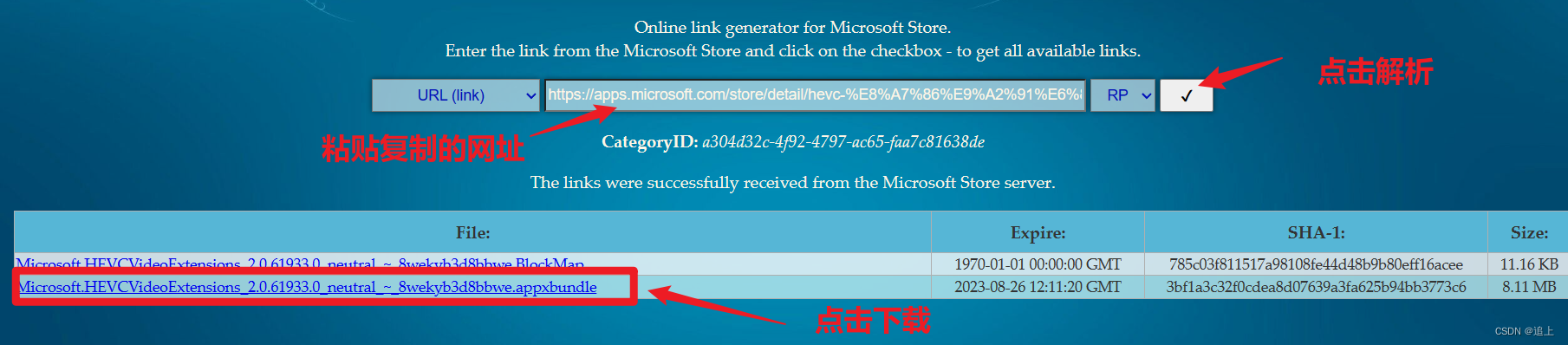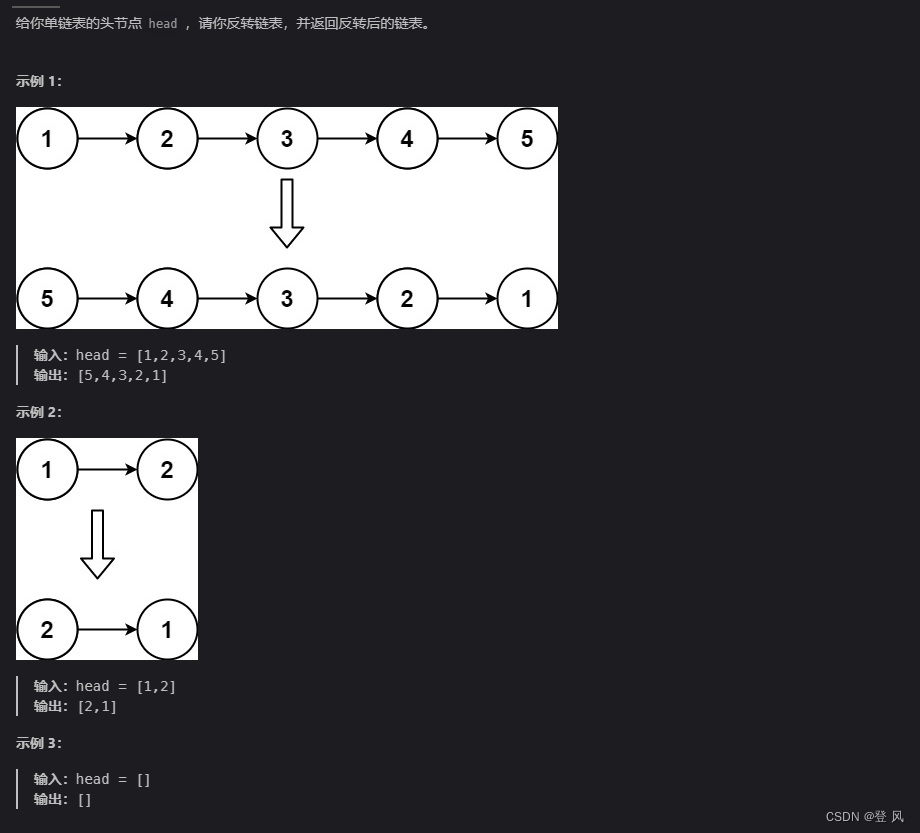
**
**
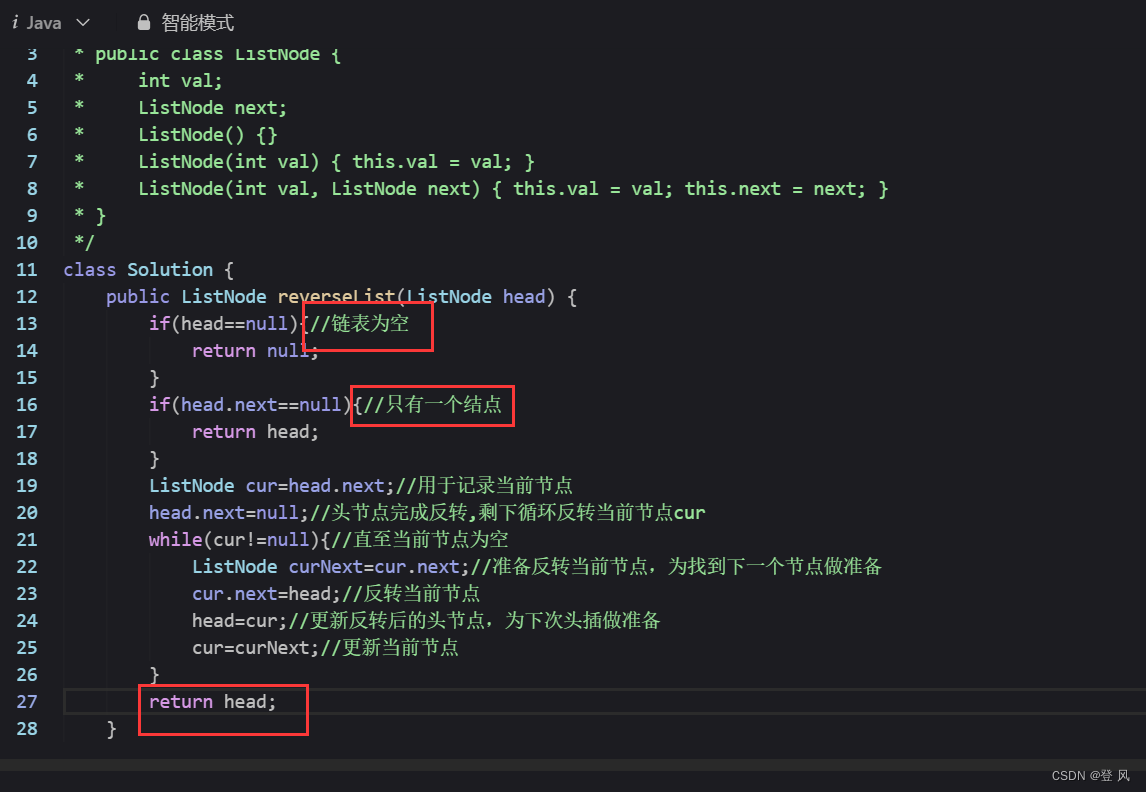
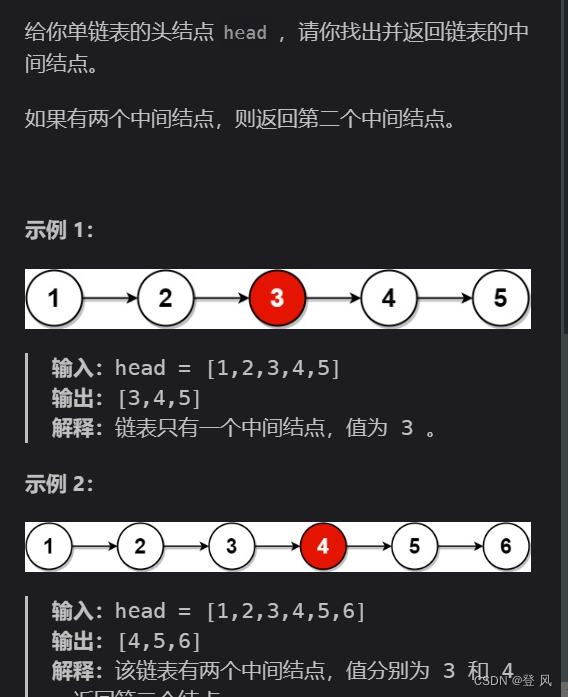
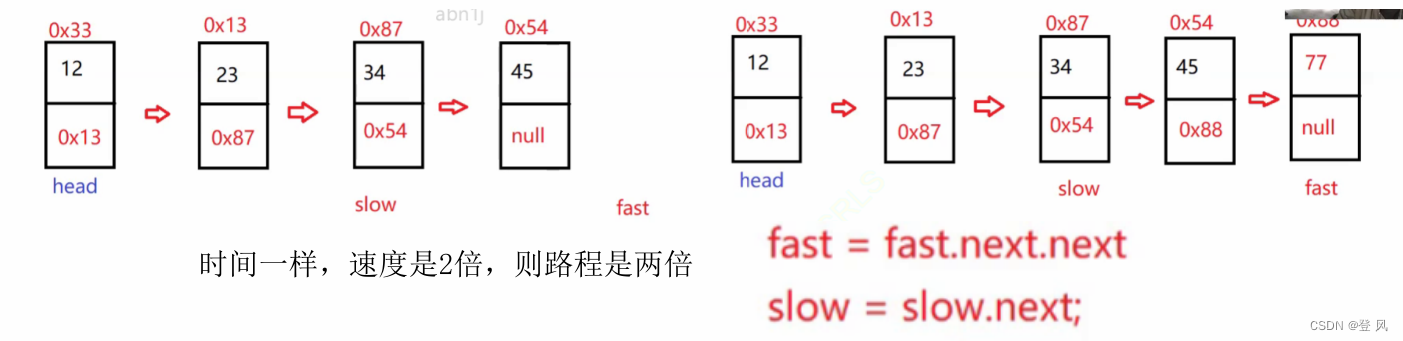
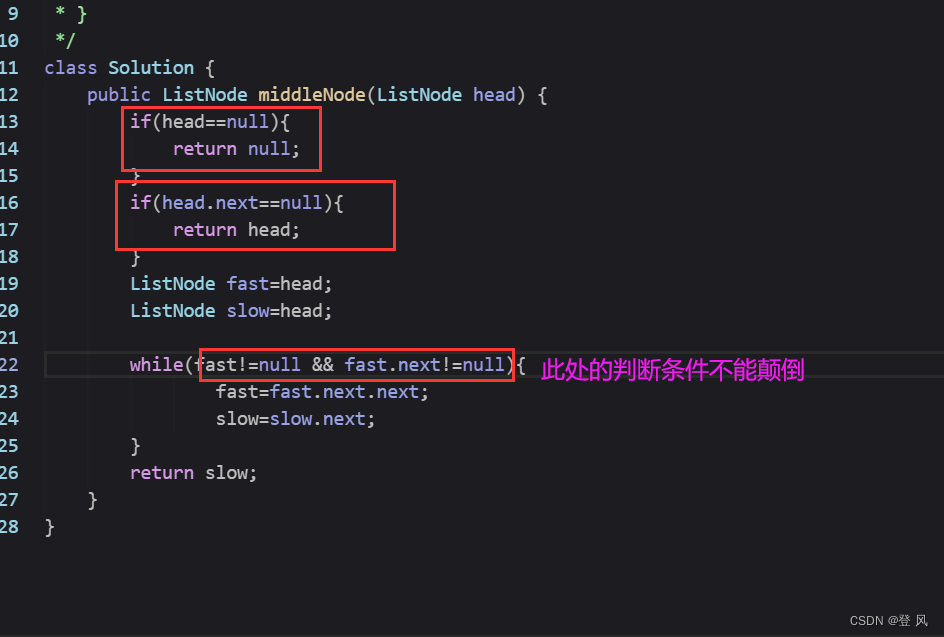
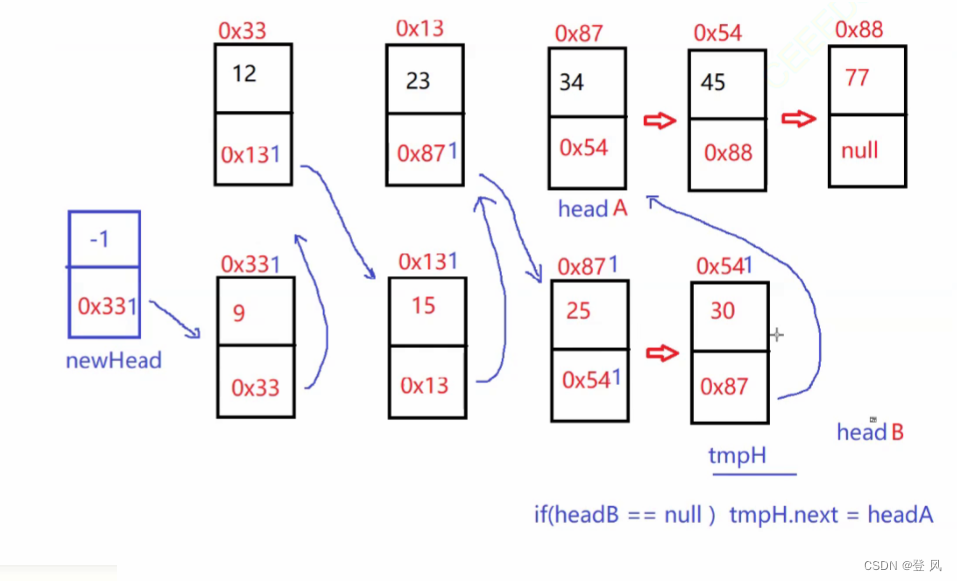
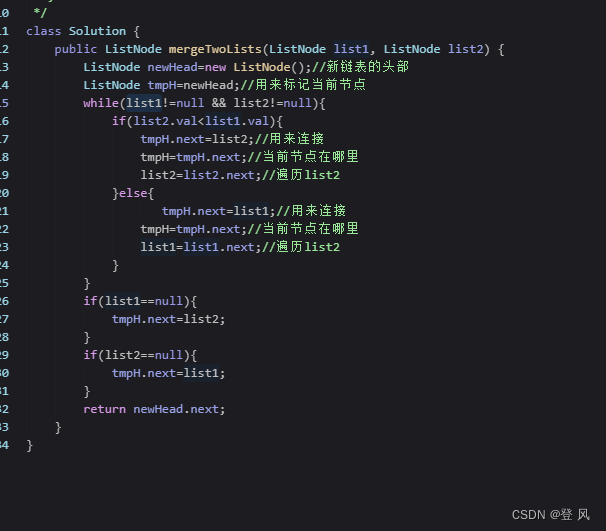
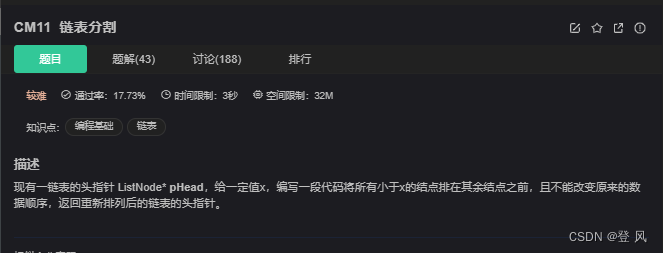
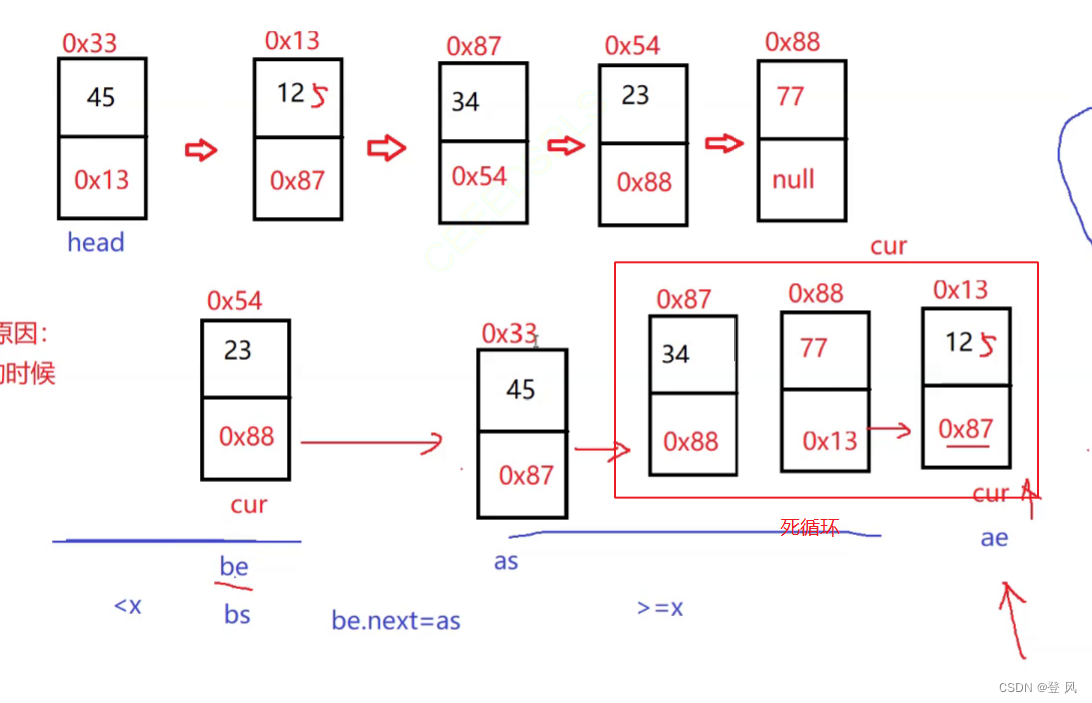
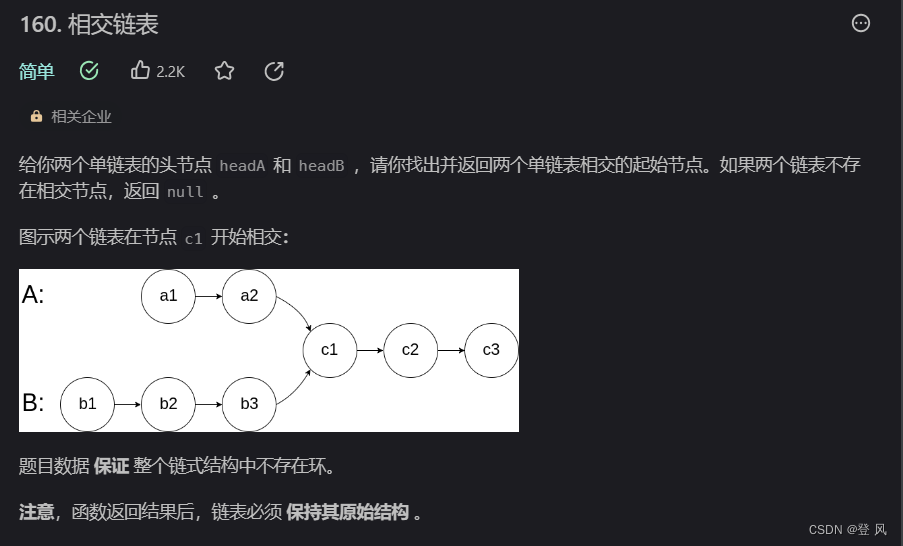

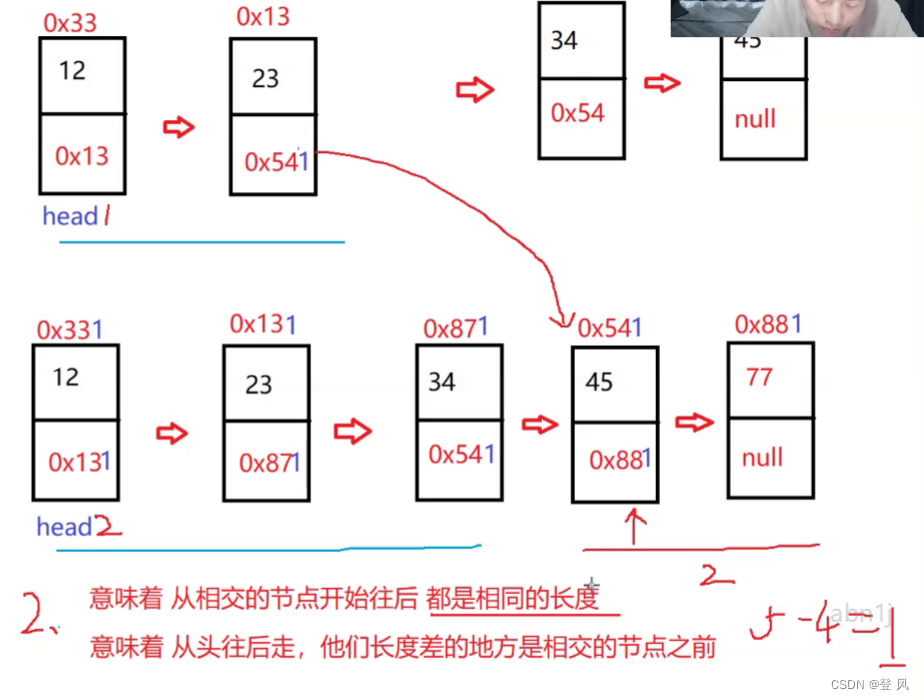
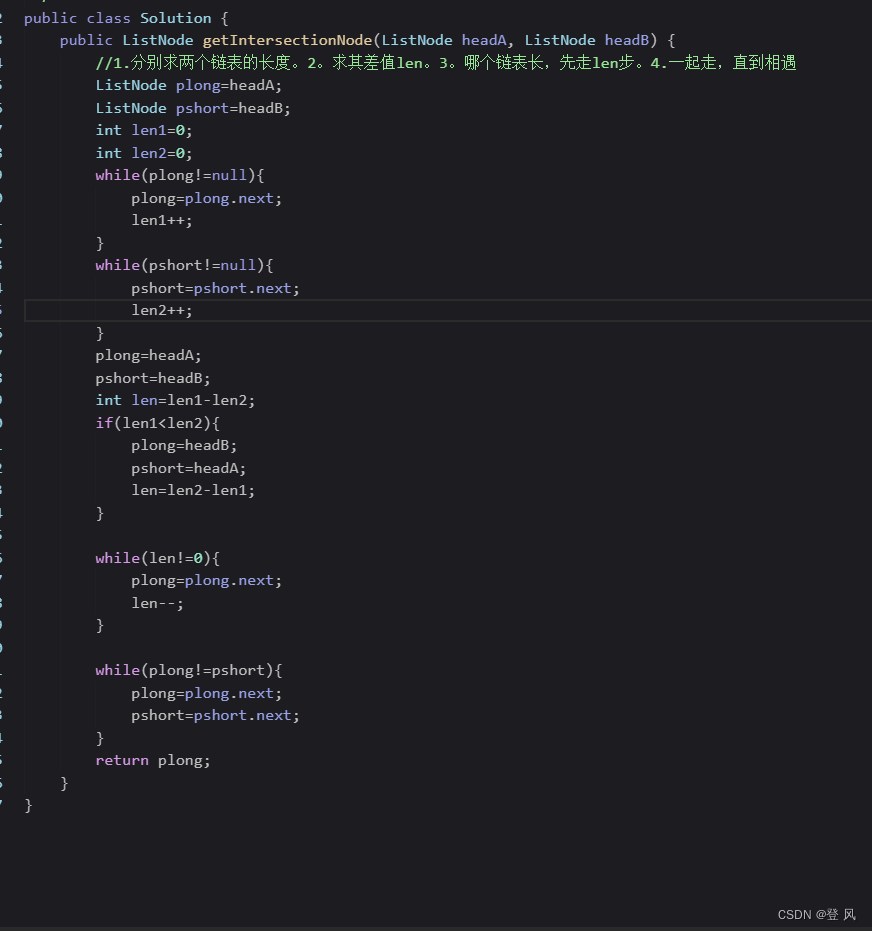

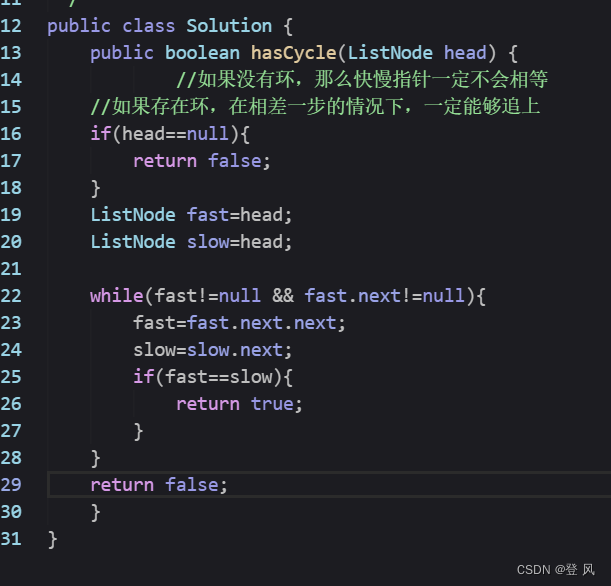

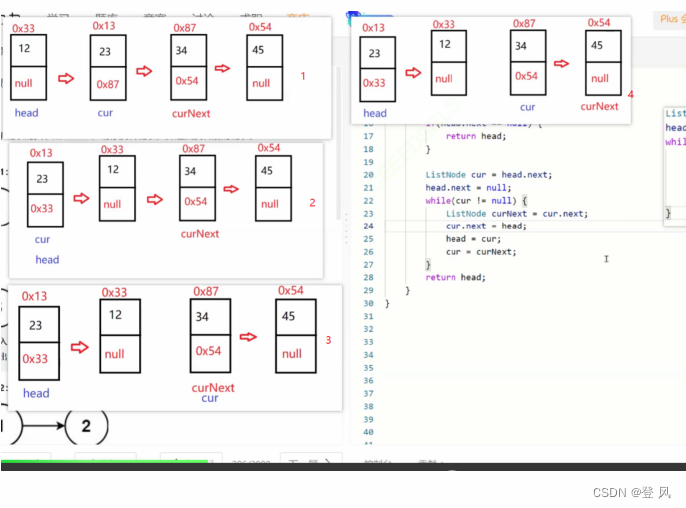
结论
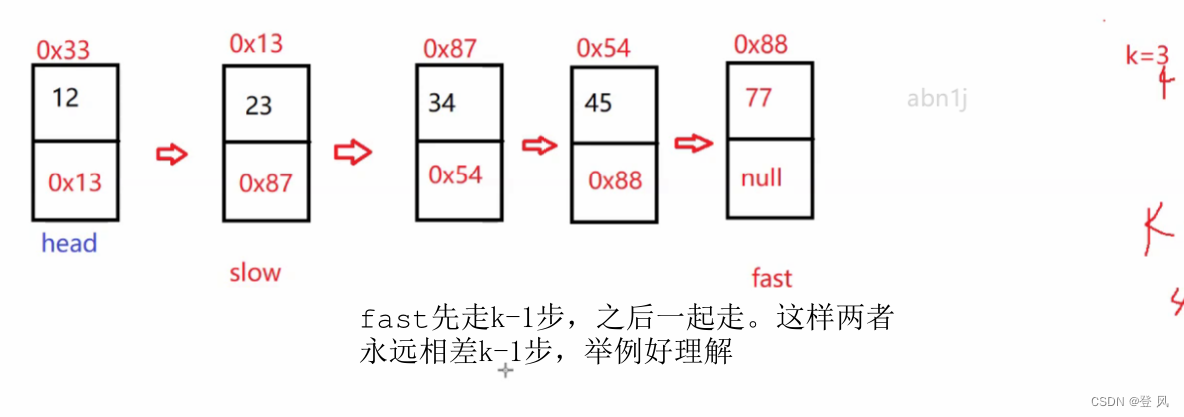
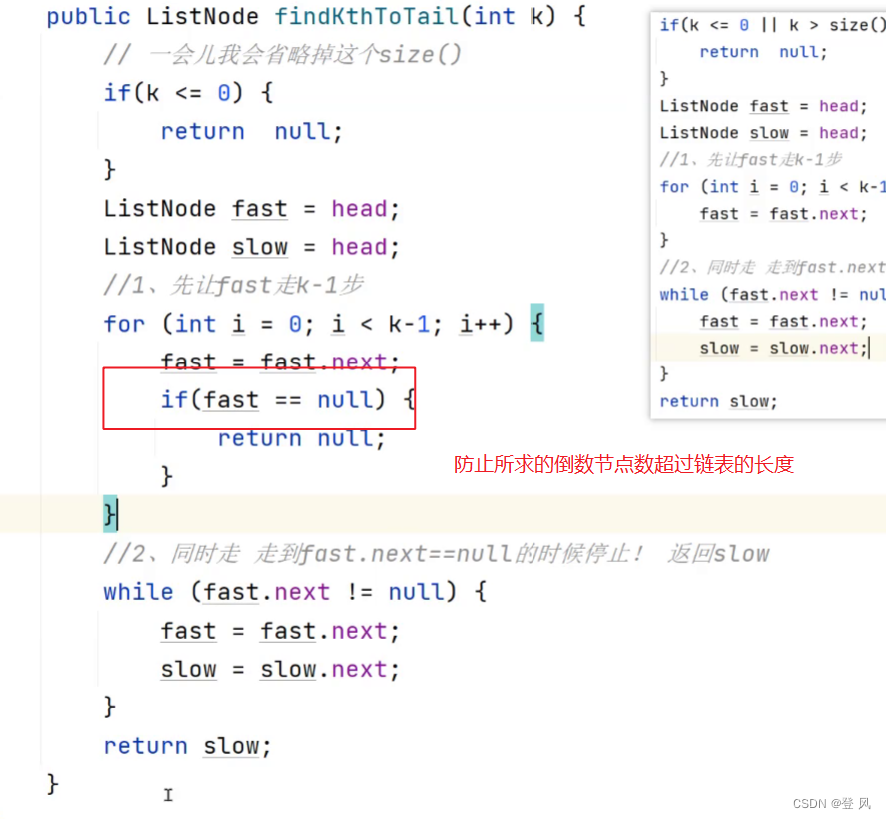
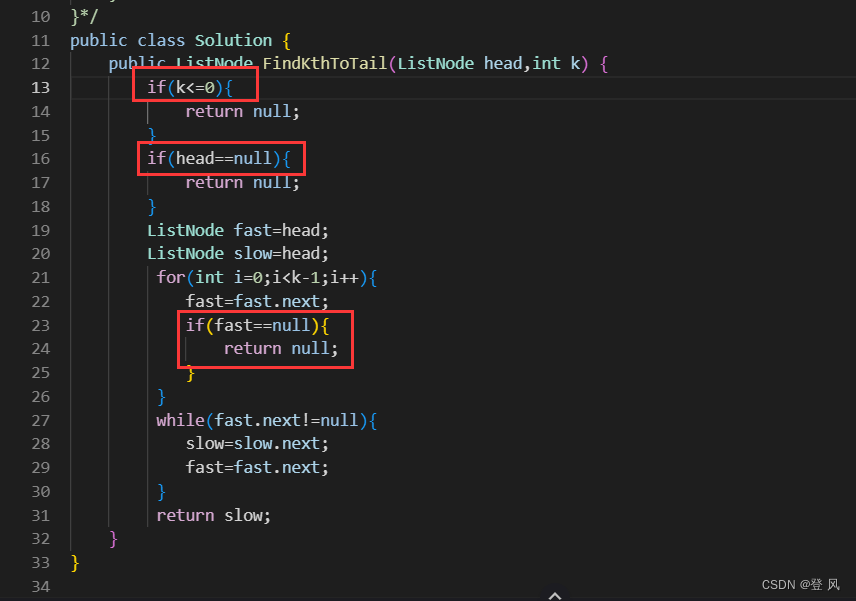
