代码随想录刷题笔记总结:
https://www.programmercarl.com/
个人学习笔记 如有错误欢迎指正交流
1. 数组
1.1 理论基础
详细介绍:https://www.programmercarl.com/%E6%95%B0%E7%BB%84%E7%90%86%E8%AE%BA%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80.html
- 数组下标都是从0开始的。
- 数组内存空间的地址是连续的
1.2 二分查找
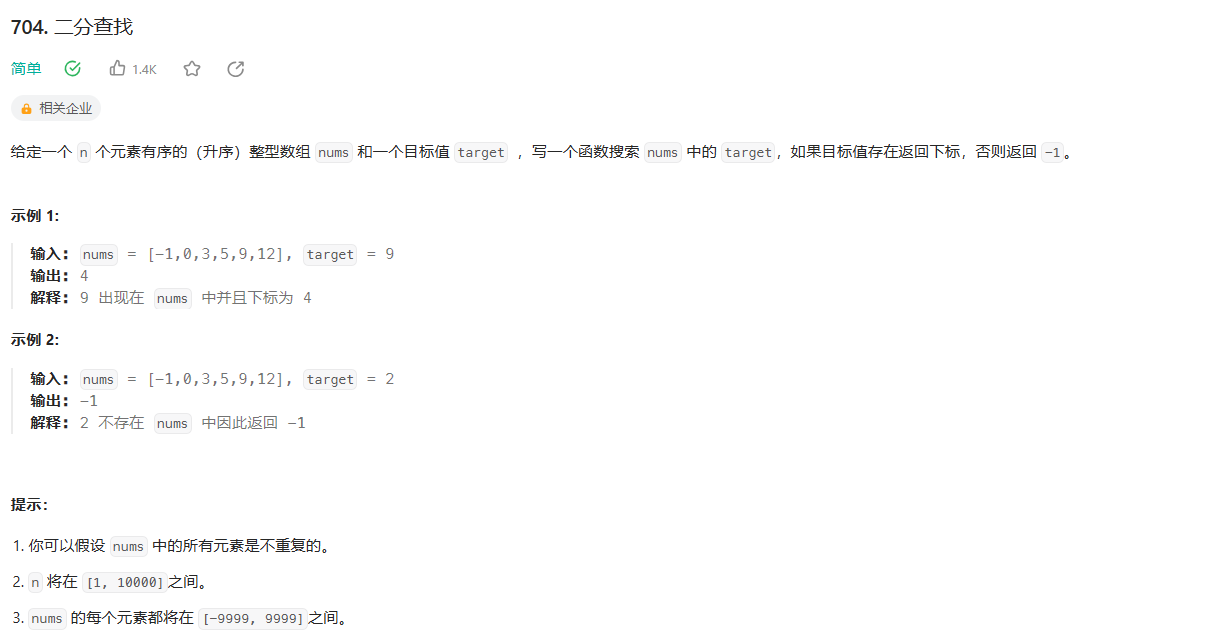
1.2.1 二分查找 (**)
1. 题目链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-search/description/
2. 思路:
-
方法1: 初始化 right = len(nums)-1, [left, right] left <= right 左闭右闭
那么right = mid-1, 因为 [mid, right] 已经考虑了 所以剩余[left, mid-1] mid -
方法2: 初始化right = len(nums), [left, right) left < right 左闭右开 那么right = mid,
因为 [mid, right) 已经考虑了 所以剩余[left, mid) 这里就考虑mid了
3. AC代码:
"""
题目: 704. 二分查找
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-search/description/
思路:
mid = left + right
方法1: 初始化 right = len(nums)-1, [left, right] left <= right 左闭右闭 那么right = mid-1, 因为 [mid, right] 已经考虑了 所以剩余[left, mid-1] mid
方法2: 初始化 right = len(nums)-1, [left, right) left < right 左闭右开 那么right = mid, 因为 [mid, right) 已经考虑了 所以剩余[left, mid) 这里就考虑mid了
两个方法的剩余考虑区间保持一致
left统一写法 left = mid +1
关键词: 有序,目标值, 查找,数组元组不重复
"""
class Solution(object):
def search(self, nums, target):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:type target: int
:rtype: int
"""
left = 0
right = len(nums) - 1
while left <= right:
mid = (left + right) // 2
if target < nums[mid]:
right = mid -1
elif target > nums[mid]:
left = left + 1
else:
return mid
return -1
if __name__ == '__main__':
nums = [-1, 0, 3, 5, 9, 12]
target = 9
solution = Solution()
result = solution.search(nums, target)
print(f"result: {result}")
1.2.2 搜索插入位置
1. 题目链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/search-insert-position/description/

2. 思路:
1. 利用二分查找
他的区别是 没有找到元素的情况返回的是元组插入的索引
关键词: 有序,目标值, 查找,数组元组不重复
3. AC代码:
"""
题目: 35 搜索插入位置
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/search-insert-position/description/
思路:
他的区别是 没有找到元素的情况返回的是元组插入的索引
关键词: 有序,目标值, 查找,数组元组不重复
"""
class Solution(object):
def searchInsert(self, nums, target):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:type target: int
:rtype: int
"""
left = 0
right = len(nums) - 1
while left <= right: # 如果元素不存在数组种 那么跳出循环的时候left = right+1的, 最终放回left和right+1都可以
mid = (left + right) // 2
if target < nums[mid]:
right = mid - 1
elif target > nums[mid]:
left = mid + 1
else:
return mid
return left
if __name__ == '__main__':
nums = [1, 3, 5, 6]
target = 2
solution = Solution()
result = solution.searchInsert(nums, target)
print(f"result: {result}")
1.2.3 在排序数组中查找元素的第一个和最后一个位置
1. 题目链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/find-first-and-last-position-of-element-in-sorted-array/

2. 思路:
方法1: 先找到一个的位置然后向左右扩散
方法2: 分别找到左边界和右边界
3. AC代码:
"""
题目: 34. 在排序数组中查找元素的第一个和最后一个位置
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/find-first-and-last-position-of-element-in-sorted-array/
思路:
方法1: 先找到一个的位置然后向左右扩散
方法2: 分别找到左边界和右边界
关键词: 有序,目标值, 查找,数组元组不重复
"""
class Solution(object):
def searchRange(self, nums, target):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:type target: int
:rtype: List[int]
"""
left = 0
right = len(nums) - 1
while left <= right:
mid = (left + right) // 2
if target < nums[mid]:
right = mid - 1
elif target > nums[mid]:
left = mid + 1
else:
temp = nums[mid]
i = mid
j = mid
while 0 <= i:
if nums[i] == target:
i -= 1
else:
break
while j <= len(nums) - 1:
if nums[j] == target:
j += 1
else:
break
return [i+1, j-1]
return [-1, -1]
if __name__ == '__main__':
nums = []
target = 6
solution = Solution()
result = solution.searchRange(nums, target)
print(f"result: {result}")
1.2.4 x 的平方根
1. 题目链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/sqrtx/description/

