概述
异步调用,通常情况下用于执行一些耗时的操作,同时能够保证当前主线程在执行异步调用之后依然能够继续向下执行。异步执行时,系统往往会创建一个新的线程,但需注意,当每一个异步执行都需要创建线程时,往往会对性能有影响。因此,使用线程池能够有效处理这一问题,避免了进行异步调用时创建、销毁线程的开销。
本片文章,结合委托和异步来对BeginInvoke()方法、EndInvoke()方法和其相关的IAsyncResult做一个简单的学习。
示例一:不使用异步调用
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApp3
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("Client application started!\n");
Console.WriteLine(DateTime.Now.ToString());
Thread.CurrentThread.Name = "Main Thread";
Calculator cal = new Calculator();
int result = cal.Add(2, 5);
Console.WriteLine("Result: {0}\n", result);
// 做某些其他的事情,模拟需要执行3秒钟
for (int i = 1; i <= 3; i++)
{
Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(i));
Console.WriteLine("{0}: Client executed {1} second(s).",
Thread.CurrentThread.Name, i);
}
Console.WriteLine(DateTime.Now.ToString());
Console.WriteLine("\nPress any key to exit...");
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
public class Calculator
{
public int Add(int x, int y)
{
//判断执行当前代码的线程是否为线程池中的线程
if (Thread.CurrentThread.IsThreadPoolThread)
{
Thread.CurrentThread.Name = "Pool Thread";
}
Console.WriteLine("Method invoked!");
// 执行某些事情,模拟需要执行2秒钟
for (int i = 1; i <= 2; i++)
{
Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(i));
Console.WriteLine("{0}: Add executed {1} second(s).",
Thread.CurrentThread.Name, i);
}
Console.WriteLine("Method complete!");
return x + y;
}
}
}
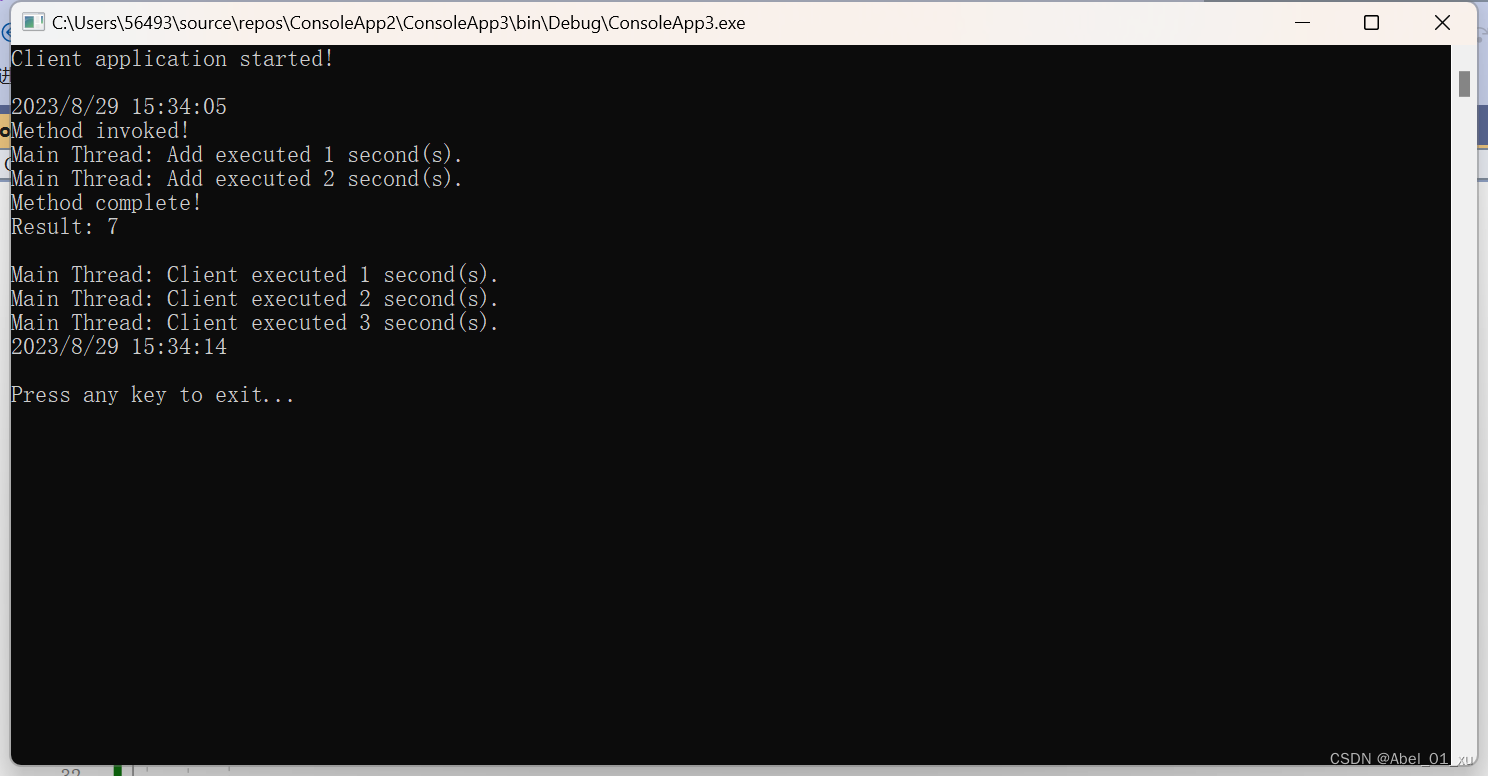
由上图可知,在不使用异步执行时,主线程大概执行了6秒左右,因为线程是串行执行的
接下来,定义一个委托 ,并使用BeginInvoke()方法来异步调用它
示例二:BeginInvoke()方法调用
1. 先看代码示例
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApp3
{
//声明委托
public delegate int AddDelegate(int x, int y);
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("Client application started!\n");
Console.WriteLine(DateTime.Now.ToString());
Thread.CurrentThread.Name = "Main Thread";
Calculator cal = new Calculator();
AddDelegate del=new AddDelegate(cal.Add);
IAsyncResult result=del.BeginInvoke(3,4,null,null);
// 做某些其他的事情,模拟需要执行3秒钟
for (int i = 1; i <= 3; i++)
{
Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(i));
Console.WriteLine("{0}: Client executed {1} second(s).",
Thread.CurrentThread.Name, i);
}
Console.WriteLine(DateTime.Now.ToString());
Console.WriteLine("\nPress any key to exit...");
