文章目录
- 链表
- BM11 链表相加(二)
- BM12 单链表的排序
- 归并排序+分割 超时
- 辅助数组
- 快排
- BM13 判断一个链表是否为回文结构
- BM14 链表的奇偶重排
- BM15 删除有序链表中重复的元素-I
- BM16 删除有序链表中重复的元素-II
- JZ35 复杂链表的复制
- 二分法
- BM17 二分查找-I
- BM18 二维数组中的查找
- BM19 寻找峰值
- BM20 数组中的逆序对
- 流输入
- 小美加法
链表
BM11 链表相加(二)
之前写过一个题目就是两个逆序链表相加,这个题是正序链表求和,思路就是先把链表反转,变成逆序链表,然后求和,再把链表反转回来。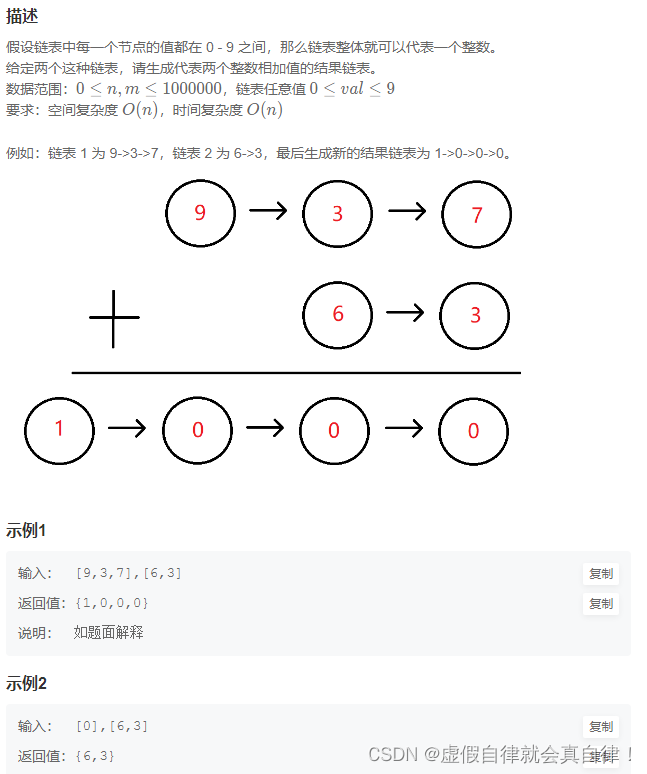
/**
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* addInList(ListNode* head1, ListNode* head2) {
int flag = 0, val = 0;
ListNode* dummyhead = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode* temp = dummyhead;
int val1 = 0, val2 = 0, sum = 0;
head1 = reverselist(head1);
head2 = reverselist(head2);
//printlist(head1);
//printlist(head2);
while(head1 || head2)
{
if(head1) val1 = head1->val;
else val1 = 0;
if(head2) val2 = head2->val;
else val2 = 0;
sum = val1 + val2 + flag;
flag = sum / 10;
sum = sum % 10;
cout << "sum:" << sum << " flag:" << flag << endl;
temp->next = new ListNode(sum);
temp = temp->next;
if(head1) head1 = head1->next;
if(head2) head2 = head2->next;
}
if(flag) temp->next = new ListNode(flag);
dummyhead->next = reverselist(dummyhead->next);
return dummyhead->next;
}
ListNode* reverselist(ListNode* node)
{
if(node == nullptr) return node;
ListNode* temp;
ListNode* cur = node;
ListNode* pre = nullptr;
while(cur)
{
temp = cur->next;
cur->next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = temp;
}
return pre;
}
void printlist(ListNode* head)
{
while(head)
{
cout << head->val << endl;
head = head->next;
}
}
};
BM12 单链表的排序

归并排序+分割 超时
因为递归O(n) 会超时,无语了
/**
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* sortInList(ListNode* head) {
if (head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr) return head;
// 分割 归并排序 超时
return cutlistTomerge(head);
}
ListNode* cutlistTomerge(ListNode* head)
{
if(head->next == nullptr) return head;
// 使用快慢指针寻找链表的中点
ListNode* fast = head;
ListNode* slow = head;
while (fast && fast->next) {
fast = fast->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
//断开链表
ListNode* temp = slow->next;
slow->next = nullptr;
// 递归左右两边进行排序
ListNode* left = cutlistTomerge(head);
ListNode* right = cutlistTomerge(temp);
return mergelist(left, right);
}
ListNode* mergelist(ListNode* head1, ListNode* head2)
{
if(head1 == nullptr) return head2;
