1.使用flasgger
Flasgger是 flasgger 组织在Github上开源的解析和渲染 SwaggerUI 的 Flask 拓展。
提供了对于Swagger文档标准的解析和SwaggerUI的生成,支持使用YAML、Python字典和Marshmallo、Schema的定义。
支持使用JSON Schema进行数据验证,支持Flask-RESTful框架的使用,对于使用Flask框架的开发者而言十分方便。
(1)安装依赖
pip innstall flasgger如果需要使用 Marshmallow Schema,那么还需要依赖
pip install marshmallow apispec(2)导入模块
from flasgger import Swagger(3)实例化对象
from flask import Flask, jsonify
from flasgger import Swagger
app = Flask(__name__)
swagger = Swagger(app)(4)示例1
①以注释形式,直接写在代码中
@app.route('/demo/score')
def Demo():
""" This is using docstrings for specifications.
---
tags:
- score #接口的名称
parameters:
- name: 接口主体
in: body(传参方式,可参考postman)
schema:
id: score(接口的名称)
required:(需要传的参数)
- id
- name
- coruse
properties:
id:
type: string
description: 学号
name:
type: string
description: 姓名
course:
type: string
description: 课程
responses:
200:
description: XX正确
400:
description: XX错误
print("swagger示例demo")
②以独立文件 yaml文件形式引入脚本中
-- 新建一个score.yml文件
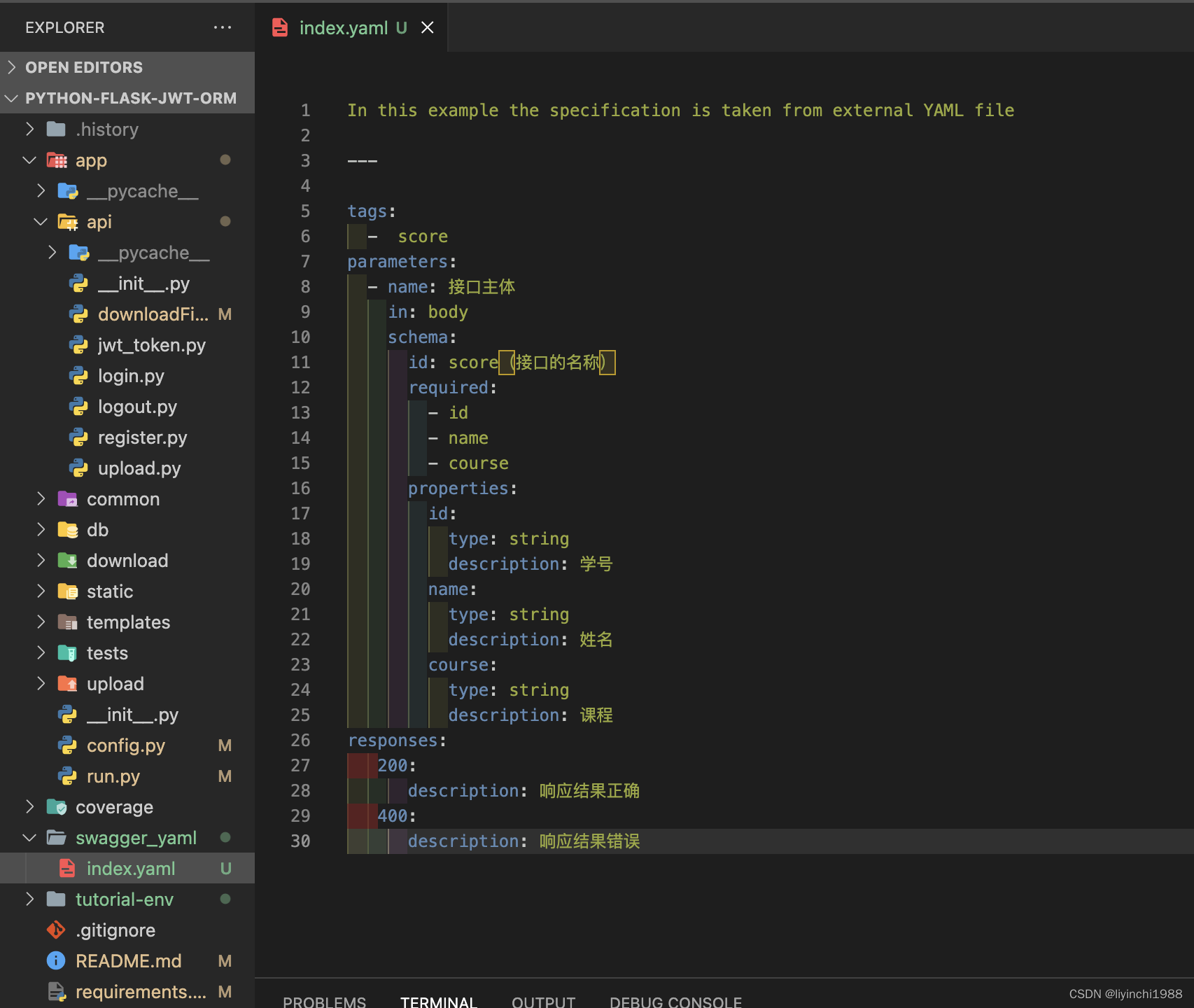
In this example the specification is taken from external YAML file
---
tags:
- score
parameters:
- name: 接口主体
in: body
schema:
id: score(接口的名称)
required:
- id
- name
- course
properties:
id:
type: string
description: 学号
name:
type: string
description: 姓名
course:
type: string
description: 课程
responses:
200:
description: 响应结果正确
400:
description: 响应结果错误-- 引用score.yml文件
from flasgger import swag_from
@app.route('/demo/score', methods=[‘POST’])
@swag_from(‘score.yml’)
def score():
...
或者 用下面的方式表示:
@app.route('/demo/score’, methods=[‘POST’])
def score():
"""
file:score.yml
"""
...③定义字典
-- 新建一个specs_dict字典
specs_dict = {
"parameters": [
{
"name": "接口主体",
"in": "body"
},
{
"schema" : {
"id": "score",
"required": {
"id",
"name",
"course"
},
"properties": {
"id":{
"type": "string",
"description": "学号“
},
"name":{
"type": "string",
"description": "姓名“
},
"course":{
"type": "string",
"description": "课程“
}
}
}
}
]
”responses": {
"200": {
"description": "xx正确“
},
”400“: {
”description": "xx错误“
}
}
}--引用字典
from flasgger import swag_from
@app.route('/demo/score’, methods=[‘POST’])
@swag_from(specs_dict)
def score():
"""
In this example the specification is taken from specs_dict
"""
...进入http://localhost:端口/apidocs/ 可显示swagger API文档
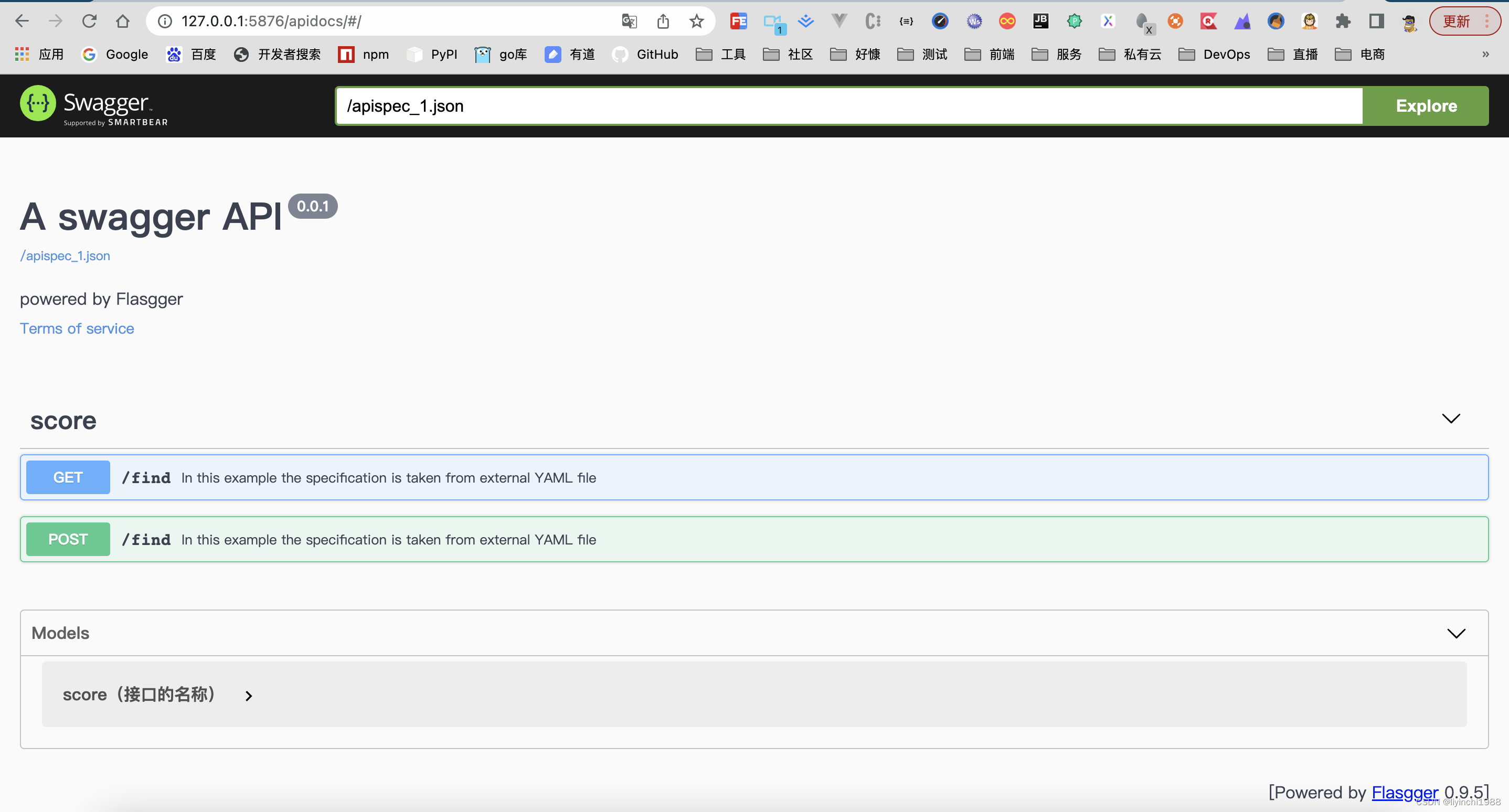
(5)示例2
定义了一个接口,它接受色调参数,返回颜色的列表
from flask import Flask, jsonify
from flasgger import Swagger
app = Flask(__name__)
swagger = Swagger(app)
@app.route('/colors//')
def colors(palette):
"""
Example endpoint returning a list of colors by palette This is using docstrings for specifications.
---
parameters:
- name: palette
in: path
type: string
enum: ['all', 'rgb', 'cmyk']
required: true