2. 思路:
这道题目和搜索插入位置题很相似 相当于从[1, 2, 3, …, x] 数组中找到根号x的插入位置
3. AC代码:
"""
题目: 69 x 的平方根
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/sqrtx/description/
思路:
这道题目和35题很相似 相当于从[1, 2, 3, ..., x] 数组中找到根号x的插入位置
"""
class Solution(object):
def mySqrt(self, x):
"""
:type x: int
:rtype: int
"""
left = 1
right = x
while left <= right:
mid = (left + right) // 2
if mid * mid < x:
left = mid + 1
elif mid * mid > x:
right = mid -1
else:
return mid
return right
if __name__ == '__main__':
x = 4
solution = Solution()
result = solution.mySqrt(9)
print(f"result: {result}")
1.2.5 有效的完全平方数
1. 题目链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/valid-perfect-square/description/

2. 思路:
相当于从[1, 2,…, x] 里面添加一个找是否存在 根号x 存在返回True 不存在则返回False
3. AC代码:
"""
题目: 367. 有效的完全平方数
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/valid-perfect-square/description/
思路:
相当于从[1, 2,..., x] 里面添加一个找是否存在 根号x 存在返回True 不存在则返回False
"""
class Solution(object):
def isPerfectSquare(self, num):
"""
:type num: int
:rtype: bool
"""
left = 1
right = num
while left <= right:
mid = (left + right) // 2
if mid * mid < num:
left = mid + 1
elif mid * mid > num:
right = mid - 1
else:
return True
return False
if __name__ == '__main__':
num = 1
solution = Solution()
result = solution.isPerfectSquare(num)
print(f"result: {result}")
1.3 移除元素
1.3.1 移除元素
1. 题目链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-element/description/

2. 思路:
方法1: 通过索引遍历元素,当前元素不等于val是指针才开始移动而且val_num加1, 那么数组的有效长度是len(nums)-val_num, 否则指针是不移动的。
方法2: 利用快慢指针进行计算,不等于的时候进行赋值, 等于的时候不用管
3.1 (方法一)AC代码:
"""
题目: 27. 移除元素
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-element/description/
思路:
方法1: 通过索引遍历元素,当前元素不等于val是指针才开始移动而且val_num加1, 那么数组的有效长度是len(nums)-val_num, 否则指针是不移动的。
方法2: 利用快慢指针进行计算,不等于的时候进行赋值, 等于的时候不用管
关键点:
"""
class Solution(object):
def removeElement(self, nums, val):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:type val: int
:rtype: int
"""
val_num = 0
i = 0
while i < len(nums)-val_num:
if nums[i] == val:
val_num += 1
for j in range(i, len(nums)-val_num):
nums[j] = nums[j+1]
else:
i += 1
return len(nums)-val_num
if __name__ == '__main__':
nums = [3, 2, 2, 3]
val = 3
solution = Solution()
result = solution.removeElement(nums, val)
print(f"result: {result}")
3.2 (方法2)AC代码:
"""
题目: 27. 移除元素
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-element/description/
思路:
方法1: 通过索引遍历元素,当前元素不等于val是指针才开始移动而且val_num加1, 那么数组的有效长度是len(nums)-val_num, 否则指针是不移动的。
方法2: 利用快慢指针进行计算,不等于的时候进行赋值, 等于的时候不用管(推荐使用这个方法 很优雅)
方法3: 双指针
关键点:
"""
class Solution(object):
def removeElement(self, nums, val):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:type val: int
:rtype: int
"""
slow = 0
for temp in nums:
if temp != val:
nums[slow] = temp
slow += 1
return slow
if __name__ == '__main__':
nums = [3, 2, 2, 3]
val = 3
solution = Solution()
result = solution.removeElement(nums, val)
print(f"result: {result}")
1.3.2 删除排序数组中的重复项
1. 题目链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-duplicates-from-sorted-array/description/

2. 思路:
方法1: slow 慢指针, 遇到新的数字进行赋值并且改变slow,
方法2: temp保存第一个出现的元素, 判断后续元素是否相同, 相同则直接跳过, 不同的话则重新对temp进行赋值
3.1 (方法1)AC代码:
"""
题目: 26 删除有序数组中的重复项
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-duplicates-from-sorted-array/description/
思路:
方法1: slow 慢指针, 遇到新的数字进行赋值并且改变slow,
方法2: temp保存第一个出现的元素, 判断后续元素是否相同, 相同则直接跳过, 不同的话则重新对temp进行赋值
"""
class Solution(object):
def removeDuplicates(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: int
"""
slow = 0
temp = nums[0]
for num in nums:
if num != temp:
slow += 1
nums[slow] = num
temp = num
print(f"slow: {slow+1}")
return slow+1
if __name__ == '__main__':
nums = [0,0,1,1,1,2,2,3,3,4]
solution = Solution()
result = solution.removeDuplicates(nums)
print(f"result: {result}, {nums[:result]}")
3.2 (方法1)AC代码:
"""
题目: 26 删除有序数组中的重复项
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-duplicates-from-sorted-array/description/
思路:
slow 慢指针, 遇到新的数字进行赋值并且改变slow
"""
class Solution(object):
def removeDuplicates(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: int
"""
slow = 0
for current in nums:
if nums[slow] != current:
slow += 1
nums[slow] = current
return slow+1
if __name__ == '__main__':
nums = [0,0,1,1,1,2,2,3,3,4]
solution = Solution()
result = solution.removeDuplicates(nums)
print(f"result: {result}, {nums[:result]}")
1.3.3 移动零
1. 题目链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/move-zeroes/description/

