external-load-balancer/#preserving-the-client-source-ip
externalTrafficPolicy: Cluster
# type: LoadBalancer
# annotations:
# service.beta.kubernetes.io/aws-load-balancer-type: nlb
externalIPs: []
http:
enabled: true
servicePort: 80
containerPort: 9080
tls:
enabled: false
servicePort: 443
containerPort: 9443
existingCASecret: ""
certCAFilename: ""
http2:
enabled: true
sslProtocols: "TLSv1.2 TLSv1.3"
# L4 proxy (TCP/UDP)
stream:
enabled: false
only: false
tcp: []
udp: []
ingress:
enabled: false
annotations: {}
# kubernetes.io/ingress.class: nginx
# kubernetes.io/tls-acme: "true"
hosts:
- host: apisix.local
paths: []
tls: []
# - secretName: apisix-tls
# hosts:
# - chart-example.local
admin:
# Enable Admin API
enabled: true
# admin service type
type: ClusterIP
# loadBalancerIP: a.b.c.d
# loadBalancerSourceRanges:
# - "143.231.0.0/16"
externalIPs: []
#
port: 9180
servicePort: 9180
# Admin API support CORS response headers
cors: true
# Admin API credentials
credentials:
admin: edd1c9f034335f136f87ad84b625c8f1
viewer: 4054f7cf07e344346cd3f287985e76a2
allow:
# The client IP CIDR allowed to access Apache APISIX Admin API service.
ipList:
- 0.0.0.0/0 #改动2 改为0.0.0.0
nginx:
workerRlimitNofile: "20480"
workerConnections: "10620"
workerProcesses: auto
enableCPUAffinity: true
envs: []
# APISIX plugins to be enabled
plugins:
- api-breaker
- authz-keycloak
- basic-auth
- batch-requests
- consumer-restriction
- cors
- echo
- fault-injection
- file-logger
- grpc-transcode
- hmac-auth
- http-logger
- ip-restriction
- ua-restriction
- jwt-auth
- kafka-logger
- key-auth
- limit-conn
- limit-count
- limit-req
- node-status
- openid-connect
- authz-casbin
- prometheus
- proxy-cache
- proxy-mirror
- proxy-rewrite
- redirect
- referer-restriction
- request-id
- request-validation
- response-rewrite
- serverless-post-function
- serverless-pre-function
- sls-logger
- syslog
- tcp-logger
- udp-logger
- uri-blocker
- wolf-rbac
- zipkin
- traffic-split
- gzip
- real-ip
- ext-plugin-pre-req
- ext-plugin-post-req
- server-info #改动3 添加此行,以便配合dashboard展示服务信息
stream_plugins:
- mqtt-proxy
- ip-restriction
- limit-conn
pluginAttrs: {}
extPlugin:
enabled: false
cmd: ["/path/to/apisix-plugin-runner/runner", "run"]
wasmPlugins:
enabled: false
plugins: []
# customPlugins allows you to mount your own HTTP plugins.
customPlugins:
enabled: false
# the lua_path that tells APISIX where it can find plugins,
# note the last ';' is required.
luaPath: "/opts/custom_plugins/?.lua"
plugins:
# plugin name.
- name: "prometheus" #改动4
# plugin attrs
attrs: ##改动5 添加如下内容
export_addr:
ip: 0.0.0.0
port: 9091
# plugin codes can be saved inside configmap object.
configMap:
# name of configmap.
name: "prometheus" #改动6
# since keys in configmap is flat, mountPath allows to define the mount
# path, so that plugin codes can be mounted hierarchically.
mounts:
- key: ""
path: ""
- key: ""
path: ""
updateStrategy: {}
# type: RollingUpdate
extraVolumes: []
# - name: extras
# emptyDir: {}
extraVolumeMounts: []
# - name: extras
# mountPath: /usr/share/extras
# readOnly: true
extraInitContainers: []
# - name: init-myservice
# image: busybox:1.28
# command: ['sh', '-c', "until nslookup myservice.$(cat /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/namespace).svc.cluster.local; do echo waiting for myservice; sleep 2; done"]
discovery:
