文章目录
- margnalize
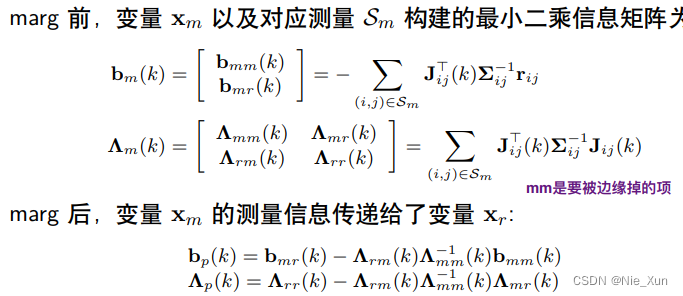
- 公式及原理:
- 测试代码及运行结果
- 解说
- 代码
- 编译命令:
- 运行结果:
- Huber
- 原理
- 代码
- Jacibian测试
- 代码
- 代码解释
- 代码
- 编译命令
- 运行结果
margnalize
公式及原理:
测试代码及运行结果
解说
/*********************************
变量:a b c 观测:u
[2 3]
a b
1a+1b = 6 (x y):(1 1) u=6
1a+2b = 8 (x y):(1 2) u=8
e = sum||ri|| = sum||ax+by - u||
J = [x y]
H = [x2 xy] = [Haa Hab]
[yx y2] [Hba Hbb]
b = -JT * ri = [ba, bb]
初始:[a b] = [0 0]
[a b] += H^-1 * b
--
来c,marg a
--
[3 5]
b c
3a+1b = 14 (y z):(3 1) u=14
1a+2b = 13 (y z):(1 2) u=13
e = sum||ri|| = sum||by+cz - u||
J = [y z]
H = [y2 yz] + Hpr
[zy z2]
b = -JT * ri + bpr
Hpr = Hbb - Hba*Haa^-1*Hab
bpr = bb - Hba*Haa^-1*ba
初始:[y z] = [b 0]
[b c] += H^-1 * (J*ri)
***************************/
代码
#include <iostream>
#include <random>
#include <vector>
#include <Eigen/Core>
#include <Eigen/Geometry>
using namespace std;
using namespace Eigen;
vector<Vector3d> xyzs;
vector<float> us;
int main()
{
std::default_random_engine generator(0);
std::normal_distribution<double> n(0., 1. / 1000.);
/*第一次观测*/
//[x y]=[1 1]
double x = 1 + n(generator);
double y = 1 + n(generator);
//u=6
double u = 5 + n(generator);
xyzs.push_back(Vector3d(x,y,0));
us.push_back(u);
/*第二次观测*/
//[x y]=[1 2]
x = 1 + n(generator);
y = 2 + n(generator);
//u=8
u = 8 + n(generator);
xyzs.push_back(Vector3d(x,y,0));
us.push_back(u);
//parameras: a b c : 0 0 0
//初始:[a b c] = [0 0 0]
Vector3d p(0,0,0);
Matrix2d H = Matrix2d::Zero();
Vector2d b(0,0);
int iters = 5;
for (int iter = 0; iter < iters; iter++) {
H.setZero(); b.setZero();
double error = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < us.size(); i++) {
//J = [x y]
Vector2d J;
J << xyzs[i].x(), xyzs[i].y();
H += J * J.transpose();
double res = xyzs[i].x() * p[0] + xyzs[i].y() *p[1] - us[i];
b -= J * res;
error += res*res;
}
Vector2d update = H.inverse() * b;
cout << "iter: " << iter << " error: " << error << endl;
cout << "update: \n" << update << endl;
if (update.norm() < 1e-6) {
// converge
break;
}
p[0] += update[0];
p[1] += update[1];
}
cout << "P:\n" << p << endl;
xyzs.clear(); us.clear();
/*第三次观测*/
//[y z]=[3 1]
y = 3 + n(generator);
double z = 1 + n(generator);
//u=8
u = 14 + n(generator);
xyzs.push_back(Vector3d(0,y,z));
us.push_back(u);
/*第四次观测*/
//[y z]=[1 2]
y = 1 + n(generator);
z = 2 + n(generator);
//u=8
u = 13 + n(generator);
xyzs.push_back(Vector3d(0,y,z));
us.push_back(u);
//----marg a----/
//Hpr = Hbb - Hba*Haa^-1*Hab
//bpr = bb - Hba*Haa^-1*ba
double hpr = H(1,1) - H(1,0)*(1/H(0,0))*H(0,1);
double bpr = b[1] - H(1,0)*(1/H(0,0))*b[0];
cout << "hpr bpr: " << hpr << " " << bpr << endl;
H.setZero(); b.setZero();
H(0,0) = hpr;
b[0] = bpr;
for (int iter = 0; iter < iters; iter++) {
H.setZero(); b.setZero();
double error = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < us.size(); i++) {
//J = [x y]
Vector2d J;