2. 思路:
- 用快慢指针对不是0的值依次赋值, 然后对slow之后的下标索引赋值为0
3. AC代码:
"""
题目: 283. 移动零
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/move-zeroes/description/
思路:
方法1: 用快慢指针对不是0的值依次赋值, 然后对slow之后的下标索引赋值为0
方法2:
关键词: 移除元素
"""
class Solution(object):
def moveZeroes(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: None Do not return anything, modify nums in-place instead.
"""
slow = 0
for num in nums:
if num != 0:
nums[slow] = num
slow += 1
for i in range(slow, len(nums)):
nums[i] = 0
# print(f"nums: {nums}")
# print(f"slow: {slow}")
return nums
if __name__ == '__main__':
nums = [0, 1, 0, 3, 12]
solution = Solution()
result = solution.moveZeroes(nums)
print(f"result: {result}")
1.3.4 比较含退格的字符串
1. 题目链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/backspace-string-compare/
2. 思路:
- 利用栈去解决, 遇到字符# 进行出栈 最终比较两个栈是否相等
关键词:退格 抵消
3. AC代码:
class Solution(object):
def backspaceCompare(self, s, t):
"""
:type s: str
:type t: str
:rtype: bool
"""
s_stack = self.backspace(s)
t_stack = self.backspace(t)
return s_stack == t_stack
def backspace(self, str):
stack = []
for word in str:
if word != '#':
stack.append(word)
else:
if stack != []:
stack.pop()
return stack
if __name__ == '__main__':
s = "ab#c"
t = "ad#c"
solution = Solution()
result = solution.backspaceCompare(s, t)
print(f"result: {result}")
1.3.5 有序数组的平方
1. 题目链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/squares-of-a-sorted-array/

2. 思路:
3.1 (方法1)AC代码:
"""
题目: 977. 有序数组的平方
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/squares-of-a-sorted-array/
思路:
方法1:最简单的方法就是用一个存入平方的值 最后排序
方法2:利用双指针依次从左从右进行遍历
关键词: 排序, 平方
"""
class Solution(object):
def sortedSquares(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: List[int]
"""
result = []
for i, num in enumerate(nums):
result.append(num * num)
return sorted(result)
if __name__ == '__main__':
nums = [-4, -1, 0, 3, 10]
solution = Solution()
result = solution.sortedSquares(nums)
print(f"result: {result}")
3.2 (方法2)AC代码:
"""
题目: 977. 有序数组的平方
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/squares-of-a-sorted-array/
思路:
方法1:最简单的方法就是用一个存入平方的值 最后排序
方法2:利用双指针依次从左从右进行遍历
关键词: 排序, 平方
"""
class Solution(object):
def sortedSquares(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: List[int]
"""
left = 0
right = len(nums) - 1
res = [None] * len(nums)
index = len(nums) - 1
while left <= right:
if nums[left] * nums[left] < nums[right] * nums[right]:
res[index] = nums[right] * nums[right]
right -= 1
else:
res[index] = nums[left] * nums[left]
left += 1
index -= 1
# print(f"res: {res}")
return res
if __name__ == '__main__':
nums = [-4, -1, 0, 3, 10]
solution = Solution()
result = solution.sortedSquares(nums)
print(f"result: {result}")
1.4 有序数组的平方
1. 题目链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/squares-of-a-sorted-array/

2. 思路:
3.1 (方法1)AC代码:
"""
题目: 977. 有序数组的平方
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/squares-of-a-sorted-array/
思路:
方法1:最简单的方法就是用一个存入平方的值 最后排序
方法2:利用双指针依次从左从右进行遍历
关键词: 排序, 平方
"""
class Solution(object):
def sortedSquares(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: List[int]
"""
result = []
for i, num in enumerate(nums):
result.append(num * num)
return sorted(result)
if __name__ == '__main__':
nums = [-4, -1, 0, 3, 10]
solution = Solution()
result = solution.sortedSquares(nums)
print(f"result: {result}")
3.2 (方法2)AC代码:
"""
题目: 977. 有序数组的平方
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/squares-of-a-sorted-array/
思路:
方法1:最简单的方法就是用一个存入平方的值 最后排序
方法2:利用双指针依次从左从右进行遍历
关键词: 排序, 平方
"""
class Solution(object):
def sortedSquares(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: List[int]
"""
left = 0
right = len(nums) - 1
res = [None] * len(nums)
index = len(nums) - 1
while left <= right:
if nums[left] * nums[left] < nums[right] * nums[right]:
res[index] = nums[right] * nums[right]
right -= 1
else:
res[index] = nums[left] * nums[left]
left += 1
index -= 1
# print(f"res: {res}")
return res
if __name__ == '__main__':
nums = [-4, -1, 0, 3, 10]
solution = Solution()
result = solution.sortedSquares(nums)
print(f"result: {result}")
1.5 长度最小的子数组
1.5.1 长度最小的子数组
1. 题目链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/minimum-size-subarray-sum/
2. 思路:
- 滑动窗口方法,满足条件时左窗口进行滑动
3. AC代码:
"""
题目: 209. 长度最小的子数组
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/minimum-size-subarray-sum/
思路:
滑动窗口方法,满足条件时左窗口进行滑动
"""
class Solution(object):
def minSubArrayLen(self, target, nums):
l = 0
sum = 0
res_min = 100001
for r, num in enumerate(nums):
sum += num
while sum >= target:
res_min = min(res_min, r-l+1)
sum -= nums[l]
l += 1
# print(f"res: {res_min}")
return 0 if res_min == 100001 else res_min
if __name__ == '__main__':
target = 7
nums = [2, 3, 1, 2, 4, 3]
solution = Solution()
result = solution.minSubArrayLen(target, nums)
print(f"result: {result}")
1.5.2 水果成篮 (**)
1. 题目链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/fruit-into-baskets/description/

2. 思路:
- 滑动窗口利用map,循环遍历fruits数组,将fruits[r]的value值加一,
- 如果map长度大于2 那么左滑动串口开始移动,直到fruit[l]的value等于0才可以删除key
- 对res_max进行赋值。返回结果
3. AC代码:
"""
题目: 904. 水果成篮
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/fruit-into-baskets/description/
思路:
滑动窗口利用map,循环遍历fruits数组,将fruits[r]的value值加一,
如果map长度大于2 那么左滑动串口开始移动,直到fruit[l]的value等于0才可以删除key
对res_max进行赋值。返回结果
"""
class Solution:
def totalFruit(self, fruits):
l = 0
res_max = float("-inf")
fruits_map = {}
for r in range(len(fruits)):
fruits_map[fruits[r]] = fruits_map.get(fruits[r], 0) + 1
while len(fruits_map) > 2:
fruits_map[fruits[l]] -= 1
if fruits_map[fruits[l]] == 0:
del fruits_map[fruits[l]]
l += 1
res_max = max(res_max, r - l + 1)
return res_max
if __name__ == '__main__':
fruits = [0,1,2,2]
solution = Solution()
result = solution.totalFruit(fruits)
print(f"result: {result}")
1.5.3 最小覆盖子串 (**)
1. 题目链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/minimum-window-substring/