enabled: false
registry: {}
# Integration service discovery registry. E.g eureka\dns\nacos\consul_kv
# reference:
# https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/discovery/#configuration-for-eureka
# https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/discovery/dns/#service-discovery-via-dns
# https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/discovery/consul_kv/#configuration-for-consul-kv
# https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/discovery/nacos/#configuration-for-nacos
# https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/discovery/kubernetes/#configuration
#
# an eureka example:
# ```
# eureka:
# host:
# - "http://${username}:${password}@${eureka_host1}:${eureka_port1}"
# - "http://${username}:${password}@${eureka_host2}:${eureka_port2}"
# prefix: "/eureka/"
# fetch_interval: 30
# weight: 100
# timeout:
# connect: 2000
# send: 2000
# read: 5000
# ```
#
# the minimal Kubernetes example:
# ```
# kubernetes: {}
# ```
#
# The prerequisites for the above minimal Kubernetes example:
# 1. [Optional] Set `.serviceAccount.create` to `true` to create a dedicated ServiceAccount.
# It is recommended to do so, otherwise the default ServiceAccount "default" will be used.
# 2. [Required] Set `.rbac.create` to `true` to create and bind the necessary RBAC resources.
# This grants the ServiceAccount in use to List-Watch Kubernetes Endpoints resources.
# 3. [Required] Include the following environment variables in `.nginx.envs` to pass them into
# nginx worker processes (https://nginx.org/en/docs/ngx_core_module.html#env):
# - KUBERNETES_SERVICE_HOST
# - KUBERNETES_SERVICE_PORT
# This is for allowing the default `host` and `port` of `.discovery.registry.kubernetes.service`.
# access log and error log configuration
logs:
enableAccessLog: true
accessLog: "/dev/stdout"
accessLogFormat: '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] $http_host \"$request\" $status $body_bytes_sent $request_time \"$http_referer\" \"$http_user_agent\" $upstream_addr $upstream_status $upstream_response_time \"$upstream_scheme://$upstream_host$upstream_uri\"'
accessLogFormatEscape: default
errorLog: "/dev/stderr"
errorLogLevel: "warn"
dns:
resolvers:
- 127.0.0.1
- 172.20.0.10
- 114.114.114.114
- 223.5.5.5
- 1.1.1.1
- 8.8.8.8
validity: 30
timeout: 5
initContainer:
image: busybox
tag: 1.28
autoscaling:
enabled: false
minReplicas: 1
maxReplicas: 100
targetCPUUtilizationPercentage: 80
targetMemoryUtilizationPercentage: 80
# Custom configuration snippet.
configurationSnippet:
main: |
httpStart: |
httpEnd: |
httpSrv: |
httpAdmin: |
stream: |
# Observability configuration.
# ref: https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/plugins/prometheus/
serviceMonitor:
enabled: true #改动7
# namespace where the serviceMonitor is deployed, by default, it is the same as the namespace of the apisix
namespace: "apisix-system" #改动8
# name of the serviceMonitor, by default, it is the same as the apisix fullname
name: ""
# interval at which metrics should be scraped
interval: 15s
# path of the metrics endpoint
path: /apisix/prometheus/metrics
# prefix of the metrics
metricPrefix: apisix_
# container port where the metrics are exposed
containerPort: 9091
# @param serviceMonitor.labels ServiceMonitor extra labels
labels: {}
# @param serviceMonitor.annotations ServiceMonitor annotations
annotations: {}
# etcd configuration
# use the FQDN address or the IP of the etcd
etcd:
# install etcd(v3) by default, set false if do not want to install etcd(v3) together
enabled: true