if(head2 == nullptr) return head1;
ListNode* dummyhead = new ListNode(0);
ListNode* cur = dummyhead;
while(head1 && head2)
{
if(head1->val < head2->val)
{
cur->next = head1;
head1 = head1->next;
}
else
{
cur->next = head2;
head2 = head2->next;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
cur->next = (head1 == nullptr) ? head2 : head1;
return dummyhead->next;
}
};
辅助数组
用一个辅助数组保存结点值,然后排序,然后从表头逐渐更改结点值,排序用的内置函数sort。
/**
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* sortInList(ListNode* head) {
if (head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr) return head;
//数组保存 二分法
vector<int> nums;
ListNode* dummyhead = head;
while(dummyhead)
{
nums.push_back(dummyhead->val);
dummyhead = dummyhead->next;
}
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());
dummyhead = head;
for(int i=0; i<nums.size(); i++)
{
dummyhead->val = nums[i];
dummyhead = dummyhead->next;
}
return head;
}
void sortbinary(vector<int>& nums)
{
int left = 0, right = nums.size();//左闭右开
int mid;
while(left < right)
{
mid = left + (left + right) / 2;
if(nums[left] > nums[mid])
}
}
};
快排
有一个将排序的博客,挺详细的,谢谢五斤w的分享,吃透排序
用了一个快排
/**
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* sortInList(ListNode* head) {
if (head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr) return head;
//数组保存 二分法
vector<int> nums;
ListNode* dummyhead = head;
while(dummyhead)
{
nums.push_back(dummyhead->val);
dummyhead = dummyhead->next;
}
quickSort(nums, 0, nums.size()-1);
dummyhead = head;
for(int i=0; i<nums.size(); i++)
{
dummyhead->val = nums[i];
dummyhead = dummyhead->next;
}
return head;
}
int divide_quicksort(vector<int>& nums, int left, int right)
{
int pivot = nums[left];
while(left < right)
{
while(left < right && nums[right] >= pivot) right--;//找到比基准值小的数了
nums[left] = nums[right];//放在左边
while(left < right && nums[left] <= pivot) left++;//找到比基准值大的数了
nums[right] = nums[left];
}
nums[left] = pivot;//left和right指针重合,写right也可以
return left;
}
void quickSort(vector<int>& nums, int left, int right)
{
if(left < right)
{
int pivot = divide_quicksort(nums, left, right);
quickSort(nums, left, pivot-1);
quickSort(nums, pivot+1, right);
}
}
};
BM13 判断一个链表是否为回文结构
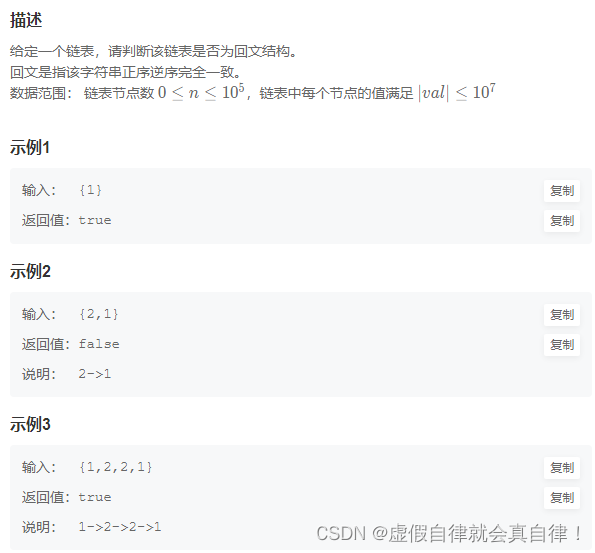
一开始想反转前半部分的,老有问题,就改成了反转后半部分了。
/**
