摘要:在本文中,我们将深入研究Spring框架中的
@Cacheable注解。我们会通过详细的Java示例,探讨如何使用这个功能强大的注解来提升应用程序性能。
一、什么是缓存?
在计算机科学中,缓存是一种存储技术,用于保存经常使用的数据,以便在后续请求中快速访问。在Web开发中,缓存被广泛用于减少对数据库的访问,提高应用程序的响应速度。
二、Spring中的缓存抽象
Spring提供了一种强大的缓存抽象,允许开发者通过简单的注解,将方法的执行结果存储在缓存中。这些注解包括@Cacheable、@CacheEvict、@CachePut等。在本文中,我们将重点关注@Cacheable注解。
三、@Cacheable注解的使用
@Cacheable注解用于标记应该被缓存的方法。当一个方法被@Cacheable注解标记后,Spring会在调用该方法前检查缓存,如果缓存中存在对应的数据,就直接返回缓存的数据,而不执行方法。如果缓存中不存在对应的数据,Spring会执行方法,然后将返回结果存入缓存。
@Cacheable注解有两个重要的属性:value和key。value用于指定缓存的名称,key用于指定缓存的键。例如:
@Cacheable(value = "users", key = "#id")
public User findUserById(Long id) {
//...
}
在上述代码中,findUserById方法的结果将被存储在名为users的缓存中,缓存的键是方法的参数id。
四、@Cacheable注解的工作原理
让我们通过一个例子来详细了解@Cacheable注解的工作原理。
假设我们有一个UserService类,该类有一个findUserById方法,用于从数据库中查询用户。我们可以使用@Cacheable注解来缓存查询结果,如下:
@Service
public class UserService {
@Autowired
private UserRepository userRepository;
@Cacheable(value = "users", key = "#id")
public User findUserById(Long id) {
return userRepository.findById(id).orElse(null);
}
}
当我们第一次调用findUserById方法时,Spring会执行方法,并将返回结果存入名为users的缓存中。缓存的键是方法的参数id。
当我们再次以相同的id调用findUserById方法时,Spring会在users缓存中查找键为id的数据。如果找到,直接返回缓存的数据,不执行方法。如果没找到,执行方法,并将返回结果存入缓存。
这就是@Cacheable注解的工作原理。通过使用@Cacheable注解,我们可以避免重复的数据库查询,提高应用程序的响应速度。
五、示例
import com.alibaba.fastjson.support.spring.FastJsonRedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.EnableCaching;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CachingConfigurerSupport;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheManager;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer;
@Configuration
@EnableCaching
public class CacheConfig extends CachingConfigurerSupport {
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory factory) {
RedisTemplate<String, Object> template = new RedisTemplate<>();
template.setConnectionFactory(factory);
//template.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
//template.setValueSerializer(new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer());
FastJsonRedisSerializer<Object> fastJsonRedisSerializer = new FastJsonRedisSerializer<>(Object.class);
template.setValueSerializer(fastJsonRedisSerializer);
template.setHashValueSerializer(fastJsonRedisSerializer);
// 设置键(key)的序列化采用StringRedisSerializer。
template.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
template.setHashKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
return template;
}
@Bean
public RedisCacheManager cacheManager(RedisConnectionFactory factory) {
return RedisCacheManager.create(factory);
}
}@Cacheable(value = "queryAllBill", key = "#billRequestDto.userId + '_' + (#billRequestDto.billStatusList != null ? #billRequestDto.billStatusList.toString() : '') " +
" + '_' + #billRequestDto.billNo + '_' + #billRequestDto.orderNo + '_' + #billRequestDto.contNo + #billRequestDto.billStatus + '_'" +
" + '_' + #billRequestDto.billType + '_' + #billRequestDto.channelName + '_' + #billRequestDto.productName + '_' + #billRequestDto.settleSubjectCode" +
" + '_' + #billRequestDto.contractCompanyCode + '_' + #billRequestDto.coInsuranceName + '_' + #billRequestDto.billBeginDate " +
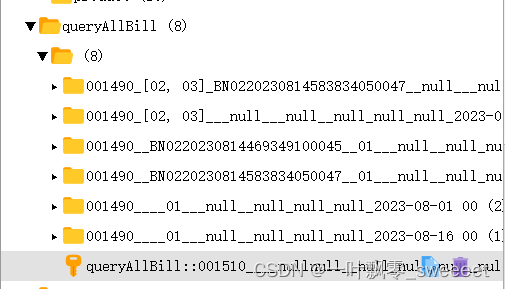
" + '_' + #billRequestDto.billEndDate+ '_' + (#billRequestDto.addBillSidList != null ? #billRequestDto.addBillSidList.toString() : '')")访问接口后查询缓存:
六、注意事项
尽管@Cacheable注解非常强大,但在使用时还是需要注意一些问题:
1.数据一致性:如果你的数据经常变化,那么你需要考虑数据一致性的问题。你可以使用@CacheEvict或@CachePut注解来清除或更新缓存。使用@Cacheable注解的确可以提高应用程序的性能,因为它可以避免重复的数据库查询。然而,如果你的数据经常变化,那么缓存的数据可能会很快就过时了。在这种情况下,你需要考虑以下几点:
-
缓存过期策略:你可以设置缓存的过期时间,使得缓存的数据在一段时间后自动清除。这样,下次查询时,将会从数据库中获取最新的数据。缺点是,如果数据在缓存过期之前就已经变化了,那么你仍然可能会得到过时的数据。
-
使用@CacheEvict注解:当数据发生变化时(例如,在更新或删除操作后),你可以使用
@CacheEvict注解来清除缓存。例如:@CacheEvict(value = "users", key = "#user.id") public void updateUser(User user) { //... }这样,每次更新用户信息后,对应的缓存将被清除。下次查询时,将会从数据库中获取最新的数据。缺点是,你需要在所有可能改变数据的操作后都清除缓存,这可能会使代码变得复杂。
-
使用@CachePut注解:
@CachePut注解会在每次方法调用后更新缓存。这意味着,即使数据发生了变化,缓存中的数据也总是最新的。例如:@CachePut(value = "users", key = "#user.id") public User updateUser(User user) { //... return user; }注意,
@CachePut注解的方法应该返回更新后的对象。这样,返回的对象将被用来更新缓存。缺点是,这可能会影响性能,因为每次方法调用都会更新缓存。
2.数据一致性缓存穿透:如果你的方法可能会接收到大量的无效参数,那么你需要考虑缓存穿透的问题。你可以在方法内部检查参数的有效性,或者使用@Cacheable注解的unless属性来排除某些结果。
3.缓存雪崩:如果你的缓存有过期时间,那么你需要考虑缓存雪崩的问题。你可以使用随机的过期时间,或者使用二级缓存来避免大量的缓存同时过期。
4.适合查询不变的数据:如果复杂数据结构的数据的状态经常改变,不建议接口缓存。
七、总结
在本文中,我们详细介绍了Spring中的@Cacheable注解。通过使用@Cacheable注解,我们可以轻松地将方法的执行结果存储在缓存中,从而提高应用程序的响应速度。然而,使用@Cacheable注解时,还需要注意数据一致性、缓存穿透和缓存雪崩等问题。
希望本文能够帮助你更好地理解和使用Spring中的@Cacheable注解。如果你有任何问题或建议,欢迎在评论区留言。
👉 💐🌸 公众号请关注 "果酱桑", 一起学习,一起进步! 🌸💐