让一个指针从链表起始位置开始遍历链表,同时让一个指针从判环时相遇点的位置开始绕环运行,两个指针都是每次均走一步,最终肯定会在入口点的位置相遇。
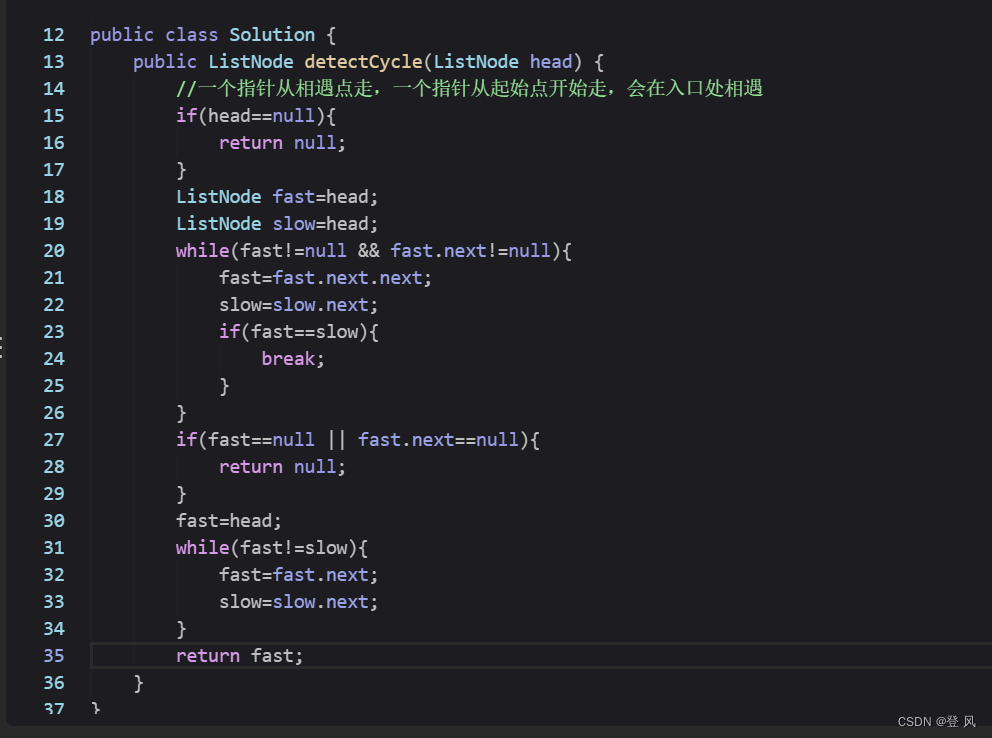
LinkedList的模拟实现
单个节点的实现
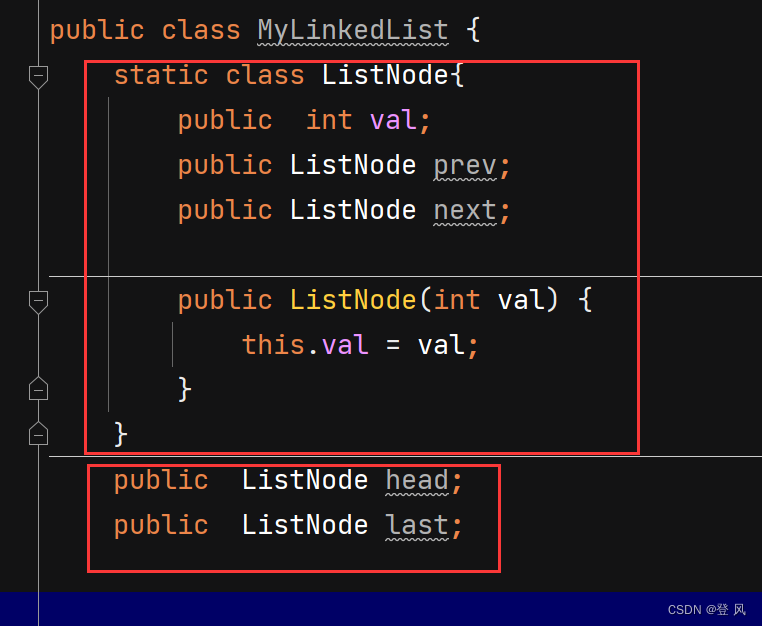
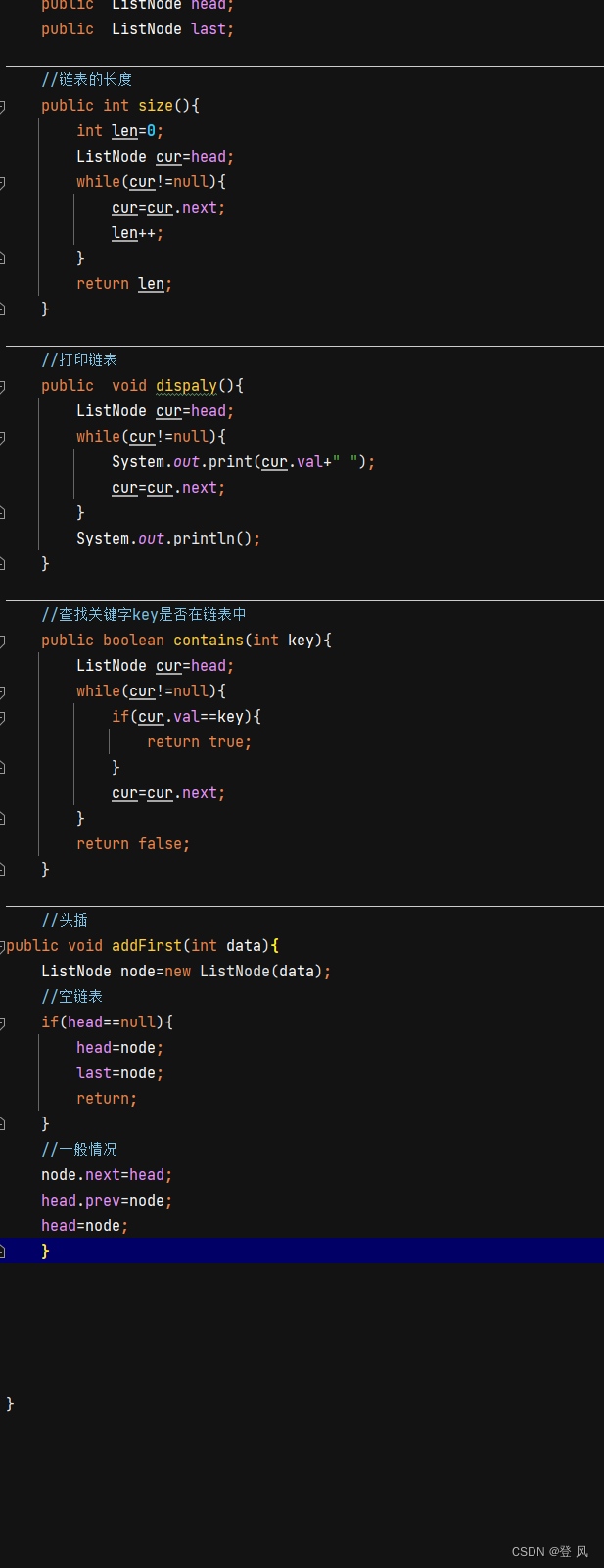
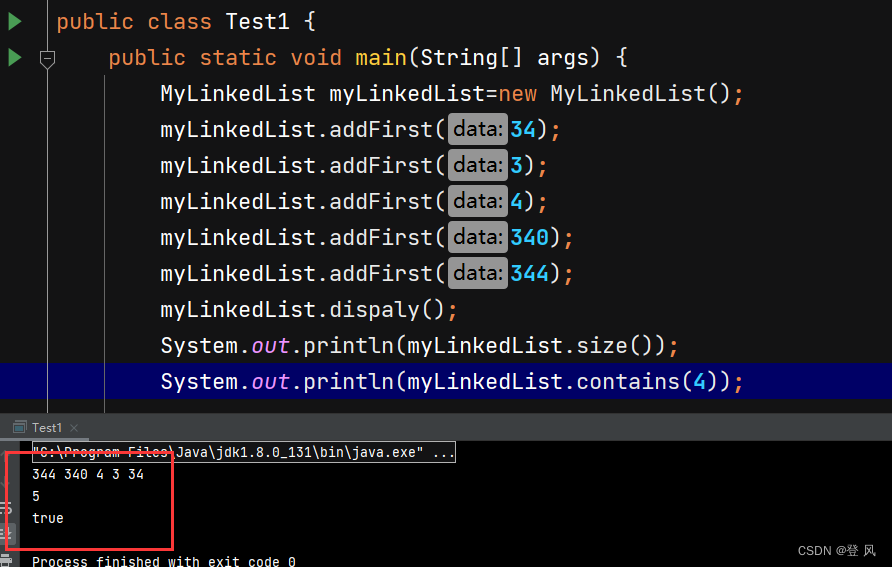
尾插
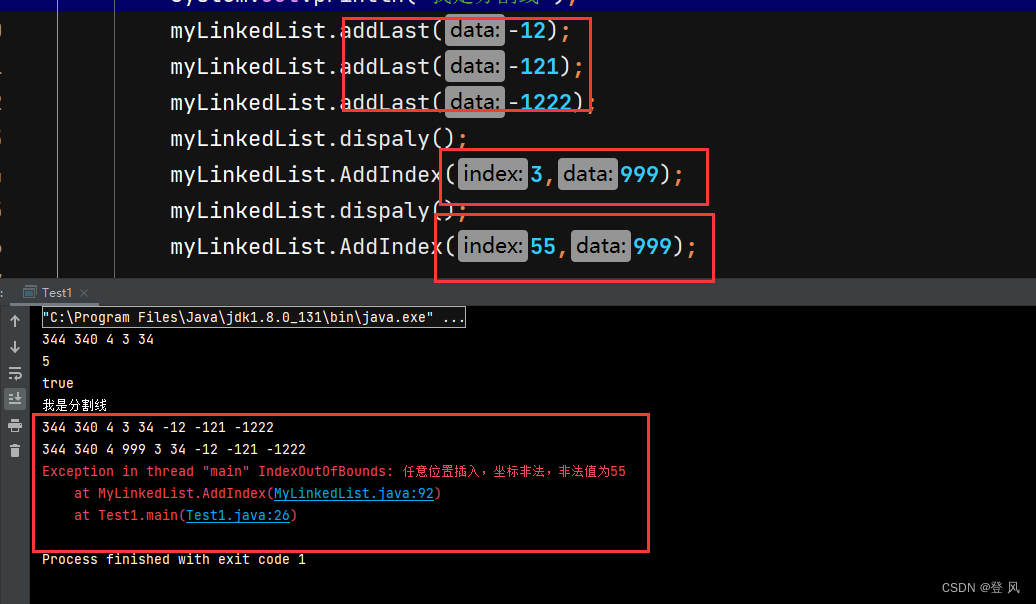
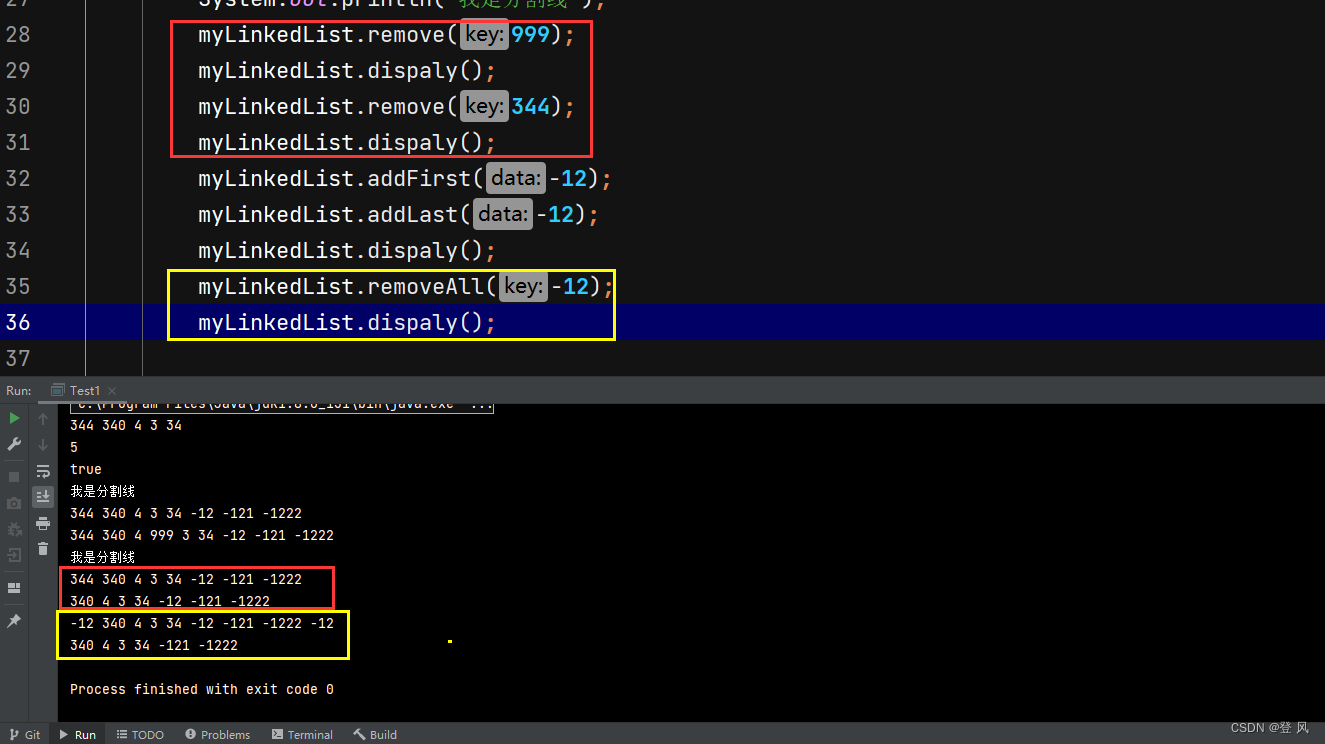
运行结果如下:
也可以暴力使用
全部代码
MyLinkedList
public class MyLinkedList {
static class ListNode{
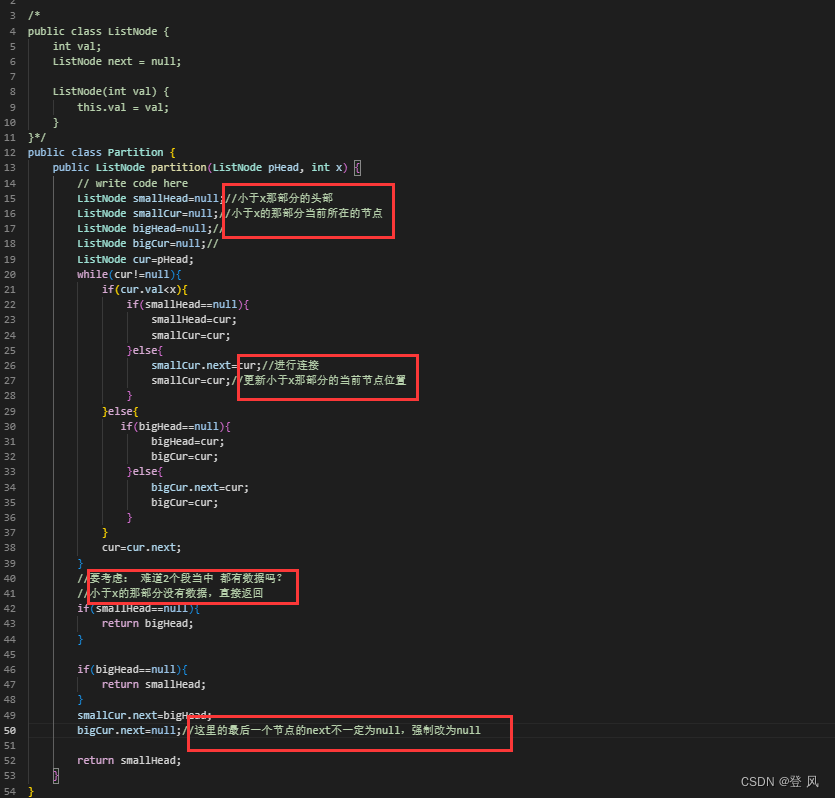
public int val;
public ListNode prev;
public ListNode next;
public ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
public ListNode head;
public ListNode last;
//链表的长度
public int size(){
int len=0;
ListNode cur=head;
while(cur!=null){