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool isPail(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* fast = head;
ListNode* slow = head;
while(fast && fast->next)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
//cout << "fast:" << fast->val << " slow" << slow->val << " slow-next" << slow->next->val << endl;
//后半部分反转 slow是中点
ListNode* reversehead = reverselist(slow);
while(reversehead)
{
//cout << "head:" << head->val << " reversehead" << reversehead->val<<endl;
if(head->val == reversehead->val)
{
head = head->next;
reversehead = reversehead->next;
}
else return false;
}
return true;
}
ListNode* reverselist(ListNode* head)
{
ListNode* pre = nullptr;
ListNode* cur = head;
ListNode* temp;
while(cur)
{
temp = cur->next;
cur->next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = temp;
}
return pre;
}
};
BM14 链表的奇偶重排

看思路的写的,一个奇数位置开始,一个偶数位置开始,奇数结点指向 偶数结点的下一个。奇数指针更新;偶数结点指向 奇数结点的下一个。偶数指针更新。
/**
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* oddEvenList(ListNode* head) {
if(head == nullptr) return head;
ListNode* odd = head;
ListNode* even = head->next;
ListNode* evenhead = even;
while(even && even->next)
{
//奇数结点指向 偶数结点的下一个
odd->next = even->next;
odd = odd->next;//更新
//偶数结点指向 奇数结点的下一个
even->next = odd->next;
even = even->next;//更新
}
odd->next = evenhead;
return head;
}
ListNode* halflist(ListNode* node)
{
ListNode* newhead = node;
ListNode* cur = newhead;
while(cur && cur->next)
{
cur->next = cur->next->next;
cur = cur->next;
}
return newhead;
}
};
BM15 删除有序链表中重复的元素-I

一个结点遍历链表,如果当前结点与下一个结点值相等,逻辑删除,当前节点连接下下个节点,否则正常遍历。要注意只有一个结点的链表和空链表。
/**
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* deleteDuplicates(ListNode* head) {
if(head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr) return head;
ListNode* pre = head;
while(pre && pre->next)
{
//如果相同 就逻辑删除 连接下一个
if(pre->val == pre->next->val)
pre->next = pre->next->next;
else pre = pre->next;//否则正常更新
}
return head;
}
};
BM16 删除有序链表中重复的元素-II

/**
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* deleteDuplicates(ListNode* head) {
if(!head || !head->next) return head;
ListNode* res = new ListNode(0);
res->next = head;
ListNode* cur = res;
while(cur->next && cur->next->next)
{
//cout << "cur:" << cur->val << " cur.next" << cur->next->val;
if(cur->next->val == cur->next->next->val)
{
