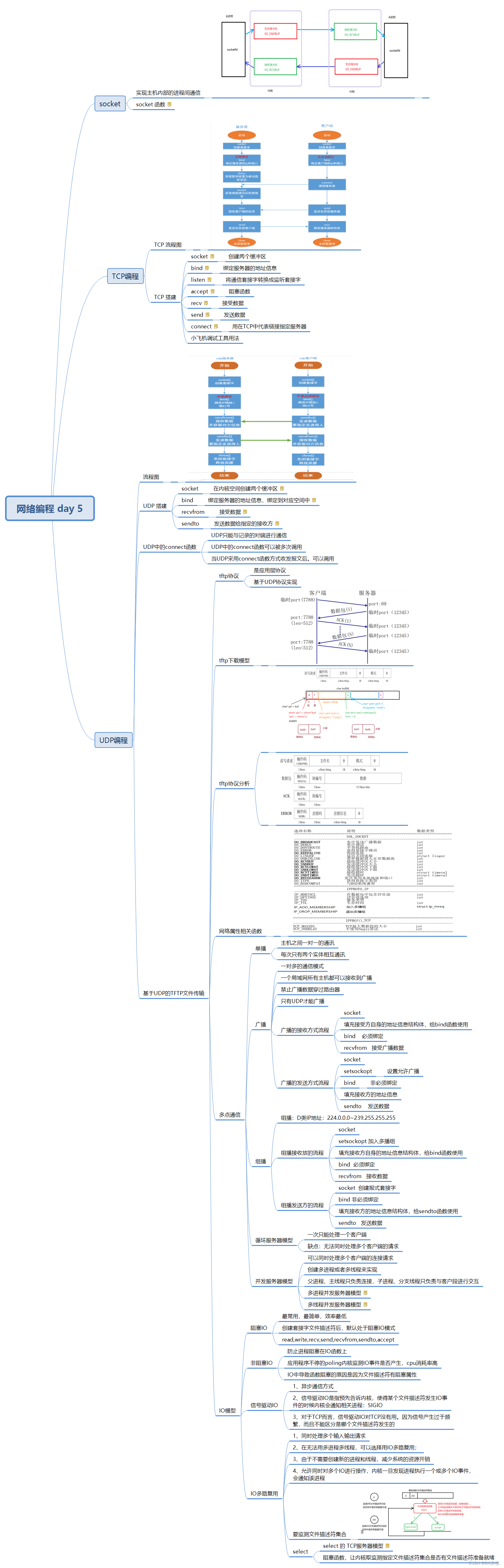
LangChain 是一个基于语言模型开发应用程序的框架。它使得应用程序具备以下特点:1.数据感知:将语言模型与其他数据源连接起来。2.代理性:允许语言模型与其环境进行交互
LangChain 的主要价值在于:组件:用于处理语言模型的抽象,以及每个抽象的多个实现集合。这些组件是模块化且易于使用的,无论您是否在使用 LangChain 框架的其他部分
现成的链式结构:由多个组件组成的结构化组合,用于完成特定的高级任务现成的链式结构使得入门变得轻松。对于更复杂的应用程序和微妙的用例,组件使得可以轻松定制现有链式结构或构建新的结构。此篇博客主要介绍Langchain的prompt相关内容。
Langchain中提供了哪些Prompt呢?具体如下图所示,是截至目前Langchain提供的所有模版,对于base类模版,在通过langchain构建应用时,一般很少用到,开发者主要用的还是ChatPromptTemplate,PromptTemplate,以及各类MessagePromptTemplate。

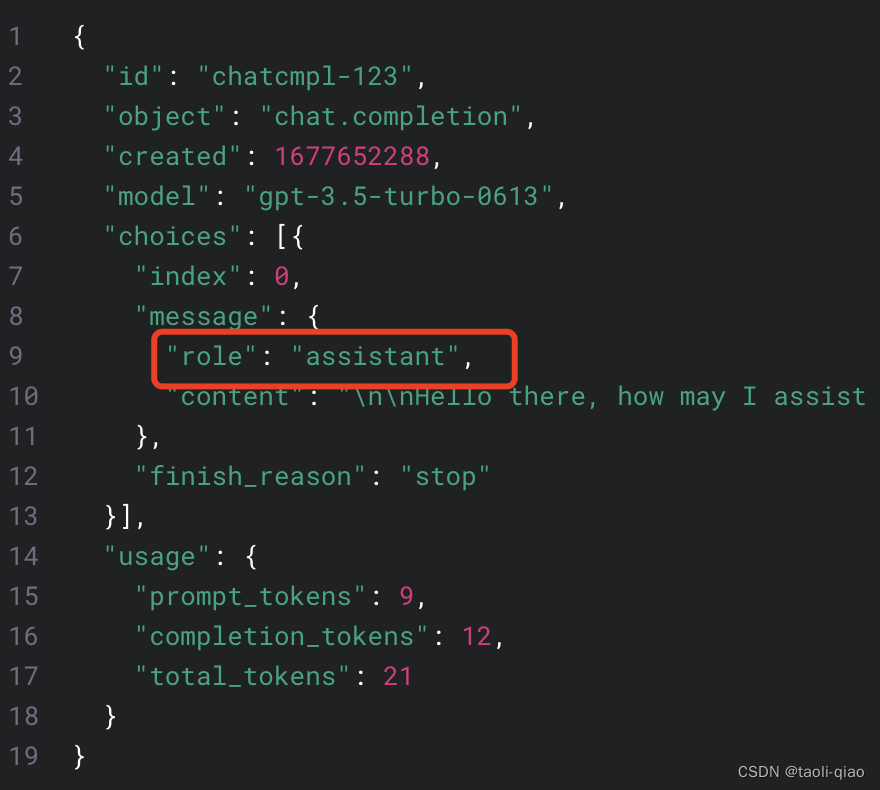
为什么Lanchain会提供不同类型的MessagePromptTemplate呢?因为Openai的原始接口中,对于chat completion这个接口,里面的user role就分为user,system,assistant三个角色,所以,这里的MessageTemplate也分为HumanMessagePromptTemplate,AIMessagePromptTemplate,SystemMessagePromptTemplate。
openai官方提供的chat completion的接口如下图所示,可以看到原始调用openai的接口中,需要传入role的信息,所以上面的三种messagePromptTemplate对应三种不同的角色。
了解了前面的基础知识后,来看看如何使用PromptTemplate。下面的代码中调用from_template
(...)传入了一份带变量的字符串,调用format信息后,打印出来的message就是将变量值于原有字符串merge后的值。另外,从结果也可以看到,PromptTemplate是一个报刊input_variables和template变量的的class。
import openai
import os
from langchain.prompts import (PromptTemplate)
prompt_template = PromptTemplate.from_template(