cur=cur.next;
len++;
}
return len;
}
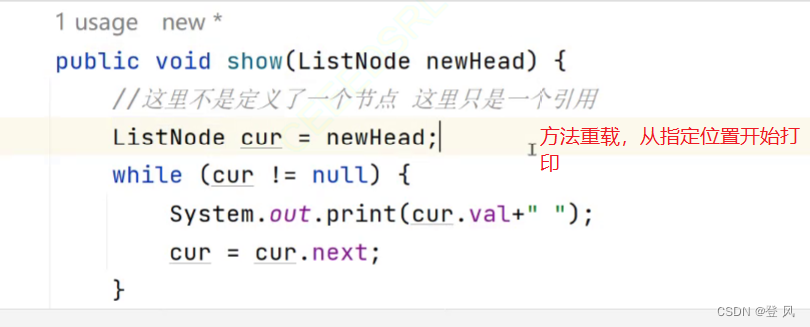
//打印链表
public void dispaly(){
ListNode cur=head;
while(cur!=null){
System.out.print(cur.val+" ");
cur=cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
//查找关键字key是否在链表中
public boolean contains(int key){
ListNode cur=head;
while(cur!=null){
if(cur.val==key){
return true;
}
cur=cur.next;
}
return false;
}
//头插
public void addFirst(int data){
ListNode node=new ListNode(data);
//空链表
if(head==null){
head=node;
last=node;
return;
}
//一般情况
node.next=head;
head.prev=node;
head=node;
}
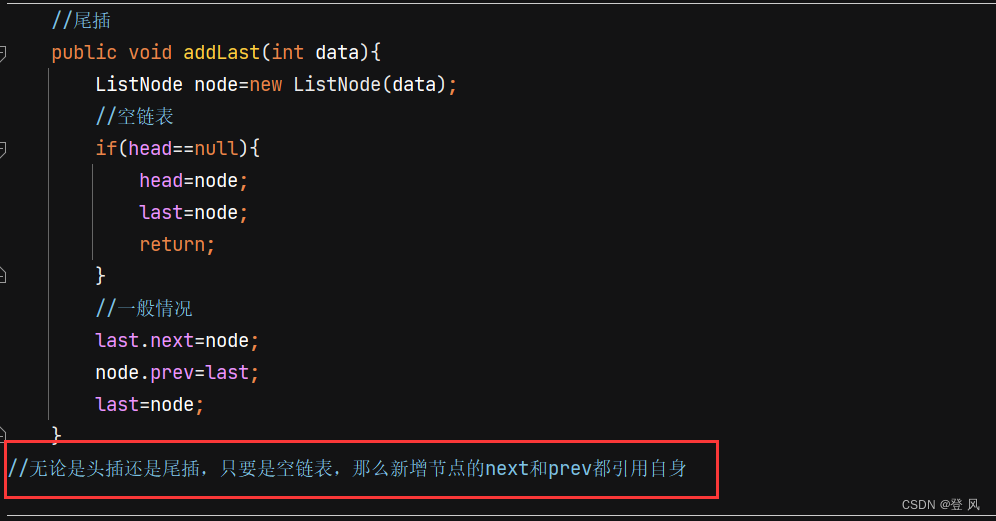
//尾插
public void addLast(int data){
ListNode node=new ListNode(data);
//空链表
if(head==null){
head=node;
last=node;
return;
}
//一般情况
