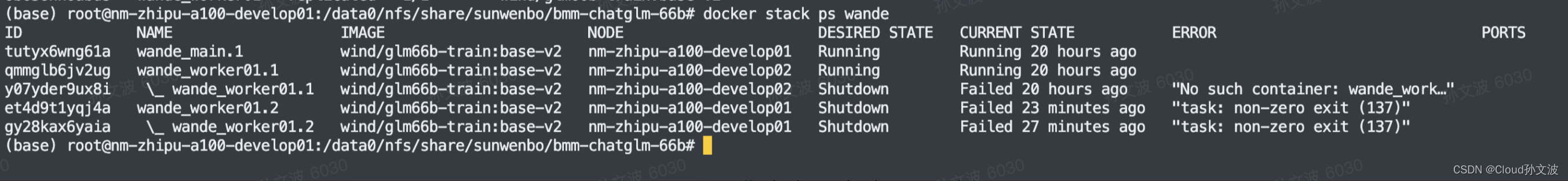
关于pthread_create()和pthread_join()
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
void *thread_func(void *arg) {
int *num = (int *)arg;
printf("Hello from thread! arg=%d\n", *num);
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
int main() {
pthread_t thread;
int arg = 10;
if (pthread_create(&thread, NULL, thread_func, &arg) != 0) {
printf("Failed to create thread\n");
return 1;
}
if (pthread_join(thread, NULL) != 0) {
printf("Failed to join thread\n");
return 1;
}
printf("Main thread ends\n");
return 0;
}
是否是在pthread_join后线程才会执行?
不是。在线程创建后,可以立即执行线程函数。但是如果在主线程中调用了pthread_join函数,主线程会等待被等待的线程执行完毕后再继续执行。所以在pthread_join函数之后,被等待的线程才会执行完毕。
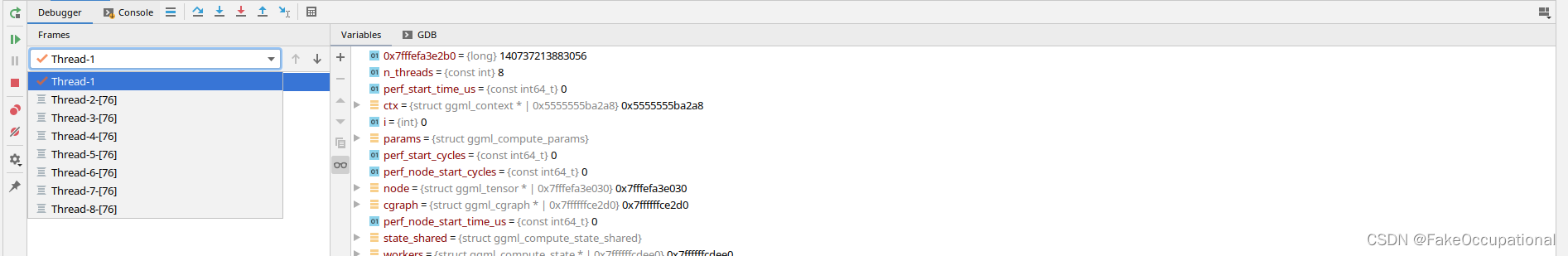
但是初始化的参数(比如以下片段中的node)是错误的,如何使得不计算出错呢?
