一、背景
因为xxl-job本身是统一的分布式任务调度框架,所以在实现定时任务的时候,就断不能再去依赖别人了。
其次,它尽可能只依赖spring框架,或者说spring boot/cloud。
也就是说,它会尽少地使用spring外的三方框架。于是,我们看到xxl-job都未使用
@EnableScheduling和@Scheduled,去实现定时任务,而是使用本文要讲的原始方式。
本文试着梳理下,它是怎么实现的。
二、入口类XxlJobAdminConfig.java
1、作为整个框架的入口
- servlet容器启动的时候,实例化
- 本身是一个单例,对外提供方法getAdminConfig()以访问其他成员变量
import org.springframework.beans.factory.DisposableBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
// 使用注解@Component实例化类,注入到spring容器里,保证单例。
@Component
public class XxlJobAdminConfig implements InitializingBean, DisposableBean {
private static XxlJobAdminConfig adminConfig = null;
public static XxlJobAdminConfig getAdminConfig() {
return adminConfig;
}
// ---------------------- XxlJobScheduler ----------------------
private XxlJobScheduler xxlJobScheduler;
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
adminConfig = this;
xxlJobScheduler = new XxlJobScheduler();
xxlJobScheduler.init();
}
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
xxlJobScheduler.destroy();
}
}
2、InitializingBean接口
还有一个替代方式,就是在方法上使用@PostConstruct 注解。
InitializingBean 是 Spring 框架中的一个接口,它定义了一个回调方法 afterPropertiesSet(),在实现了这个接口的 Bean 在初始化完成之后会被自动调用。
具体来说,当 Spring 容器创建一个 Bean 并完成依赖注入(包括属性的设置和依赖的注入)后,会检查该 Bean 是否实现了 InitializingBean 接口。如果实现了,容器会在完成依赖注入之后,调用 afterPropertiesSet() 方法,这样你可以在这个方法中进行一些初始化操作。
举个例子,在你的 Bean 类中实现了 InitializingBean 接口,并且在 afterPropertiesSet() 方法中做了一些初始化操作,当这个 Bean 被 Spring 容器创建并完成属性注入时,afterPropertiesSet() 方法就会被自动调用。
在xxl-job这里,是创建XxlJobScheduler实例对象,并且执行其init()方法。
3、DisposableBean接口
还有一个替代方式,就是在方法上使用@PreDestroy注解。
DisposableBean 是 Spring 框架中的另一个接口,它定义了一个回调方法 destroy(),在实现了这个接口的 Bean 在销毁时会被自动调用。
与 InitializingBean 类似,当 Spring 容器检测到一个 Bean 实现了 DisposableBean 接口时,在该 Bean 被销毁前(例如应用程序关闭时)会调用其 destroy() 方法,以便你可以在这个方法中执行一些资源释放或清理的操作。
举个例子,在你的 Bean 类中实现了 DisposableBean 接口,并在 destroy() 方法中释放了某些资源,当该 Bean 被 Spring 容器销毁时,destroy() 方法会被自动调用。
在xxl-job这里,是执行XxlJobScheduler的destroy()方法。
下面就看一看XxlJobScheduler的init()和destroy()
三、XxlJobScheduler.java
public void init() throws Exception {
// admin log report start
JobLogReportHelper.getInstance().start();
}
public void destroy() throws Exception {
// admin log report stop
JobLogReportHelper.getInstance().toStop();
}
本身没什么代码量,值得一看是下面的缓存实现。
根据地址反查ExecutorBiz;ExecutorBizClient实现了接口ExecutorBiz。
不要看它的变量名是executorBizRepository,可和数据库没有啥关系,只是一个Map集合。
// ---------------------- executor-client ----------------------
private static ConcurrentMap<String, ExecutorBiz> executorBizRepository = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, ExecutorBiz>();
public static ExecutorBiz getExecutorBiz(String address) throws Exception {
// valid
if (address==null || address.trim().length()==0) {