host:
# host or ip e.g. http://172.20.128.89:2379
- http://etcd.host:2379
prefix: "/apisix"
timeout: 30
# if etcd.enabled is true, set more values of bitnami/etcd helm chart
auth:
rbac:
# No authentication by default
create: false
user: ""
password: ""
tls:
enabled: false
existingSecret: ""
certFilename: ""
certKeyFilename: ""
verify: true
sni: ""
service:
port: 2379
replicaCount: 3
#改动9
dashboard: #开启并添加如下内容,实现访问
enabled: true
service:
type: NodePort
#改动10
ingress-controller: #开启并添加如下内容,实现监控。
enabled: true
config:
apisix:
serviceNamespace: apisix-system
ServiceMonitor:
enabled: true
namespace: 'apisix-system'
interval: 15s
vault:
enabled: false
host: ""
timeout: 10
token: ""
prefix: ""
点击部署,等一会查看部署情况,网络不行可能出现镜像拉取失败的情况
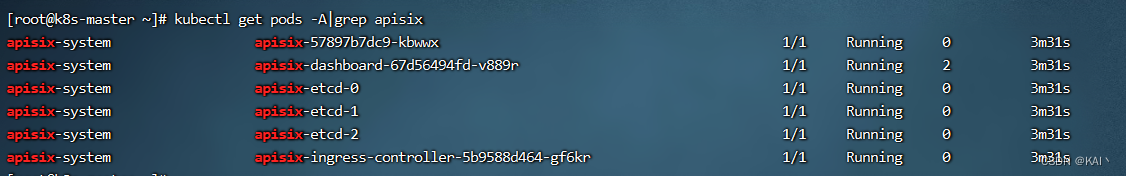
部署成功
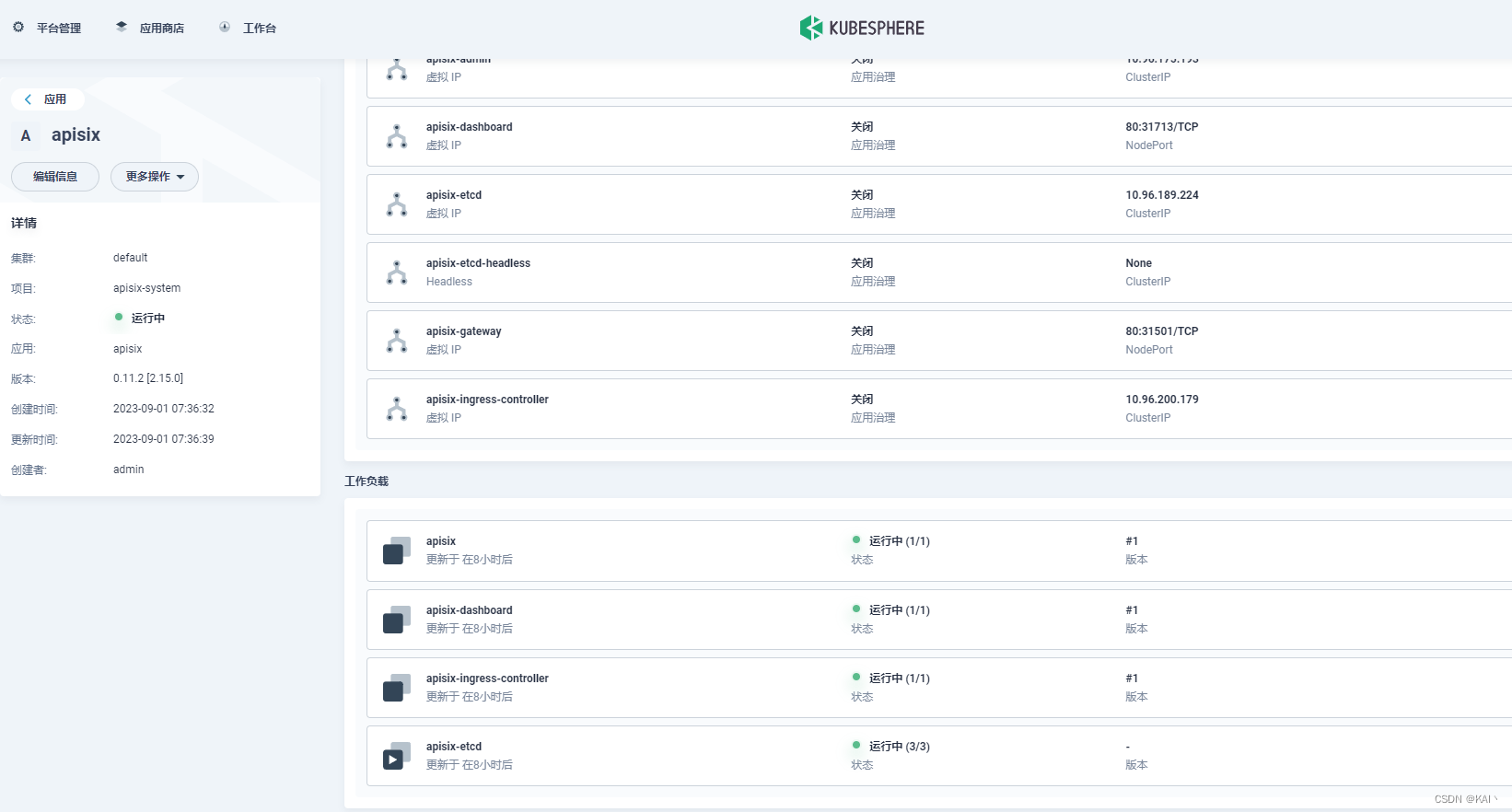
测试访问
测试访问dashboard
查看服务信息

默认账户密码
admin
admin
使用apisix