int temp = cur->next->val;
while(cur->next != nullptr && cur->next->val == temp)
{
cur->next = cur->next->next;
}
}
else cur = cur->next;
//cout << endl;
}
return res->next;
}
};
JZ35 复杂链表的复制
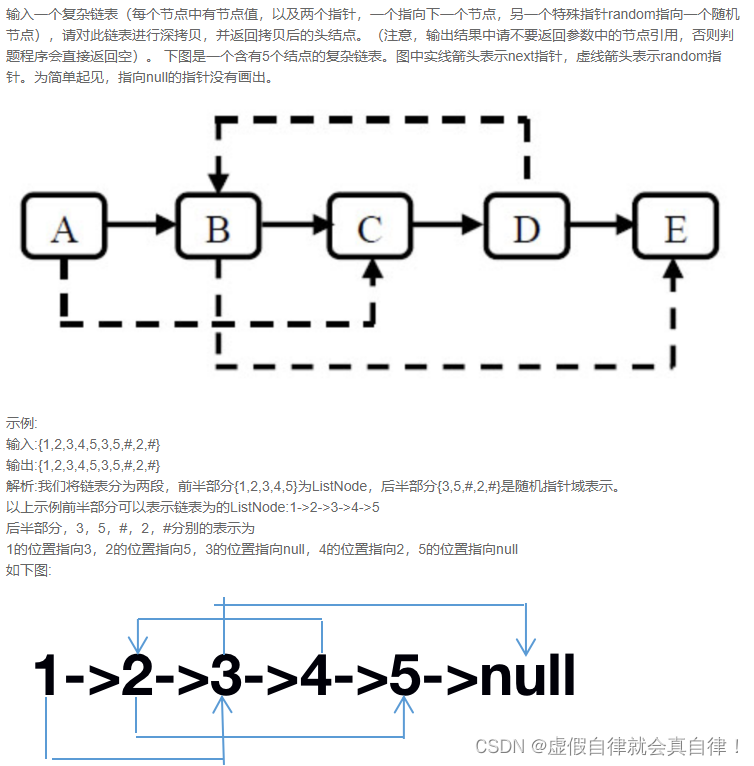
第二次写了,还是不会,又回去看了下第一次写的思路。
思路:用哈希表保存结点值及其指向。首先,复制新结点,此时哈希表只有单个新的结点,然后遍历哈希表内的结点,复制对应原结点的指向。
/*
struct RandomListNode {
int label;
struct RandomListNode *next, *random;
RandomListNode(int x) :
label(x), next(NULL), random(NULL) {
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
RandomListNode* Clone(RandomListNode* pHead) {
if(pHead == nullptr) return nullptr;
unordered_map<RandomListNode*, RandomListNode*> hashmap;
//复制单个新的节点
for(RandomListNode* cur = pHead; cur != nullptr; cur = cur->next)
{
hashmap[cur] = new RandomListNode(cur->label);
}
//复制指向
for(RandomListNode* cur = pHead; cur != nullptr; cur = cur->next)
{
//新结点的next指向
hashmap[cur]->next = hashmap[cur->next];
hashmap[cur]->random = hashmap[cur->random];
}
return hashmap[pHead];
}
};
二分法
BM17 二分查找-I
简单的二分查找,如果目标值在中间值的左边,left=mid+1;否则right=mid-1
class Solution {
public:
int search(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
if(nums.size() == 0) return -1;
int left = 0, right = nums.size()-1, mid = 0;
while(left <= right)
{
mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if(nums[mid] == target) return mid;
if(target > nums[mid]) left = mid + 1;//在mid的右边
else right = mid-1;//在mid的左边
}
return -1;
}
};
BM18 二维数组中的查找

这是一个行列都递增的数组,有两种做法,一是从右上角往左下角逼近,二是每一行都二分查找。
- 每一行二分查找
class Solution {
public:
bool Find(int target, vector<vector<int> >& array) {
if(array.size() == 0) return false;
//每一行二分查找
for(int i=0; i<array.size(); i++)
if(binaryserach(array[i], target)) return true;
return false;
}
bool binaryserach(vector<int>& array, int target)
{
int left = 0, right = array.size()-1, mid = 0;
while(left <= right)//注意取等号 否则无法取区间两边的值
{
mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if(target == array[mid]) return true;
if(target < array[mid]) right = mid - 1;//target在左边 缩小右边界
else left = mid + 1;
}
return false;
}
};
- 右上角往左下角逼近
class Solution {
public:
bool Find(int target, vector<vector<int> >& array) {
if(array.size() == 0) return false;
//右上角往左下角逼近
int row = 0, col = array[0].size()-1;
while (row < array.size() && col >= 0)
{