J << xyzs[i].y(), xyzs[i].z();
H += J * J.transpose();
double res = xyzs[i].y() * p[1] + xyzs[i].z() *p[2] - us[i];
b -= J * res;
error += res*res;
}
Vector2d update = H.inverse() * b;
cout << "iter: " << iter << " error: " << error << endl;
cout << "update: \n" << update << endl;
if (update.norm() < 1e-6) {
// converge
break;
}
p[1] += update[0];
p[2] += update[1];
}
cout << "truth: 2 3 5" <<< endl;
cout << "P:\n" << p << endl;
}
编译命令:
g++ marginalize_test.cpp `pkg-config eigen3 --libs --cflags`
运行结果:
iter: 0 error: 89.0188
update:
2.00557
2.99861
iter: 1 error: 1.14385e-28
update:
-8.87247e-15
8.78737e-16
P:
2.00557
2.99861
0
hpr bpr: 0.502553 4.41612e-16
iter: 0 error: 125.068
update:
0.00475064
4.9929
iter: 1 error: 0
update:
0
0
P:
2.00557
3.00336
4.9929
Huber
原理
常用 Huber 核:

当误差 r 大于阈值 δ 后,函数增长由二次形式变成了一次形式,相当 于限制了梯度的最大值。同时,Huber 核函数又是光滑的,可以很方便地求导。如下图所示。

Huber核函数使用说明
设待求解最小二乘问题:
e
=
∑
‖
r
i
‖
e=∑‖r_i ‖
e=∑‖ri‖
当加入Huber核,最小二乘问题变为:
e
=
∑
‖
H
u
b
e
r
(
r
i
)
‖
e=∑‖Huber(r_i)‖
e=∑‖Huber(ri)‖
则雅可比矩阵对应变动,设待优化参数为ξ:
r
i
→
H
u
b
e
r
(
r
i
)
r_i→Huber(r_i)
ri→Huber(ri)
J
=
(
∂
r
i
)
/
∂
ξ
→
J
=
(
∂
H
u
b
e
r
(
r
i
)
)
/
∂
ξ
J=(∂r_i)/∂ξ → J=(∂ Huber(r_i))/∂ξ
J=(∂ri)/∂ξ→J=(∂Huber(ri))/∂ξ

而后可使用高斯牛顿方法求解:
J
i
T
J
i
⋅
∆
ξ
=
−
J
i
T
⋅
H
u
b
e
r
(
r
i
)
J_i^T J_i \cdot∆ξ=-J_i^T \cdot Huber(r_i)
JiTJi⋅∆ξ=−JiT⋅Huber(ri)
代码
代码1:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
#include <Eigen/Dense>
#include <unsupported/Eigen/AutoDiff>
using namespace Eigen;
// Huber loss function
template<typename T>
T huber_loss(T delta, T epsilon) {
if (std::abs(delta) <= epsilon) {
return 0.5 * delta * delta;
} else {
return epsilon * (std::abs(delta) - 0.5 * epsilon);
}
}
// Gauss-Newton optimization
template<typename T>
Vector3d gauss_newton_optimization(const Vector3d& initial_estimate, const std::vector<T>& measurements, T epsilon) {
Vector3d parameters = initial_estimate;
for (int iter = 0; iter < 10; ++iter) {
Matrix<T, Dynamic, 3> jacobian(measurements.size(), 3);
Vector<T, Dynamic> residuals(measurements.size());
for (size_t i = 0; i < measurements.size(); ++i) {
AutoDiffScalar<Vector3d> ad_params(parameters);
AutoDiffScalar<T> ad_meas(measurements[i]);
residuals(i) = ad_meas - (ad_params[0] * ad_meas * ad_meas + ad_params[1] * ad_meas + ad_params[2]);
if (std::abs(residuals(i)) <= epsilon) {
jacobian(i, 0) = -residuals(i) * ad_meas * ad_meas;
jacobian(i, 1) = -residuals(i) * ad_meas;
jacobian(i, 2) = -residuals(i);
} else {
jacobian(i, 0) = -epsilon * std::copysign(T(1.0), residuals(i)) * ad_meas * ad_meas;
jacobian(i, 1) = -epsilon * std::copysign(T(1.0), residuals(i)) * ad_meas;
jacobian(i, 2) = -epsilon * std::copysign(T(1.0), residuals(i));
}
}
Vector3d delta = (jacobian.transpose() * jacobian).ldlt().solve(jacobian.transpose() * residuals);
parameters += delta;
if (delta.norm() < 1e-6) {
break;
