今天主要来学习异步通讯技术MQ,主要包括初识MQ,RabbitMQ快速入门,SpringAMQP三大部分,下面就来一起学习吧。路漫漫其修远兮,吾将上下而求索,继续加油吧,少年。
目录
一、初识MQ
1.1、同步通讯和异步通讯的优缺点
1.2、MQ常见技术介绍
1.3、RabbitMQ介绍与安装
1.4、RabbitMQ消息队列模型
二、SpringAMQP
2.1、基本介绍
2.2、SpringAMQP入门案例之消息发送
2.3、SpringAMQP入门案例之消息接收
2.4、SpringAMQP之工作队列Work Queue
2.5、SpringAMQP之发布-订阅模型广播交换机
2.6、SpringAMQP之发布-订阅模型路由交换机
2.7、SpringAMQP之发布-订阅模型主题交换机
2.8、SpringAMQP之消息转换器
一、初识MQ
1.1、同步通讯和异步通讯的优缺点
我们先看一下同步调用的优缺点,同步调用是实时响应,可以立即得到结果。但是同步调用一般耦合度较高,性能偏低,还存在级联失败等问题。

下面我们看一下微服务之间的异步调用,异步调用主要是解决了同步调用存在的一些问题,异步调用的优点:发布订阅的模式,耦合度低,不不要等待,吞吐量高,故障隔离,不会出现级联失败的问题,流量销峰,broker缓存,微服务根据自己的能力从broker 中获取。

1.2、MQ常见技术介绍
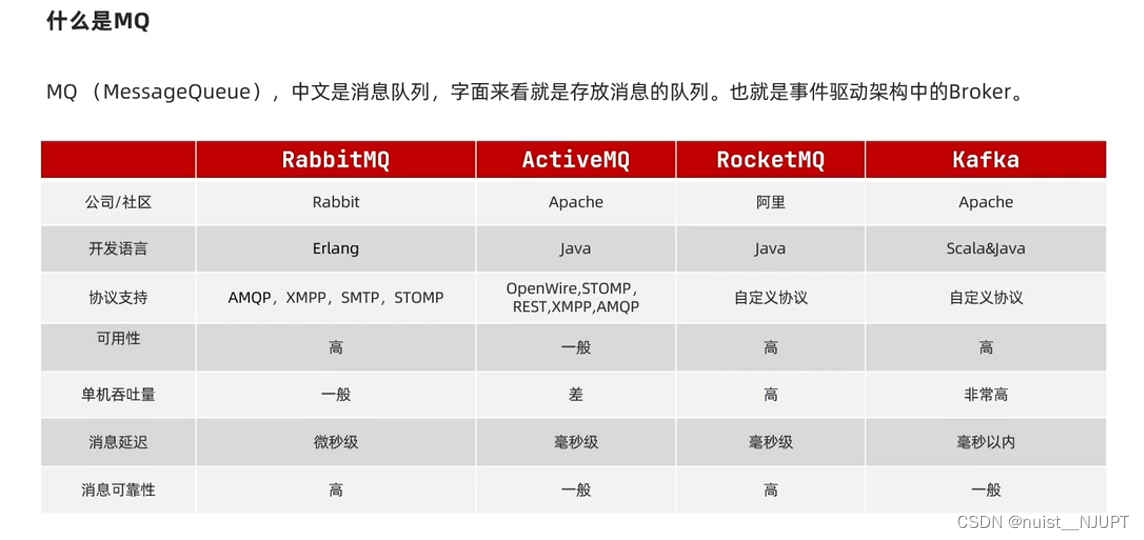
MQ即Message Queue,消息队列,就是存放消息的队列,也就是事件驱动架构中的Broker,常用的四种消息队列:RabbitMQ,ActiveMQ,RocketMQ,Kafka。对于稳定性要求较高的情况下,一般使用RabbitMQ或RocketMQ,对于数据量比较大,性能要求比较高的一般用Kafka。
1.3、RabbitMQ介绍与安装
我们先看一下RabbitMQ的架构,首先发布者发布消息到交换即,交换即通过哦队列进行缓存消息,最后消费者通过订阅从队列中取消息。
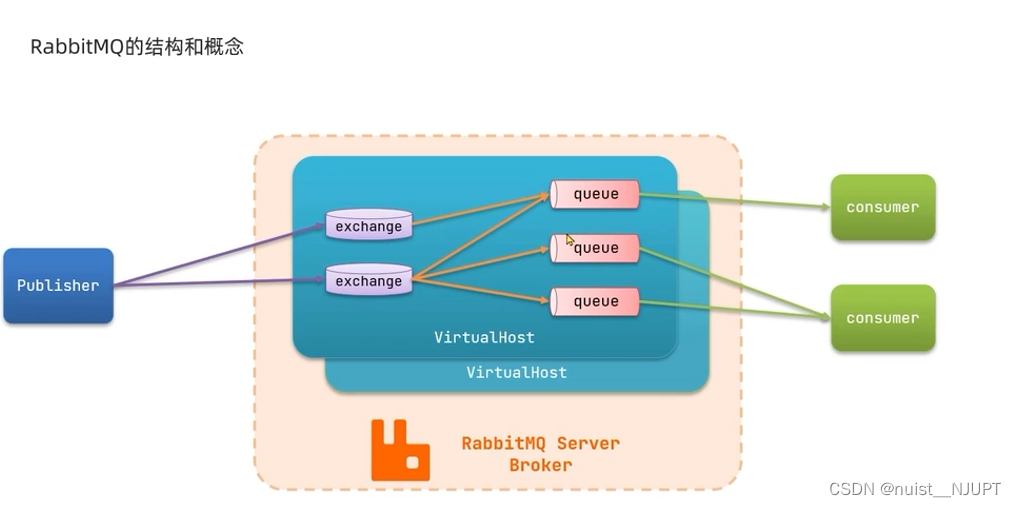
我们先了解一下RabbitMQ中的一些概念,channel用于操作MQ,exchange是交换机,用来路由消息到队列中,队列queue用于缓存消息,virtual host是虚拟主机,用于对队列和交换即等进行逻辑分组。
 下面我们进行RabbitMQ的安装过程如下,我们在centos7虚拟机中使用docker进行安装。
下面我们进行RabbitMQ的安装过程如下,我们在centos7虚拟机中使用docker进行安装。
有两种方式下载MQ,第一种是在线拉取镜像包,如下:
docker pull rabbitmq:3-management第二种,下载方式,是本地已经有了镜像包,通过Xftp进行上传到虚拟机,然后使用dokcer命令加载镜像即可。
docker load -i mq.tar镜像加载完成后,可以使用docker images进行查看,具体如下,可以发现MQ镜像导入成功:
加载好MQ的镜像后,就需要使用指令进行安装,指令如下:
该指令设置了MQ的用户名和密码变量,设置名称和主机名,设置两个端口,一个MQ管理平台的端口,另外一个是作消息通信的一个端口。
docker run \
-e RABBITMQ_DEFAULT_USER=root \
-e RABBITMQ_DEFAULT_PASS=123456 \
--name mq \
--hostname mq1 \
-p 15672:15672 \
-p 5672:5672 \
-d \
rabbitmq:3-management安装完成后,通过设置的用户名和密码进行MQ的管理页面,如下:
1.4、RabbitMQ消息队列模型
RabbitMQ常见的5种消息队列模型如下,主要分为两大类,第一类是基本消息队列和工作消息队列,不包含交换机,第二种是发布订阅模式的,根据交换机的不同,分为三种类型:广播、路由和主题。

下面先来看一下简单的消息队列模型,只包括三个部分,即发布者、消息队列、订阅者。
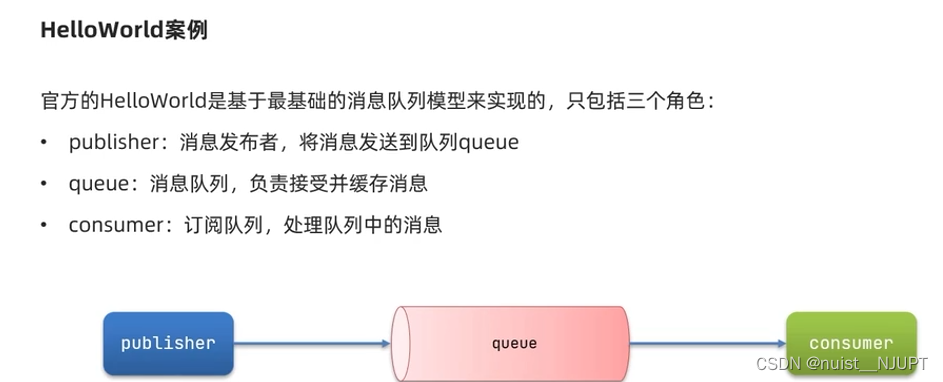
下面总结一下基本消息队列的发送和接收流程,基本消息的发送首先需要建立连接,然后建立channel通道,利用通道进行声明队列和消息发送,将消息发送到队列中;基本消息队列的接收流程为:建立连接,创建通道,利用通道声明队列,先定义消费者的消费行为,然后利用通道channel将消费者与队列绑定,消费者就可以消费队列中的消息了。

二、SpringAMQP
2.1、基本介绍
我们先看一下什么是AMQP,AMQP是高级消息队列协议,是用于应用程序或传递业务消息的开放标准,SpringAMQP是Spring基于AMQP协议的一套API规范。

SpringAMQP的官方地址如下:https://spring.io/projects/spring-amqp
我们进入官方业面查看,可以发现,该项目主要包含两个部分,一个是基础抽象,另一个是RabbitAQ的基础实现。
可以发现amqp主要包含三个特征,第一个是用于异步处理消息的侦听器容器, 用于接收和发送给消息的RabbitTemplate,用于自动声明队列以及交换和绑定的RabbitAdmin。

2.2、SpringAMQP入门案例之消息发送
先看一下发送消息的基本案例,具体如如下,首先引入amqp依赖,然后利用RabbitTemplate对象发送消息到队列,在消费者中绑定该队列。
 首先需要引入amqp的依赖,具体如下:
首先需要引入amqp的依赖,具体如下:
<!--AMQP依赖,包含RabbitMQ-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId>
</dependency>在发布者中创建一个类,用于创建队列和消息并把消息发送到队列中。
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest()
