文章目录
- 260. 只出现一次的数字 III(字典 / 位运算)
- 136. 只出现一次的数字(字典)
- 137. 只出现一次的数字 II(字典)
- 169. 求众数(字典)
- 229. 求众数 II(字典)
- 2006. 差的绝对值为 K 的数对数目(字典)
- 944. 删列造序(zip(*list))
- 867. 转置矩阵(zip(*list))
更多有关 dict 的相关背景和 leetcode 题解可参考:
- 【Programming】
- 【python】dict(7)
260. 只出现一次的数字 III(字典 / 位运算)
给定一个整数数组 nums,其中恰好有两个元素只出现一次,其余所有元素均出现两次。 找出只出现一次的那两个元素。
-
示例 :
输入: [1,2,1,3,2,5]
输出: [3,5] -
注意:
结果输出的顺序并不重要,对于上面的例子, [5, 3] 也是正确答案。
你的算法应该具有线性时间复杂度。你能否仅使用常数空间复杂度来实现?
思路1:用字典,key 是数字,value 是频数,出现了两次,就删掉,最后输出字典中有的元素
class Solution(object):
def singleNumber(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: List[int]
"""
dict1 = {}
for i in nums:
if i in dict1:
del dict1[i]
else:
dict1[i] = 1
list1 = []
for i in dict1:
list1.append(i)
return list1
还有一种用二进制与操作的方法,很懵!(bryant)
LeetCode Medium 260 找单独的数III Python
136. 只出现一次的数字(字典)
给定一个非空整数数组,除了某个元素只出现一次以外,其余每个元素均出现两次。找出那个只出现了一次的元素。
-
说明:
你的算法应该具有线性时间复杂度。 你可以不使用额外空间来实现吗? -
示例 1:
输入: [2,2,1]
输出: 1 -
示例 2:
输入: [4,1,2,1,2]
输出: 4
可以用 260. 只出现一次的数字 III(字典) 的方法!
class Solution(object):
def singleNumber(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: int
"""
dict1 = {}
for i in nums:
if i in dict1:
del dict1[i]
else:
dict1[i] = 1
for i in dict1:
return i
137. 只出现一次的数字 II(字典)
给定一个非空整数数组,除了某个元素只出现一次以外,其余每个元素均出现了三次。找出那个只出现了一次的元素。
-
说明:
你的算法应该具有线性时间复杂度。 你可以不使用额外空间来实现吗? -
示例 1:
输入: [2,2,3,2]
输出: 3 -
示例 2:
输入: [0,1,0,1,0,1,99]
输出: 99
这个出现了三次,不能像 260. 只出现一次的数字 III(字典) 那样,出现第二次的时候删掉字典键值对,所以我们中规中矩,把数字和频数存在字典中,然后,遍历字典,输出频数为 1 的数
class Solution(object):
def singleNumber(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: int
"""
dict1 = {}
for i in nums:
if i not in dict1:
dict1[i] = 0
dict1[i] += 1
else:
dict1[i] +=1
for i in dict1:
if dict1[i] == 1:
return i
169. 求众数(字典)
给定一个大小为 n 的数组,找到其中的众数。众数是指在数组中出现次数大于 ⌊ n/2 ⌋ 的元素。
你可以假设数组是非空的,并且给定的数组总是存在众数。
-
示例 1:
输入: [3,2,3]
输出: 3
示例 2: -
输入: [2,2,1,1,1,2,2]
输出: 2
还是可以用 137. 只出现一次的数字 II 的思路,存在字典中,keys 是数字,values 是频数,然后根据频数筛选出最终答案!
class Solution(object):
def majorityElement(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: int
"""
dict1 = {}
for i in nums:
if i not in dict1:
dict1[i] = 1
else:
dict1[i] += 1
for i in dict1:
if dict1[i] > len(nums)/2:
return i
还可以,直接排序,然后输出后半段的数字就可以了!反正众数一定存在,而且不管是比其他数大还是小,都占了一半以上!