}
}
return parameters;
}
int main() {
std::vector<double> measurements{1.2, 2.3, 3.5, 4.7, 5.9};
Vector3d initial_estimate(1.0, 1.0, 1.0);
double epsilon = 0.5;
Vector3d optimized_parameters = gauss_newton_optimization(initial_estimate, measurements, epsilon);
std::cout << "Optimized parameters: " << optimized_parameters.transpose() << std::endl;
return 0;
}
代码2(局部):
double x = Pc.x();
double y = Pc.y();
double z = Pc.z();
double z_2 = z * z;
Matrix<double,2,3> PiFunc;
PiFunc << 1/z, 0, 0, 0, 1/z, 0;
//经典特征点法:TPw - u (当前帧的图像坐标差) Pc=TPw
Vector2d res = PiFunc * Pc - it.second;
//T的导数
Matrix<double,2,6> jacobian_Ti;
jacobian_Ti(0, 0) = 1/z;
jacobian_Ti(0, 1) = 0;
jacobian_Ti(0, 2) = -x / z_2;
jacobian_Ti(0, 3) = -x * y / z_2;
jacobian_Ti(0, 4) = 1 + x * x / z_2;
jacobian_Ti(0, 5) = -y/z;
jacobian_Ti(1, 0) = 0;
jacobian_Ti(1, 1) = 1/z;
jacobian_Ti(1, 2) = -y / z_2;
jacobian_Ti(1, 3) = -1 - y * y / z_2;
jacobian_Ti(1, 4) = x * y / z_2;
jacobian_Ti(1, 5) = x/z;
for (int j = 0; j < 2; j++) {
if (fabs(res[j]) <= epsi) {
jacobian_Ti.row(j) = res[j] * jacobian_Ti.row(j);
} else {
jacobian_Ti.row(j) = epsi * sign(res[j]) * jacobian_Ti.row(j);
}
}
//P的导数
Matrix<double,2,3> jacobian_uv_Pc;
jacobian_uv_Pc << 1/z, 0 , -x/z_2, 0, 1/z, -y/z_2;
Matrix<double,2,3> jacobian_Pj = jacobian_uv_Pc * Rcw;
for (int j = 0; j < 2; j++) {
if (fabs(res[j]) <= epsi) {
jacobian_Pj.row(j) = res[j] * jacobian_Pj.row(j);
} else {
jacobian_Pj.row(j) = epsi * sign(res[j]) * jacobian_Pj.row(j);
}
}
Vector2d error2 = HuberLoss(res, epsi);
error += error2.transpose() * error2;
H += J.transpose() * J;
b -= J.transpose() * error2;
Jacibian测试
代码
代码解释
以经典特征点法为例:归一化坐标
10 //P2 = R21 * P1 +t21
11 //func(\xi) = \pi(R21 * P1 +t21) - p2
12 //J: (2*6):
13 //J(0, 0) = 1/z;
14 //J(0, 1) = 0;
15 //J(0, 2) = -x / z_2;
16 //J(0, 3) = -x * y / z_2;
17 //J(0, 4) = 1 + x * x / z_2;
18 //J(0, 5) = -y/z;
19 //J(1, 0) = 0;
20 //J(1, 1) = 1/z;
21 //J(1, 2) = -y / z_2;
22 //J(1, 3) = -1 - y * y / z_2;
23 //J(1, 4) = x * y / z_2;
24 //J(1, 5) = x/z;
25
26 //value:
27 //J := func(\xi + \delta) - func(\xi) / \delta
28
29 //\pi(): P/P.z
30 //piFunc << 1/z, 0, 0, 0, 1/z, 0; piFunc * P
代码
typedef Eigen::Matrix<double, 6, 1> Vector6d;
int main()
{
std::default_random_engine generator(time(NULL));
std::uniform_real_distribution<double> xy_rand(-3, 3);
std::uniform_real_distribution<double> z_rand(2., 6.);
Vector3d P1(xy_rand(generator), xy_rand(generator), z_rand(generator));
Vector3d p1 = P1 / P1.z();
double theta = 2 * M_PI / 30;
float radius = 8;
// 绕 z轴 旋转
Matrix3d R_th;
R_th = AngleAxisd(theta, Vector3d::UnitZ());
Vector3d t_th = Vector3d(radius * cos(theta) - radius, radius * sin(theta), 1 * sin(2 * theta));
Vector3d P2_th = R_th * P1 + t_th;
Vector3d p2 = P2_th / P2_th.z();
//T求导值
Sophus::SE3d T_e = Sophus::SE3d(Eigen::Matrix4d::Identity());