public class SpringTests {
@Autowired
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate ;
@Test
public void testSend(){
String queueName = "simple.queue" ;
String message = "Spring amqp" ;
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(queueName,message);
}
}
当然需要配置MQ的ip地址和端口号,以及登录名和密码,之前设置的。
logging:
pattern:
dateformat: MM-dd HH:mm:ss:SSS
spring:
rabbitmq:
host: 192.168.102.130 # rabbitMQ的ip地址
port: 5672 # 端口
username: root
password: 123456
virtual-host: /可以在浏览器的rabbitMQ管理界面查看到发送到队列的消息,如下所示。
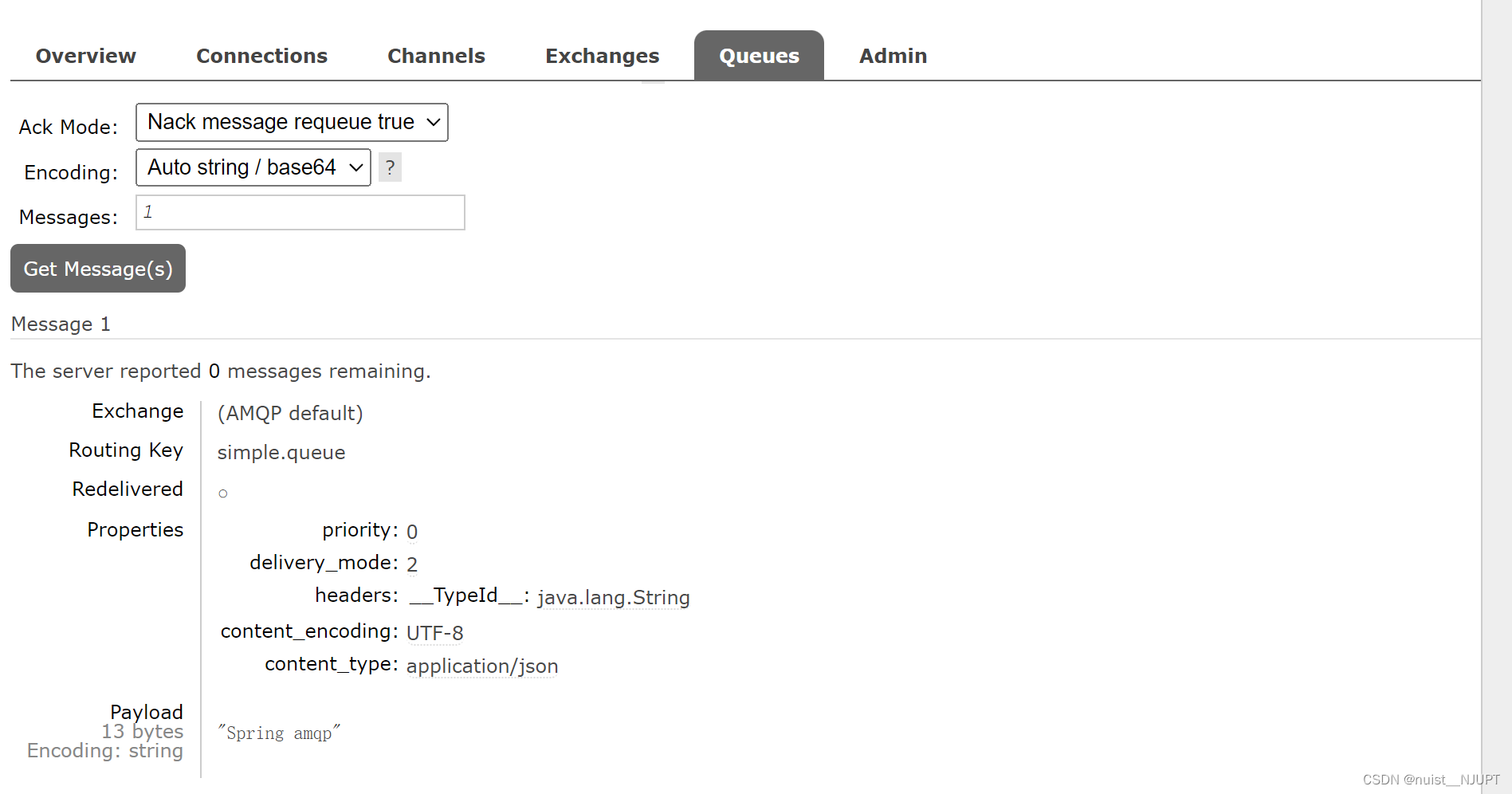
总结一下,SpringAMQP发送消息的流程,具体如下:
2.3、SpringAMQP入门案例之消息接收
首引入starter依赖,指定MQ地址,然后定义类使用@Component注解成bean交给Spring管理,然后在类的方法中@RabbitListener去监听消息队列,并获取消息。
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.time.LocalTime;
import java.util.Map;
@Component
public class SpringRabbitListener {
@RabbitListener(queues = "simple.queue")
public void listenSimpleQueue(String msg) {
System.out.println("消费者接收到simple.queue的消息:【" + msg + "】");
}
}2.4、SpringAMQP之工作队列Work Queue
工作队列模型有两个消费者,可以很好低提高消息处理的速度,避免队列消息堆积。
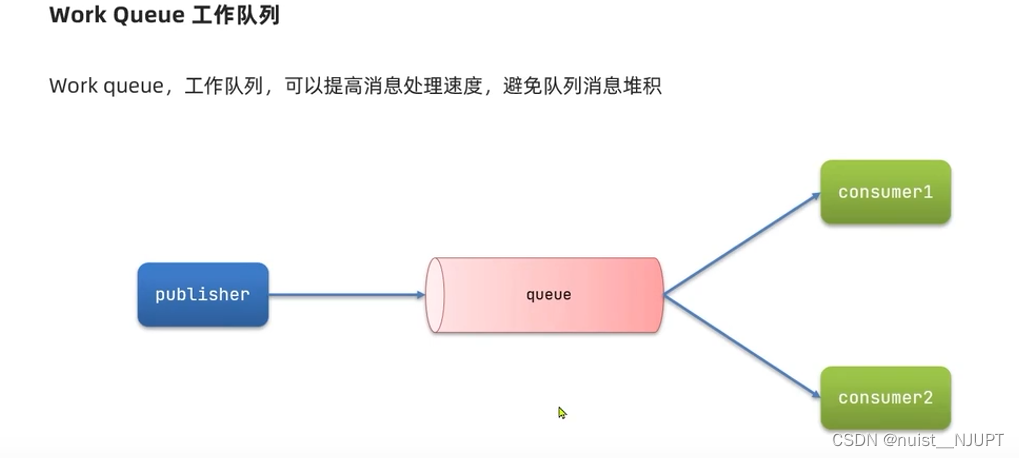
我们看下面的work queue的案例,实现一个队列绑定两个消费者。

设置publisher发送消息,每20ms发送一次,1s发送50次消息,具体如下:
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest()
public class SpringTests {
