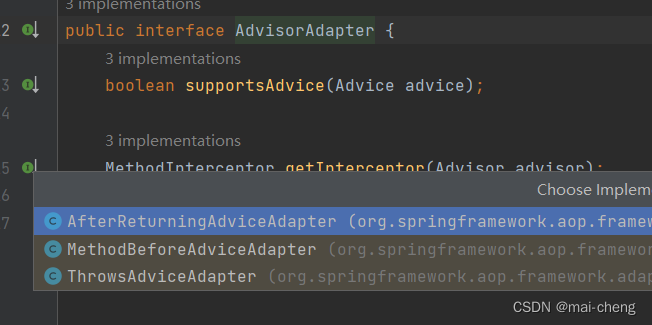
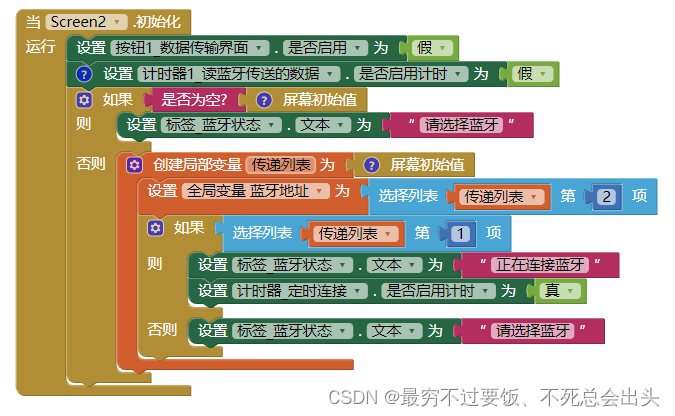
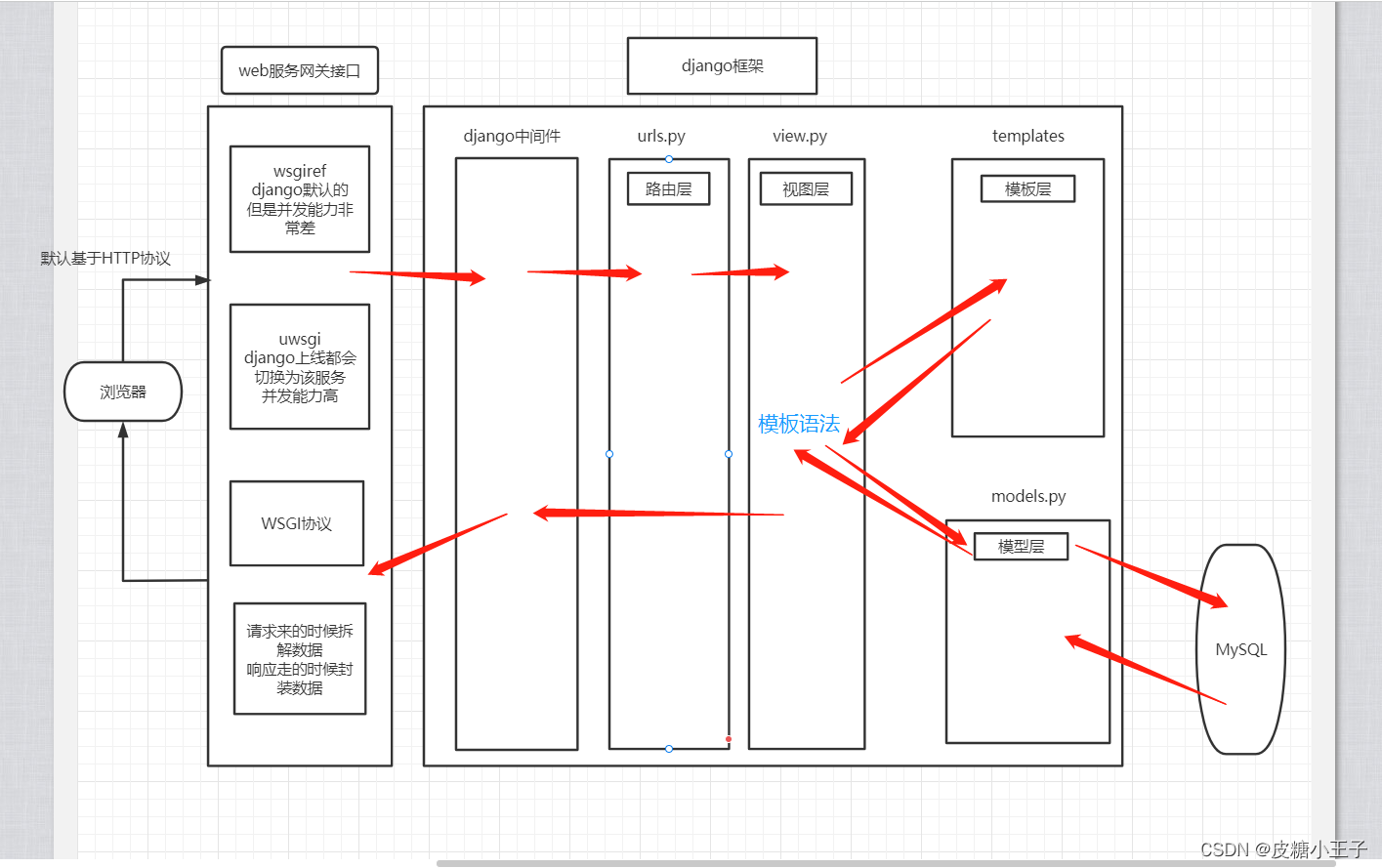
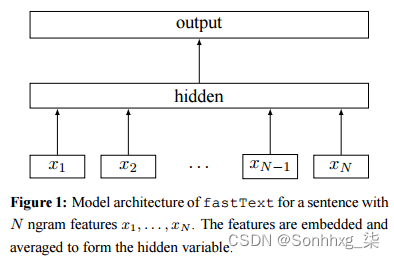
安装
下载:https://github.com/Martinsos/edlib
cd build && cmake -D CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release .. && make
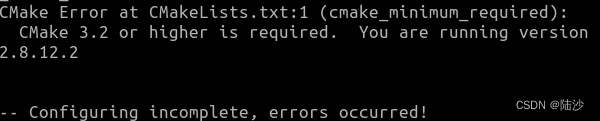
升级cmake
https://cmake.org/download/ 下载tar.gz包,我这里下载的是:
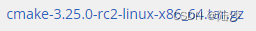
拷贝到 /home/xxx/app 下解压:
sudo tar xf cmake-3.25.0-rc2-linux-x86_64.tar.gz
此时/home/xxx/app/cmake-3.25.0-rc2-linux-x86_64/bin 下的cmake就是我们需要的,建立软链接:
sudo ln -sf /home/xxx/app/cmake-3.25.0-rc2-linux-x86_64/bin/cmake /usr/bin/cmake
检查版本:cmake --version
cmake version 3.25.0-rc2
CMake suite maintained and supported by Kitware (kitware.com/cmake).
linux下调用可执行程序
cd edlib-master/build/bin
time ./edlib-aligner src.txt tgt.txt -m HW -p -f NICE > st1.txt
real 0m0.002s
user 0m0.002s
sys 0m0.000s
其中src有826个碱基,tgt有1917个碱基,st1.txt部分内容如图所示:
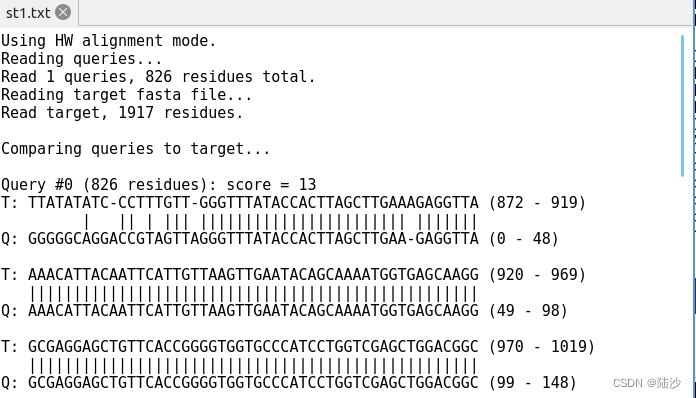
中间省略

参数说明:
XXX@XXX-pc:~/Desktop/edlib-master/build/bin$ ./edlib-aligner
Usage: ./edlib-aligner [options...] <queries.fasta> <target.fasta>
Options:
-s If specified, there will be no score or alignment output (silent mode).