//printf("%d %d %d\n", row, col, array[row][col]);
if(target == array[row][col]) return true;
if(target < array[row][col]) col--;//列数往回走
else row++;//行数往下走
}
return false;
}
};
BM19 寻找峰值
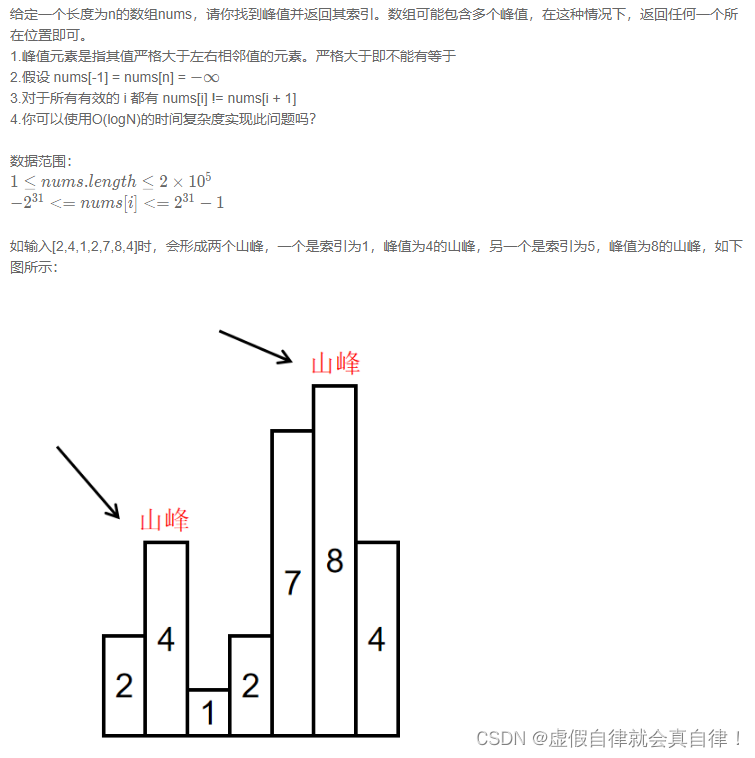
思路是记录左边的值,逐个比较,如果当前值比左右两边值大,或者当前值比左边大且到数组末尾,都认为当前值是峰值。
class Solution {
public:
int findPeakElement(vector<int>& nums) {
if(nums.size() < 2) return 0;
int left = nums[0];
for(int i=1; i<nums.size(); i++)
{
if(nums[i] > left && (nums[i] > nums[i+1] || i==nums.size()-1)) return i;
else left = nums[i];
}
return 0;
}
};
二分查找
class Solution {
public:
int findPeakElement(vector<int>& nums) {
if(nums.size() < 2) return 0;
int left = 0, right = nums.size()-1, mid = 0;
while (left < right)
{
mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
//右边是往下,不一定有坡峰
if(nums[mid] > nums[mid+1]) right = mid;
else left = mid+1;
}
return right;
}
};
BM20 数组中的逆序对

思路:两层for循环暴力,外循环固定当前值,内循环从当前值的后一个开始遍历,找到一个小的数字就计数,当前值统计完了,内循环结束,外循环开始下一轮。
其实,暴力法在找到最小值的时候重复了很多遍。比如,内循环找到一个小的值,如果此时外循环继续后移的话,就省去了很多麻烦。
class Solution {
public:
using ll = long long;
ll mod = 1000000007;
int InversePairs(vector<int>& nums) {
if(nums.size() <= 1) return 0;
ll res = 0;
for(int i=0; i<nums.size(); i++)
res += getreversenum(nums, i);
return res%mod;
}
ll getreversenum(vector<int>& nums, int index)
{
ll count = 0;
for(int i=index+1; i<nums.size(); i++)
{
//printf("%d %d %lld", nums[i], nums[index], count);
if(nums[i] < nums[index]) count++;
}
return count % mod;
}
};
并归排序做法 不是很会
class Solution {
private:
using ll = long long;
const int mod = 1000000007;
public:
int InversePairs(vector<int>& nums) {
if(nums.size() <= 1) return 0;
ll res = 0;
//并归排序
vector<int> temp(nums.size());
mergesort(nums, temp, 0, nums.size()-1, res);
return res;
}
// 递归划分
void mergesort(vector<int>& nums, vector<int>& temp, int left, int right, ll& res)
{
// 只有一个数字,则停止划分
if(left >= right)
return;
int mid = left + ((right - left) >> 1);//int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
mergesort(nums, temp, left, mid, res);
mergesort(nums, temp, mid+1, right, res);
// 合并两个有序区间
merge_sorted(nums, temp, left, mid, right, res);
}
//合并
void merge_sorted(vector<int>& nums, vector<int>& temp, int left, int mid, int right, ll& res)
{
int i = left, j = mid + 1, k = 0;
while(i <= mid && j<= right)
{