2. 思路:
- 利用map+滑动窗口
- 首先将字符串t的所有字符组成key value的形式, 以及初始化总的字符个数
- 然后遍历字符串s, 判断当前字符s[r] 是否在t_map的key中, 如果在则s[r]对应的value-1, 判断value是否为0, 如果为0, 那么require_char 可以见第减1
- 判断require_char==0, 表示当前滑动窗口包含t字符串, res_str进行赋值, 左滑动窗口向后移动进行找到最小的滑动窗口
- 返回res_str
3. AC代码:
"""
题目: 76. 最小覆盖子串
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/minimum-window-substring/
思路:
1. 利用map+滑动窗口
2. 首先将字符串t的所有字符组成key value的形式, 以及初始化总的字符个数
3. 然后遍历字符串s, 判断当前字符s[r] 是否在t_map的key中, 如果在则s[r]对应的value-1, 判断value是否为0, 如果为0, 那么require_char 可以见第减1
4. 判断require_char==0, 表示当前滑动窗口包含t字符串, res_str进行赋值, 左滑动窗口向后移动进行找到最小的滑动窗口
5. 返回res_str
"""
class Solution(object):
def minWindow(self, s, t):
res_str = ""
t_map = {}
res_min = float("inf")
for char in t:
t_map[char] = t_map.get(char, 0) + 1
require_char = len(t_map)
l = 0
r = 0
while r < len(s):
# s_map[s[r]] = s_map.get(s[r], 0) + 1
if s[r] in t_map:
t_map[s[r]] -= 1
if t_map[s[r]] == 0:
require_char -= 1
while require_char == 0: # 满足要求的时候保存字串的大小
if r - l + 1 < res_min:
res_min = min(res_min, r - l + 1)
res_str = s[l:r+1]
# print(f"res_str: {res_str}")
if s[l] in t_map:
t_map[s[l]] += 1
if t_map[s[l]] > 0:
require_char += 1
l +=1
r += 1
return res_str
if __name__ == '__main__':
s = "ADOBECODEBANC"
t = "ABC"
solution = Solution()
result = solution.minWindow(s, t)
print(f"result: {result}")
1.6 螺旋矩阵 II
1. 题目链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/spiral-matrix-ii/

2. 思路:
- 初始化top, down, left, right = 0, n-1, 0, n-1,
- 然后顺时针螺旋依次进行赋值, top赋值之后+1, down-1, left+1, right+1依次这样缩小范围即可
3. AC代码:
"""
题目: 59. 螺旋矩阵 II
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/spiral-matrix-ii/
思路:
初始化top, down, left, right = 0, n-1, 0, n-1,
然后顺时针螺旋依次进行赋值, top赋值之后+1, down-1, left+1, right+1依次这样缩小范围即可
"""
class Solution(object):
def generateMatrix(self, n):
num = 1
top, down, left, right = 0, n-1, 0, n-1
res = [[0] * n for _ in range(n)]
while num <= n * n:
for i in range(left, right+1):
res[top][i] = num
num += 1
top += 1
for i in range(top, down+1):
res[i][right] = num
num += 1
right -= 1
for i in range(right, left-1, -1):
res[down][i] = num
num += 1
down -= 1
for i in range(down, top-1, -1):
res[i][left] = num
num += 1
left += 1
return res
if __name__ == '__main__':
n = 3
solution = Solution()
result = solution.generateMatrix(n)
print(f"result: {result}")
1.7 数组总结
详细总结: https://www.programmercarl.com/%E6%95%B0%E7%BB%84%E6%80%BB%E7%BB%93%E7%AF%87.html
2. 链表
本章预览:
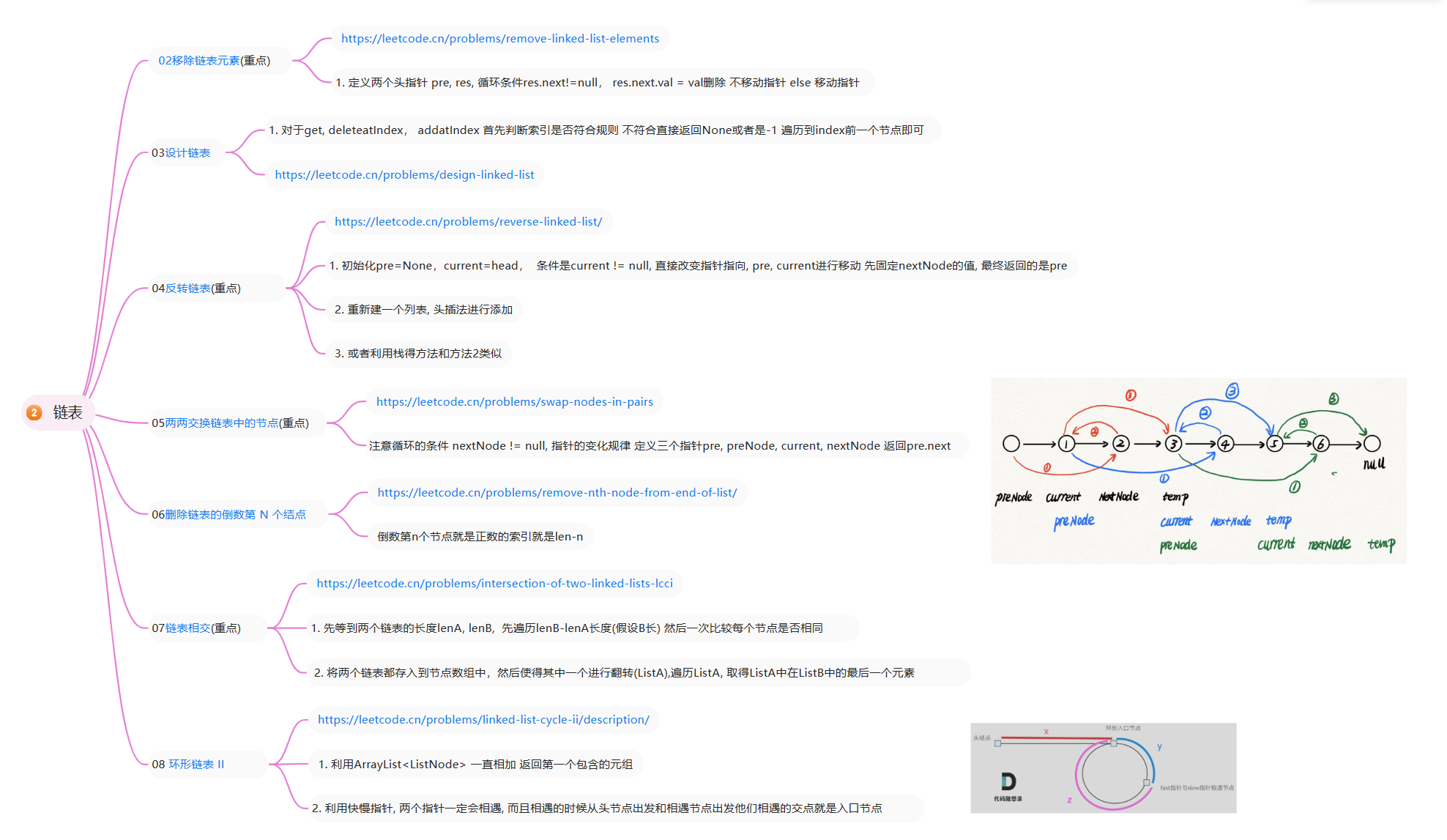
2.1 理论基础
什么是链表,链表是一种通过指针串联在一起的线性结构,每一个节点由两部分组成,一个是数据域一个是指针域(存放指向下一个节点的指针),最后一个节点的指针域指向null(空指针的意思)。
详细介绍: https://www.programmercarl.com/%E9%93%BE%E8%A1%A8%E7%90%86%E8%AE%BA%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80.html
2.2 移除链表元素 (**)
- 刷题链接:
https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-linked-list-elements/description/