last.next=node;
node.prev=last;
last=node;
}
//无论是头插还是尾插,只要是空链表,那么新增节点的next和prev都引用自身
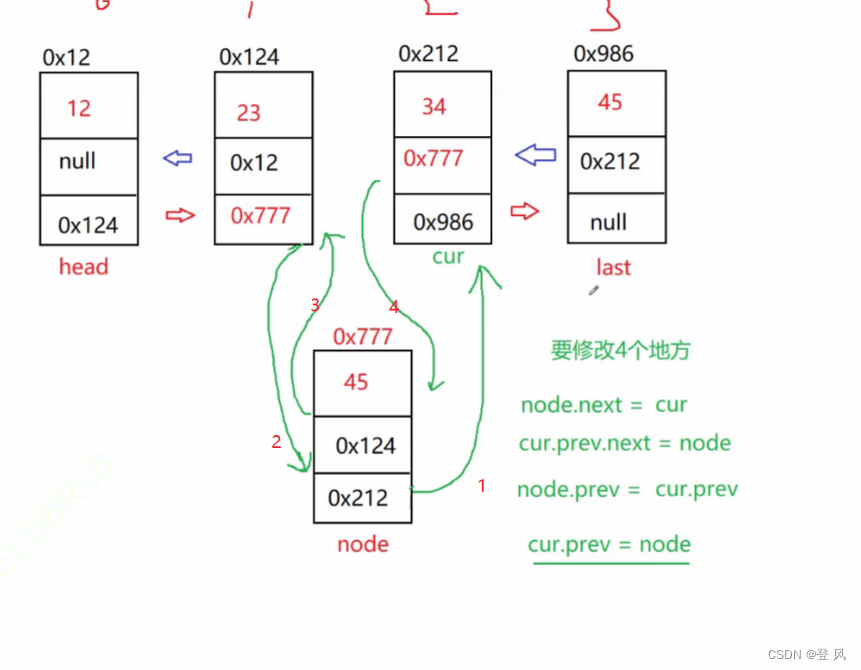
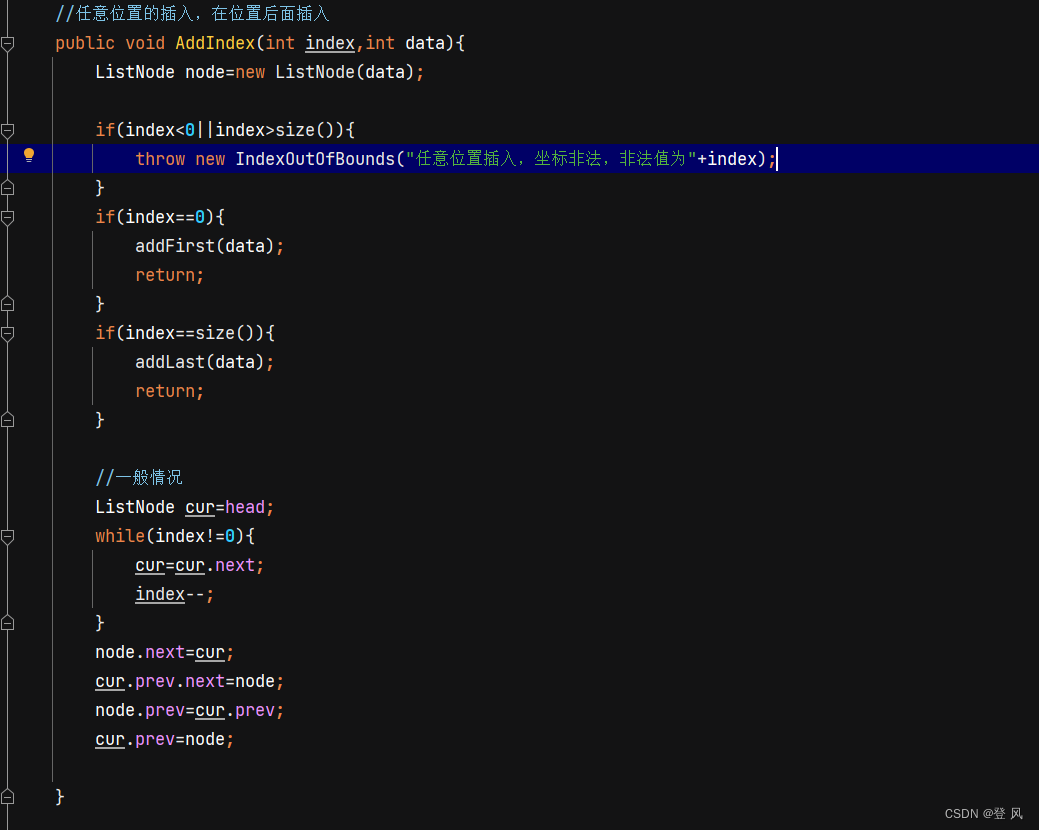
//任意位置的插入,在位置后面插入
public void AddIndex(int index,int data){
ListNode node=new ListNode(data);
if(index<0||index>size()){
throw new IndexOutOfBounds("任意位置插入,坐标非法,非法值为"+index);
}
if(index==0){
addFirst(data);
return;
}
if(index==size()){
addLast(data);
return;
}
//一般情况
ListNode cur=head;
while(index!=0){
cur=cur.next;
index--;
}
node.next=cur;
cur.prev.next=node;
node.prev=cur.prev;
cur.prev=node;
}
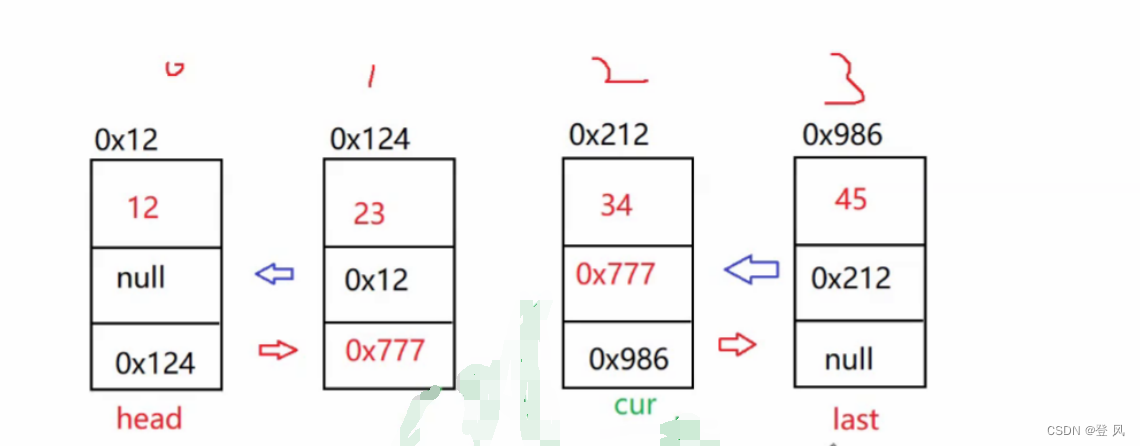
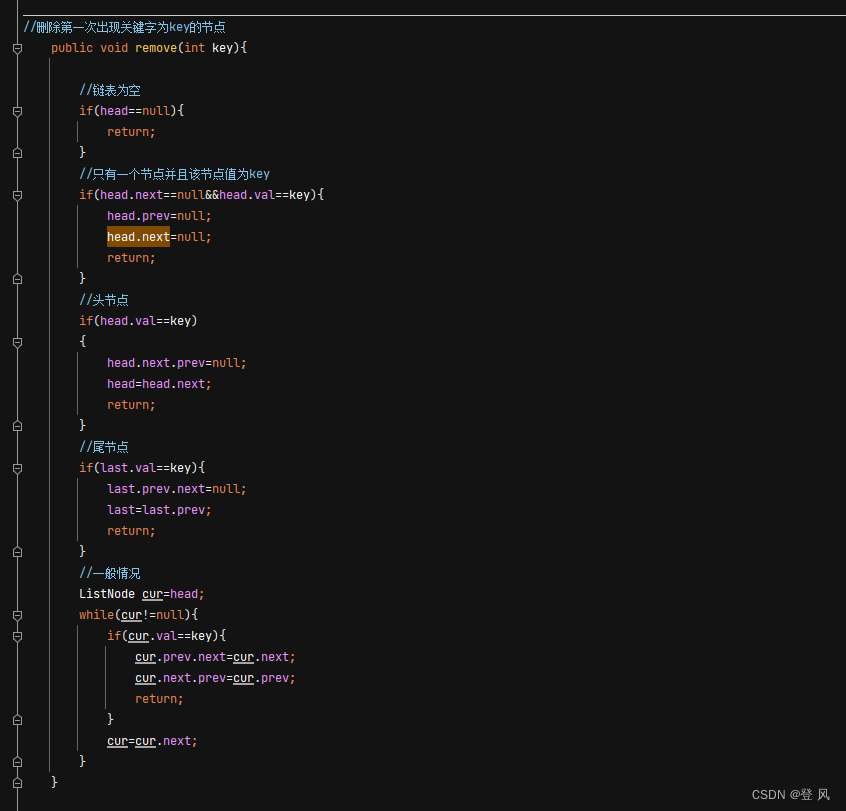
//删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点
public void remove(int key){