Vector3d P2_e = T_e * P1;
double x = P2_e.x();
double y = P2_e.y();
double z = P2_e.z();
double z_2 = z * z;
//解析值:
Matrix<double,2,6> jacobian_Ti;
jacobian_Ti(0, 0) = 1/z;
jacobian_Ti(0, 1) = 0;
jacobian_Ti(0, 2) = -x / z_2;
jacobian_Ti(0, 3) = -x * y / z_2;
jacobian_Ti(0, 4) = 1 + x * x / z_2;
jacobian_Ti(0, 5) = -y/z;
jacobian_Ti(1, 0) = 0;
jacobian_Ti(1, 1) = 1/z;
jacobian_Ti(1, 2) = -y / z_2;
jacobian_Ti(1, 3) = -1 - y * y / z_2;
jacobian_Ti(1, 4) = x * y / z_2;
jacobian_Ti(1, 5) = x/z;
cout << "J: \n" << jacobian_Ti << endl;
//func(\xi + \delta)
double eps = 1e-6;
Vector6d delta;
delta << eps, 0,0,0,0,0;
Matrix<double,2,3> PiFunc;
Vector3d P2a = Sophus::SE3d::exp(delta) * T_e * P1;
z = P2a.z();
PiFunc << 1/z, 0, 0, 0, 1/z, 0;
Vector2d p2a = PiFunc * P2a;
//Vector3d p2a = Sophus::SE3d::exp(delta) * T_e * P1;
//P2a = p2a / p2a.z();
Vector3d P2b = T_e * P1;
z = P2b.z();
PiFunc << 1/z, 0, 0, 0, 1/z, 0;
Vector2d p2b = PiFunc * P2b;
Vector2d J0 = (p2a - p2b) / eps;
delta << 0, eps, 0,0,0,0;
P2a = Sophus::SE3d::exp(delta) * T_e * P1;
z = P2a.z();
PiFunc << 1/z, 0, 0, 0, 1/z, 0;
p2a = PiFunc * P2a;
P2b = T_e * P1;
z = P2b.z();
PiFunc << 1/z, 0, 0, 0, 1/z, 0;
p2b = PiFunc * P2b;
Vector2d J1 = (p2a - p2b) / eps;
delta << 0, 0, eps,0,0,0;
P2a = Sophus::SE3d::exp(delta) * T_e * P1;
z = P2a.z();
PiFunc << 1/z, 0, 0, 0, 1/z, 0;
p2a = PiFunc * P2a;
P2b = T_e * P1;
z = P2b.z();
PiFunc << 1/z, 0, 0, 0, 1/z, 0;
p2b = PiFunc * P2b;
Vector2d J2 = (p2a - p2b) / eps;
delta << 0, 0, 0, eps, 0,0;
P2a = Sophus::SE3d::exp(delta) * T_e * P1;
z = P2a.z();
PiFunc << 1/z, 0, 0, 0, 1/z, 0;
p2a = PiFunc * P2a;
P2b = T_e * P1;
z = P2b.z();
PiFunc << 1/z, 0, 0, 0, 1/z, 0;
p2b = PiFunc * P2b;
Vector2d J3 = (p2a - p2b) / eps;
delta << 0, 0, 0, 0, eps, 0;
P2a = Sophus::SE3d::exp(delta) * T_e * P1;
z = P2a.z();
PiFunc << 1/z, 0, 0, 0, 1/z, 0;
p2a = PiFunc * P2a;
P2b = T_e * P1;
z = P2b.z();
PiFunc << 1/z, 0, 0, 0, 1/z, 0;
p2b = PiFunc * P2b;
Vector2d J4 = (p2a - p2b) / eps;
delta << 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, eps;
P2a = Sophus::SE3d::exp(delta) * T_e * P1;
z = P2a.z();
PiFunc << 1/z, 0, 0, 0, 1/z, 0;
p2a = PiFunc * P2a;
P2b = T_e * P1;
z = P2b.z();
PiFunc << 1/z, 0, 0, 0, 1/z, 0;
p2b = PiFunc * P2b;
Vector2d J5 = (p2a - p2b) / eps;
cout << "value compute: \n" << J0[0] << " " << J0[1] << endl
<< J1[0] << " " << J1[1] << endl
<< J2[0] << " " << J2[1] << endl
<< J3[0] << " " << J3[1] << endl
<< J4[0] << " " << J4[1] << endl
<< J5[0] << " " << J5[1] << endl;
}
编译命令
g++ jacobian_test.cpp -L ~/Download/softpackages/Sophus/build -I ~/Download/softpackages/Sophus `pkg-config eigen3 --libs --cflags`
运行结果
J:
0.258424 0 0.0200104 -0.0521547 1.006 0.673549
0 0.258424 0.174061 -1.45367 0.0521547 -0.0774327
value compute:
0.258424 0
0 0.258424
0.0200104 0.174061
-0.0521548 -1.45367
1.006 0.0521544
0.673549 -0.0774323