2. 思路
- 首先定义构造列表和遍历列表的方法(不是必要的)
- 利用pre节点
- if pre.next.val = val 删除当前节点 操作为pre.next = pre.next.next (如果当前节点的值等于val)
- 否则指针继续移动
3. AC代码
"""
题目: 203. 移除链表元素
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-linked-list-elements/description/
思路:
1. 首先定义构造列表和遍历列表的方法(不是必要的)
2. 利用pre节点 删除当前节点 操作为pre.next = pre.next.next (如果当前节点的值等于val)
3. 否则指针继续移动
"""
class ListNode(object):
def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
self.val = val
self.next = next
class Solution(object):
def removeElements(self, head, val):
pre = ListNode(0)
pre.next = head
temp = pre
while temp.next != None:
if temp.next.val == val:
temp.next = temp.next.next
else:
temp = temp.next
return pre.next
def create_linklist(array): # 构造单链表
if not array:
return None
preNode = ListNode()
pre = preNode
for value in array:
current = ListNode(value)
pre.next = current
pre = current
get_linklist(preNode.next)
return preNode.next
def get_linklist(head): # 遍历单链表的元素
if head == None:
return head
temp = head
res = []
while temp != None:
res.append(temp.val)
temp = temp.next
# print(f"len: {len(res)}")
# print(f"linklist: {res}")
return res
if __name__ == '__main__':
head = [1, 2, 6, 3, 4, 5, 6]
val = 6
head = create_linklist(head)
solution = Solution()
head = solution.removeElements(head, val)
get_linklist(head)
print(f"head: {head}")
2.3 设计链表
- 刷题链接:
https://leetcode.cn/problems/design-linked-list/description/

2. 思路
- 初始化pre节点和链表长度len
- 对于get, deleteatIndex, addatIndex 首先判断索引是否符合规则 不符合直接返回None或者是-1 遍历到index前一个节点即可
- 头插法和尾插入法
3. AC代码
"""
题目: 707. 设计链表
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/design-linked-list/description/
思路:
1. 初始化pre节点和链表长度len
2. 对于get, deleteatIndex, addatIndex 首先判断索引是否符合规则 不符合直接返回None或者是-1 遍历到index前一个节点即可
3. 头插法和尾插入法
"""
class ListNode(object):
def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
self.val = val
self.next = next
class MyLinkedList(object):
def __init__(self):
self.pre = ListNode(0)
self.len = 0
# 得到链表的长度
def get_len(self, pre):
temp = self.pre.next
len = 0
while temp != None:
temp = temp.next
len += 1
return len
# 得到index索引的节点
def get(self, index):
"""
:type index: int
:rtype: int
"""
if index >= self.len:
return -1
temp = self.pre.next
for i in range(index):
temp = temp.next
return temp.val
# 头插法
def addAtHead(self, val):
"""
:type val: int
:rtype: None
"""
currentNode = ListNode(val)
head = self.pre.next
currentNode.next = head
self.pre.next = currentNode
self.len += 1
# 尾插法
def addAtTail(self, val):
"""
:type val: int
:rtype: None
"""
tail = self.pre
tailNode = ListNode(val)
while tail.next != None:
tail = tail.next
tail.next = tailNode
self.len += 1
# val插入到index
def addAtIndex(self, index, val):
"""
:type index: int
:type val: int
:rtype: None
"""
if index > self.len:
return None
temp = self.pre
for i in range(index):
temp = temp.next
valNode = ListNode(val)
valNode.next = temp.next
temp.next = valNode
self.len += 1
# 删除index位置的节点
def deleteAtIndex(self, index):
"""
:type index: int
:rtype: None
"""
if index >= self.len:
return None
temp = self.pre
for i in range(index):
temp = temp.next
temp.next = temp.next.next
self.len -= 1
if __name__ == '__main__':
print("hello solution")
2.4 反转链表 (**)
1. 刷题链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-linked-list/

