💞💞欢迎来到 Claffic 的博客💞💞
👉 专栏:《是C++,不是C艹》👈


前言:
恍惚间,已经两个月没更新了 (;´д`)ゞ 我忏悔...
但C++的学习不能停止!这期带大家实践一波,手把手教大家实现一个Date类,以感受C++类的魅力
注:
你最好是学完了C语言,并学过一些初阶的数据结构。
(没有目录) ヽ( ̄ω ̄( ̄ω ̄〃)ゝ
Part1:一个引子
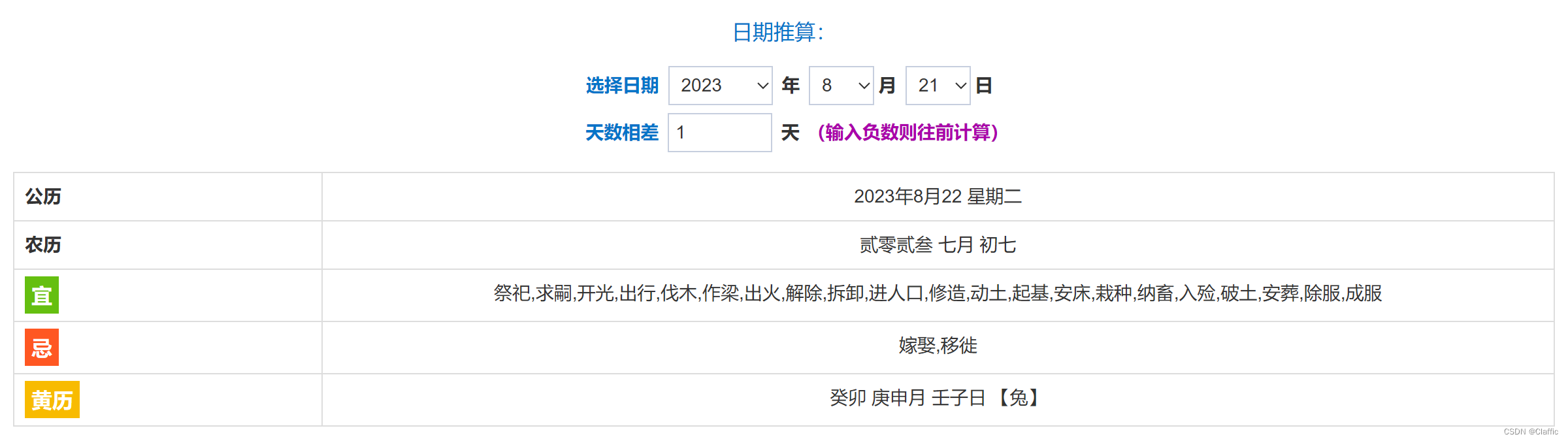
🌰我猜你用过倒数日:

🪄这其实是一种简单的日期机算器,用来计算某事件 已经 / 还有 多少天
那么我们搜索 日期计算器 会看到它的两大功能:
日期推算:
计算日期差:

❓那么这些功能是怎么实现的呢?
接下来就由我来带你揭开它的神秘面纱!
Part2:思路
1.日期推算
❓你想,先扔给你一个日期,再给你一个整数(正往后,负往前),你会怎么推算新日期?
简单情况:日相加,得到的日部分不超过当前月份的天数,就如 2023-8-21 与 1,得 2023-8-22 。
进位情况:日相加,得到的日部分超出当前月份的天数,给月进位,如 2023-8-21 与 12,得 2023-9-2;
另有月满13,需要月重置1,再给年进位,如 2023-8-21 与 133,得 2024-1-1
🚨注意还要考虑闰年 / 非闰年:闰年2月有29日 非闰年2月有28日。
2.计算日期差
❓再想,扔给你两个日期,你怎么计算两者之间间隔了多少天?
你是不是这样想的:年先做差,月再做差,日再做差,然后都换算成日,最后相加?