@Autowired
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate ;
@Test
public void testWorkQueueSend() throws InterruptedException {
String queueName = "simple.queue" ;
String message = "hello message" ;
for(int i=0; i<50; i++){ //1s发送50次
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(queueName,message+i);
Thread.sleep(20); //每发送一次消息,间隔20ms
}
}
}
使用两个消费者来消费消息,通过设置睡眠时间模拟消费者的消费能力,如下:
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.time.LocalTime;
import java.util.Map;
@Component
public class SpringRabbitListener {
/*
@RabbitListener(queues = "simple.queue")
public void listenSimpleQueue(String msg) {
System.out.println("消费者接收到simple.queue的消息:【" + msg + "】");
}*/
@RabbitListener(queues = "simple.queue") //监听队列
public void listenWorkQueue1(String msg) throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("消费者1接收到消息:【" + msg + "】" + LocalTime.now());
Thread.sleep(20);
}
@RabbitListener(queues = "simple.queue")
public void listenWorkQueue2(String msg) throws InterruptedException {
System.err.println("消费者2........接收到消息:【" + msg + "】" + LocalTime.now());
Thread.sleep(200);
}
}对于消费者,配置prefetch可以设置每次只能取一个进行消费,消费完成再取,防止消费能力弱的消费者一次取多个,导致性能差。
logging:
pattern:
dateformat: MM-dd HH:mm:ss:SSS
spring:
rabbitmq:
host: 192.168.102.131 # rabbitMQ的ip地址
port: 5672 # 端口