2.1 (方法一) 思路
- 首先遍历一篇将所有节点存入到栈中
- 然后依次出战进行赋值构建新的链表
3. (方法一) AC代码
"""
题目: 206. 反转链表
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-linked-list/
思路:
1. 首先遍历一篇将所有节点存入到栈中
2. 然后依次出战进行赋值构建新的链表
"""
class ListNode(object):
def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
self.val = val
self.next = next
class Solution(object):
def reverseList(self, head):
"""
:type head: ListNode
:rtype: ListNode
"""
if not head:
return None
stack = []
while head != None:
stack.append(head)
head = head.next
stack[0].next = None
res = stack.pop()
pre = res
while stack:
current = stack.pop()
pre.next = current
pre = current
get_linklist(res)
return res
def create_linklist(array): # 构造单链表
if not array:
return None
head = ListNode(array[0])
temp = head
for value in array[1:]:
current = ListNode(value)
temp.next = current
temp = temp.next
get_linklist(head)
return head
def get_linklist(head): # 遍历单链表的元素
if head == None:
return head
temp = head
res = []
while temp != None:
res.append(temp.val)
temp = temp.next
print(f"linklist: {res}")
return res
if __name__ == '__main__':
head = []
head = create_linklist(head)
solution = Solution()
solution.reverseList(head)
2.2 (方法一) 思路
- pre 指向前一个节点 初始话一定要为null
- current 指向当前节点
- 直接改变指针的指向,
- 要注意每次改变时候pre, current指针的变化
3.2 (方法二)AC代码
"""
题目: 206. 反转链表
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-linked-list/
思路:
pre 指向前一个节点 初始话一定要为null
current 指向当前节点
直接改变指针的指向,
要注意每次改变时候pre, current指针的变化
"""
class ListNode(object):
def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
self.val = val
self.next = next
class Solution(object):
def reverseList(self, head):
if not head:
return None
pre = None
current = head
while current != None:
nextNode = current.next
current.next = pre
pre = current
current = nextNode
# print(f"nextNode: {pre.val}")
# print(f"nextNode: {nextNode.next.val}")
# get_linklist(pre)
return pre
def create_linklist(array): # 构造单链表
if not array:
return None
head = ListNode(array[0])
temp = head
for value in array[1:]:
current = ListNode(value)
temp.next = current
temp = temp.next
get_linklist(head)
return head
def get_linklist(head): # 遍历单链表的元素
if head == None:
return head
temp = head
res = []
while temp != None:
res.append(temp.val)
temp = temp.next
print(f"linklist: {res}")
return res
if __name__ == '__main__':
head = [1,2,3,4,5]
head = create_linklist(head)
solution = Solution()
solution.reverseList(head)
2.5 两两交换链表中的节点 (**)
1. 刷题链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/swap-nodes-in-pairs/description/

2. 思路

3. AC代码
"""
题目: 24. 两两交换链表中的节点
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/swap-nodes-in-pairs/description/
思路:
"""
class ListNode(object):
def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
self.val = val
self.next = next
class Solution(object):
def swapPairs(self, head):
"""
:type head: ListNode
:rtype: ListNode
"""
print(f"hello world")
if not head or head.next == None:
return head
pre = ListNode()
res = pre
current = head
nextNode = head.next
while nextNode != None:
temp = nextNode.next
pre.next = nextNode
nextNode.next = current
current.next = temp
pre = current
current = temp
if temp:
nextNode = temp.next
else:
nextNode = temp
get_linklist(res.next)
return res.next
def create_linklist(array): # 构造单链表
if not array:
return None
preNode = ListNode()
pre = preNode
for value in array:
current = ListNode(value)
pre.next = current
pre = current
get_linklist(preNode.next)
return preNode.next
def get_linklist(head): # 遍历单链表的元素
if head == None:
return head
temp = head
res = []
while temp != None:
res.append(temp.val)
temp = temp.next
# print(f"len: {len(res)}")
print(f"linklist: {res}")
return res
if __name__ == '__main__':
head = [1, 2, 3, 4]
head = create_linklist(head)
solution = Solution()
solution.swapPairs(head)
2.6 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点
1. 刷题链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-nth-node-from-end-of-list/

2. 思路
- 倒数滴n个节点相当于 index = len-n+1
- 循环遍历到索引index即可 然后执行删除操作
3. AC代码
"""
题目: 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-nth-node-from-end-of-list/
思路:
倒数滴n个节点相当于 index = len-n+1
循环遍历到索引index即可 然后执行删除操作
"""
class ListNode(object):
def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
self.val = val
self.next = next
class Solution(object):
def removeNthFromEnd(self, head, n):
"""
:type head: ListNode
:type n: int
:rtype: ListNode
"""
if not head:
return head
len = self.get_len(head)
index = len - n
# print(f"index: {index}")
pre = ListNode()
res = pre
pre.next = head
for i in range(index):
pre = pre.next
pre.next = pre.next.next
# get_linklist(res.next)
return res.next
def get_len(self, head):
temp = head
len = 0
while temp != None:
temp = temp.next
len += 1
return len
def create_linklist(array): # 构造单链表
if not array:
return None
preNode = ListNode()
pre = preNode
for value in array:
current = ListNode(value)
pre.next = current
pre = current
get_linklist(preNode.next)
return preNode.next
def get_linklist(head): # 遍历单链表的元素
if head == None:
return head
temp = head
res = []
while temp != None:
res.append(temp.val)
temp = temp.next
# print(f"len: {len(res)}")
print(f"linklist: {res}")
return res
if __name__ == '__main__':
head = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
n = 2
solution = Solution()
head = create_linklist(head)
solution.removeNthFromEnd(head, n)
2.7 链表相交 (**)
1. 刷题链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists-lcci/description/

2.1 (方法1)思路
- 将两个链表都存入到数组中
- 然后使得其中一个进行翻转(ListA),
- 遍历ListA, 取得ListA中在ListB中的最后一个元素
3.1 (方法1)AC代码
"""
题目: 面试题 02.07. 链表相交
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists-lcci/description/
思路:
将两个链表都存入到数组中
然后使得其中一个进行翻转(ListA),
遍历ListA, 取得ListA中在ListB中的最后一个元素
"""
class ListNode(object):
def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
self.val = val
self.next = next
class Solution(object):
def getIntersectionNode(self, headA, headB):
"""
:type head1, head1: ListNode
:rtype: ListNode
"""
listA = self.get_NodeList(headA)
listB = self.get_NodeList(headB)
reversed(listA)
print(listA)
print(listB)
for currentNode in listA:
if currentNode in listB:
print(f"currentNode: {currentNode.val}")
return currentNode
return None
def get_NodeList(self, head):
res_list = []
temp = head
while temp != None:
res_list.append(temp)
temp = temp.next
return res_list
def create_linklist(array): # 构造单链表
if not array:
return None
preNode = ListNode()
pre = preNode
for value in array:
current = ListNode(value)
pre.next = current
pre = current
get_linklist(preNode.next)
return preNode.next
def get_linklist(head): # 遍历单链表的元素
if head == None:
return head
temp = head
res = []
while temp != None:
res.append(temp.val)
temp = temp.next
# print(f"len: {len(res)}")
print(f"linklist: {res}")
return res
if __name__ == '__main__':
listA = [4, 1, 8, 4, 5]
print(listA.reverse())
print(listA)
listB = [5, 0, 1, 8, 4, 5]
listA = create_linklist(listA)
listB = create_linklist(listB)
solution = Solution()
solution.getIntersectionNode(listA, listB)
2.2 (方法2)思路
- 首先翻转两个链表
- 找到最后一个相似得节点保存下来进行返回
3.2 (方法2)AC代码
"""
题目: 面试题 02.07. 链表相交
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists-lcci/description/
思路:
首先翻转两个链表
找到最后一个相似得节点保存下来进行返回
"""
2.8 环形链表 II
1. 刷题链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/linked-list-cycle-ii/description/