"Tell me a joke about {context}")
message = prompt_template.format(context="chidren")
print(prompt_template)
print(type(prompt_template))
print(message)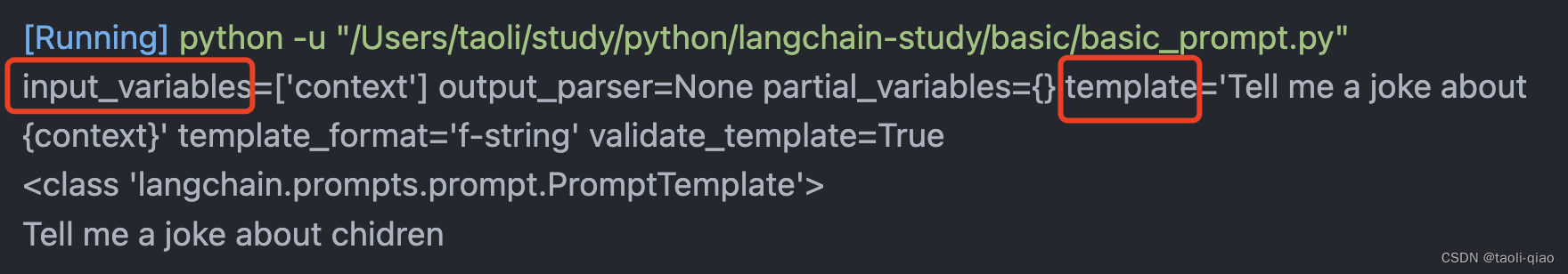
除了通过from_template()的方法初始化一个PromptTemplate的class外,还可以通过下面的方法初始化这个class
prompt_template_two = PromptTemplate(
input_variables=['name'],
template="what is your {name}"
)
print(prompt_template_two)接着来看看SystemMessagePromptTemplate的使用,在创建好一个PromptTemplate后,可以将prompt赋值给SystemMessagePromptTemplate。可以看到SystemMessagePromptTemplate除了prompt变量外,还有template_format,validate_template变量。
prompt = PromptTemplate(
template="You are a helpful assistant that translates {input_language} to {output_language}.",
input_variables=["input_language", "output_language"],
)
system_message_prompt = SystemMessagePromptTemplate(prompt=prompt)
print(system_message_prompt)
print(type(system_message_prompt))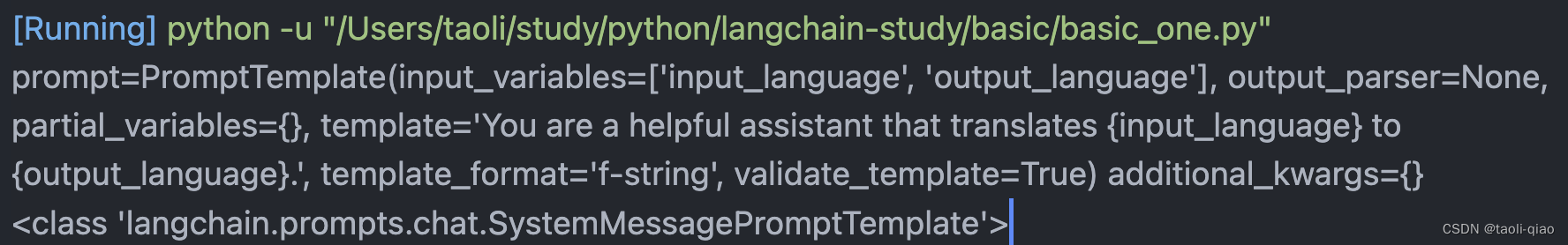
除了上面的方式初始化一个SystemMessageTemplate外,还可以通过调用from_template的方式进行初始化。可以看到初始化出来的对象是一样的。
prompt_string = """Translate the text \
that is delimited by triple backticks \
into a style that is {style}. \
text: ```{text}```
"""
system_message_prompt_two = SystemMessagePromptTemplate.from_template(