username: root
password: 123456
virtual-host: /
listener:
simple:
prefetch: 12.5、SpringAMQP之发布-订阅模型广播交换机
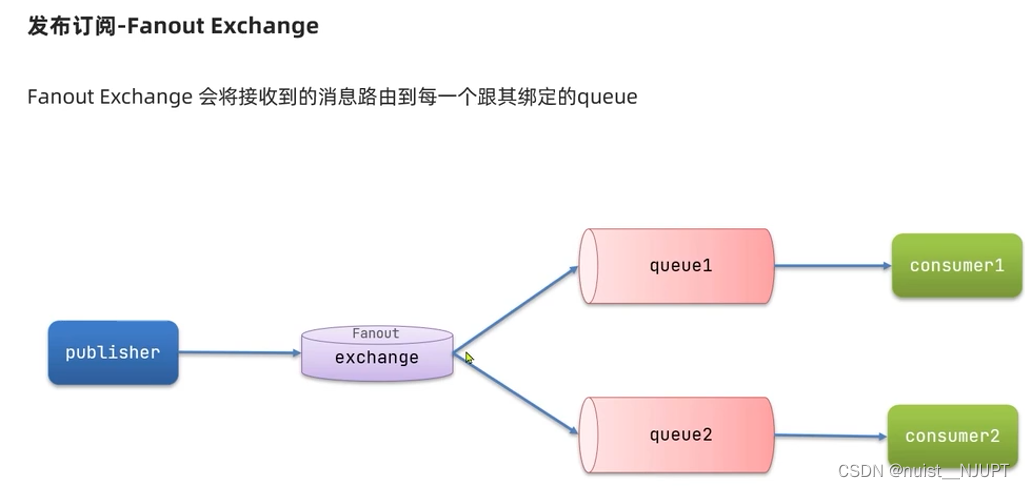
发布订阅模型是允许将一个消息发送给多个消费者,通过交换机实现,三种常用的交换机分别为广播、路由和话题。不过需要注意的是交换机负责消息路由,而不存储消息,如果路由失败,则消息丢失。
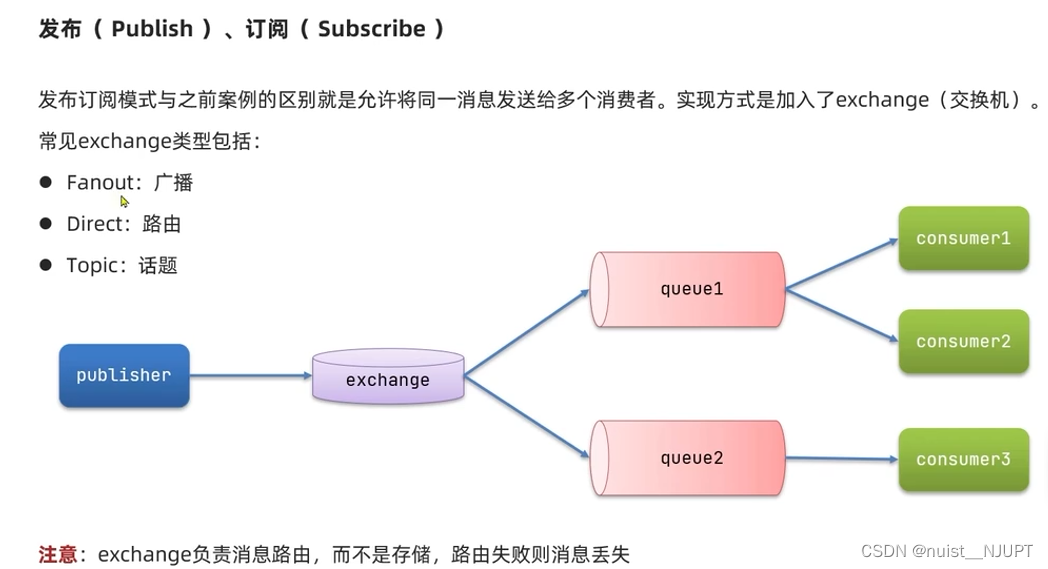
我们先看第一种发布订阅模式,广播的方式,交换机将收到的消息路由给每个与其绑定的队列。
我们使用SpringAMQP实现广播交换机的案例,具体如下:
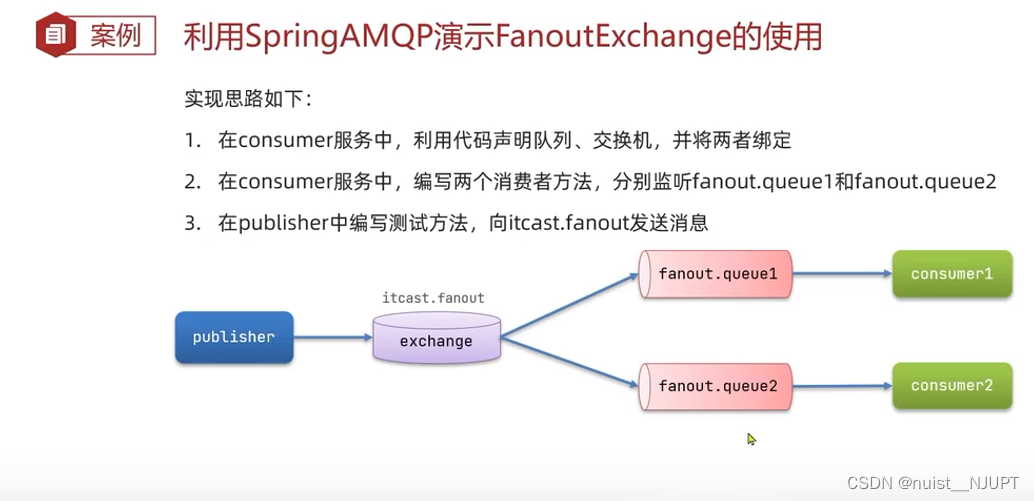

即将一个消费者绑定到两个队列,如下:
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Binding;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.BindingBuilder;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.FanoutExchange;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class FanoutConfig {
//声明广播类型的交换机1
@Bean
public FanoutExchange fanoutExchange(){
return new FanoutExchange("fanout");
}
//声明队列1
@Bean
public Queue fanoutQueue1(){
return new Queue("fanout.queue1");
}
// 绑定队列1到交换机
@Bean
public Binding fanoutBinding1(Queue fanoutQueue1, FanoutExchange fanoutExchange){
return BindingBuilder
.bind(fanoutQueue1)
.to(fanoutExchange);
}
// 声明队列2
@Bean
public Queue fanoutQueue2(){
return new Queue("fanout.queue2");
}
// 绑定队列2到交换机
@Bean
public Binding fanoutBinding2(Queue fanoutQueue2, FanoutExchange fanoutExchange){
return BindingBuilder
.bind(fanoutQueue2)
.to(fanoutExchange);
}
@Bean