嗯,这是很直接的思路,可以,但没必要。
✅这里提供另一种思路:
两个日期,必然有大有小(暂时忽略相等),找出较小者,让较小者往较大者增长,每次增加一日(++),加个计数器,计出来的就是两者的日期差。
或许你会感到麻烦,那你还是C语言的思维!
📢别忘了:C++是面向对象的语言!我们完全可以创建一个日期类来完成相关的计算和比较
Part3:实现
1.创建类
一个日期,包含年月日三个基本数据,这些不需要对用户公开,私有即可:
class Date
{
public:
// todo
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};另外添加一些基本的方法:
先来解决最基础的问题:那就是每个月有几天
我们不妨来封装一个方法,来获取这个月里有几天:
int Date::GetMonthDay(int year, int month) // 年份是来判断是否是闰年的
{
// 第一个元素无实际效用,但就能保证 下标 == 月数
static int arr[13] = { 0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31 }; // 一三五七八十腊...
// 2月前提下再判断年的情况,减少消耗
if (month == 2 && ((year % 4 == 0) && (year % 100 != 0) || (year % 400 == 0)))
return 29;
else
return arr[month];
}构造:
Date::Date(int year, int month, int day)
{
// 判断合法性
if (month > 0 && month < 13
&& day > 0 && day < GetMonthDay(year, month))
{
_year = year;
_month = month;
_day = day;
}
else
{
cout << "非法日期" << endl;
assert(false);
}
}这里可以给一个全缺省,不给数据就默认是这个日期,还蛮香~
Date(int year = 2008, int month = 1, int day = 1);展示:
// 代码较短,在类中写就OK,不用跨文件了
void Print() const
{
cout << _year << "-" << _month << "-" << _day << endl;
}2.日期推算
⚔️我们期望得到这样的效果:
void DateTest1()
{
Date d1(2023,8,21);
Date d2 = d1 + 133;
d1.Print();
d2.Print();
}👁️🗨️运行结果:

我们知道,普通的 + 是对整型,浮点型,字符型等内置类型起效的,而这里的 + 在 Date 和 int 之间起作用了,为甚?
没错,这就是C++大名鼎鼎的运算符重载!(其实 = 也重载了)
// 日期 + 天数
Date Date::operator+(int day)
{
Date tmp(*this); // + 是不修改本身的!所以要先拷贝一份,最后返回的是拷贝修改后的内容
tmp._day += day;
// 月与年的进位
while (tmp._day > GetMonthDay(tmp._year, tmp._month))
{
tmp._day -= GetMonthDay(tmp._year, tmp._month);
tmp._month++;
if (tmp._month == 13)
{
tmp._year++;
tmp._month = 1;
}
}
return tmp;
}// 赋值运算符重载
Date& Date::operator=(const Date& d) // 原内容无需修改,加const
{
_day = d._day;
_month = d._month;
_year = d._year;
return *this;
}3.计算日期差
⚔️预期效果:
void DateTest3()
{
Date d5(2023, 8, 21);
Date d6(2004, 3, 30);
cout << d5 - d6 << endl;
cout << d6 - d5 << endl;
}
👁️🗨️运行结果:

很明显,这是重载了 - ,使得 - 能在两个 Date 类之间起作用
🗡️按照二趴提供的思路,写下这样的代码:
int Date::operator-(const Date& d) const
{
Date max = *this;
Date min = d;
int flag = 1; // 巧妙的flag,调节最后结果的正负
if (*this < d)
{
max = d;
min = *this;
flag = -1;
}
int n = 0;
while (min != max)
{
++min;
++n;
}
return n * flag;
}🗡️我们发现,里面的 <, !=, ++ 都是需要针对 Date 进行重载的:
// <运算符重载
bool Date::operator<(const Date& d) const
{
if (_year < d._year)
{
return true;
}
else if (_year == d._year && _month < d._month)
{
return true;
}
else if (_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day < d._day)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}// ==运算符重载
bool Date::operator==(const Date& d) const
{
return _year == d._year
&& _month == d._month
&& _day == d._day;
}
// !=运算符重载
bool Date::operator != (const Date& d) const
{
return !(*this == d);
}// 前置++
Date& Date::operator++()
{
*this += 1; // 还需重载 +=
return *this;
}
// 日期+=天数
Date& Date::operator+=(int day) // += 需要修改本身
{
_day += day;
while (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month))
{
_day -= GetMonthDay(_year, _month);
_month++;
if (_month == 13)
{
_year++;
_month = 1;
}
}
return *this;
}经过一系列重载后,就可以达到计算日期差的效果咯!