//链表为空
if(head==null){
return;
}
//只有一个节点并且该节点值为key
if(head.next==null&&head.val==key){
head.prev=null;
head.next=null;
return;
}
//头节点
if(head.val==key)
{
head.next.prev=null;
head=head.next;
return;
}
//尾节点
if(last.val==key){
last.prev.next=null;
last=last.prev;
return;
}
//一般情况
ListNode cur=head;
while(cur!=null){
if(cur.val==key){
cur.prev.next=cur.next;
cur.next.prev=cur.prev;
return;
}
cur=cur.next;
}
}
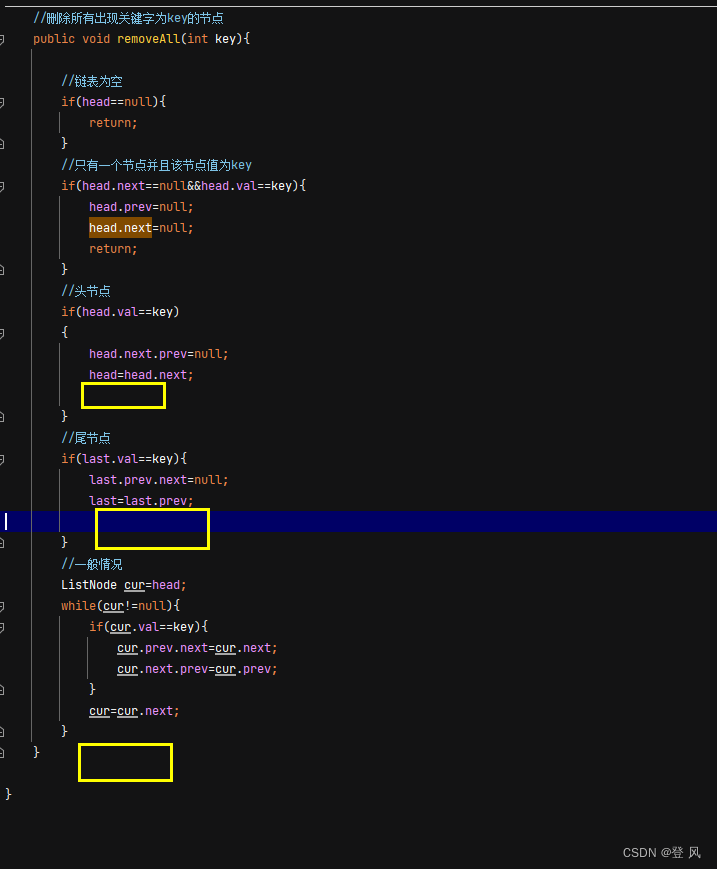
//删除所有出现关键字为key的节点
public void removeAll(int key){
//链表为空
if(head==null){
return;
}
//只有一个节点并且该节点值为key
if(head.next==null&&head.val==key){
head.prev=null;
head.next=null;
return;
}
//头节点
if(head.val==key)
{
head.next.prev=null;
head=head.next;
}
//尾节点
if(last.val==key){