return null;
}
// load-cache
address = address.trim();
ExecutorBiz executorBiz = executorBizRepository.get(address);
if (executorBiz != null) {
return executorBiz;
}
// set-cache
executorBiz = new ExecutorBizClient(address, XxlJobAdminConfig.getAdminConfig().getAccessToken());
executorBizRepository.put(address, executorBiz);
return executorBiz;
}
四、本文的重点类JobLogReportHelper.java
前面都是实例化和引用,现在是核心的实现了。
首先看它的成员变量:
- private Thread logrThread;
- private volatile boolean toStop = false;
1、成员变量logrThread
在方法init()中进行定义并启动。
logrThread = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
// 略
}
});
logrThread.setDaemon(true);
logrThread.setName("xxl-job, admin JobLogReportHelper");
logrThread.start();
2、成员变量toStop
它是一个布尔类型,默认是false–不停止。那么在什么时候停止呢,答案是在方法toStop()被调用的时候,设置为ture–停止。
另外,由volatile关键词修饰它,做到线程安全。
3、方法toStop()
中断子线程 logrThread 并等待它执行完毕。如果等待过程中发生了中断,会在日志中记录错误信息。
public void toStop(){
toStop = true;
// interrupt and wait
logrThread.interrupt();
try {
logrThread.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
logger.error(e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
4、重点方法start()的实现
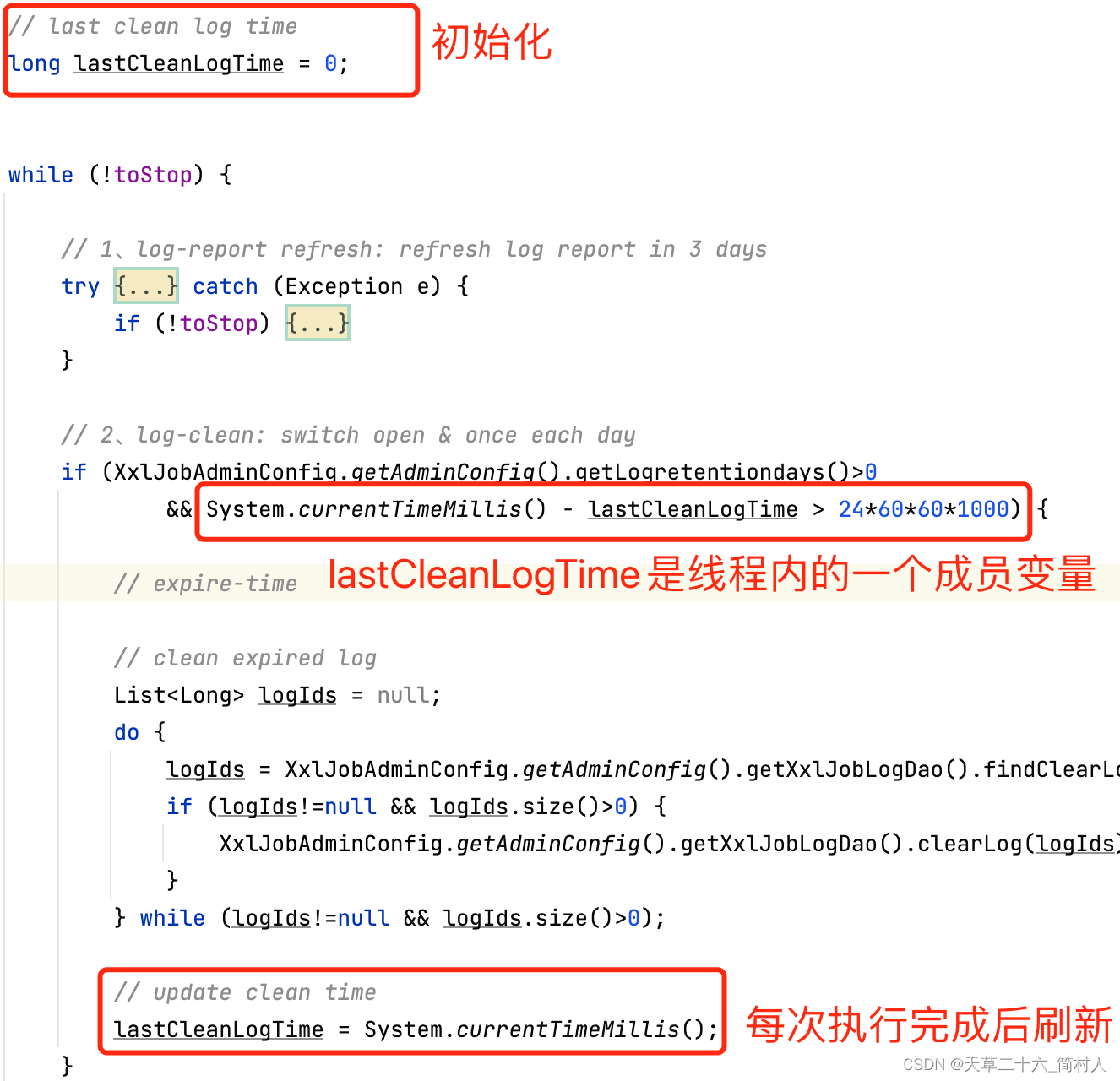
删除Log记录的频率为1天一次。在删除的时候,每次先拉取1000条记录的logId,然后删除,循环,直至没有拉取到记录为止。第三点,每次删除完,线程会进行延时1分钟。
换句话说,每分钟会循环执行一次,从判断的入口开始。
逻辑上讲,线程延时1分钟,和删除的时间区间为1天,存在冲突,并不是很好地配合。
线程虽然每隔1分钟来检测,是否有需要删除的日志,皆是徒劳。
// 判断条件:当前时间-最后一次删除时间 > 24小时
if (XxlJobAdminConfig.getAdminConfig().getLogretentiondays()>0
&& System.currentTimeMillis() - lastCleanLogTime > 24*60*60*1000) {
// expire-time
Calendar expiredDay = Calendar.getInstance();
expiredDay.add(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH, -1 * XxlJobAdminConfig.getAdminConfig().getLogretentiondays());
expiredDay.set(Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAY, 0);
expiredDay.set(Calendar.MINUTE, 0);
expiredDay.set(Calendar.SECOND, 0);
expiredDay.set(Calendar.MILLISECOND, 0);
Date clearBeforeTime = expiredDay.getTime();
// clean expired log
// 每次拉取1000条log记录,循环删除
List<Long> logIds = null;
do {
logIds = XxlJobAdminConfig.getAdminConfig().getXxlJobLogDao().findClearLogIds(0, 0, clearBeforeTime, 0, 1000);
if (logIds!=null && logIds.size()>0) {
XxlJobAdminConfig.getAdminConfig().getXxlJobLogDao().clearLog(logIds);
}
} while (logIds!=null && logIds.size()>0);
// update clean time
// 更新最后一次删除的时间戳
lastCleanLogTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
try {
// 延时一分钟
TimeUnit.MINUTES.sleep(1);
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!toStop) {
logger.error(e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
- 时间戳机制
使用了一个时间戳变量,用来记录上一次的删除时间,才有了时间区间的判断入口。
五、总结
本文从xxl-job源码,分析了如何在spring框架下,既不使用注解@Scheduled,也不使用第三方框架,如何实现定时任务。