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
public class Calculator
{
public int Add(int x, int y)
{
//判断执行当前代码的线程是否为线程池中的线程
if (Thread.CurrentThread.IsThreadPoolThread)
{
Thread.CurrentThread.Name = "Pool Thread";
}
Console.WriteLine("Method invoked!");
// 执行某些事情,模拟需要执行2秒钟
for (int i = 1; i <= 2; i++)
{
Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(i));
Console.WriteLine("{0}: Add executed {1} second(s).",
Thread.CurrentThread.Name, i);
}
Console.WriteLine("Method complete!");
return x + y;
}
}
}

①BeginInvoke()方法参数
BeginInvoke()除了最后两个参数为AsyncCallback类型和Object类型以外,前面的参数类型和个数与委托定义相同
AsyncCallback参数
AsyncCallback是一个委托类型,它用于方法的回调,也就是说当异步方法执行完毕时自动进行调用的方法
Object类型参数
Object类型用于传递任何想要的数据类型,它可以通过IAsyncResult的AsyncState属性获得
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Runtime.Remoting.Messaging;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApp3
{
//声明委托
public delegate int AddDelegate(int x, int y);
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("Client application started!\n");
Console.WriteLine(DateTime.Now.ToString());
Thread.CurrentThread.Name = "Main Thread";
Calculator cal = new Calculator();
AddDelegate del=new AddDelegate(cal.Add);
AsyncCallback async = new AsyncCallback(OnAddComplete);
string data = "在OnAddComplete()方法中获得了调用BeginInvoke()时最后一个参数传递的值";
IAsyncResult result=del.BeginInvoke(3,4,async,data);
// 做某些其他的事情,模拟需要执行3秒钟
for (int i = 1; i <= 3; i++)
{
Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(i));
Console.WriteLine("{0}: Client executed {1} second(s).",
Thread.CurrentThread.Name, i);
}
Console.WriteLine(DateTime.Now.ToString());
Console.WriteLine("\nPress any key to exit...");
Console.ReadKey();
}
/// <summary>
///
/// </summary>
/// <param name="asyncResult">在调用BeginInvoke()后不再需要保存IAsyncResult了,因为AsyncCallback委托将该对象定义在了回调方法的参数列表中;</param>
static void OnAddComplete(IAsyncResult asyncResult)
{
AsyncResult result = (AsyncResult)asyncResult;
AddDelegate del = (AddDelegate)result.AsyncDelegate;
string data = (string)asyncResult.AsyncState;
int rtn = del.EndInvoke(asyncResult);
Console.WriteLine("{0}: Result, {1}; Data: {2}\n",
Thread.CurrentThread.Name, rtn, data);
}
}
public class Calculator
{
public int Add(int x, int y)
{
//判断执行当前代码的线程是否为线程池中的线程
