摘要
- intent classification 意图分类。
- dialogue systems 对话系统
- 已经存在的系统并没有能力去处理快速增长的意图。
- zero-shot intent classifcation: 零样本意图分类。
Nevertheless 不过。
incipient stage 初期阶段
今年来提出的IntentCapsNet
- two unaddressed limitations:两个未解决的限制。
- 在提取语义胶囊的时候,并不能够处理多义性。
- 在广义零样本意图分类序列中,几乎不能够识别不可见意图的语句。
- 为了克服这个限制,我们提出了重新构建零样本意图分类的胶囊网络。
方法
- 引入:
- a dimensional attention mechanism to fight against polysemy
- we reconstruct the transformation matrices for unseen intents by utilizing abundant latent information of the labeled utterances.
- 实验结果: two task-oriented dialogue datasets
介绍
- task-oriented spoken dialogue systems :任务导向型的语言对话系统。
- 为了提升商业效率和用户满意度,准确在用户语句之后识别用户意图。
- user queries are sometimes short and expressed diversely
(用户查询更短而且表达更加多元化) - 传统的用户意图分类方法在大量标签数据集上训练监督学习模型。在识别越来越增长的不可见意图并没有效率。
- external resources:外部资源
label ontologies
manually defined attributes
(手动定义属性)
方法1
-
utilize neural networks to project intent labels and data samples to the same semantic space. and then measure their similarity.
-
学习一个好的映射函数是非常困难的。
-
IntentCapsNet 可以使用胶囊网络去提取高维度语义特征。 then transfers the prediction vectors for seen intents to unseen intents
-

训练过程
-
- labeled utterances are first encoded by Bi-LSTM
- a set of semantic capsules are extracted via the dimensional attention module
- these semantic capsules are fed to a capsule network to train a model for predicting the seen intents
测试过程
-
to predict the unseen intents, a metric learning method is trained on labeled utterances and intent label embeddings to learn the similarities between the unseen and seen intents。
-
the learned similarities and the transformation matrices for the seen intents trained by capsule networks are used to construct the transformation matrices for the unseen intents

-
ReCapsNet-ZS 有两个成分组成:
-
其引进 a dimensional attention module to alleviate the polysemy problem. (这能为胶囊网络帮助提取语义特征)
-
Second, it computes the similarities between unseen and seen intents by utilizing the rich latent information of labeled utterances
-
*** constructs the transformation matrices** for unseen intents with the computed similarities.
-
the trained transformation matrices for seen intents.
相关工作
Zero-shot Intent Classification
- 零样本分类目的是使用从可见类别中学习到的知识。
- 得到外部资源是困难的。
Capsule Networks
- 胶囊网络的提出是为了解决卷积神经网络的缺陷。
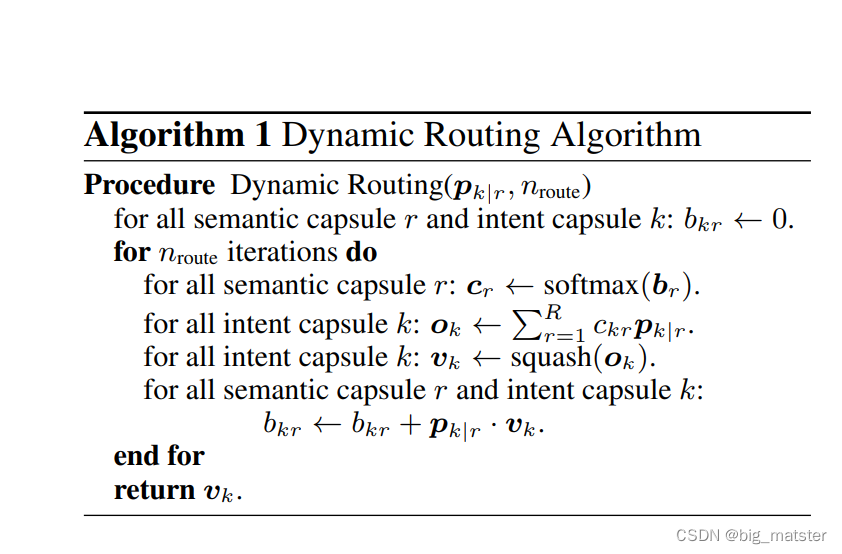
- the dynamic routing algorithm 动态路由算法。和零样文本分类的元学习框架。
Problem Formulation
- the set of all intent labels:
Y = Y s ⋃ Y u Y = Y^s \bigcup Y^u Y=Ys⋃Yu
Y s = { y 1 s , y 2 s , ⋯ , y k s } Y^s = \{y^s_1,y^s_2,\cdots,y^s_k\} Ys={y1s,y2s,⋯,yks}
Y u = { y 1 u , y 2 u , ⋯ , y L u } Y^u = \{y^u_1,y^u_2,\cdots,y^u_{L}\} Yu={y1u,y2u,⋯,yLu}
是可见类别和不可见类别各自的用户标签。
Y s ⋂ Y u = ∅ Y^s \bigcap Y^u = \emptyset Ys⋂Yu=∅
K 和 L K和L K和L是可见类别和不可见类别用户标签的各自数量。 - 可见类别和不可见类别用户标签的嵌入。embedding.
E s = { e 1 s , e 2 s , ⋯ , e k s } E^s = \{e^s_1,e^s_2,\cdots,e^s_k\} Es={e1s,e2s,⋯,eks}
E u = { e 1 u , e 2 u , ⋯ , e L u } E^u = \{e^u_1,e^u_2,\cdots,e^u_L\} Eu={e1u,e2u,⋯,eLu}
每个嵌入都是 a d − d i m e n s i o n a l v e c t o r a d-dimensional vector ad−dimensionalvector
-
-
可见类别和不可见类别用户标签的联合嵌入可以使用。
- 可见类别和不可见类别的样本语句集被标注为:
X s = { x 1 s , x 2 s , ⋯ , x n s s } X^s = \{x^s_1,x^s_2,\cdots,x^s_{n_s}\} Xs={x1s,x2s,⋯,xnss}
X u = { x 1 u , x 2 u , ⋯ , x n u u } X^u = \{x^u_1,x^u_2,\cdots,x^u_{n_u}\} Xu={x1u,x2u,⋯,xnuu} - n s n_s ns is the number of instances of the seen labels
- n u n_u nu is the number of instances of the unseen labels
- 可见类别和不可见类别的样本语句集被标注为:
Zero-shot Intent Classification

Generalized Zero-shot Intent Classification
Limitations of IntentCapsNet
- a multi-dimensional embedding::多维度嵌入。 表示单词。
- different dimensions of a word embedding may tend to represent different semantic meanings.

- ∣ ∣ ⋅ ∣ ∣ || \cdot|| ∣∣⋅∣∣ is the L2-norm of a vector
-
R
R
R is the number of semantic capsules






提出的方法



动态路由算法
总结
先大致了解一波。然后慢慢的从胶囊网络开始研究,将代码啥的全部都将其搞透彻,将其研究彻底,全部研究彻底都行啦的样子。
会将零样本常用的额技术罗列起来,然后会自己堆砌,形成自己的网络结构。