last.prev.next=null;
last=last.prev;
}
//一般情况
ListNode cur=head;
while(cur!=null){
if(cur.val==key){
cur.prev.next=cur.next;
cur.next.prev=cur.prev;
}
cur=cur.next;
}
}
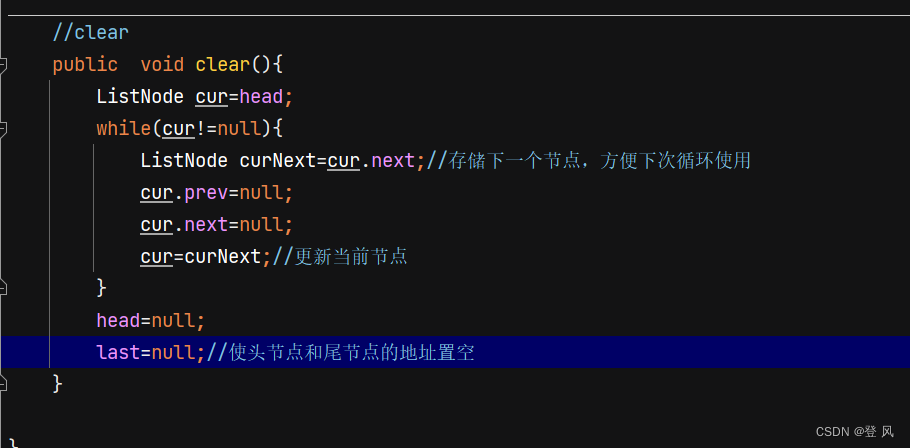
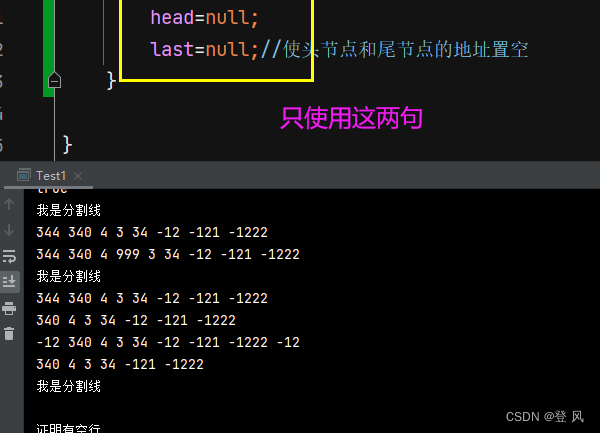
//clear
public void clear(){
/* ListNode cur=head;
while(cur!=null){
ListNode curNext=cur.next;//存储下一个节点,方便下次循环使用
cur.prev=null;
cur.next=null;
cur=curNext;//更新当前节点
}*/
head=null;
last=null;//使头节点和尾节点的地址置空
}
}
IndexOutOfBounds
public class IndexOutOfBounds extends RuntimeException{
public IndexOutOfBounds() {
}
public IndexOutOfBounds(String message) {
super(message);
}
}
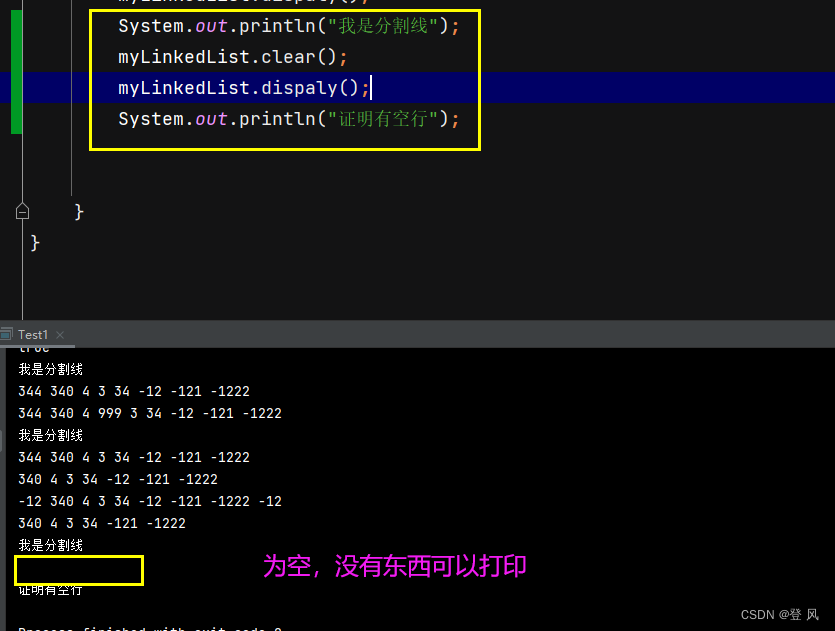
Test1
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyLinkedList myLinkedList=new MyLinkedList();