workers[j] = (struct ggml_compute_state) {
.thrd = 0,
.params = {
.type = GGML_TASK_COMPUTE,
.ith = j + 1,
.nth = n_threads,
.wsize = cgraph->work ? ggml_nbytes(cgraph->work) : 0,
.wdata = cgraph->work ? cgraph->work->data : NULL,
},
.node = NULL,
.shared = &state_shared,
};
int rc = pthread_create(&workers[j].thrd, NULL, ggml_graph_compute_thread, &workers[j]);
自旋锁;自旋锁的旋指的是线程在获取锁时,如果发现锁已经被其他线程占用,会进入一个忙等待的状态,不断地检查锁是否被释放。这个过程称为旋转,因为线程会像旋转一样不断地尝试获取锁,直到成功为止。旋转是一种快速的等待方式,可以减少线程切换的开销,但也会消耗CPU资源。
项目使用自旋锁当参数被正确设置之后才会执行
thread_ret_t ggml_graph_compute_thread(void * data) {
//将data指针转换为ggml_compute_state类型的指针state。
struct ggml_compute_state * state = (struct ggml_compute_state *) data;
const int n_threads = state->shared->n_threads;
while (true) {
// 如果当前线程是最后一个准备好的线程
if (atomic_fetch_add(&state->shared->n_ready, 1) == n_threads - 1) {
atomic_store(&state->shared->has_work, false);//则将 has_work 设置为 false
} else {
// 如果 has_work 为 true,则等待直到 has_work 变为 false
while (atomic_load(&state->shared->has_work)) {
// 如果 stop 为 true,则返回 0
if (atomic_load(&state->shared->stop)) {
return 0;
}
ggml_lock_lock (&state->shared->spin);
ggml_lock_unlock(&state->shared->spin);
}
}
atomic_fetch_sub(&state->shared->n_ready, 1);
// 等待有工作要做
while (!atomic_load(&state->shared->has_work)) {
// 如果 stop 为 true,则返回 0
if (atomic_load(&state->shared->stop)) {
return 0;
}
ggml_lock_lock (&state->shared->spin);
ggml_lock_unlock(&state->shared->spin);
}
// 检查是否应该停止
if (atomic_load(&state->shared->stop)) {
break;
}
// 执行计算并将 state->node 设置为 NULL
if (state->node) {
ggml_compute_forward(&state->params, state->node);
state->node = NULL;
} else {
break;
}
}
return 0;
}
在非阶段 GGML_TASK_INIT , GGML_TASK_FINALIZE执行运算
void ggml_compute_forward_add_f32(
const struct ggml_compute_params * params,
const struct ggml_tensor * src0,
const struct ggml_tensor * src1,
struct ggml_tensor * dst) {
GGML_ASSERT(ggml_are_same_shape(src0, src1) && ggml_are_same_shape(src0, dst));
if (params->type == GGML_TASK_INIT || params->type == GGML_TASK_FINALIZE) {
return;
}
const int ith = params->ith;
const int nth = params->nth;
const int n = ggml_nrows(src0);
const int nc = src0->ne[0];
const size_t nb00 = src0->nb[0];
const size_t nb01 = src0->nb[1];
const size_t nb10 = src1->nb[0];
const size_t nb11 = src1->nb[1];
const size_t nb0 = dst->nb[0];
const size_t nb1 = dst->nb[1];
GGML_ASSERT( nb0 == sizeof(float));
GGML_ASSERT(nb00 == sizeof(float));
if (nb10 == sizeof(float)) {
const int j0 = (n/nth)*ith;
const int j1 = ith == nth - 1 ? n : (n/nth)*(ith + 1);
for (int j = j0; j < j1; j++) {
ggml_vec_add_f32(nc,
(float *) ((char *) dst->data + j*nb1),
(float *) ((char *) src0->data + j*nb01),
(float *) ((char *) src1->data + j*nb11));
}
} else {
// src1 is not contiguous
for (int j = ith; j < n; j += nth) {
float * dst_ptr = (float *) ((char *) dst->data + j*nb1);
float * src0_ptr = (float *) ((char *) src0->data + j*nb01);
for (int i = 0; i < nc; i++) {
float * src1_ptr = (float *) ((char *) src1->data + j*nb11 + i*nb10);
dst_ptr[i] = src0_ptr[i] + *src1_ptr;
}
}
}
}




![10万字智慧政务大数据平台项目建设方案222页[Word]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/2dc2c6ade877991a5dc7888403cfbc68.jpeg)