if (Thread.CurrentThread.IsThreadPoolThread)
{
Thread.CurrentThread.Name = "Pool Thread";
}
Console.WriteLine("Method invoked!");
// 执行某些事情,模拟需要执行2秒钟
for (int i = 1; i <= 2; i++)
{
Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(i));
Console.WriteLine("{0}: Add executed {1} second(s).",
Thread.CurrentThread.Name, i);
}
Console.WriteLine("Method complete!");
return x + y;
}
}
}

②BeginInvoke()方法结果返回类型
BeginInvoke()方法返回了一个实现了IAsyncResult接口的对象

AsyncResult的用途有这么几个:传递参数,它包含了对调用了BeginInvoke()的委托的引用;它还包含了BeginInvoke()的最后一个Object类型的参数;它可以鉴别出是哪个方法的哪一次调用,因为通过同一个委托变量可以对同一个方法调用多次
③EndInvoke()方法
EndInvoke()方法接受IAsyncResult类型的对象,所以在调用BeginInvoke()之后,需要保留IAsyncResult,以便在调用EndInvoke()时进行传递。这里最重要的就是EndInvoke()方法的返回值,它就是方法的返回值。除此以外,当客户端调用EndInvoke()时,如果异步调用的方法没有执行完毕,则会中断当前线程而去等待该方法,只有当异步方法执行完毕后才会继续执行后面的代码。所以在调用完BeginInvoke()后立即执行EndInvoke()是没有任何意义的。我们通常在尽可能早的时候调用BeginInvoke(),然后在需要方法的返回值的时候再去调用EndInvoke() ,或者根据情况在晚些时候调用
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ConsoleApp3
{
//声明委托
public delegate int AddDelegate(int x, int y);
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("Client application started!\n");
Console.WriteLine(DateTime.Now.ToString());
Thread.CurrentThread.Name = "Main Thread";
Calculator cal = new Calculator();
AddDelegate del=new AddDelegate(cal.Add);
IAsyncResult result=del.BeginInvoke(3,4,null,null);
// 做某些其他的事情,模拟需要执行3秒钟
for (int i = 1; i <= 3; i++)
{
Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(i));
Console.WriteLine("{0}: Client executed {1} second(s).",
Thread.CurrentThread.Name, i);
}
var rtn=del.EndInvoke(result);
Console.WriteLine("获取结果:{0}\n", rtn);
Console.WriteLine(DateTime.Now.ToString());
Console.WriteLine("\nPress any key to exit...");
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
public class Calculator
{
public int Add(int x, int y)
{
//判断执行当前代码的线程是否为线程池中的线程
if (Thread.CurrentThread.IsThreadPoolThread)
{
Thread.CurrentThread.Name = "Pool Thread";
}
Console.WriteLine("Method invoked!");
// 执行某些事情,模拟需要执行2秒钟
for (int i = 1; i <= 2; i++)
{
Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(i));
Console.WriteLine("{0}: Add executed {1} second(s).",
Thread.CurrentThread.Name, i);
}
Console.WriteLine("Method complete!");
return x + y;
}
}
}