1. 前言
缓存穿透大家都知道,这里简单过一下
缓存和数据库中都没有的数据,而用户不断发起请求。比如查询id = -1 的值
想着很多面向C端的查询接口,可能都需要做一下缓存操作,这里简单写了个自定义注解,将查询结果(包含null值)做个缓存
这个只能预防单秒内接口高频次请求,要是一直搞随机值请求这个只能采取其他手段处理了(比如IP拉黑什么的…)
工具类留底,以后兴许可以直接抄~( ̄▽ ̄)"
2. 正文
直接上代码了
2.1 自定义注解
CacheResult
import java.lang.annotation.*;
/**
* <pre>
* 接口缓存
* 根据接口的第一个入参对象,和返回值进行缓存
* 缓存的前缀为 TEMPORARY_CACHE:类名:方法名:key值
* 示例:@CacheResult(key="userId + '_' + ecommerceId", seconds = 2L)
* 缓存的key:TEMPORARY_CACHE:EcommerceController:getOrderList:407622341504839680_527203683850731520
* </pre>
* @author weiheng
* @date 2023-08-25
**/
@Documented
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ElementType.TYPE,ElementType.METHOD})
public @interface CacheResult {
/** 入参支持 SpEL表达式 做参数提取,比如入参对象有属性userId和ecommerceId -> key="userId + '_' + ecommerceId" */
String key();
/** 缓存时长,单位:秒 */
long seconds();
}
2.2 统一做缓存处理的切面
CacheAspect
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.redisson.api.RBucket;
import org.springframework.expression.EvaluationContext;
import org.springframework.expression.Expression;
import org.springframework.expression.ExpressionParser;
import org.springframework.expression.spel.standard.SpelExpressionParser;
import org.springframework.expression.spel.support.StandardEvaluationContext;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
/**
* 缓存统一处理
* @author weiheng
* @date 2023-08-25
**/
@Slf4j
@Aspect
@Component
public class CacheAspect {
/** 临时缓存的统一前缀 */
public static final String DEFAULT_PREFIX = "TEMPORARY_CACHE:";
/** 缓存分隔符 */
public static final String DELIMITER = ":";
@Resource
private RedissonHelper redissonHelper;
/**
* 拦截通知
*
* @param proceedingJoinPoint 入参
* @return Object
*/
@Around("@annotation(cacheSeconds)")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint, CacheResult cacheSeconds) {
Object[] args = proceedingJoinPoint.getArgs();
if (args.length == 0) {
// 方法没有入参,不做缓存
return proceed(proceedingJoinPoint);
}
// 1. 判断缓存中是否存在,有则直接返回
Object firstArg = args[0];
// 获取用户指定的参数
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
EvaluationContext context = new StandardEvaluationContext(firstArg);
Expression keyExpression = parser.parseExpression(cacheSeconds.key());
String businessKey = keyExpression.getValue(context, String.class);
// 拼装缓存key
String className = proceedingJoinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getSimpleName();
String methodName = proceedingJoinPoint.getSignature().getName();
String prefix = className + DELIMITER + methodName;
String cacheKey = DEFAULT_PREFIX + prefix + DELIMITER + businessKey;
RBucket<?> bucket = redissonHelper.getBucket(cacheKey);
boolean exists = bucket.isExists();
if (exists) {
// 缓存中有值,直接返回
return bucket.get();
}
// 2. 执行方法体
Object returnValue = proceed(proceedingJoinPoint);
// 3. 做个N秒的缓存
long seconds = cacheSeconds.seconds();
redissonHelper.setValueAndSeconds(cacheKey, returnValue, seconds);
return returnValue;
}
private Object proceed(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) {
Object returnValue;
try {
returnValue = proceedingJoinPoint.proceed();
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.error("error msg:", e);
if (e instanceof SystemException) {
throw (SystemException) e;
}
throw new SystemException(e.getMessage());
}
return returnValue;
}
3. 使用示例
原本定义个2秒就OK了,这里为了方便看测试结果,给了60秒
@CacheResult(key=“userId + ‘_’ + ecommerceId”, seconds = 60L)
redis缓存如下:
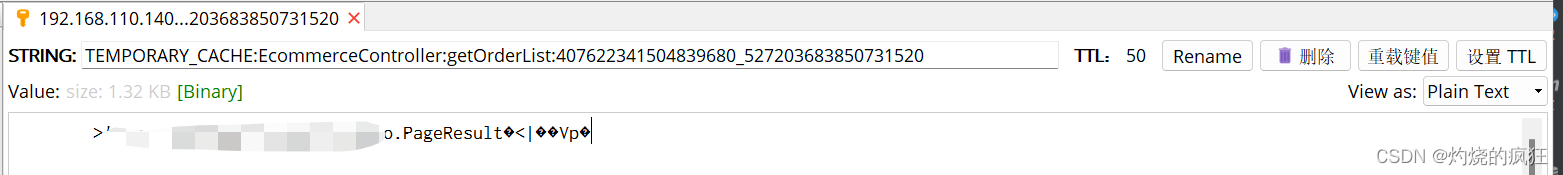
就到这里了