if(nums[i] > nums[j])
{
temp[k++] = nums[j++];
res += (mid - i + 1);//统计逆序数的个数 只统计逆序对里边数字较大的个数
res %= mod;
}
else temp[k++] = nums[i++];
}
while(i <= mid)
temp[k++] = nums[i++];
while(j <= right)
temp[k++] = nums[j++];
for(k = 0, i = left; i<=right; ++i, ++k)
{
nums[i] = temp[k];
}
}
};
流输入
写题的时候碰到输入要作为字符串进行分割的,因为不会就真的很烦,碰到这个题,学习一下。
istringstream是C++的输入输出控制类。C++引入了ostringstream、istringstream、stringstream这三个类,要使用他们创建对象就必须包含这个头文件。
①istringstream类用于执行C++风格的串流的输入操作。
②ostringstream类用于执行C风格的串流的输出操作。
③strstream类同时可以支持C风格的串流的输入输出操作。
istringstream的构造函数原形如下:istringstream::istringstream(string str);,作用是从string对象str中读取字符。
- 用法1,读取每个字符,空格结束,如下:
#include<iostream>
#include<sstream> //istringstream 必须包含这个头文件
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string str="this is istringstream";
//istringstream读取str中的每一个字符
istringstream iss(str);
string temp;
while(iss >> temp)
cout << temp << endl;
return 0;
}
输出就是逐行打印temp字符串
this
is
istringstream
- 用法2,结合getline()函数分割字符,如BM22题
#include<iostream>
#include<sstream> //istringstream 必须包含这个头文件
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string str="this is istringstream";
vector<string> num1;
istringstream ss1(version1);
string temp;
//按照 . 分割流输入
while(getline(ss1, temp, '.'))
num1.push_back(temp);
}
num1数组里边存放的依次是this、is、istringstream字符串。
小美加法
第一次写的时候理解错题意了,以为找到最大的两个数字的乘积就好了。但其实是,要找的乘积要满足:两个数相邻,且这个乘积使得整体和最大。
- 所以先求原来的和,如果不使用魔法就返回原来的和;
- 然后两两一组取乘积,再用原来的和sum - num1 - num2 + num1 * num2,把这个结果保存起来,我存在了数组里边,也可以仅维护每一次的最大值就好。
- 最后取数组的最大值和原来的和比较,输出两者较大者即可。如果第二步维护最大值,这一步就不用取数组最大值了,直接比较就好了。

#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
using ll = long long;
vector<ll> getsum(vector<ll>& v, ll sum)
{
vector<ll> result(v.size(), 0);
ll res = 0;
int index = 0;
for(int i=0; i<v.size(); i++)
{
res = sum - v[i] - v[i+1] + v[i] * v[i+1];
result[index++] = res;
//printf("%lld %lld %lld %lld %lld %d\n", sum, v[i], v[i+1], v[i]*v[i+1], res, index);
}
return result;
}
int main() {
ll n, a;
cin >> n;
vector<ll> v;
ll sum = 0;//初始和
for(ll i=0; i<n; i++)
{
cin >> a;
sum += a;
v.push_back(a);
}
//printf("%lld\n", sum);
/*for(int i=0; i<v.size(); i++)
printf("%d ", v[i]);
*/
vector<ll> result = getsum(v, sum);
ll res = sum;
for(auto r : result)
res = max(res, r);
printf("%lld", res);
return 0;
}
// 64 位输出请用 printf("%lld")