prompt_string)
print(system_message_prompt_two)
接下来再看看ChatPromptTemplate,这里先创建了一个HumanMessagePromptTemplate,然后通过from_message,将创建了promptTemplate赋值给了ChatPromptTemplate
human_prompt_template = HumanMessagePromptTemplate.from_template(prompt_string)
print(human_prompt_template)
print('-------------------')
chat_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([human_prompt_template])
print(chat_prompt)执行结果如下图所示,可以看到直接打印的话,HumanMessagePromptTemplate和前面的SystemMessagePromptTemplate无区别,class包含的字段都一样。组装出来的ChatPromptTemplate包含input_variables,output_parser,messages三个变量,messages的值就是生成的HumanMessagePromptTemplate.

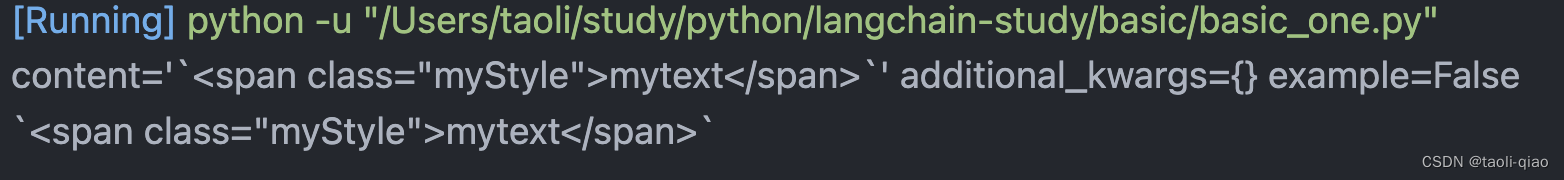
调用ChatPromptTemplate的format_messages()方法,可以将变量值和原有的prompt中的文字进行合并。结果如下图所示,返回的message是一个List,List只有一个值就是HumanMessage对象,HumanMessage对象又包含content,additional_kwargs={},example变量。
message = chat_prompt.format_messages(style="myStyle", text="mytext")
print(message)
可以看到不同promptTemplate之间有一点绕,这可能也和AI技术不断在更新,langchain也在不断迭代有关吧。
message对象生成好后,就可以调用model生成内容了,代码如下所示:
chat = ChatOpenAI(model_name="gpt-3.5-turbo", verbose=True)
response = chat(message)
print(response)
print(response.content)调用大模型生成的内容如下图所示:
以上就是对Langchain中Prompt的使用介绍。