-m HW|NW|SHW Alignment mode that will be used. [default: NW]
-n N Score will be calculated only for N best sequences (best = with smallest score). If N = 0 then all sequences will be calculated. Specifying small N can make total calculation much faster. [default: 0]
-k K Sequences with score > K will be discarded. Smaller k, faster calculation. If -1, no sequences will be discarded. [default: -1]
-p If specified, alignment path will be found and printed. This may significantly slow down the calculation.
-l If specified, start locations will be found and printed. Each start location corresponds to one end location. This may somewhat slow down the calculation, but is still faster then finding alignment path and does not consume any extra memory.
-f NICE|CIG_STD|CIG_EXT Format that will be used to print alignment path, can be used only with -p. NICE will give visually attractive format, CIG_STD will give standard cigar format and CIG_EXT will give extended cigar format. [default: NICE]
-r N Core part of calculation will be repeated N times. This is useful only for performance measurement, when single execution is too short to measure. [default: 1]
其中这个cigar,是排列的字符串形式描述。解释方法如下:
| 字符 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| X | mismatch (extended format) |
| I | insertion |
| D | deletion |
| = | match |
| M | mismatch (standard format) |
所以如果想得到cigar,可以用如下的命令:
xxx@xxx-pc:~/Desktop/edlib-master/build/bin$ time ./edlib-aligner src.txt tgt.txt -m HW -p -f CIG_EXT
Using HW alignment mode.
Reading queries...
Read 1 queries, 826 residues total.
Reading target fasta file...
Read target, 1917 residues.
Comparing queries to target...
Query #0 (826 residues): score = 13
Cigar:
6X1=2X1I2=1X1=1X3=1I23=1D784=
Cpu time of searching: 0.000217
real 0m0.002s
user 0m0.000s
sys 0m0.001s
所以上面示例的cigar可以解释为:6X (6个mismatch) 1= (1个match) 2X (2个mismatch) 。。。784= (784个match)
正对应这一段的匹配图:
T: TTATATATC-CCTTTGTT-GGGTTTATACCACTTAGCTTGAAAGAGGTTA (872 - 919)
| || | ||| ||||||||||||||||||||||| |||||||
Q: GGGGGCAGGACCGTAGTTAGGGTTTATACCACTTAGCTTGAA-GAGGTTA (0 - 48)
python版
https://pypi.org/project/edlib/
如果对c++版本有要求参见上面的cmake。pip直接安装,页面有示例
举个例子:
import edlib
# source和target使用的分别是826个和1917个碱基的序列,内容略
source = "XXX...XXXXX"
target = "xxx......XX"
alignment = edlib.align(source, target, mode="HW", task="path")
print(alignment)
print("-------------------------------------------")
s = t = ""
# - 表示gap
print(edlib.getNiceAlignment(alignment, s, t, "-"))
# 输出
# locations表示匹配的位置
{'editDistance': 13, 'alphabetLength': 4, 'locations': [(872, 1696)], 'cigar': '6X1=2X1I2=1X1=1X3=1I23=1D784='}
-------------------------------------------
{'query_aligned': '-', 'matched_aligned': '......|..-||.|.|||-|||||||||||||||||||||||-||中间省略||||||||||||||||||', 'target_aligned': '--'}
作者说还提供了R等版本,不再测试,都类似。
c#调用dll
待更新。。。