myLinkedList.addFirst(34);
myLinkedList.addFirst(3);
myLinkedList.addFirst(4);
myLinkedList.addFirst(340);
myLinkedList.addFirst(344);
myLinkedList.dispaly();
System.out.println(myLinkedList.size());
System.out.println(myLinkedList.contains(4));
System.out.println("我是分割线");
myLinkedList.addLast(-12);
myLinkedList.addLast(-121);
myLinkedList.addLast(-1222);
myLinkedList.dispaly();
myLinkedList.AddIndex(3,999);
myLinkedList.dispaly();
// myLinkedList.AddIndex(55,999);
System.out.println("我是分割线");
myLinkedList.remove(999);
myLinkedList.dispaly();
myLinkedList.remove(344);
myLinkedList.dispaly();
myLinkedList.addFirst(-12);
myLinkedList.addLast(-12);
myLinkedList.dispaly();
myLinkedList.removeAll(-12);
myLinkedList.dispaly();
System.out.println("我是分割线");
myLinkedList.clear();
myLinkedList.dispaly();
System.out.println("证明有空行");
}
}
什么是LinkedList
LinkedList的底层是双向链表结构(链表后面介绍),由于链表没有将元素存储在连续的空间中,元素存储在单独的节点中,然后通过引用将节点连接起来了,因此在在任意位置插入或者删除元素时,不需要搬移元素,效率比较高。
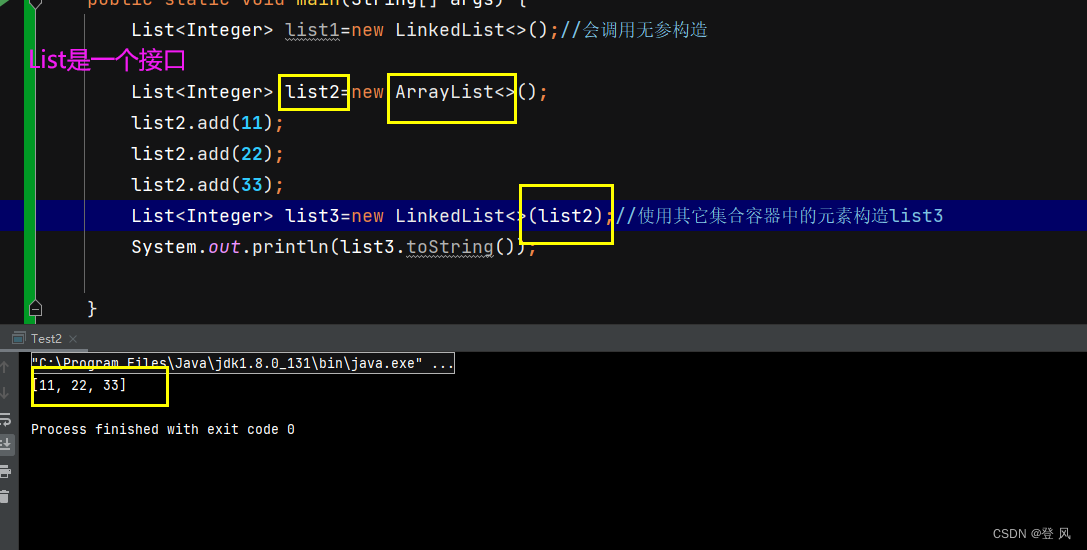
LinkedList的使用
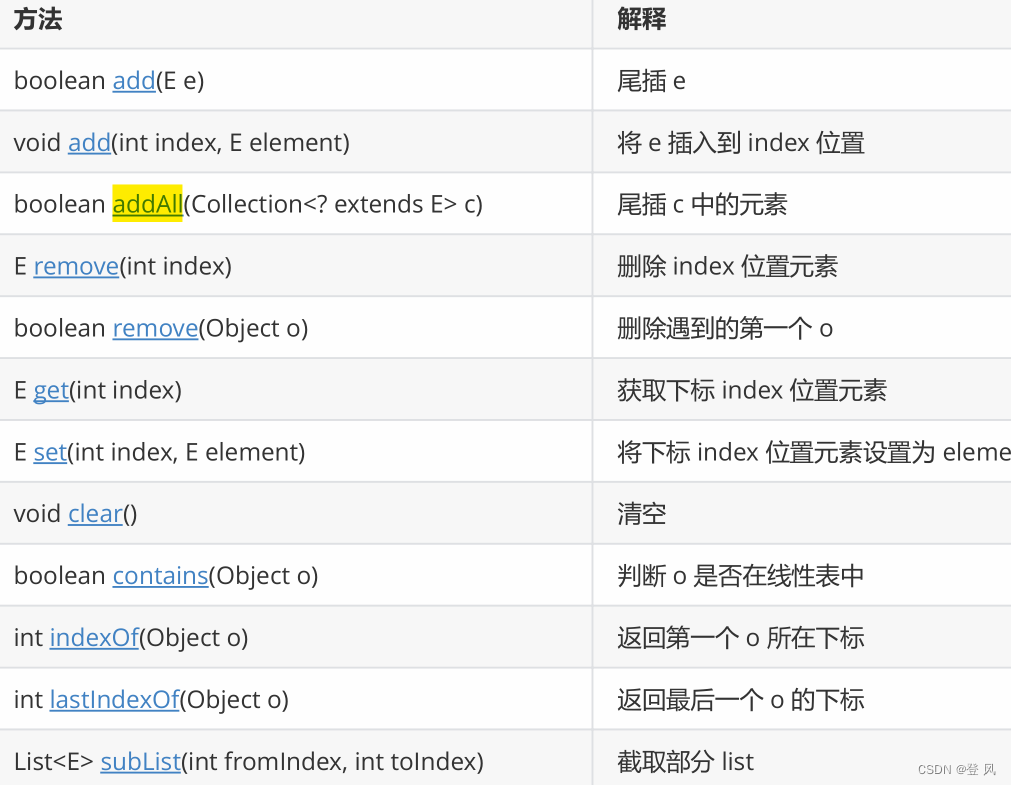
LinkedList的其他常用方法
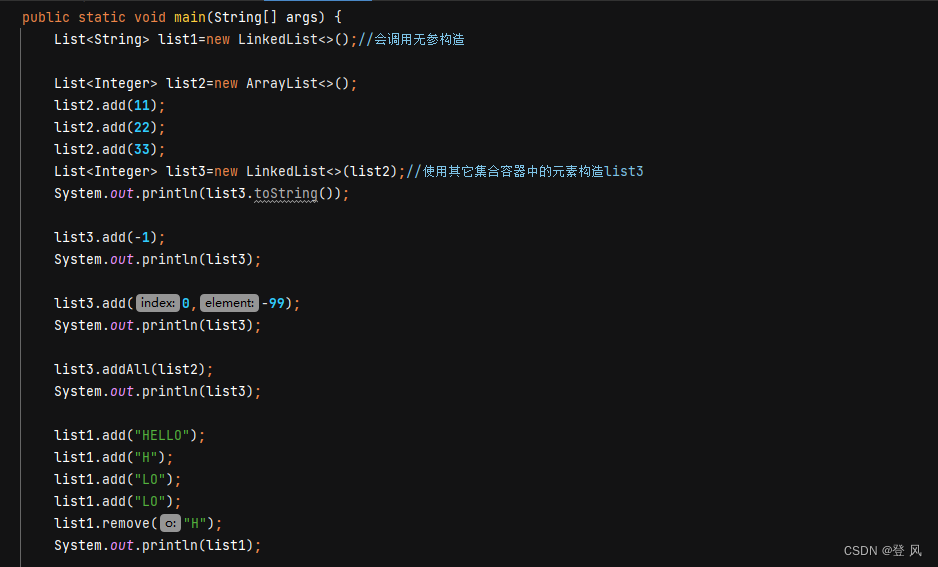
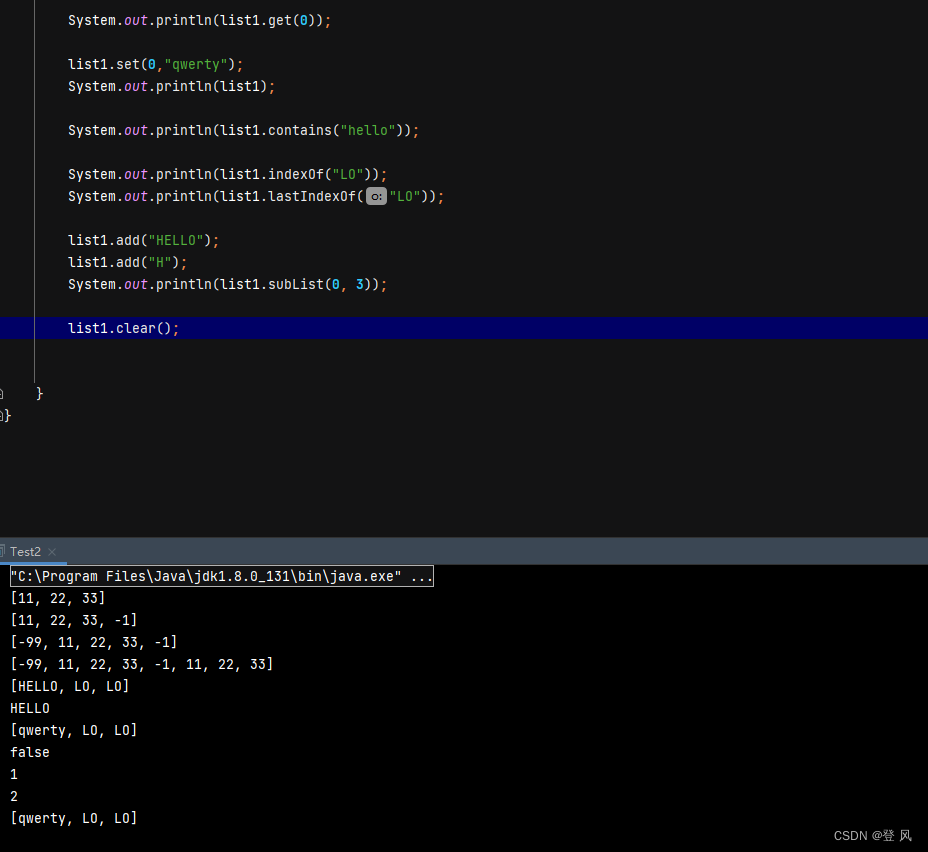
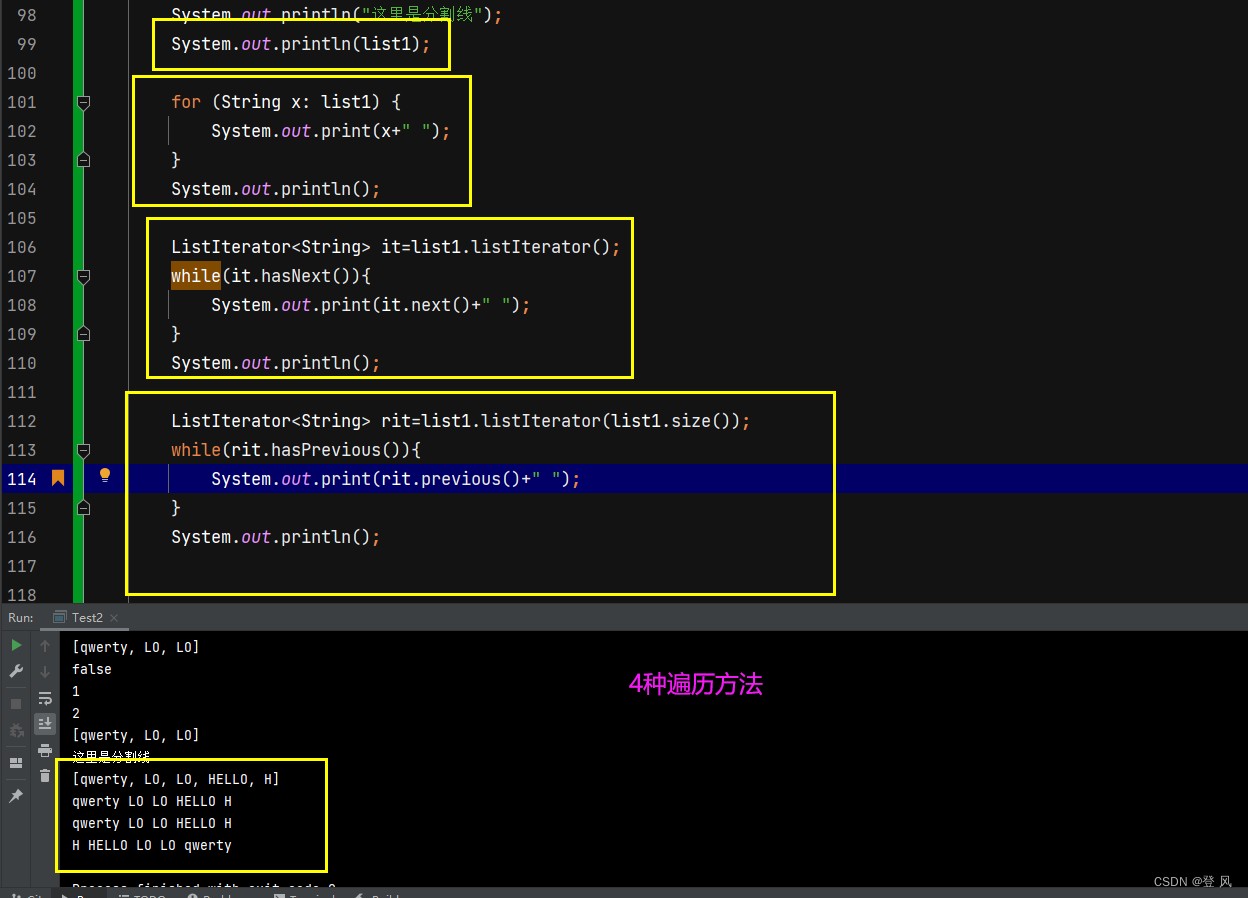
LinkedList的遍历
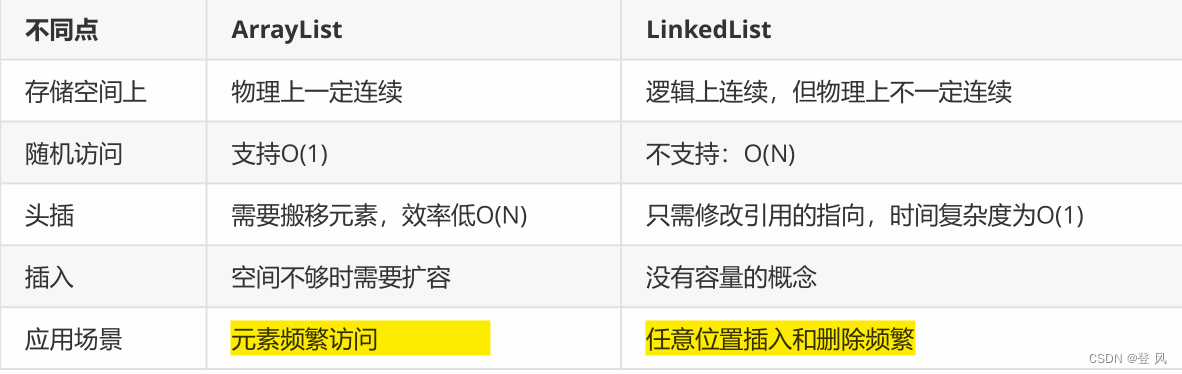
ArrayList和LinkedList的区别

![[Open-source tool] 可搭配PHP和SQL的表單開源工具_Form tools(1):簡介和建置](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/6c0dc324998d48569a9eb692f8576296.png)