2.1 (方法1)思路
- 利用一个数组存储节点, 遍历链表节点,不存在则将列表加入数组, 存在说明有环则返回
3.1 (方法1)AC代码
"""
题目: 142. 环形链表 II
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/linked-list-cycle-ii/description/
思路:
利用一个数组存储节点, 遍历链表节点,不存在则将列表加入数组, 存在说明有环则返回
"""
class ListNode(object):
def __int__(self, val=0, next=None):
self.val = val
self.next = next
class Solution(object):
def detectCycle(self, head):
"""
:type head: ListNode
:rtype: ListNode
"""
res_list = []
current = head
while current != None:
if current not in res_list:
res_list.append(current)
else:
return current
current = current.next
return -1
2.2 (方法2)思路
- 利用一个数组存储节点, 遍历链表节点,不存在则将列表加入数组, 存在说明有环则返回
3.2 (方法2)AC代码
2.9 总结
详细总结:
https://www.programmercarl.com/%E9%93%BE%E8%A1%A8%E6%80%BB%E7%BB%93%E7%AF%87.html#%E9%93%BE%E8%A1%A8%E7%9A%84%E7%90%86%E8%AE%BA%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80
3. 哈希表
章节预览:

3.1 理论基础
详细介绍:https://www.programmercarl.com/%E5%93%88%E5%B8%8C%E8%A1%A8%E7%90%86%E8%AE%BA%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80.html
常见得三种hash数据结构。
- 数组
- set (集合)
- map(映射)
3.2 有效的字母异位词
1. 刷题链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/valid-anagram/description/

2. 思路:
利用map解决就行 类似76. 最小覆盖子串这道题目
利用一个requires和map就可以解决
首先将字符串s转化为一个数组, 然后依次遍历t的字符判断,
不存在直接返回False, 存在则减去1, 如果value为0并且require_chars-1
3. AC代码:
"""
题目: 242. 有效的字母异位词
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/valid-anagram/description/
思路:
利用map解决就行 类似76. 最小覆盖子串这道题目
利用一个requires和map就可以解决
首先将字符串s转化为一个数组, 然后依次遍历t的字符判断,
不存在直接返回False, 存在则减去1, 如果value为0并且require_chars-1
"""
class Solution(object):
def isAnagram(self, s, t):
"""
:type s: str
:type t: str
:rtype: bool
"""
if len(s) != len(t):
return False
s_map = {}
for char in s:
s_map[char] = s_map.get(char, 0) + 1
require_chars = len(s_map)
for char in t:
if char in s_map:
s_map[char] -= 1
if s_map[char] == 0: # 等于0 去除
require_chars -= 1
del s_map[char]
else:
return False
# print(require_chars)
return require_chars == 0
if __name__ == '__main__':
s = "anagram"
t = "nagaram"
# s = "rat"
# t = "car"
solution = Solution()
res = solution.isAnagram(s, t)
print(res)
3.3 两个数组的交集
1. 刷题链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/intersection-of-two-arrays/description/

2. 思路
- 定义res用于存放最终结果
- 遍历nums1中的每个元素 如果num在nums2列表中且不存在res 那么res列表加入当前元组
- 最终返回res列表
3. AC代码
"""
题目: 349. 两个数组的交集
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/intersection-of-two-arrays/description/
思路:
1. 定义res用于存放最终结果
2. 遍历nums1中的每个元素 如果num在nums2列表中且不存在res 那么res列表加入当前元组
3. 最终返回res列表
"""
class Solution(object):
def intersection(self, nums1, nums2):
"""
:type nums1: List[int]
:type nums2: List[int]
:rtype: List[int]
"""
res = []
for num in nums1:
if num in nums2 and num not in res:
res.append(num)
return res
if __name__ == '__main__':
nums1 = [1, 2, 2, 1]
nums2 = [2, 2]
solution = Solution()
res = solution.intersection(nums1, nums2)
print(res)
3.4 快乐数
1. 刷题链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/happy-number/description/

2. 思路
- 创建一个res列表存放在sum数字,首先编写一个通过num得到sum的函数,
- 然后利用一个列表加入sum,如果当前sum在res列表中则返回False, 其他情况继续调用isHappy(sum)
- 如果1在res中返回True
sum会重复出现,这对解题很重要!
3. AC代码
"""
题目: 202. 快乐数
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/happy-number/description/
思路:
1. 创建一个res列表存放在sum数字,首先编写一个通过num得到sum的函数,
2. 然后利用一个列表加入sum,如果当前sum在res列表中则返回False, 其他情况继续调用isHappy(sum)
3. 如果1在res中返回True
sum会重复出现,这对解题很重要!
"""
class Solution(object):
def __init__(self):
self.res = []
def isHappy(self, n):
"""
:type n: int
:rtype: bool
"""
self.res.append(n)
current = self.getNumSum(n)
if 1 in self.res:
return True
elif current in self.res:
return False
else:
return self.isHappy(current)
def getNumSum(self, n):
sum = 0
while n > 0:
temp = n % 10
n //= 10
sum = sum + temp * temp
return sum
if __name__ == '__main__':
n = 18
solution = Solution()
res = solution.isHappy(n)
print(res)
3.5 两数之和
1. 刷题链接 https://leetcode.cn/problems/two-sum/description/

2.1 (方法一)思路
- 最简单的方法就是利用两个for循环遍历即可 但是性能比较低
3.1 (方法一)AC代码
"""
题目: 1. 两数之和
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/two-sum/description/
思路:
最简单的方法就是利用两个for循环遍历即可 但是性能比较低
"""
class Solution(object):
def twoSum(self, nums, target):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:type target: int
:rtype: List[int]
"""
for i in range(len(nums)):
for j in range(i+1, len(nums)):
if nums[i] + nums[j] == target:
return [i, j]
if __name__ == '__main__':
nums = [2, 7, 11, 15]
target = 9
solution = Solution()
res = solution.twoSum(nums, target)
print(res)
2.2 (方法二)思路
- 利用map记录 key:value=元素值:索引
- 依次判断target-元素值 是否在map中 在则直接返回 不在则map[key] = value继续判断
3.2 (方法二)AC代码
"""
题目: 1. 两数之和
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/two-sum/description/
思路:
最简单的方法就是利用两个for循环遍历即可 但是性能比较低
"""
class Solution(object):
def twoSum(self, nums, target):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:type target: int
:rtype: List[int]
"""
for i in range(len(nums)):
for j in range(i+1, len(nums)):
if nums[i] + nums[j] == target:
return [i, j]
if __name__ == '__main__':
nums = [2, 7, 11, 15]
target = 9
solution = Solution()
res = solution.twoSum(nums, target)
print(res)
3.6 四数相加 II
1. 刷题链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/4sum-ii/