public Queue objectQueue(){
return new Queue("object.queue");
}
}

在消费者的监听类中监听两个队列的消息,获取可以获取消息进行消费,如下:
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.time.LocalTime;
@Component
public class SpringRabbitListener {
@RabbitListener(queues = "simple.queue") //监听队列
public void listenWorkQueue1(String msg) throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("消费者1接收到消息:【" + msg + "】" + LocalTime.now());
Thread.sleep(20);
}
@RabbitListener(queues = "simple.queue")
public void listenWorkQueue2(String msg) throws InterruptedException {
System.err.println("消费者2........接收到消息:【" + msg + "】" + LocalTime.now());
Thread.sleep(200);
}
} 最后,将消息发送到交换机,交换机会把消息路由给队列,这个交换是广播交换机,即广播给每个队列,如下:
最后,将消息发送到交换机,交换机会把消息路由给队列,这个交换是广播交换机,即广播给每个队列,如下:
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest()
public class SpringTests {
@Autowired
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate ;
@Test
public void testExchange1(){
//交换机名称
String exchangeName = "fanout" ;
//消息
String message = "hello" ;
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(exchangeName,"",message);
}
}
2.6、SpringAMQP之发布-订阅模型路由交换机
我们看一下路由交换机,这个的模式是根据规则将消息路由到指定的队列,即通过对比key的方式进行路由消息到相应的队列。
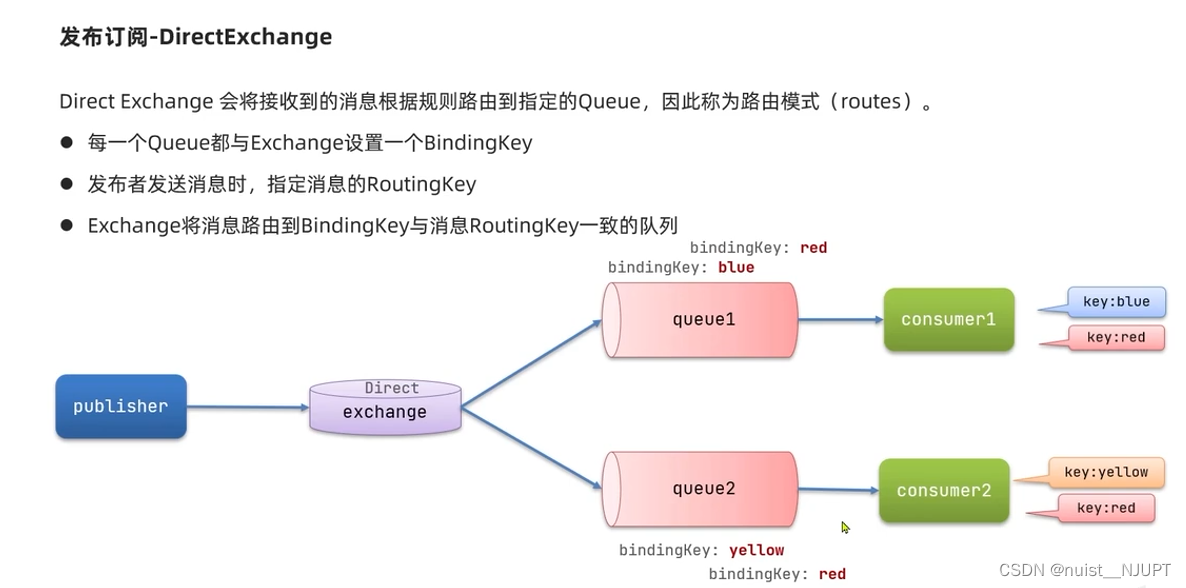

需要先监听两个队列,然后 绑定队列到交换机,为每个队列设置相应的key。
@RabbitListener(queues = "fanout.queue1")