Part4:其他功能
1.输入输出
❓在实现了两种主要的功能之后,既然把 Date 当作一个类了,那为甚马不能搞得像输入一个整数那样进行输入呢?
⚔️预期效果:
void DateTest4()
{
Date d7;
cin >> d7;
cout << d7 << endl;
}👁️🗨️运行结果:

🗡️没错,这需要将 cin 和 cout 进行重载:
istream& operator>>(istream& in, Date& d)
{
int year, month, day;
in >> year >> month >> day;
if (month > 0 && month < 13
&& day > 0 && day < d.GetMonthDay(year, month))
{
d._year = year;
d._month = month;
d._day = day;
}
else
{
cout << "非法日期" << endl;
assert(false);
}
return in;
}ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& d)
{
out << d._year << "年" << d._month << "月" << d._day << "日" << endl;
return out;
}
但是这样还不行,因为 cin 修改了私有的数据,哪有什么办法能让这个重载能访问私有的数据呢?
对,那就是友元!
可以在类中声明,这个重载是类的朋友,允许他访问私密~
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& d);
friend istream& operator>>(istream& in, Date& d);2.前置和后置
❓我们知道,++ / -- 是有前置和后置之分的,那么在重载中前置和后置又是怎么区分的呢?
这里就以 ++ 为例吧:
// 前置++
Date& Date::operator++()
{
*this += 1;
return *this;
}
// 后置++
Date Date::operator++(int)
{
Date tmp = *this;
*this += 1;
return tmp;
}前置:先计算,后使用
后置:先使用,后计算
在实现中,后置事先拷贝了自身,返回的还是原来的值,做到了后计算;而前置直接修改自身,返回自身,做到了先计算;
在传参中,后置用 int 来与前置重载做区分,语法这样规定;
在返回值上,后置返回类型,前置返回引用。
源码在此
Date.h:
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
#include<cassert>
using namespace std;
class Date
{
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& d);
friend istream& operator>>(istream& in, Date& d);
public:
// 获取某年某月的天数
int GetMonthDay(int year, int month);
void Print() const
{
cout << _year << "-" << _month << "-" << _day << endl;
}
// 全缺省的构造函数
Date(int year = 2008, int month = 1, int day = 1);
// 赋值运算符重载
Date& operator=(const Date& d);
// 日期+=天数
Date& operator+=(int day);
// 日期+天数
Date operator+(int day);
// 日期-天数
Date operator-(int day);
// 日期-=天数
Date& operator-=(int day);
// 前置++
Date& operator++();
// 后置++
Date operator++(int);
// 后置--
Date operator--(int);
// 前置--
Date& operator--();
// >运算符重载
bool operator>(const Date& d) const;
// ==运算符重载
bool operator==(const Date& d) const;
// >=运算符重载
bool operator >= (const Date& d) const;
// <运算符重载
bool operator < (const Date& d) const;
// <=运算符重载
bool operator <= (const Date& d) const;
// !=运算符重载
bool operator != (const Date& d) const;
// 日期-日期 返回天数
int operator-(const Date& d) const;
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
Date.cpp:
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"Date.h"
// 获取某年某月的天数
int Date::GetMonthDay(int year, int month)
{
static int arr[13] = { 0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31 };
if (month == 2 && ((year % 4 == 0) && (year % 100 != 0) || (year % 400 == 0)))
return 29;
else
return arr[month];
}
// 全缺省的构造函数
Date::Date(int year, int month, int day)
{
if (month > 0 && month < 13
&& day > 0 && day < GetMonthDay(year, month))
{
_year = year;
_month = month;
_day = day;
}
else
{
cout << "非法日期" << endl;
assert(false);
}
}
// 赋值运算符重载