2. 思路
- 三/四层for循环超出时间限制, 两层for循环可以解决
- 利用两个map,用两层的for循环进行解决
- left_map存放num1, num2的和 元素和:个数
- right_map存放num3, num4的和 元素和:个数
- 最终判断key, -key是存在 存在则相加计算最终个数
3. AC代码
"""
题目: 四数相加 II
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/4sum-ii/
思路:
三/四层for循环超出时间限制, 两层for循环可以解决
利用两个map,用两层的for循环进行解决
left_map存放num1, num2的和 元素和:个数
right_map存放num3, num4的和 元素和:个数
最终判断key, -key是存在 存在则相加计算最终个数
"""
class Solution(object):
def fourSumCount(self, nums1, nums2, nums3, nums4):
"""
:type nums1: List[int]
:type nums2: List[int]
:type nums3: List[int]
:type nums4: List[int]
:rtype: int
"""
n = len(nums1)
res = 0
left_map = {}
right_map = {}
for i in range(n):
for j in range(n):
key = nums1[i]+nums2[j]
left_map[key] = left_map.get(key, 0) + 1
for k in range(n):
for l in range(n):
key = nums3[k] + nums4[l]
right_map[key] = right_map.get(key, 0) + 1
# print(left_map)
# print(right_map)
for key, value in left_map.items():
if -key in right_map:
res = res + (left_map[key] * right_map[-key])
return res
if __name__ == '__main__':
nums1 = [1,2]
nums2 = [-2,-1]
nums3 = [-1,2]
nums4 = [0,2]
solution = Solution()
res = solution.fourSumCount(nums1, nums2, nums3, nums4)
print(res)
3.7 赎金信
1. 刷题链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/ransom-note/description/

2. 思路
- 将ransonNote转化为map, require_char是需要的长度
- 遍历magazine 元素, 如果在map中那么–, 最终判断require_char是否为0从而返回True or False
3. AC代码
"""
题目: 383. 赎金信
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/ransom-note/description/
思路:
1. 将ransonNote转化为map, require_char是需要的长度
2. 遍历magazine 元素, 如果在map中那么--, 最终判断require_char是否为0从而返回True or False
"""
class Solution(object):
def canConstruct(self, ransomNote, magazine):
"""
:type ransomNote: str
:type magazine: str
:rtype: bool
"""
r_map = {}
for char in ransomNote:
r_map[char] = r_map.get(char, 0) + 1
require_char = len(r_map)
print(require_char)
print(r_map)
for char in magazine:
if char in r_map:
r_map[char] -= 1
if r_map[char] == 0:
require_char -= 1
if require_char == 0:
return True
del r_map[char]
return False
if __name__ == '__main__':
ransomNote = "aa"
magazine = "aab"
solution = Solution()
res = solution.canConstruct(ransomNote, magazine)
print(res)
3.8 三数之和 (**)
1. 刷题链接 https://leetcode.cn/problems/3sum/

2. 思路
1. 首先得对nums进行排序
2. 利用双指针 每次遍历nums,遍历i时 左指针和右指针分别为i+1 len(nums)-1
3. 然后就是去重操作 针对i得去重就是 i > 0 and nums[i] == num[i-1]
3. AC代码
"""
题目: 15. 三数之和
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/3sum/
思路:
1. 暴力解法超出时间限制 只能过99%
2.
首先得对nums进行排序
利用双指针 每次遍历nums,遍历i时 左指针和右指针分别为i+1 len(nums)-1
然后就是去重操作 针对i得去重就是 i > 0 and nums[i] == num[i-1]
"""
class Solution(object):
def threeSum(self, nums):
nums.sort()
res = []
for i in range(len(nums)-2):
if i > 0 and nums[i] == nums[i-1]:
continue
l = i+1
r = len(nums) - 1
while l < r:
total = nums[i] + nums[l] + nums[r]
if total == 0:
res.append([nums[i], nums[l], nums[r]])
# while l < r and nums[l] == nums[l+1]: # l 去重
# l += 1
# while l < r and nums[r] == nums[r-1]: # r 去重
# r -= 1
l += 1
r -= 1
elif total < 0:
l += 1
else:
r -= 1
return res
if __name__ == '__main__':
nums = [-1, 0, 1, 2, -1, -4]
solution = Solution()
res = solution.threeSum(nums)
print(res)
3.9 四数之和 (**)
1. 刷题链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/4sum/description/

2. 思路
- 和三数之和类似, 不同之处是需要去重不同
- i 去重 if i > 0 and nums[i] == nums[i-1]:
- j 去重 j > i+1 and nums[j] == nums[j-1]:
3. AC代码
"""
题目: 18. 四数之和
链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/4sum/description/
思路:
和三数之和类似, 不同之处是需要去重不同
i 去重 if i > 0 and nums[i] == nums[i-1]:
j 去重 j > i+1 and nums[j] == nums[j-1]:
"""
class Solution(object):
def fourSum(self, nums, target):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:type target: int
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
nums.sort()
res = []
for i in range(len(nums)-3):
if i > 0 and nums[i] == nums[i-1]:
continue
for j in range(i+1, len(nums)-2):
if j > i+1 and nums[j] == nums[j-1]: # 注意这里是i+1而不是1
continue
l = j+1
r = len(nums) - 1
while l < r:
total = nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[l] + nums[r]
if total == target:
res.append([nums[i], nums[j], nums[l], nums[r]])
while l < r and nums[l] == nums[l+1]:
l += 1
while l < r and nums[r] == nums[r-1]:
r -= 1
l += 1
r -= 1
elif total < target:
l += 1
else:
r -= 1
return res
if __name__ == '__main__':
nums = [-2,-1,-1,1,1,2,2]
target = 0
solution = Solution()
res = solution.fourSum(nums, target)
print(res)
3.10 哈希表总结
详细总结: https://www.programmercarl.com/%E5%93%88%E5%B8%8C%E8%A1%A8%E6%80%BB%E7%BB%93.html