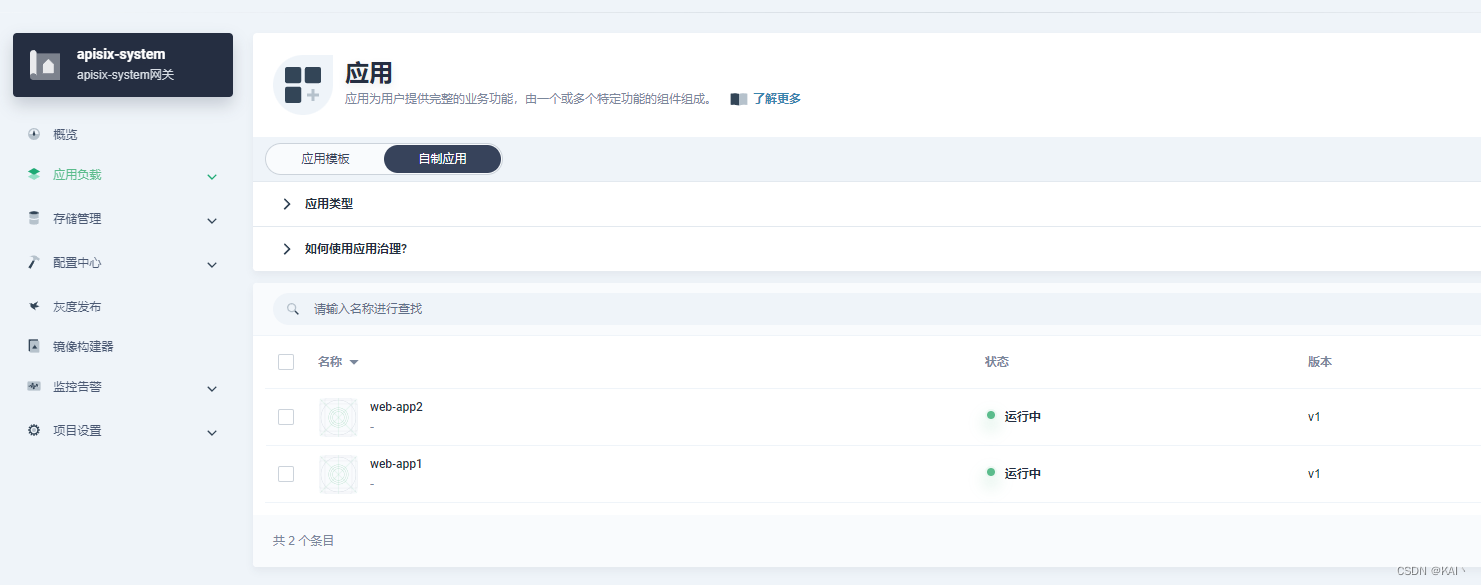
创建两个nginx服务,不暴露外网访问
web-app1
web-app2
#挂载一下index.html文件,或者部署好直进入容器中修改index.html
#为了测试apisix网关的效果
#修改一下Nginx中的内容
#进入上面创建的两个服务中
#进入该目录/usr/share/nginx/html
#分别修改index.html的内容为
#web-app1.kw.cn
#web-app2.kw.cn
#进入该目录
cd /usr/share/nginx/html
#清空内容
>index.html
#没有vi命令,使用追加命令
echo "web-app1.kw.cn" >> index.html
#查看是否修改成功
cat index.html
web-app1.kw.cn
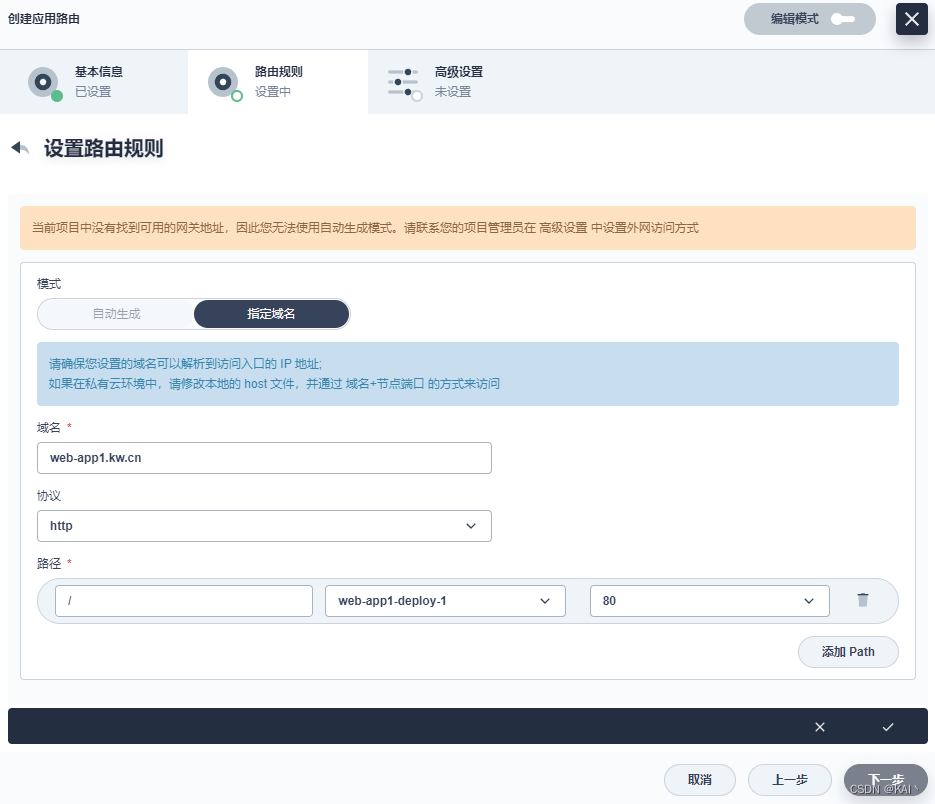
创建应用路由
上面创建的两个ng服务,这里分别增加对应的应用路由
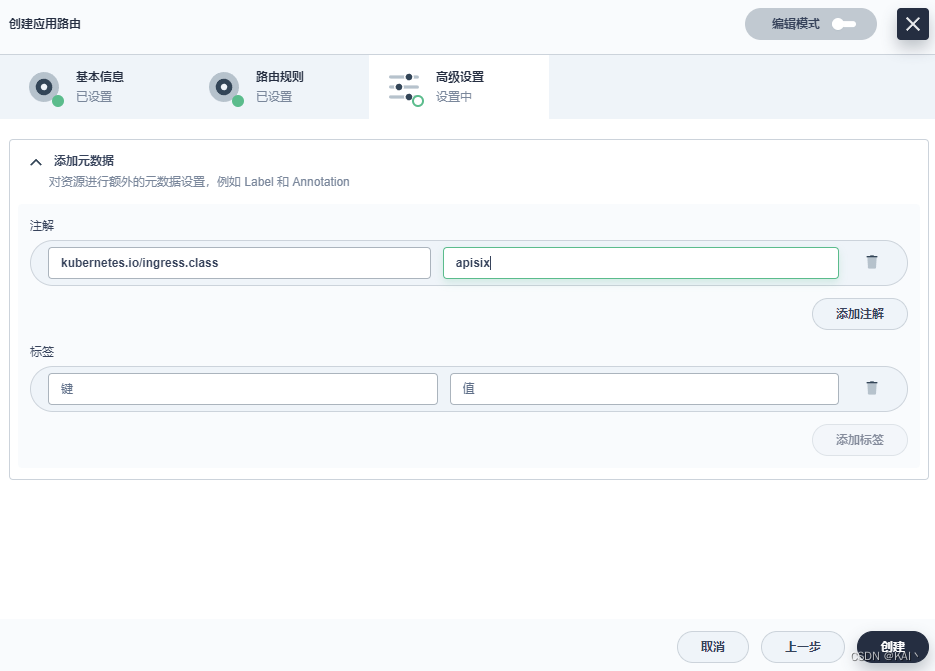
下一步添加元数据注解
#元数据,添加注解
kubernetes.io/ingress.class:apisix
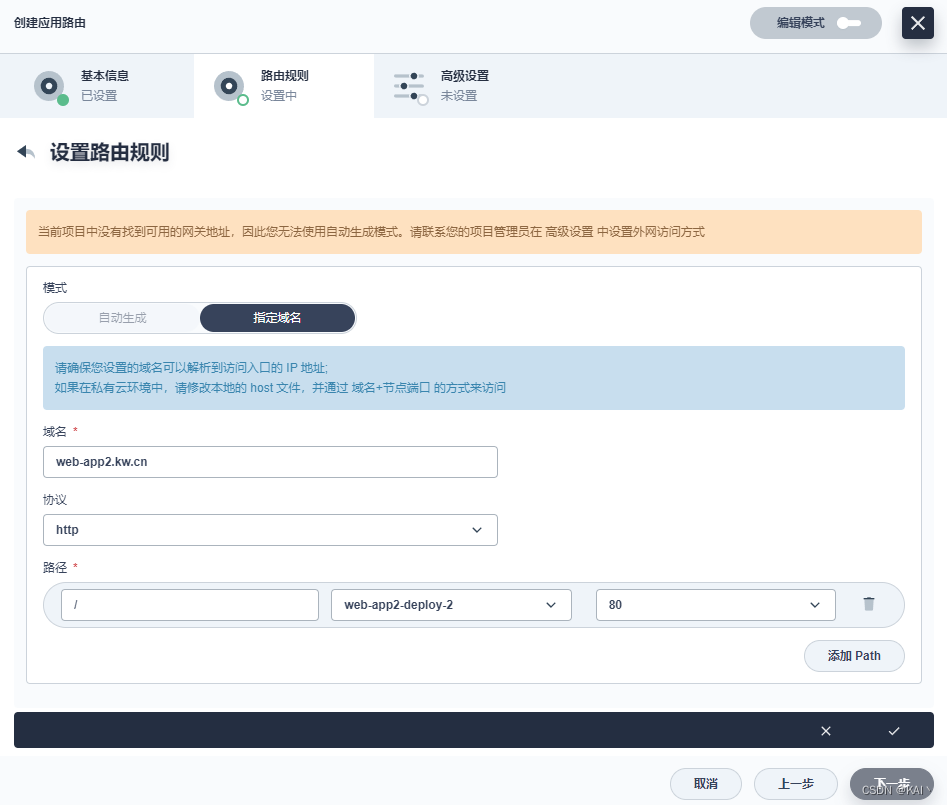
第二个服务同上
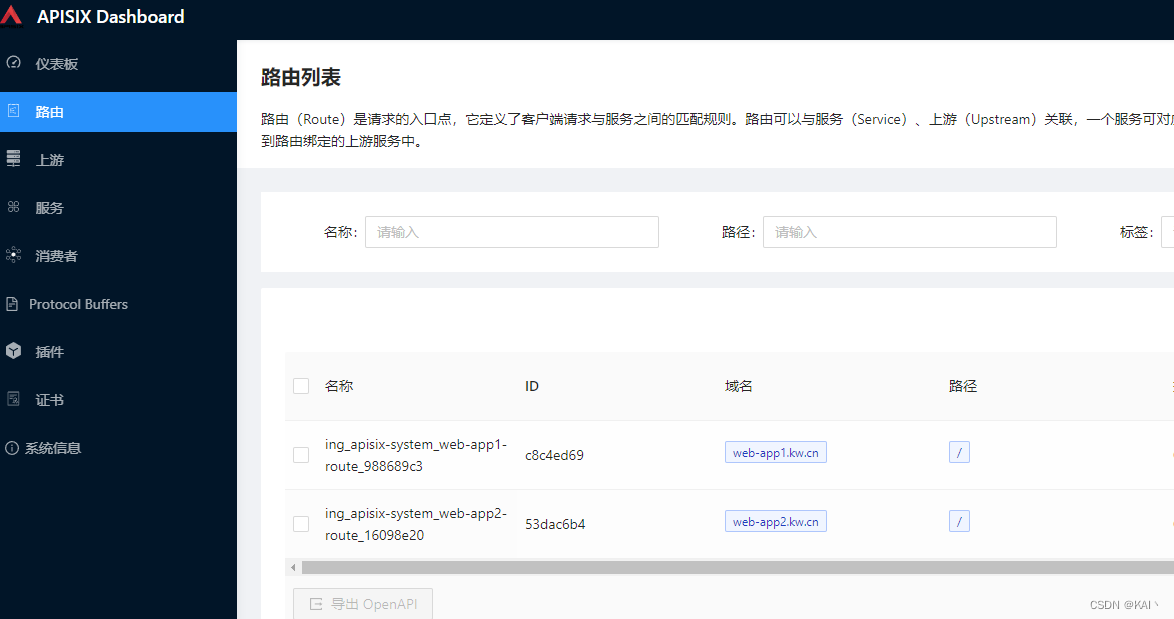
查看apisix dashboard,路由菜单,
可以看到显示了刚刚创建的两个应用路由
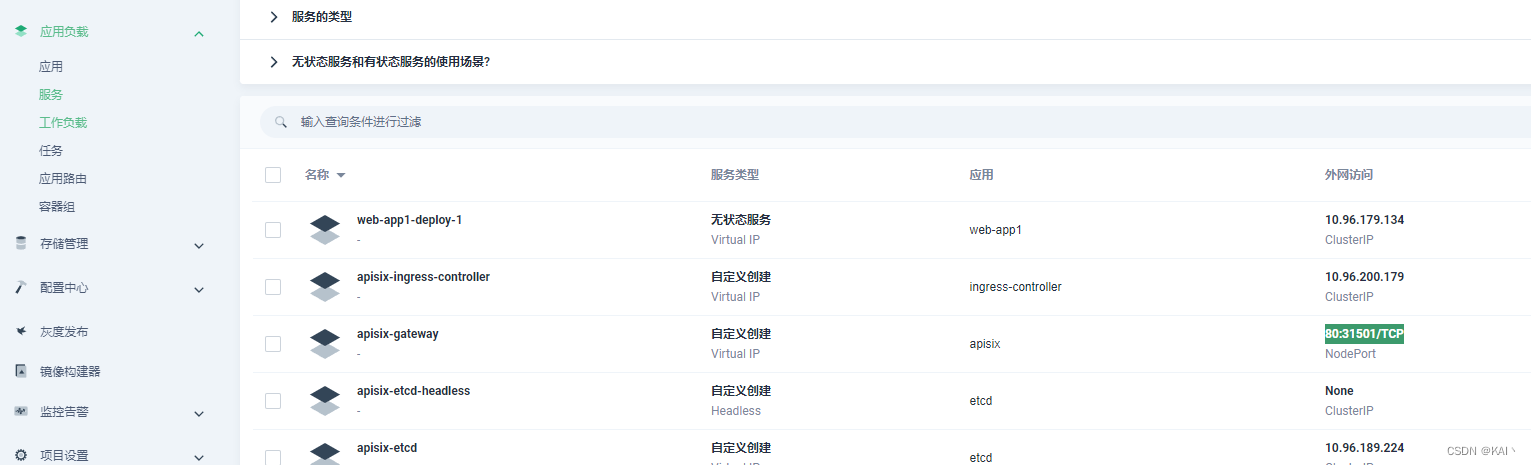
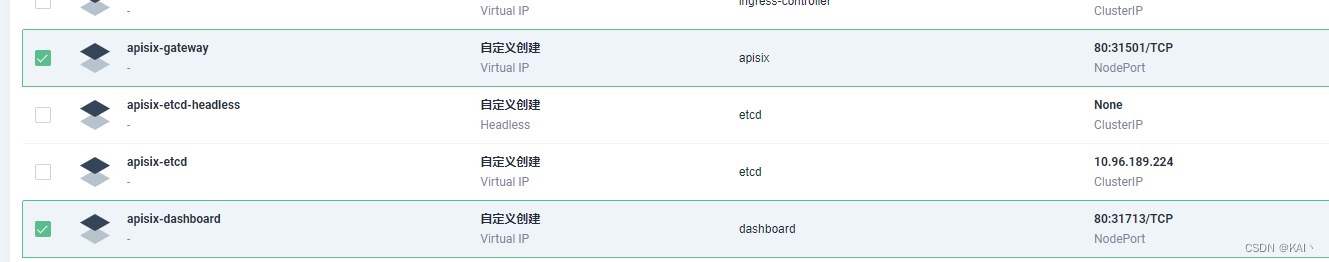
查看网关服务
查看apisix-gateway服务
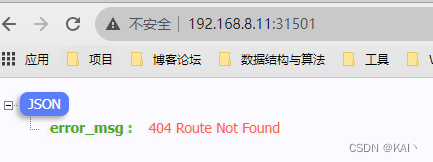
测试效果
#配置域名解析
192.168.8.11 web-app1.kw.cn