Date& Date::operator=(const Date& d)
{
_day = d._day;
_month = d._month;
_year = d._year;
return *this;
}
// <运算符重载
bool Date::operator<(const Date& d) const
{
if (_year < d._year)
{
return true;
}
else if (_year == d._year && _month < d._month)
{
return true;
}
else if (_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day < d._day)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
// ==运算符重载
bool Date::operator==(const Date& d) const
{
return _year == d._year
&& _month == d._month
&& _day == d._day;
}
// >=运算符重载 d1 >= d2
bool Date::operator >= (const Date& d) const
{
return !(*this < d);
}
// >运算符重载
bool Date::operator > (const Date& d) const
{
return !(*this <= d);
}
// <=运算符重载
bool Date::operator <= (const Date& d) const
{
return *this < d || *this == d;
}
// !=运算符重载
bool Date::operator != (const Date& d) const
{
return !(*this == d);
}
// 日期+=天数
Date& Date::operator+=(int day)
{
_day += day;
while (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month))
{
_day -= GetMonthDay(_year, _month);
_month++;
if (_month == 13)
{
_year++;
_month = 1;
}
}
return *this;
}
// 日期+天数
Date Date::operator+(int day)
{
Date tmp(*this);
tmp._day += day;
while (tmp._day > GetMonthDay(tmp._year, tmp._month))
{
tmp._day -= GetMonthDay(tmp._year, tmp._month);
tmp._month++;
if (tmp._month == 13)
{
tmp._year++;
tmp._month = 1;
}
}
return tmp;
}
// 日期-=天数
Date& Date::operator-=(int day)
{
_day -= day;
while (_day <= 0)
{
_day += GetMonthDay(_year, _month);
_month--;
if (_month == 0)
{
_year--;
_month = 12;
}
}
return *this;
}
// 日期-天数
Date Date::operator-(int day)
{
Date tmp = *this;
tmp._day -= day;
while (tmp._day <= 0)
{
tmp._day += GetMonthDay(tmp._year, tmp._month);
tmp._month--;
if (tmp._month == 0)
{
tmp._year--;
tmp._month = 12;
}
}
return tmp;
}
// 前置++
Date& Date::operator++()
{
*this += 1;
return *this;
}
// 后置++
Date Date::operator++(int)
{
Date tmp = *this;
*this += 1;
return tmp;
}
// 前置--
Date& Date::operator--()
{
*this -= 1;
return *this;
}
// 后置--
Date Date::operator--(int)
{
Date tmp = *this;
*this -= 1;
return tmp;
}
// 日期-日期 返回天数
int Date::operator-(const Date& d) const
{
Date max = *this;
Date min = d;
int flag = 1;
if (*this < d) // C艹,多了个分号 -- bug 记录
{
max = d;
min = *this;
flag = -1;
}
int n = 0;
while (min != max)
{
++min;
++n;
}
return n * flag;
}
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& d)
{
out << d._year << "年" << d._month << "月" << d._day << "日" << endl;
return out;
}
istream& operator>>(istream& in, Date& d)
{
int year, month, day;
in >> year >> month >> day;
if (month > 0 && month < 13
&& day > 0 && day < d.GetMonthDay(year, month))
{
d._year = year;
d._month = month;
d._day = day;
}
else
{
cout << "非法日期" << endl;
assert(false);
}
return in;
}
代码已上传至 我的 gitee
拿走不谢~
总结:
实现 Date 类,并没有那么难,明确类的特征,捕捉到必要数据,再进行方法的实现即可,这次用了不少运算符重载。
码文不易
如果你觉得这篇文章还不错并且对你有帮助,不妨支持一波哦 💗💗💗