default: all
definitions:
Palette:
type: object
properties:
palette_name:
type: array
items:
$ref: '#/definitions/Color'
Color: t
ype: string
responses:
200:
description: A list of colors (may be filtered by palette)
schema:
$ref: '#/definitions/Palette'
examples:
rgb: ['red', 'green', 'blue']
"""
all_colors = { 'cmyk': ['cian', 'magenta', 'yellow', 'black'], 'rgb': ['red', 'green', 'blue'] }
if palette == 'all':
result = all_colors
else:
result = {palette: all_colors.get(palette)}
return jsonify(result)
app.run(debug=True)直接把Swagger的文档定义直接放在接口的docstring中,进行了包括参数、数据结构定义、示例响应等的定义。
运行应用,Flassger就会对文档定义进行解析,并生成SwaggerUI的文档界面。
运行后,访问 http://localhost:5000/apidocs/,就会看到生成的文档界面。
(2)YAML中写再引用到脚本中
我们还可以把文档写在独立的YAML文件中,再在接口中引用。
可以使用装饰器来引用:
from flasgger import swag_from
@app.route('/colors//')
@swag_from('colors.yml')def colors(palette):
# 也可以在docstring中使用file来标注:
@app.route('/colors//')
def colors(palette):
"""
file: colors.yml
"""
pass参考:
在flask中使用swagger(flasgger使用方法及效果展示)
利用flasgger生成FlaskAPI文档_彭世瑜的博客-CSDN博客
2.使用flask-restplus
pip install flask-restplus参考:
flask如何嵌入swagger文档 - 简书
flask项目集成swagger - 种树飞 - 博客园
Swagger documentation — Flask-RESTPlus 0.13.0 documentation








![[激光原理与应用-58]:激光器 - 光学 - 常见光学镜片的特性](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/10e6ac605f0443559baf6328d3f58272.png)