class Solution(object):
def majorityElement(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: int
"""
sort_nums = sorted(nums)
return sort_nums[len(nums)//2]
229. 求众数 II(字典)
给定一个大小为 n 的数组,找出其中所有出现超过 ⌊ n/3 ⌋ 次的元素。
-
说明: 要求算法的时间复杂度为 O(n),空间复杂度为 O(1)。
-
示例 1:
输入: [3,2,3]
输出: [3] -
示例 2:
输入: [1,1,1,3,3,2,2,2]
输出: [1,2]
还是可以用字典
class Solution(object):
def majorityElement(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: List[int]
"""
dict1 = {}
list1 = []
for i in nums:
if i not in dict1:
dict1[i] = 1
else:
dict1[i] += 1
for i in dict1:
if dict1[i] > len(nums)/3:
list1.append(i)
return list1
2006. 差的绝对值为 K 的数对数目(字典)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/count-number-of-pairs-with-absolute-difference-k
给你一个整数数组 nums 和一个整数 k ,请你返回数对 (i, j) 的数目,满足 i < j 且 |nums[i] - nums[j]| == k 。
|x| 的值定义为:
如果 x >= 0 ,那么值为 x 。
如果 x < 0 ,那么值为 -x 。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [1,2,2,1], k = 1
输出:4
解释:差的绝对值为 1 的数对为:
- [1,2,2,1]
- [1,2,2,1]
- [1,2,2,1]
- [1,2,2,1]
1)暴力法
res = 0
for i in nums:
for j in nums:
if abs(i-j) == k:
res += 1
return res
2)统计数字出现的频数,把符合条件的频数相乘
from collections import Counter
num_dict = Counter(nums)
res = 0
for i in num_dict:
if i+k in num_dict:
res += num_dict[i]*num_dict[i+k]
return res
当然,可以自己通过字典来实现统计频数
num_dict = {}
for i in nums:
if i in num_dict:
num_dict[i] += 1
else:
num_dict[i] = 1
res = 0
for i in num_dict:
if i+k in num_dict:
res += num_dict[i]*num_dict[i+k]
return res
944. 删列造序(zip(*list))
给定由 N 个小写字母字符串组成的数组 A,其中每个字符串长度相等。
删除 操作的定义是:选出一组要删掉的列,删去 A 中对应列中的所有字符,形式上,第 n 列为 [A[0][n], A[1][n], …, A[A.length-1][n]])。
比如,有 A = [“abcdef”, “uvwxyz”],
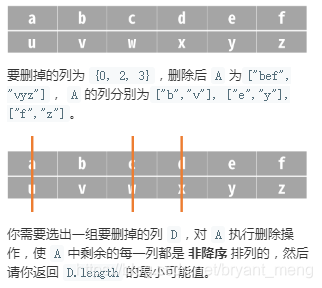
思路:列表中的的行的组合变成列的组合,然后判断是否升序
class Solution(object):
def minDeletionSize(self, A):
"""
:type A: List[str]
:rtype: int
"""
B = []
# 交换行列
for i in range(len(A[0])): #遍历列
s = ""
for j in range(len(A)): #遍历行
s+=A[j][i]
B.append(s)
count = 0
# 比较大小
for i in range(len(B)):
for j in range(len(B[0])-1):#第i组的第j个元素
if B[i][j]>B[i][j+1]: #比较大小
count+=1
break
return count
这么做太暴力了,需要柔美一点的,是否非降序可以用排序前后的对比,行列的互换可以用 zip(*list)
class Solution(object):
def minDeletionSize(self, A):
"""
:type A: List[str]
:rtype: int
"""
count = 0
for item in zip(*A):
if sorted(item)!=list(item): #这里注意 item 是元组,排序完是list
count+=1
return count
867. 转置矩阵(zip(*list))
给定一个矩阵 A, 返回 A 的转置矩阵。
矩阵的转置是指将矩阵的主对角线翻转,交换矩阵的行索引与列索引。
示例 1:
输入:[[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]]
输出:[[1,4,7],[2,5,8],[3,6,9]]
思路:可以l两层便利 a,b = b,a,也可以利用 zip(*list)
class Solution(object):
def transpose(self, A):
"""
:type A: List[List[int]]
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
list1 = []
for i in zip(*A):
list1.append(list(i))
return list1
更简洁的写法是
class Solution(object):
def transpose(self, A):
"""
:type A: List[List[int]]
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
return [list(i) for i in zip(*A)]