public void listenFanoutQueue1(String msg) {
System.out.println("消费者接收到fanout.queue1的消息:【" + msg + "】");
}
@RabbitListener(queues = "fanout.queue2")
public void listenFanoutQueue2(String msg) {
System.out.println("消费者接收到fanout.queue2的消息:【" + msg + "】");
}
@RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding(
value = @Queue(name = "direct.queue1"),
exchange = @Exchange(name = "itcast.direct", type = ExchangeTypes.DIRECT),
key = {"red", "blue"}
))
public void listenDirectQueue1(String msg){
System.out.println("消费者接收到direct.queue1的消息:【" + msg + "】");
}
@RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding(
value = @Queue(name = "direct.queue2"),
exchange = @Exchange(name = "itcast.direct", type = ExchangeTypes.DIRECT),
key = {"red", "yellow"}
))
public void listenDirectQueue2(String msg){
System.out.println("消费者接收到direct.queue2的消息:【" + msg + "】");
}然后发送响应的消息到交换机就可以,需要指定key,通过对比key路由到指定的消息队列。
@Test
public void testExchange2(){
//交换机名称
String exchangeName = "itcast.direct" ;
//消息
String message = "hello, blue" ;
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(exchangeName,"blue",message);
}
2.7、SpringAMQP之发布-订阅模型主题交换机
下面看一下主题交换机和路由交换机的区别,主要就是绑定的方式不一样,主题交换机可以通过通配符的形式进行绑定,比较方便。
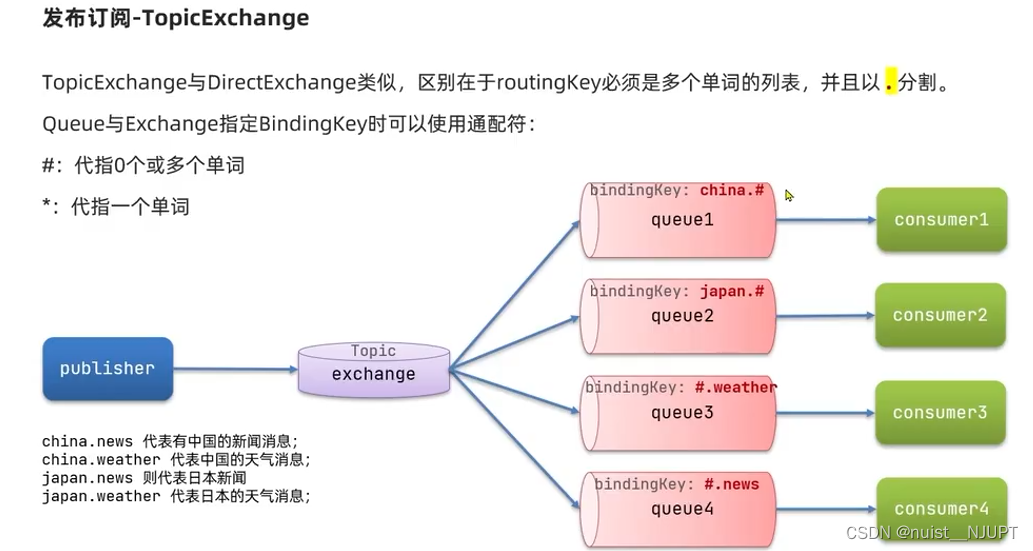
首先需要在消费者的监听器中绑定交换机和队列,并使用通配符的模式指定key,如下:
@RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding(
value = @Queue(name = "topic.queue1"),
exchange = @Exchange(name = "itcast.topic", type = ExchangeTypes.TOPIC),
key = "china.#"
))
public void listenTopicQueue1(String msg){
System.out.println("消费者接收到topic.queue1的消息:【" + msg + "】");
}
@RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding(
value = @Queue(name = "topic.queue2"),
exchange = @Exchange(name = "itcast.topic", type = ExchangeTypes.TOPIC),
key = "#.news"
))
public void listenTopicQueue2(String msg){
System.out.println("消费者接收到topic.queue2的消息:【" + msg + "】");
}按照key发送消息到交换机,交换机会路由到相应的队列,如下:
@Test
public void testExchange3(){
//交换机名称
String exchangeName = "itcast.topic" ;
//消息
String message = "大厂offer" ;
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(exchangeName,"china.news",message);
}
2.8、SpringAMQP之消息转换器
SpringAMQP会将对象序列化成字节后发送,然后进行反序列化即可接收。

首先引入依赖,json的依赖,如下:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
</dependency>在发布者和消费者的配置类中声明消息转换器,即序列化和反序列化,实现消息转换。
@Bean
public MessageConverter messageConverter(){
return new Jackson2JsonMessageConverter();
}剩下的就是发送消息,监听并消费消息即可。

![SpringSecurity[3]-自定义登录逻辑,自定义登录页面,以及认证过程的其他配置](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/c525c1e81f9f44d6ae2a073d0af3763a.png)