192.168.8.11 web-app2.kw.cn
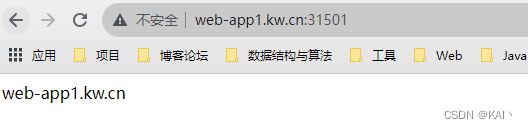
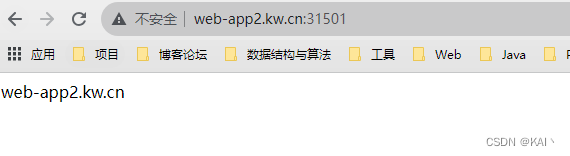
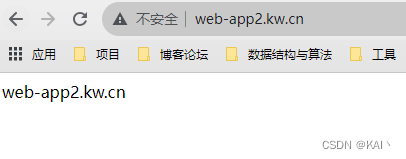
成功访问到了对应的ng服务,说明apisix配置成功。
但不应该携带端口,即应该使用默认端口80,那么就需要调整apisix-gateway的外网访问方式。
使用openelb配置apisix
需要修改这两项,不再使用NodePort方式访问apisix服务
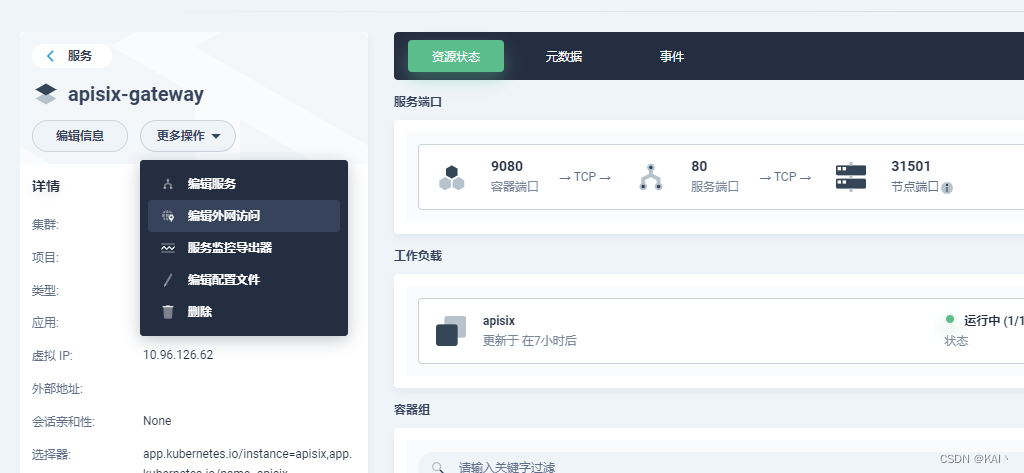
修改apisix-gateway服务
编辑外网访问
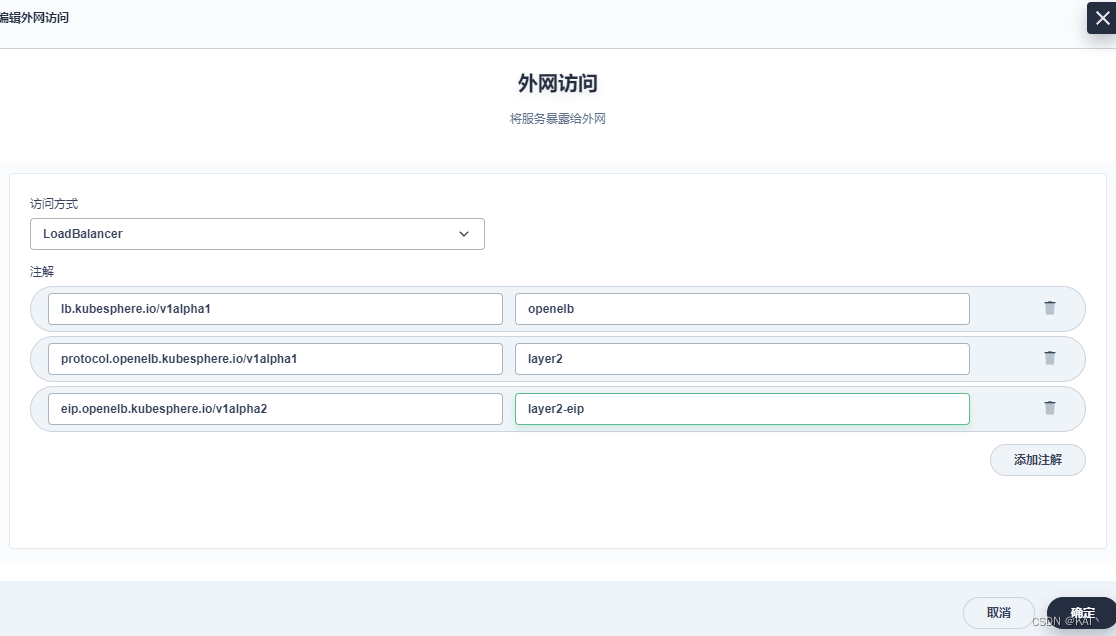
访问方式修改为LoadBalancer
#将下面的键值对填写到注解列表中
lb.kubesphere.io/v1alpha1:openelb
protocol.openelb.kubesphere.io/v1alpha1:layer2
eip.openelb.kubesphere.io/v1alpha2:layer2-eip
有了外网访问地址
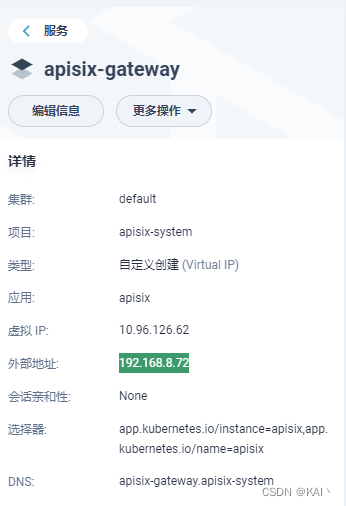
此时,使用80端口,即可访问apisix-gateway
修改apisix-dashboard
同上操作,修改apisix-dashboard
此时,使用80端口,即可访问apisix-dashboard
给dashboard创建一个应用路由,配置域名解析
测试访问
测试访问2个ng服务
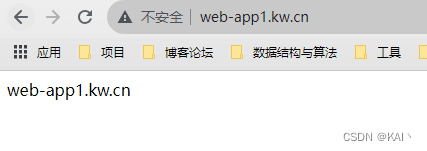
配置域名解析,72为上面使用openelb之后,给apisix-gateway分配的ip

测试访问
可以看到不需要携带显示端口就可以访问对应的服务了
对apisix监控
略,没整好。。。监控不到数据,后续正好补充。